mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
synced 2025-12-28 23:39:39 +08:00
Compare commits
1 Commits
v0.15.0
...
fix-tensor
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
41ba3224fe |
1
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
1
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
@@ -13,7 +13,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
with:
|
||||
commit_sha: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
package: diffusers
|
||||
notebook_folder: diffusers_doc
|
||||
languages: en ko
|
||||
secrets:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.HUGGINGFACE_PUSH }}
|
||||
|
||||
1
.github/workflows/pr_quality.yml
vendored
1
.github/workflows/pr_quality.yml
vendored
@@ -47,4 +47,3 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/check_copies.py
|
||||
python utils/check_dummies.py
|
||||
make deps_table_check_updated
|
||||
|
||||
7
.github/workflows/pr_tests.yml
vendored
7
.github/workflows/pr_tests.yml
vendored
@@ -31,16 +31,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-flax-cpu
|
||||
report: flax_cpu
|
||||
- name: Fast ONNXRuntime CPU tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: onnxruntime
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-onnxruntime-cpu
|
||||
report: onnx_cpu
|
||||
- name: PyTorch Example CPU tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: pytorch_examples
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_example_cpu
|
||||
report: torch_cpu
|
||||
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.config.name }}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
5
.github/workflows/push_tests.yml
vendored
5
.github/workflows/push_tests.yml
vendored
@@ -29,11 +29,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runner: docker-tpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-flax-tpu
|
||||
report: flax_tpu
|
||||
- name: Slow ONNXRuntime CUDA tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: onnxruntime
|
||||
runner: docker-gpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-onnxruntime-cuda
|
||||
report: onnx_cuda
|
||||
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.config.name }}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
7
.github/workflows/push_tests_fast.yml
vendored
7
.github/workflows/push_tests_fast.yml
vendored
@@ -29,16 +29,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-flax-cpu
|
||||
report: flax_cpu
|
||||
- name: Fast ONNXRuntime CPU tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: onnxruntime
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-onnxruntime-cpu
|
||||
report: onnx_cpu
|
||||
- name: PyTorch Example CPU tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: pytorch_examples
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_example_cpu
|
||||
report: torch_cpu
|
||||
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.config.name }}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2
.gitignore
vendored
2
.gitignore
vendored
@@ -172,5 +172,3 @@ tags
|
||||
|
||||
# ruff
|
||||
.ruff_cache
|
||||
|
||||
wandb
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ community include:
|
||||
* Accepting responsibility and apologizing to those affected by our mistakes,
|
||||
and learning from the experience
|
||||
* Focusing on what is best not just for us as individuals, but for the
|
||||
overall diffusers community
|
||||
overall community
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of unacceptable behavior include:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -34,7 +34,6 @@ Examples of unacceptable behavior include:
|
||||
* Public or private harassment
|
||||
* Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or email
|
||||
address, without their explicit permission
|
||||
* Spamming issues or PRs with links to projects unrelated to this library
|
||||
* Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a
|
||||
professional setting
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
561
CONTRIBUTING.md
561
CONTRIBUTING.md
@@ -1,350 +1,94 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
<!---
|
||||
Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# How to contribute to Diffusers 🧨
|
||||
# How to contribute to diffusers?
|
||||
|
||||
We ❤️ contributions from the open-source community! Everyone is welcome, and all types of participation –not just code– are valued and appreciated. Answering questions, helping others, reaching out, and improving the documentation are all immensely valuable to the community, so don't be afraid and get involved if you're up for it!
|
||||
Everyone is welcome to contribute, and we value everybody's contribution. Code
|
||||
is thus not the only way to help the community. Answering questions, helping
|
||||
others, reaching out and improving the documentations are immensely valuable to
|
||||
the community.
|
||||
|
||||
Everyone is encouraged to start by saying 👋 in our public Discord channel. We discuss the latest trends in diffusion models, ask questions, show off personal projects, help each other with contributions, or just hang out ☕. <a href="https://Discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR"><img alt="Join us on Discord" src="https://img.shields.io/Discord/823813159592001537?color=5865F2&logo=Discord&logoColor=white"></a>
|
||||
It also helps us if you spread the word: reference the library from blog posts
|
||||
on the awesome projects it made possible, shout out on Twitter every time it has
|
||||
helped you, or simply star the repo to say "thank you".
|
||||
|
||||
Whichever way you choose to contribute, we strive to be part of an open, welcoming, and kind community. Please, read our [code of conduct](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md) and be mindful to respect it during your interactions. We also recommend you become familiar with the [ethical guidelines](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/ethical_guidelines) that guide our project and ask you to adhere to the same principles of transparency and responsibility.
|
||||
Whichever way you choose to contribute, please be mindful to respect our
|
||||
[code of conduct](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md).
|
||||
|
||||
We enormously value feedback from the community, so please do not be afraid to speak up if you believe you have valuable feedback that can help improve the library - every message, comment, issue, and pull request (PR) is read and considered.
|
||||
## You can contribute in so many ways!
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
There are 4 ways you can contribute to diffusers:
|
||||
* Fixing outstanding issues with the existing code;
|
||||
* Implementing [new diffusion pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines#contribution), [new schedulers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers) or [new models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models)
|
||||
* [Contributing to the examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples) or to the documentation;
|
||||
* Submitting issues related to bugs or desired new features.
|
||||
|
||||
You can contribute in many ways ranging from answering questions on issues to adding new diffusion models to
|
||||
the core library.
|
||||
In particular there is a special [Good First Issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/contribute) listing.
|
||||
It will give you a list of open Issues that are open to anybody to work on. Just comment in the issue that you'd like to work on it.
|
||||
In that same listing you will also find some Issues with `Good Second Issue` label. These are
|
||||
typically slightly more complicated than the Issues with just `Good First Issue` label. But if you
|
||||
feel you know what you're doing, go for it.
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we give an overview of different ways to contribute, ranked by difficulty in ascending order. All of them are valuable to the community.
|
||||
*All are equally valuable to the community.*
|
||||
|
||||
* 1. Asking and answering questions on [the Diffusers discussion forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers) or on [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR).
|
||||
* 2. Opening new issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose)
|
||||
* 3. Answering issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues)
|
||||
* 4. Fix a simple issue, marked by the "Good first issue" label, see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22).
|
||||
* 5. Contribute to the [documentation](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source).
|
||||
* 6. Contribute a [Community Pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3Acommunity-examples)
|
||||
* 7. Contribute to the [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples).
|
||||
* 8. Fix a more difficult issue, marked by the "Good second issue" label, see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22).
|
||||
* 9. Add a new pipeline, model, or scheduler, see ["New Pipeline/Model"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22) and ["New scheduler"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22) issues. For this contribution, please have a look at [Design Philosophy](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/PHILOSOPHY.md).
|
||||
## Submitting a new issue or feature request
|
||||
|
||||
As said before, **all contributions are valuable to the community**.
|
||||
In the following, we will explain each contribution a bit more in detail.
|
||||
Do your best to follow these guidelines when submitting an issue or a feature
|
||||
request. It will make it easier for us to come back to you quickly and with good
|
||||
feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
For all contributions 4.-9. you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in [Opening a pull requst](#how-to-open-a-pr)
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Asking and answering questions on the Diffusers discussion forum or on the Diffusers Discord
|
||||
|
||||
Any question or comment related to the Diffusers library can be asked on the [discussion forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/) or on [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR). Such questions and comments include (but are not limited to):
|
||||
- Reports of training or inference experiments in an attempt to share knowledge
|
||||
- Presentation of personal projects
|
||||
- Questions to non-official training examples
|
||||
- Project proposals
|
||||
- General feedback
|
||||
- Paper summaries
|
||||
- Asking for help on personal projects that build on top of the Diffusers library
|
||||
- General questions
|
||||
- Ethical questions regarding diffusion models
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
|
||||
Every question that is asked on the forum or on Discord actively encourages the community to publicly
|
||||
share knowledge and might very well help a beginner in the future that has the same question you're
|
||||
having. Please do pose any questions you might have.
|
||||
In the same spirit, you are of immense help to the community by answering such questions because this way you are publicly documenting knowledge for everybody to learn from.
|
||||
|
||||
**Please** keep in mind that the more effort you put into asking or answering a question, the higher
|
||||
the quality of the publicly documented knowledge. In the same way, well-posed and well-answered questions create a high-quality knowledge database accessible to everybody, while badly posed questions or answers reduce the overall quality of the public knowledge database.
|
||||
In short, a high quality question or answer is *precise*, *concise*, *relevant*, *easy-to-understand*, *accesible*, and *well-formated/well-posed*. For more information, please have a look through the [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue) section.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE about channels**:
|
||||
[*The forum*](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) is much better indexed by search engines, such as Google. Posts are ranked by popularity rather than chronologically. Hence, it's easier to look up questions and answers that we posted some time ago.
|
||||
In addition, questions and answers posted in the forum can easily be linked to.
|
||||
In contrast, *Discord* has a chat-like format that invites fast back-and-forth communication.
|
||||
While it will most likely take less time for you to get an answer to your question on Discord, your
|
||||
question won't be visible anymore over time. Also, it's much harder to find information that was posted a while back on Discord. We therefore strongly recommend using the forum for high-quality questions and answers in an attempt to create long-lasting knowledge for the community. If discussions on Discord lead to very interesting answers and conclusions, we recommend posting the results on the forum to make the information more available for future readers.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Opening new issues on the GitHub issues tab
|
||||
### Did you find a bug?
|
||||
|
||||
The 🧨 Diffusers library is robust and reliable thanks to the users who notify us of
|
||||
the problems they encounter. So thank you for reporting an issue.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember, GitHub issues are reserved for technical questions directly related to the Diffusers library, bug reports, feature requests, or feedback on the library design.
|
||||
First, we would really appreciate it if you could **make sure the bug was not
|
||||
already reported** (use the search bar on Github under Issues).
|
||||
|
||||
In a nutshell, this means that everything that is **not** related to the **code of the Diffusers library** (including the documentation) should **not** be asked on GitHub, but rather on either the [forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) or [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR).
|
||||
### Do you want to implement a new diffusion pipeline / diffusion model?
|
||||
|
||||
**Please consider the following guidelines when opening a new issue**:
|
||||
- Make sure you have searched whether your issue has already been asked before (use the search bar on GitHub under Issues).
|
||||
- Please never report a new issue on another (related) issue. If another issue is highly related, please
|
||||
open a new issue nevertheless and link to the related issue.
|
||||
- Make sure your issue is written in English. Please use one of the great, free online translation services, such as [DeepL](https://www.deepl.com/translator) to translate from your native language to English if you are not comfortable in English.
|
||||
- Check whether your issue might be solved by updating to the newest Diffusers version. Before posting your issue, please make sure that `python -c "import diffusers; print(diffusers.__version__)"` is higher or matches the latest Diffusers version.
|
||||
- Remember that the more effort you put into opening a new issue, the higher the quality of your answer will be and the better the overall quality of the Diffusers issues.
|
||||
Awesome! Please provide the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
New issues usually include the following.
|
||||
* Short description of the diffusion pipeline and link to the paper;
|
||||
* Link to the implementation if it is open-source;
|
||||
* Link to the model weights if they are available.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.1. Reproducible, minimal bug reports.
|
||||
If you are willing to contribute the model yourself, let us know so we can best
|
||||
guide you.
|
||||
|
||||
A bug report should always have a reproducible code snippet and be as minimal and concise as possible.
|
||||
This means in more detail:
|
||||
- Narrow the bug down as much as you can, **do not just dump your whole code file**
|
||||
- Format your code
|
||||
- Do not include any external libraries except for Diffusers depending on them.
|
||||
- **Always** provide all necessary information about your environment; for this, you can run: `diffusers-cli env` in your shell and copy-paste the displayed information to the issue.
|
||||
- Explain the issue. If the reader doesn't know what the issue is and why it is an issue, she cannot solve it.
|
||||
- **Always** make sure the reader can reproduce your issue with as little effort as possible. If your code snippet cannot be run because of missing libraries or undefined variables, the reader cannot help you. Make sure your reproducible code snippet is as minimal as possible and can be copy-pasted into a simple Python shell.
|
||||
- If in order to reproduce your issue a model and/or dataset is required, make sure the reader has access to that model or dataset. You can always upload your model or dataset to the [Hub](https://huggingface.co) to make it easily downloadable. Try to keep your model and dataset as small as possible, to make the reproduction of your issue as effortless as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, please have a look through the [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue) section.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a bug report [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.2. Feature requests.
|
||||
### Do you want a new feature (that is not a model)?
|
||||
|
||||
A world-class feature request addresses the following points:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Motivation first:
|
||||
* Is it related to a problem/frustration with the library? If so, please explain
|
||||
why. Providing a code snippet that demonstrates the problem is best.
|
||||
* Is it related to something you would need for a project? We'd love to hear
|
||||
about it!
|
||||
* Is it something you worked on and think could benefit the community?
|
||||
Awesome! Tell us what problem it solved for you.
|
||||
* Is it related to a problem/frustration with the library? If so, please explain
|
||||
why. Providing a code snippet that demonstrates the problem is best.
|
||||
* Is it related to something you would need for a project? We'd love to hear
|
||||
about it!
|
||||
* Is it something you worked on and think could benefit the community?
|
||||
Awesome! Tell us what problem it solved for you.
|
||||
2. Write a *full paragraph* describing the feature;
|
||||
3. Provide a **code snippet** that demonstrates its future use;
|
||||
4. In case this is related to a paper, please attach a link;
|
||||
5. Attach any additional information (drawings, screenshots, etc.) you think may help.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a feature request [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feature_request.md&title=).
|
||||
If your issue is well written we're already 80% of the way there by the time you
|
||||
post it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.3 Feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
Feedback about the library design and why it is good or not good helps the core maintainers immensely to build a user-friendly library. To understand the philosophy behind the current design philosophy, please have a look [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy). If you feel like a certain design choice does not fit with the current design philosophy, please explain why and how it should be changed. If a certain design choice follows the design philosophy too much, hence restricting use cases, explain why and how it should be changed.
|
||||
If a certain design choice is very useful for you, please also leave a note as this is great feedback for future design decisions.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open an issue about feedback [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.4 Technical questions.
|
||||
|
||||
Technical questions are mainly about why certain code of the library was written in a certain way, or what a certain part of the code does. Please make sure to link to the code in question and please provide detail on
|
||||
why this part of the code is difficult to understand.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open an issue about a technical question [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&template=bug-report.yml).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.5 Proposal to add a new model, scheduler, or pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
If the diffusion model community released a new model, pipeline, or scheduler that you would like to see in the Diffusers library, please provide the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
* Short description of the diffusion pipeline, model, or scheduler and link to the paper or public release.
|
||||
* Link to any of its open-source implementation.
|
||||
* Link to the model weights if they are available.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are willing to contribute to the model yourself, let us know so we can best guide you. Also, don't forget
|
||||
to tag the original author of the component (model, scheduler, pipeline, etc.) by GitHub handle if you can find it.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a request for a model/pipeline/scheduler [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=New+model%2Fpipeline%2Fscheduler&template=new-model-addition.yml).
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Answering issues on the GitHub issues tab
|
||||
|
||||
Answering issues on GitHub might require some technical knowledge of Diffusers, but we encourage everybody to give it a try even if you are not 100% certain that your answer is correct.
|
||||
Some tips to give a high-quality answer to an issue:
|
||||
- Be as concise and minimal as possible
|
||||
- Stay on topic. An answer to the issue should concern the issue and only the issue.
|
||||
- Provide links to code, papers, or other sources that prove or encourage your point.
|
||||
- Answer in code. If a simple code snippet is the answer to the issue or shows how the issue can be solved, please provide a fully reproducible code snippet.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, many issues tend to be simply off-topic, duplicates of other issues, or irrelevant. It is of great
|
||||
help to the maintainers if you can answer such issues, encouraging the author of the issue to be
|
||||
more precise, provide the link to a duplicated issue or redirect them to [the forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) or [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)
|
||||
|
||||
If you have verified that the issued bug report is correct and requires a correction in the source code,
|
||||
please have a look at the next sections.
|
||||
|
||||
For all of the following contributions, you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in the [Opening a pull requst](#how-to-open-a-pr) section.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Fixing a "Good first issue"
|
||||
|
||||
*Good first issues* are marked by the [Good first issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22) label. Usually, the issue already
|
||||
explains how a potential solution should look so that it is easier to fix.
|
||||
If the issue hasn't been closed and you would like to try to fix this issue, you can just leave a message "I would like to try this issue.". There are usually three scenarios:
|
||||
- a.) The issue description already proposes a fix. In this case and if the solution makes sense to you, you can open a PR or draft PR to fix it.
|
||||
- b.) The issue description does not propose a fix. In this case, you can ask what a proposed fix could look like and someone from the Diffusers team should answer shortly. If you have a good idea of how to fix it, feel free to directly open a PR.
|
||||
- c.) There is already an open PR to fix the issue, but the issue hasn't been closed yet. If the PR has gone stale, you can simply open a new PR and link to the stale PR. PRs often go stale if the original contributor who wanted to fix the issue suddenly cannot find the time anymore to proceed. This often happens in open-source and is very normal. In this case, the community will be very happy if you give it a new try and leverage the knowledge of the existing PR. If there is already a PR and it is active, you can help the author by giving suggestions, reviewing the PR or even asking whether you can contribute to the PR.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Contribute to the documentation
|
||||
|
||||
A good library **always** has good documentation! The official documentation is often one of the first points of contact for new users of the library, and therefore contributing to the documentation is a **highly
|
||||
valuable contribution**.
|
||||
|
||||
Contributing to the library can have many forms:
|
||||
|
||||
- Correcting spelling or grammatical errors.
|
||||
- Correct incorrect formatting of the docstring. If you see that the official documentation is weirdly displayed or a link is broken, we are very happy if you take some time to correct it.
|
||||
- Correct the shape or dimensions of a docstring input or output tensor.
|
||||
- Clarify documentation that is hard to understand or incorrect.
|
||||
- Update outdated code examples.
|
||||
- Translating the documentation to another language.
|
||||
|
||||
Anything displayed on [the official Diffusers doc page](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index) is part of the official documentation and can be corrected, adjusted in the respective [documentation source](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source).
|
||||
|
||||
Please have a look at [this page](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs) on how to verify changes made to the documentation locally.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[Pipelines](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/overview) are usually the first point of contact between the Diffusers library and the user.
|
||||
Pipelines are examples of how to use Diffusers [models](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models) and [schedulers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/schedulers/overview).
|
||||
We support two types of pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
- Official Pipelines
|
||||
- Community Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Both official and community pipelines follow the same design and consist of the same type of components.
|
||||
|
||||
Official pipelines are tested and maintained by the core maintainers of Diffusers. Their code
|
||||
resides in [src/diffusers/pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines).
|
||||
In contrast, community pipelines are contributed and maintained purely by the **community** and are **not** tested.
|
||||
They reside in [examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) and while they can be accessed via the [PyPI diffusers package](https://pypi.org/project/diffusers/), their code is not part of the PyPI distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
The reason for the distinction is that the core maintainers of the Diffusers library cannot maintain and test all
|
||||
possible ways diffusion models can be used for inference, but some of them may be of interest to the community.
|
||||
Officially released diffusion pipelines,
|
||||
such as Stable Diffusion are added to the core src/diffusers/pipelines package which ensures
|
||||
high quality of maintenance, no backward-breaking code changes, and testing.
|
||||
More bleeding edge pipelines should be added as community pipelines. If usage for a community pipeline is high, the pipeline can be moved to the official pipelines upon request from the community. This is one of the ways we strive to be a community-driven library.
|
||||
|
||||
To add a community pipeline, one should add a <name-of-the-community>.py file to [examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) and adapt the [examples/community/README.md](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community/README.md) to include an example of the new pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
An example can be seen [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/2400).
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipeline PRs are only checked at a superficial level and ideally they should be maintained by their original authors.
|
||||
|
||||
Contributing a community pipeline is a great way to understand how Diffusers models and schedulers work. Having contributed a community pipeline is usually the first stepping stone to contributing an official pipeline to the
|
||||
core package.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Contribute to training examples
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers examples are a collection of training scripts that reside in [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples).
|
||||
|
||||
We support two types of training examples:
|
||||
|
||||
- Official training examples
|
||||
- Research training examples
|
||||
|
||||
Research training examples are located in [examples/research_projects](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects) whereas official training examples include all folders under [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples) except the `research_projects` and `community` folders.
|
||||
The official training examples are maintained by the Diffusers' core maintainers whereas the research training examples are maintained by the community.
|
||||
This is because of the same reasons put forward in [6. Contribute a community pipeline](#contribute-a-community-pipeline) for official pipelines vs. community pipelines: It is not feasible for the core maintainers to maintain all possible training methods for diffusion models.
|
||||
If the Diffusers core maintainers and the community consider a certain training paradigm to be too experimental or not popular enough, the corresponding training code should be put in the `research_projects` folder and maintained by the author.
|
||||
|
||||
Both official training and research examples consist of a directory that contains one or more training scripts, a requirements.txt file, and a README.md file. In order for the user to make use of the
|
||||
training examples, it is required to clone the repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
as well as to install all additional dependencies required for training:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install -r /examples/<your-example-folder>/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore when adding an example, the `requirements.txt` file shall define all pip dependencies required for your training example so that once all those are installed, the user can run the example's training script. See, for example, the [DreamBooth `requirements.txt` file](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/requirements.txt).
|
||||
|
||||
Training examples of the Diffusers library should adhere to the following philosophy:
|
||||
- All the code necessary to run the examples should be found in a single Python file
|
||||
- One should be able to run the example from the command line with `python <your-example>.py --args`
|
||||
- Examples should be kept simple and serve as **an example** on how to use Diffusers for training. The purpose of example scripts is **not** to create state-of-the-art diffusion models, but rather to reproduce known training schemes without adding too much custom logic. As a byproduct of this point, our examples also strive to serve as good educational materials.
|
||||
|
||||
To contribute an example, it is highly recommended to look at already existing examples such as [dreambooth](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py) to get an idea of how they should look like.
|
||||
We strongly advise contributors to make use of the [Accelerate library](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate) as it's tightly integrated
|
||||
with Diffusers.
|
||||
Once an example script works, please make sure to add a comprehensive `README.md` that states how to use the example exactly. This README should include:
|
||||
- An example command on how to run the example script as shown [here e.g.](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#running-locally-with-pytorch).
|
||||
- A link to some training results (logs, models, ...) that show what the user can expect as shown [here e.g.](https://api.wandb.ai/report/patrickvonplaten/xm6cd5q5).
|
||||
- If you are adding a non-official/research training example, **please don't forget** to add a sentence that you are maintaining this training example which includes your git handle as shown [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/intel_opts#diffusers-examples-with-intel-optimizations).
|
||||
|
||||
If you are contributing to the official training examples, please also make sure to add a test to [examples/test_examples.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/test_examples.py). This is not necessary for non-official training examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Fixing a "Good second issue"
|
||||
|
||||
*Good second issues* are marked by the [Good second issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22) label. Good second issues are
|
||||
usually more complicated to solve than [Good first issues](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22).
|
||||
The issue description usually gives less guidance on how to fix the issue and requires
|
||||
a decent understanding of the library by the interested contributor.
|
||||
If you are interested in tackling a second good issue, feel free to open a PR to fix it and link the PR to the issue. If you see that a PR has already been opened for this issue but did not get merged, have a look to understand why it wasn't merged and try to open an improved PR.
|
||||
Good second issues are usually more difficult to get merged compared to good first issues, so don't hesitate to ask for help from the core maintainers. If your PR is almost finished the core maintainers can also jump into your PR and commit to it in order to get it merged.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Adding pipelines, models, schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines, models, and schedulers are the most important pieces of the Diffusers library.
|
||||
They provide easy access to state-of-the-art diffusion technologies and thus allow the community to
|
||||
build powerful generative AI applications.
|
||||
|
||||
By adding a new model, pipeline, or scheduler you might enable a new powerful use case for any of the user interfaces relying on Diffusers which can be of immense value for the whole generative AI ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers has a couple of open feature requests for all three components - feel free to gloss over them
|
||||
if you don't know yet what specific component you would like to add:
|
||||
- [Model or pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22)
|
||||
- [Scheduler](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22)
|
||||
|
||||
Before adding any of the three components, it is strongly recommended that you give the [Philosophy guide](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22) a read to better understand the design of any of the three components. Please be aware that
|
||||
we cannot merge model, scheduler, or pipeline additions that strongly diverge from our design philosophy
|
||||
as it will lead to API inconsistencies. If you fundamentally disagree with a design choice, please
|
||||
open a [Feedback issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=) instead so that it can be discussed whether a certain design
|
||||
pattern/design choice shall be changed everywhere in the library and whether we shall update our design philosophy. Consistency across the library is very important for us.
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure to add links to the original codebase/paper to the PR and ideally also ping the
|
||||
original author directly on the PR so that they can follow the progress and potentially help with questions.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are unsure or stuck in the PR, don't hesitate to leave a message to ask for a first review or help.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to write a good issue
|
||||
|
||||
**The better your issue is written, the higher the chances that it will be quickly resolved.**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Make sure that you've used the correct template for your issue. You can pick between *Bug Report*, *Feature Request*, *Feedback about API Design*, *New model/pipeline/scheduler addition*, *Forum*, or a blank issue. Make sure to pick the correct one when opening [a new issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose).
|
||||
2. **Be precise**: Give your issue a fitting title. Try to formulate your issue description as simple as possible. The more precise you are when submitting an issue, the less time it takes to understand the issue and potentially solve it. Make sure to open an issue for one issue only and not for multiple issues. If you found multiple issues, simply open multiple issues. If your issue is a bug, try to be as precise as possible about what bug it is - you should not just write "Error in diffusers".
|
||||
3. **Reproducibility**: No reproducible code snippet == no solution. If you encounter a bug, maintainers **have to be able to reproduce** it. Make sure that you include a code snippet that can be copy-pasted into a Python interpreter to reproduce the issue. Make sure that your code snippet works, *i.e.* that there are no missing imports or missing links to images, ... Your issue should contain an error message **and** a code snippet that can be copy-pasted without any changes to reproduce the exact same error message. If your issue is using local model weights or local data that cannot be accessed by the reader, the issue cannot be solved. If you cannot share your data or model, try to make a dummy model or dummy data.
|
||||
4. **Minimalistic**: Try to help the reader as much as you can to understand the issue as quickly as possible by staying as concise as possible. Remove all code / all information that is irrelevant to the issue. If you have found a bug, try to create the easiest code example you can to demonstrate your issue, do not just dump your whole workflow into the issue as soon as you have found a bug. E.g., if you train a model and get an error at some point during the training, you should first try to understand what part of the training code is responsible for the error and try to reproduce it with a couple of lines. Try to use dummy data instead of full datasets.
|
||||
5. Add links. If you are referring to a certain naming, method, or model make sure to provide a link so that the reader can better understand what you mean. If you are referring to a specific PR or issue, make sure to link it to your issue. Do not assume that the reader knows what you are talking about. The more links you add to your issue the better.
|
||||
6. Formatting. Make sure to nicely format your issue by formatting code into Python code syntax, and error messages into normal code syntax. See the [official GitHub formatting docs](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/writing-on-github/getting-started-with-writing-and-formatting-on-github/basic-writing-and-formatting-syntax) for more information.
|
||||
7. Think of your issue not as a ticket to be solved, but rather as a beautiful entry to a well-written encyclopedia. Every added issue is a contribution to publicly available knowledge. By adding a nicely written issue you not only make it easier for maintainers to solve your issue, but you are helping the whole community to better understand a certain aspect of the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to write a good PR
|
||||
|
||||
1. Be a chameleon. Understand existing design patterns and syntax and make sure your code additions flow seamlessly into the existing code base. Pull requests that significantly diverge from existing design patterns or user interfaces will not be merged.
|
||||
2. Be laser focused. A pull request should solve one problem and one problem only. Make sure to not fall into the trap of "also fixing another problem while we're adding it". It is much more difficult to review pull requests that solve multiple, unrelated problems at once.
|
||||
3. If helpful, try to add a code snippet that displays an example of how your addition can be used.
|
||||
4. The title of your pull request should be a summary of its contribution.
|
||||
5. If your pull request addresses an issue, please mention the issue number in
|
||||
the pull request description to make sure they are linked (and people
|
||||
consulting the issue know you are working on it);
|
||||
6. To indicate a work in progress please prefix the title with `[WIP]`. These
|
||||
are useful to avoid duplicated work, and to differentiate it from PRs ready
|
||||
to be merged;
|
||||
7. Try to formulate and format your text as explained in [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue).
|
||||
8. Make sure existing tests pass;
|
||||
9. Add high-coverage tests. No quality testing = no merge.
|
||||
- If you are adding new `@slow` tests, make sure they pass using
|
||||
`RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest tests/test_my_new_model.py`.
|
||||
CircleCI does not run the slow tests, but GitHub actions does every night!
|
||||
10. All public methods must have informative docstrings that work nicely with markdown. See `[pipeline_latent_diffusion.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/latent_diffusion/pipeline_latent_diffusion.py)` for an example.
|
||||
11. Due to the rapidly growing repository, it is important to make sure that no files that would significantly weigh down the repository are added. This includes images, videos, and other non-text files. We prefer to leverage a hf.co hosted `dataset` like
|
||||
[`hf-internal-testing`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing) or [huggingface/documentation-images](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images) to place these files.
|
||||
If an external contribution, feel free to add the images to your PR and ask a Hugging Face member to migrate your images
|
||||
to this dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to open a PR
|
||||
## Start contributing! (Pull Requests)
|
||||
|
||||
Before writing code, we strongly advise you to search through the existing PRs or
|
||||
issues to make sure that nobody is already working on the same thing. If you are
|
||||
@@ -355,105 +99,146 @@ You will need basic `git` proficiency to be able to contribute to
|
||||
manual. Type `git --help` in a shell and enjoy. If you prefer books, [Pro
|
||||
Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2) is a very good reference.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow these steps to start contributing ([supported Python versions](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/setup.py#L244)):
|
||||
Follow these steps to start contributing ([supported Python versions](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/setup.py#L426)):
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) by
|
||||
clicking on the 'Fork' button on the repository's page. This creates a copy of the code
|
||||
under your GitHub user account.
|
||||
clicking on the 'Fork' button on the repository's page. This creates a copy of the code
|
||||
under your GitHub user account.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Clone your fork to your local disk, and add the base repository as a remote:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git clone git@github.com:<your Github handle>/diffusers.git
|
||||
$ cd diffusers
|
||||
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git clone git@github.com:<your Github handle>/diffusers.git
|
||||
$ cd diffusers
|
||||
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Create a new branch to hold your development changes:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git checkout -b a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git checkout -b a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Do not** work on the `main` branch.
|
||||
**Do not** work on the `main` branch.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Set up a development environment by running the following command in a virtual environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pip install -e ".[dev]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pip install -e ".[dev]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have already cloned the repo, you might need to `git pull` to get the most recent changes in the
|
||||
library.
|
||||
(If diffusers was already installed in the virtual environment, remove
|
||||
it with `pip uninstall diffusers` before reinstalling it in editable
|
||||
mode with the `-e` flag.)
|
||||
|
||||
To run the full test suite, you might need the additional dependency on `transformers` and `datasets` which requires a separate source
|
||||
install:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
|
||||
$ cd transformers
|
||||
$ pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/huggingface/datasets
|
||||
$ cd datasets
|
||||
$ pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have already cloned that repo, you might need to `git pull` to get the most recent changes in the `datasets`
|
||||
library.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Develop the features on your branch.
|
||||
|
||||
As you work on the features, you should make sure that the test suite
|
||||
passes. You should run the tests impacted by your changes like this:
|
||||
As you work on the features, you should make sure that the test suite
|
||||
passes. You should run the tests impacted by your changes like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pytest tests/<TEST_TO_RUN>.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Before you run the tests, please make sure you install the dependencies required for testing. You can do so
|
||||
with this command:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pytest tests/<TEST_TO_RUN>.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pip install -e ".[test]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
You can also run the full suite with the following command, but it takes
|
||||
a beefy machine to produce a result in a decent amount of time now that
|
||||
Diffusers has grown a lot. Here is the command for it:
|
||||
|
||||
You can run the full test suite with the following command, but it takes
|
||||
a beefy machine to produce a result in a decent amount of time now that
|
||||
Diffusers has grown a lot. Here is the command for it:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make test
|
||||
```
|
||||
For more information about tests, check out the
|
||||
[dedicated documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/testing)
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers relies on `black` and `isort` to format its source code
|
||||
consistently. After you make changes, apply automatic style corrections and code verifications
|
||||
that can't be automated in one go with:
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers relies on `black` and `isort` to format its source code
|
||||
consistently. After you make changes, apply automatic style corrections and code verifications
|
||||
that can't be automated in one go with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make style
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make style
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers also uses `ruff` and a few custom scripts to check for coding mistakes. Quality
|
||||
control runs in CI, however, you can also run the same checks with:
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers also uses `ruff` and a few custom scripts to check for coding mistakes. Quality
|
||||
control runs in CI, however you can also run the same checks with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make quality
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make quality
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once you're happy with your changes, add changed files using `git add` and
|
||||
make a commit with `git commit` to record your changes locally:
|
||||
Once you're happy with your changes, add changed files using `git add` and
|
||||
make a commit with `git commit` to record your changes locally:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git add modified_file.py
|
||||
$ git commit
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git add modified_file.py
|
||||
$ git commit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is a good idea to sync your copy of the code with the original
|
||||
repository regularly. This way you can quickly account for changes:
|
||||
It is a good idea to sync your copy of the code with the original
|
||||
repository regularly. This way you can quickly account for changes:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git pull upstream main
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git fetch upstream
|
||||
$ git rebase upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Push the changes to your account using:
|
||||
Push the changes to your account using:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git push -u origin a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git push -u origin a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Once you are satisfied, go to the
|
||||
webpage of your fork on GitHub. Click on 'Pull request' to send your changes
|
||||
to the project maintainers for review.
|
||||
6. Once you are satisfied (**and the checklist below is happy too**), go to the
|
||||
webpage of your fork on GitHub. Click on 'Pull request' to send your changes
|
||||
to the project maintainers for review.
|
||||
|
||||
7. It's ok if maintainers ask you for changes. It happens to core contributors
|
||||
too! So everyone can see the changes in the Pull request, work in your local
|
||||
branch and push the changes to your fork. They will automatically appear in
|
||||
the pull request.
|
||||
too! So everyone can see the changes in the Pull request, work in your local
|
||||
branch and push the changes to your fork. They will automatically appear in
|
||||
the pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Checklist
|
||||
|
||||
1. The title of your pull request should be a summary of its contribution;
|
||||
2. If your pull request addresses an issue, please mention the issue number in
|
||||
the pull request description to make sure they are linked (and people
|
||||
consulting the issue know you are working on it);
|
||||
3. To indicate a work in progress please prefix the title with `[WIP]`. These
|
||||
are useful to avoid duplicated work, and to differentiate it from PRs ready
|
||||
to be merged;
|
||||
4. Make sure existing tests pass;
|
||||
5. Add high-coverage tests. No quality testing = no merge.
|
||||
- If you are adding new `@slow` tests, make sure they pass using
|
||||
`RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest tests/test_my_new_model.py`.
|
||||
- If you are adding a new tokenizer, write tests, and make sure
|
||||
`RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest tests/test_tokenization_{your_model_name}.py` passes.
|
||||
CircleCI does not run the slow tests, but github actions does every night!
|
||||
6. All public methods must have informative docstrings that work nicely with sphinx. See `modeling_bert.py` for an
|
||||
example.
|
||||
7. Due to the rapidly growing repository, it is important to make sure that no files that would significantly weigh down the repository are added. This includes images, videos and other non-text files. We prefer to leverage a hf.co hosted `dataset` like
|
||||
the ones hosted on [`hf-internal-testing`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing) in which to place these files and reference
|
||||
them by URL. We recommend putting them in the following dataset: [huggingface/documentation-images](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images).
|
||||
If an external contribution, feel free to add the images to your PR and ask a Hugging Face member to migrate your images
|
||||
to this dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tests
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -467,7 +252,7 @@ repository, here's how to run tests with `pytest` for the library:
|
||||
$ python -m pytest -n auto --dist=loadfile -s -v ./tests/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, that's how `make test` is implemented!
|
||||
In fact, that's how `make test` is implemented (sans the `pip install` line)!
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify a smaller set of tests in order to test only the feature
|
||||
you're working on.
|
||||
@@ -480,18 +265,26 @@ have enough disk space and a good Internet connection, or a lot of patience!
|
||||
$ RUN_SLOW=yes python -m pytest -n auto --dist=loadfile -s -v ./tests/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`unittest` is fully supported, here's how to run tests with it:
|
||||
This means `unittest` is fully supported. Here's how to run tests with
|
||||
`unittest`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ python -m unittest discover -s tests -t . -v
|
||||
$ python -m unittest discover -s examples -t examples -v
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Style guide
|
||||
|
||||
For documentation strings, 🧨 Diffusers follows the [google style](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html).
|
||||
|
||||
**This guide was heavily inspired by the awesome [scikit-learn guide to contributing](https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md).**
|
||||
|
||||
### Syncing forked main with upstream (HuggingFace) main
|
||||
|
||||
To avoid pinging the upstream repository which adds reference notes to each upstream PR and sends unnecessary notifications to the developers involved in these PRs,
|
||||
when syncing the main branch of a forked repository, please, follow these steps:
|
||||
1. When possible, avoid syncing with the upstream using a branch and PR on the forked repository. Instead, merge directly into the forked main.
|
||||
1. When possible, avoid syncing with the upstream using a branch and PR on the forked repository. Instead merge directly into the forked main.
|
||||
2. If a PR is absolutely necessary, use the following steps after checking out your branch:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git checkout -b your-branch-for-syncing
|
||||
@@ -499,7 +292,3 @@ $ git pull --squash --no-commit upstream main
|
||||
$ git commit -m '<your message without GitHub references>'
|
||||
$ git push --set-upstream origin your-branch-for-syncing
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Style guide
|
||||
|
||||
For documentation strings, 🧨 Diffusers follows the [google style](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html).
|
||||
|
||||
110
PHILOSOPHY.md
110
PHILOSOPHY.md
@@ -1,110 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Philosophy
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers provides **state-of-the-art** pretrained diffusion models across multiple modalities.
|
||||
Its purpose is to serve as a **modular toolbox** for both inference and training.
|
||||
|
||||
We aim at building a library that stands the test of time and therefore take API design very seriously.
|
||||
|
||||
In a nutshell, Diffusers is built to be a natural extension of PyTorch. Therefore, most of our design choices are based on [PyTorch's Design Principles](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/community/design.html#pytorch-design-philosophy). Let's go over the most important ones:
|
||||
|
||||
## Usability over Performance
|
||||
|
||||
- While Diffusers has many built-in performance-enhancing features (see [Memory and Speed](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/optimization/fp16)), models are always loaded with the highest precision and lowest optimization. Therefore, by default diffusion pipelines are always instantiated on CPU with float32 precision if not otherwise defined by the user. This ensures usability across different platforms and accelerators and means that no complex installations are required to run the library.
|
||||
- Diffusers aim at being a **light-weight** package and therefore has very few required dependencies, but many soft dependencies that can improve performance (such as `accelerate`, `safetensors`, `onnx`, etc...). We strive to keep the library as lightweight as possible so that it can be added without much concern as a dependency on other packages.
|
||||
- Diffusers prefers simple, self-explainable code over condensed, magic code. This means that short-hand code syntaxes such as lambda functions, and advanced PyTorch operators are often not desired.
|
||||
|
||||
## Simple over easy
|
||||
|
||||
As PyTorch states, **explicit is better than implicit** and **simple is better than complex**. This design philosophy is reflected in multiple parts of the library:
|
||||
- We follow PyTorch's API with methods like [`DiffusionPipeline.to`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/diffusion_pipeline#diffusers.DiffusionPipeline.to) to let the user handle device management.
|
||||
- Raising concise error messages is preferred to silently correct erroneous input. Diffusers aims at teaching the user, rather than making the library as easy to use as possible.
|
||||
- Complex model vs. scheduler logic is exposed instead of magically handled inside. Schedulers/Samplers are separated from diffusion models with minimal dependencies on each other. This forces the user to write the unrolled denoising loop. However, the separation allows for easier debugging and gives the user more control over adapting the denoising process or switching out diffusion models or schedulers.
|
||||
- Separately trained components of the diffusion pipeline, *e.g.* the text encoder, the unet, and the variational autoencoder, each have their own model class. This forces the user to handle the interaction between the different model components, and the serialization format separates the model components into different files. However, this allows for easier debugging and customization. Dreambooth or textual inversion training
|
||||
is very simple thanks to diffusers' ability to separate single components of the diffusion pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tweakable, contributor-friendly over abstraction
|
||||
|
||||
For large parts of the library, Diffusers adopts an important design principle of the [Transformers library](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers), which is to prefer copy-pasted code over hasty abstractions. This design principle is very opinionated and stands in stark contrast to popular design principles such as [Don't repeat yourself (DRY)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Don%27t_repeat_yourself).
|
||||
In short, just like Transformers does for modeling files, diffusers prefers to keep an extremely low level of abstraction and very self-contained code for pipelines and schedulers.
|
||||
Functions, long code blocks, and even classes can be copied across multiple files which at first can look like a bad, sloppy design choice that makes the library unmaintainable.
|
||||
**However**, this design has proven to be extremely successful for Transformers and makes a lot of sense for community-driven, open-source machine learning libraries because:
|
||||
- Machine Learning is an extremely fast-moving field in which paradigms, model architectures, and algorithms are changing rapidly, which therefore makes it very difficult to define long-lasting code abstractions.
|
||||
- Machine Learning practitioners like to be able to quickly tweak existing code for ideation and research and therefore prefer self-contained code over one that contains many abstractions.
|
||||
- Open-source libraries rely on community contributions and therefore must build a library that is easy to contribute to. The more abstract the code, the more dependencies, the harder to read, and the harder to contribute to. Contributors simply stop contributing to very abstract libraries out of fear of breaking vital functionality. If contributing to a library cannot break other fundamental code, not only is it more inviting for potential new contributors, but it is also easier to review and contribute to multiple parts in parallel.
|
||||
|
||||
At Hugging Face, we call this design the **single-file policy** which means that almost all of the code of a certain class should be written in a single, self-contained file. To read more about the philosophy, you can have a look
|
||||
at [this blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/transformers-design-philosophy).
|
||||
|
||||
In diffusers, we follow this philosophy for both pipelines and schedulers, but only partly for diffusion models. The reason we don't follow this design fully for diffusion models is because almost all diffusion pipelines, such
|
||||
as [DDPM](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.12.0/en/api/pipelines/ddpm), [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.12.0/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview#stable-diffusion-pipelines), [UnCLIP (Dalle-2)](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.12.0/en/api/pipelines/unclip#overview) and [Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/) all rely on the same diffusion model, the [UNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models#diffusers.UNet2DConditionModel).
|
||||
|
||||
Great, now you should have generally understood why 🧨 Diffusers is designed the way it is 🤗.
|
||||
We try to apply these design principles consistently across the library. Nevertheless, there are some minor exceptions to the philosophy or some unlucky design choices. If you have feedback regarding the design, we would ❤️ to hear it [directly on GitHub](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=).
|
||||
|
||||
## Design Philosophy in Details
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's look a bit into the nitty-gritty details of the design philosophy. Diffusers essentially consist of three major classes, [pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines), [models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models), and [schedulers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers).
|
||||
Let's walk through more in-detail design decisions for each class.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines are designed to be easy to use (therefore do not follow [*Simple over easy*](#simple-over-easy) 100%)), are not feature complete, and should loosely be seen as examples of how to use [models](#models) and [schedulers](#schedulers) for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Pipelines follow the single-file policy. All pipelines can be found in individual directories under src/diffusers/pipelines. One pipeline folder corresponds to one diffusion paper/project/release. Multiple pipeline files can be gathered in one pipeline folder, as it’s done for [`src/diffusers/pipelines/stable-diffusion`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion). If pipelines share similar functionality, one can make use of the [#Copied from mechanism](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/125d783076e5bd9785beb05367a2d2566843a271/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_img2img.py#L251).
|
||||
- Pipelines all inherit from [`DiffusionPipeline`]
|
||||
- Every pipeline consists of different model and scheduler components, that are documented in the [`model_index.json` file](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/blob/main/model_index.json), are accessible under the same name as attributes of the pipeline and can be shared between pipelines with [`DiffusionPipeline.components`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/diffusion_pipeline#diffusers.DiffusionPipeline.components) function.
|
||||
- Every pipeline should be loadable via the [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/diffusion_pipeline#diffusers.DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained) function.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be used **only** for inference.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be very readable, self-explanatory, and easy to tweak.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be designed to build on top of each other and be easy to integrate into higher-level APIs.
|
||||
- Pipelines are **not** intended to be feature-complete user interfaces. For future complete user interfaces one should rather have a look at [InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI), [Diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers), and [lama-cleaner](https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner)
|
||||
- Every pipeline should have one and only one way to run it via a `__call__` method. The naming of the `__call__` arguments should be shared across all pipelines.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be named after the task they are intended to solve.
|
||||
- In almost all cases, novel diffusion pipelines shall be implemented in a new pipeline folder/file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Models
|
||||
|
||||
Models are designed as configurable toolboxes that are natural extensions of [PyTorch's Module class](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html). They only partly follow the **single-file policy**.
|
||||
|
||||
The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Models correspond to **a type of model architecture**. *E.g.* the [`UNet2DConditionModel`] class is used for all UNet variations that expect 2D image inputs and are conditioned on some context.
|
||||
- All models can be found in [`src/diffusers/models`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models) and every model architecture shall be defined in its file, e.g. [`unet_2d_condition.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unet_2d_condition.py), [`transformer_2d.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/transformer_2d.py), etc...
|
||||
- Models **do not** follow the single-file policy and should make use of smaller model building blocks, such as [`attention.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/attention.py), [`resnet.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/resnet.py), [`embeddings.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/embeddings.py), etc... **Note**: This is in stark contrast to Transformers' modeling files and shows that models do not really follow the single-file policy.
|
||||
- Models intend to expose complexity, just like PyTorch's module does, and give clear error messages.
|
||||
- Models all inherit from `ModelMixin` and `ConfigMixin`.
|
||||
- Models can be optimized for performance when it doesn’t demand major code changes, keeps backward compatibility, and gives significant memory or compute gain.
|
||||
- Models should by default have the highest precision and lowest performance setting.
|
||||
- To integrate new model checkpoints whose general architecture can be classified as an architecture that already exists in Diffusers, the existing model architecture shall be adapted to make it work with the new checkpoint. One should only create a new file if the model architecture is fundamentally different.
|
||||
- Models should be designed to be easily extendable to future changes. This can be achieved by limiting public function arguments, configuration arguments, and "foreseeing" future changes, *e.g.* it is usually better to add `string` "...type" arguments that can easily be extended to new future types instead of boolean `is_..._type` arguments. Only the minimum amount of changes shall be made to existing architectures to make a new model checkpoint work.
|
||||
- The model design is a difficult trade-off between keeping code readable and concise and supporting many model checkpoints. For most parts of the modeling code, classes shall be adapted for new model checkpoints, while there are some exceptions where it is preferred to add new classes to make sure the code is kept concise and
|
||||
readable longterm, such as [UNet blocks](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unet_2d_blocks.py) and [Attention processors](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/cross_attention.py).
|
||||
|
||||
### Schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
Schedulers are responsible to guide the denoising process for inference as well as to define a noise schedule for training. They are designed as individual classes with loadable configuration files and strongly follow the **single-file policy**.
|
||||
|
||||
The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- All schedulers are found in [`src/diffusers/schedulers`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers).
|
||||
- Schedulers are **not** allowed to import from large utils files and shall be kept very self-contained.
|
||||
- One scheduler python file corresponds to one scheduler algorithm (as might be defined in a paper).
|
||||
- If schedulers share similar functionalities, we can make use of the `#Copied from` mechanism.
|
||||
- Schedulers all inherit from `SchedulerMixin` and `ConfigMixin`.
|
||||
- Schedulers can be easily swapped out with the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/configuration#diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config) method as explained in detail [here](./using-diffusers/schedulers.mdx).
|
||||
- Every scheduler has to have a `set_num_inference_steps`, and a `step` function. `set_num_inference_steps(...)` has to be called before every denoising process, *i.e.* before `step(...)` is called.
|
||||
- Every scheduler exposes the timesteps to be "looped over" via a `timesteps` attribute, which is an array of timesteps the model will be called upon
|
||||
- The `step(...)` function takes a predicted model output and the "current" sample (x_t) and returns the "previous", slightly more denoised sample (x_t-1).
|
||||
- Given the complexity of diffusion schedulers, the `step` function does not expose all the complexity and can be a bit of a "black box".
|
||||
- In almost all cases, novel schedulers shall be implemented in a new scheduling file.
|
||||
600
README.md
600
README.md
@@ -15,140 +15,45 @@
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is the go-to library for state-of-the-art pretrained diffusion models for generating images, audio, and even 3D structures of molecules. Whether you're looking for a simple inference solution or training your own diffusion models, 🤗 Diffusers is a modular toolbox that supports both. Our library is designed with a focus on [usability over performance](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy#usability-over-performance), [simple over easy](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy#simple-over-easy), and [customizability over abstractions](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy#tweakable-contributorfriendly-over-abstraction).
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers provides pretrained diffusion models across multiple modalities, such as vision and audio, and serves
|
||||
as a modular toolbox for inference and training of diffusion models.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers offers three core components:
|
||||
More precisely, 🤗 Diffusers offers:
|
||||
|
||||
- State-of-the-art [diffusion pipelines](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/overview) that can be run in inference with just a few lines of code.
|
||||
- Interchangeable noise [schedulers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/schedulers/overview) for different diffusion speeds and output quality.
|
||||
- Pretrained [models](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models) that can be used as building blocks, and combined with schedulers, for creating your own end-to-end diffusion systems.
|
||||
- State-of-the-art diffusion pipelines that can be run in inference with just a couple of lines of code (see [src/diffusers/pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines)). Check [this overview](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/README.md#pipelines-summary) to see all supported pipelines and their corresponding official papers.
|
||||
- Various noise schedulers that can be used interchangeably for the preferred speed vs. quality trade-off in inference (see [src/diffusers/schedulers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers)).
|
||||
- Multiple types of models, such as UNet, can be used as building blocks in an end-to-end diffusion system (see [src/diffusers/models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models)).
|
||||
- Training examples to show how to train the most popular diffusion model tasks (see [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples), *e.g.* [unconditional-image-generation](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/unconditional_image_generation)).
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend installing 🤗 Diffusers in a virtual environment from PyPi or Conda. For more details about installing [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) and [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/installation.html), please refer to their official documentation.
|
||||
### For PyTorch
|
||||
|
||||
### PyTorch
|
||||
|
||||
With `pip` (official package):
|
||||
**With `pip`** (official package)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade diffusers[torch]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With `conda` (maintained by the community):
|
||||
**With `conda`** (maintained by the community)
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
conda install -c conda-forge diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Flax
|
||||
### For Flax
|
||||
|
||||
With `pip` (official package):
|
||||
**With `pip`**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade diffusers[flax]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Apple Silicon (M1/M2) support
|
||||
**Apple Silicon (M1/M2) support**
|
||||
|
||||
Please refer to the [How to use Stable Diffusion in Apple Silicon](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/optimization/mps) guide.
|
||||
Please, refer to [the documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/optimization/mps).
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
Generating outputs is super easy with 🤗 Diffusers. To generate an image from text, use the `from_pretrained` method to load any pretrained diffusion model (browse the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads) for 4000+ checkpoints):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline("An image of a squirrel in Picasso style").images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also dig into the models and schedulers toolbox to build your own diffusion system:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cat-256")
|
||||
model = UNet2DModel.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cat-256").to("cuda")
|
||||
scheduler.set_timesteps(50)
|
||||
|
||||
sample_size = model.config.sample_size
|
||||
noise = torch.randn((1, 3, sample_size, sample_size)).to("cuda")
|
||||
input = noise
|
||||
|
||||
for t in scheduler.timesteps:
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
noisy_residual = model(input, t).sample
|
||||
prev_noisy_sample = scheduler.step(noisy_residual, t, input).prev_sample
|
||||
input = prev_noisy_sample
|
||||
|
||||
image = (input / 2 + 0.5).clamp(0, 1)
|
||||
image = image.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1).numpy()[0]
|
||||
image = Image.fromarray((image * 255).round().astype("uint8"))
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [Quickstart](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/quicktour) to launch your diffusion journey today!
|
||||
|
||||
## How to navigate the documentation
|
||||
|
||||
| **Documentation** | **What can I learn?** |
|
||||
|---------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| Tutorial | A basic crash course for learning how to use the library's most important features like using models and schedulers to build your own diffusion system, and training your own diffusion model. |
|
||||
| Loading | Guides for how to load and configure all the components (pipelines, models, and schedulers) of the library, as well as how to use different schedulers. |
|
||||
| Pipelines for inference | Guides for how to use pipelines for different inference tasks, batched generation, controlling generated outputs and randomness, and how to contribute a pipeline to the library. |
|
||||
| Optimization | Guides for how to optimize your diffusion model to run faster and consume less memory. |
|
||||
| [Training](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/training/overview) | Guides for how to train a diffusion model for different tasks with different training techniques. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Paper | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [alt_diffusion](./api/pipelines/alt_diffusion) | [**AltDiffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [audio_diffusion](./api/pipelines/audio_diffusion) | [**Audio Diffusion**](https://github.com/teticio/audio-diffusion.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [controlnet](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/controlnet) | [**ControlNet with Stable Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [cycle_diffusion](./api/pipelines/cycle_diffusion) | [**Cycle Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.05559) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [dance_diffusion](./api/pipelines/dance_diffusion) | [**Dance Diffusion**](https://github.com/williamberman/diffusers.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [ddpm](./api/pipelines/ddpm) | [**Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [ddim](./api/pipelines/ddim) | [**Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [**High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [**High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion_uncond](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond) | [**High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [paint_by_example](./api/pipelines/paint_by_example) | [**Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13227) | Image-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [pndm](./api/pipelines/pndm) | [**Pseudo Numerical Methods for Diffusion Models on Manifolds**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09778) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_ve](./api/pipelines/score_sde_ve) | [**Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations**](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_vp](./api/pipelines/score_sde_vp) | [**Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations**](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [semantic_stable_diffusion](./api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion) | [**Semantic Guidance**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12247) | Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_text2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img) | [**Stable Diffusion**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_img2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) | [**Stable Diffusion**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_inpaint](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/inpaint) | [**Stable Diffusion**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_panorama](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/panorama) | [**MultiDiffusion**](https://multidiffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Panorama Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix) | [**InstructPix2Pix**](https://github.com/timothybrooks/instruct-pix2pix) | Text-Guided Image Editing|
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix_zero](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero) | [**Zero-shot Image-to-Image Translation**](https://pix2pixzero.github.io/) | Text-Guided Image Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_attend_and_excite](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/attend_and_excite) | [**Attend and Excite for Stable Diffusion**](https://attendandexcite.github.io/Attend-and-Excite/) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_self_attention_guidance](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/self_attention_guidance) | [**Self-Attention Guidance**](https://ku-cvlab.github.io/Self-Attention-Guidance) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_image_variation](./stable_diffusion/image_variation) | [**Stable Diffusion Image Variations**](https://github.com/LambdaLabsML/lambda-diffusers#stable-diffusion-image-variations) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_latent_upscale](./stable_diffusion/latent_upscale) | [**Stable Diffusion Latent Upscaler**](https://twitter.com/StabilityAI/status/1590531958815064065) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Stable Diffusion 2**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Stable Diffusion 2**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Depth-Conditional Stable Diffusion**](https://github.com/Stability-AI/stablediffusion#depth-conditional-stable-diffusion) | Depth-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Stable Diffusion 2**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_safe](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe) | [**Safe Stable Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105) | Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | **Stable unCLIP** | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | **Stable unCLIP** | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stochastic_karras_ve](./api/pipelines/stochastic_karras_ve) | [**Elucidating the Design Space of Diffusion-Based Generative Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00364) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [unclip](./api/pipelines/unclip) | [Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06125) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Image Variations Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Dual Image and Text Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [vq_diffusion](./api/pipelines/vq_diffusion) | [Vector Quantized Diffusion Model for Text-to-Image Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.14822) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
|
||||
## Contribution
|
||||
## Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
We ❤️ contributions from the open-source community!
|
||||
If you want to contribute to this library, please check out our [Contribution guide](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md).
|
||||
@@ -160,13 +65,486 @@ You can look out for [issues](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues) y
|
||||
Also, say 👋 in our public Discord channel <a href="https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR"><img alt="Join us on Discord" src="https://img.shields.io/discord/823813159592001537?color=5865F2&logo=discord&logoColor=white"></a>. We discuss the hottest trends about diffusion models, help each other with contributions, personal projects or
|
||||
just hang out ☕.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
In order to get started, we recommend taking a look at two notebooks:
|
||||
|
||||
- The [Getting started with Diffusers](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/diffusers_intro.ipynb) [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/diffusers_intro.ipynb) notebook, which showcases an end-to-end example of usage for diffusion models, schedulers and pipelines.
|
||||
Take a look at this notebook to learn how to use the pipeline abstraction, which takes care of everything (model, scheduler, noise handling) for you, and also to understand each independent building block in the library.
|
||||
- The [Training a diffusers model](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/training_example.ipynb) [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/training_example.ipynb) notebook summarizes diffusion models training methods. This notebook takes a step-by-step approach to training your
|
||||
diffusion models on an image dataset, with explanatory graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion is fully compatible with `diffusers`!
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion is a text-to-image latent diffusion model created by the researchers and engineers from [CompVis](https://github.com/CompVis), [Stability AI](https://stability.ai/), [LAION](https://laion.ai/) and [RunwayML](https://runwayml.com/). It's trained on 512x512 images from a subset of the [LAION-5B](https://laion.ai/blog/laion-5b/) database. This model uses a frozen CLIP ViT-L/14 text encoder to condition the model on text prompts. With its 860M UNet and 123M text encoder, the model is relatively lightweight and runs on a GPU with at least 4GB VRAM.
|
||||
See the [model card](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-to-Image generation with Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
First let's install
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade diffusers transformers accelerate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend using the model in [half-precision (`fp16`)](https://pytorch.org/blog/accelerating-training-on-nvidia-gpus-with-pytorch-automatic-mixed-precision/) as it gives almost always the same results as full
|
||||
precision while being roughly twice as fast and requiring half the amount of GPU RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Running the model locally
|
||||
|
||||
You can also simply download the model folder and pass the path to the local folder to the `StableDiffusionPipeline`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git lfs install
|
||||
git clone https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming the folder is stored locally under `./stable-diffusion-v1-5`, you can run stable diffusion
|
||||
as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you are limited by GPU memory, you might want to consider chunking the attention computation in addition
|
||||
to using `fp16`.
|
||||
The following snippet should result in less than 4GB VRAM.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
pipe.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you wish to use a different scheduler (e.g.: DDIM, LMS, PNDM/PLMS), you can instantiate
|
||||
it before the pipeline and pass it to `from_pretrained`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import LMSDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LMSDiscreteScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
image.save("astronaut_rides_horse.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to run Stable Diffusion on CPU or you want to have maximum precision on GPU,
|
||||
please run the model in the default *full-precision* setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
|
||||
# disable the following line if you run on CPU
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
image.save("astronaut_rides_horse.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### JAX/Flax
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers offers a JAX / Flax implementation of Stable Diffusion for very fast inference. JAX shines specially on TPU hardware because each TPU server has 8 accelerators working in parallel, but it runs great on GPUs too.
|
||||
|
||||
Running the pipeline with the default PNDMScheduler:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import jax
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from flax.jax_utils import replicate
|
||||
from flax.training.common_utils import shard
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", revision="flax", dtype=jax.numpy.bfloat16
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 50
|
||||
|
||||
num_samples = jax.device_count()
|
||||
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
|
||||
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
# shard inputs and rng
|
||||
params = replicate(params)
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.split(prng_seed, jax.device_count())
|
||||
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
|
||||
images = pipeline.numpy_to_pil(np.asarray(images.reshape((num_samples,) + images.shape[-3:])))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**:
|
||||
If you are limited by TPU memory, please make sure to load the `FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline` in `bfloat16` precision instead of the default `float32` precision as done above. You can do so by telling diffusers to load the weights from "bf16" branch.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import jax
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from flax.jax_utils import replicate
|
||||
from flax.training.common_utils import shard
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", revision="bf16", dtype=jax.numpy.bfloat16
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 50
|
||||
|
||||
num_samples = jax.device_count()
|
||||
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
|
||||
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
# shard inputs and rng
|
||||
params = replicate(params)
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.split(prng_seed, jax.device_count())
|
||||
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
|
||||
images = pipeline.numpy_to_pil(np.asarray(images.reshape((num_samples,) + images.shape[-3:])))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers also has a Image-to-Image generation pipeline with Flax/Jax
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import jax
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import jax.numpy as jnp
|
||||
from flax.jax_utils import replicate
|
||||
from flax.training.common_utils import shard
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from diffusers import FlaxStableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
def create_key(seed=0):
|
||||
return jax.random.PRNGKey(seed)
|
||||
rng = create_key(0)
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
init_img = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
init_img = init_img.resize((768, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
prompts = "A fantasy landscape, trending on artstation"
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", revision="flax",
|
||||
dtype=jnp.bfloat16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
num_samples = jax.device_count()
|
||||
rng = jax.random.split(rng, jax.device_count())
|
||||
prompt_ids, processed_image = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt=[prompts]*num_samples, image = [init_img]*num_samples)
|
||||
p_params = replicate(params)
|
||||
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
|
||||
processed_image = shard(processed_image)
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt_ids=prompt_ids,
|
||||
image=processed_image,
|
||||
params=p_params,
|
||||
prng_seed=rng,
|
||||
strength=0.75,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
jit=True,
|
||||
height=512,
|
||||
width=768).images
|
||||
|
||||
output_images = pipeline.numpy_to_pil(np.asarray(output.reshape((num_samples,) + output.shape[-3:])))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers also has a Text-guided inpainting pipeline with Flax/Jax
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import jax
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from flax.jax_utils import replicate
|
||||
from flax.training.common_utils import shard
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import FlaxStableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
def download_image(url):
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
return PIL.Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
img_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo.png"
|
||||
mask_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo_mask.png"
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = download_image(img_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
mask_image = download_image(mask_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained("xvjiarui/stable-diffusion-2-inpainting")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Face of a yellow cat, high resolution, sitting on a park bench"
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 50
|
||||
|
||||
num_samples = jax.device_count()
|
||||
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
|
||||
init_image = num_samples * [init_image]
|
||||
mask_image = num_samples * [mask_image]
|
||||
prompt_ids, processed_masked_images, processed_masks = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt, init_image, mask_image)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# shard inputs and rng
|
||||
params = replicate(params)
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.split(prng_seed, jax.device_count())
|
||||
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
|
||||
processed_masked_images = shard(processed_masked_images)
|
||||
processed_masks = shard(processed_masks)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, processed_masks, processed_masked_images, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
|
||||
images = pipeline.numpy_to_pil(np.asarray(images.reshape((num_samples,) + images.shape[-3:])))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Image-to-Image text-guided generation with Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
The `StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline` lets you pass a text prompt and an initial image to condition the generation of new images.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
# load the pipeline
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
model_id_or_path = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id_or_path, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
# or download via git clone https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
|
||||
# and pass `model_id_or_path="./stable-diffusion-v1-5"`.
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
# let's download an initial image
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
init_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
init_image = init_image.resize((768, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, trending on artstation"
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, strength=0.75, guidance_scale=7.5).images
|
||||
|
||||
images[0].save("fantasy_landscape.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
You can also run this example on colab [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/image_2_image_using_diffusers.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
### In-painting using Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
The `StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline` lets you edit specific parts of an image by providing a mask and a text prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
def download_image(url):
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
return PIL.Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
|
||||
img_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo.png"
|
||||
mask_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo_mask.png"
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = download_image(img_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
mask_image = download_image(mask_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Face of a yellow cat, high resolution, sitting on a park bench"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Tweak prompts reusing seeds and latents
|
||||
|
||||
You can generate your own latents to reproduce results, or tweak your prompt on a specific result you liked.
|
||||
Please have a look at [Reusing seeds for deterministic generation](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/using-diffusers/reusing_seeds).
|
||||
|
||||
## Fine-Tuning Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
Fine-tuning techniques make it possible to adapt Stable Diffusion to your own dataset, or add new subjects to it. These are some of the techniques supported in `diffusers`:
|
||||
|
||||
Textual Inversion is a technique for capturing novel concepts from a small number of example images in a way that can later be used to control text-to-image pipelines. It does so by learning new 'words' in the embedding space of the pipeline's text encoder. These special words can then be used within text prompts to achieve very fine-grained control of the resulting images.
|
||||
|
||||
- Textual Inversion. Capture novel concepts from a small set of sample images, and associate them with new "words" in the embedding space of the text encoder. Please, refer to [our training examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/textual_inversion) or [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/training/text_inversion) to try for yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
- Dreambooth. Another technique to capture new concepts in Stable Diffusion. This method fine-tunes the UNet (and, optionally, also the text encoder) of the pipeline to achieve impressive results. Please, refer to [our training example](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth) and [training report](https://huggingface.co/blog/dreambooth) for additional details and training recommendations.
|
||||
|
||||
- Full Stable Diffusion fine-tuning. If you have a more sizable dataset with a specific look or style, you can fine-tune Stable Diffusion so that it outputs images following those examples. This was the approach taken to create [a Pokémon Stable Diffusion model](https://huggingface.co/justinpinkney/pokemon-stable-diffusion) (by Justing Pinkney / Lambda Labs), [a Japanese specific version of Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/spaces/rinna/japanese-stable-diffusion) (by [Rinna Co.](https://github.com/rinnakk/japanese-stable-diffusion/) and others. You can start at [our text-to-image fine-tuning example](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/text_to_image) and go from there.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion Community Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
The release of Stable Diffusion as an open source model has fostered a lot of interesting ideas and experimentation.
|
||||
Our [Community Examples folder](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) contains many ideas worth exploring, like interpolating to create animated videos, using CLIP Guidance for additional prompt fidelity, term weighting, and much more! [Take a look](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview) and [contribute your own](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/using-diffusers/contribute_pipeline).
|
||||
|
||||
## Other Examples
|
||||
|
||||
There are many ways to try running Diffusers! Here we outline code-focused tools (primarily using `DiffusionPipeline`s and Google Colab) and interactive web-tools.
|
||||
|
||||
### Running Code
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to run the code yourself 💻, you can try out:
|
||||
- [Text-to-Image Latent Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/ldm-text2im-large-256)
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# !pip install diffusers["torch"] transformers
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
model_id = "CompVis/ldm-text2im-large-256"
|
||||
|
||||
# load model and scheduler
|
||||
ldm = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
ldm = ldm.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
# run pipeline in inference (sample random noise and denoise)
|
||||
prompt = "A painting of a squirrel eating a burger"
|
||||
image = ldm([prompt], num_inference_steps=50, eta=0.3, guidance_scale=6).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# save image
|
||||
image.save("squirrel.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [Unconditional Diffusion with discrete scheduler](https://huggingface.co/google/ddpm-celebahq-256)
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# !pip install diffusers["torch"]
|
||||
from diffusers import DDPMPipeline, DDIMPipeline, PNDMPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "google/ddpm-celebahq-256"
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
|
||||
# load model and scheduler
|
||||
ddpm = DDPMPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id) # you can replace DDPMPipeline with DDIMPipeline or PNDMPipeline for faster inference
|
||||
ddpm.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
# run pipeline in inference (sample random noise and denoise)
|
||||
image = ddpm().images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# save image
|
||||
image.save("ddpm_generated_image.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [Unconditional Latent Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/ldm-celebahq-256)
|
||||
- [Unconditional Diffusion with continuous scheduler](https://huggingface.co/google/ncsnpp-ffhq-1024)
|
||||
|
||||
**Other Image Notebooks**:
|
||||
* [image-to-image generation with Stable Diffusion](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/image_2_image_using_diffusers.ipynb) ,
|
||||
* [tweak images via repeated Stable Diffusion seeds](https://colab.research.google.com/github/pcuenca/diffusers-examples/blob/main/notebooks/stable-diffusion-seeds.ipynb) ,
|
||||
|
||||
**Diffusers for Other Modalities**:
|
||||
* [Molecule conformation generation](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/geodiff_molecule_conformation.ipynb) ,
|
||||
* [Model-based reinforcement learning](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/reinforcement_learning_with_diffusers.ipynb) ,
|
||||
|
||||
### Web Demos
|
||||
If you just want to play around with some web demos, you can try out the following 🚀 Spaces:
|
||||
| Model | Hugging Face Spaces |
|
||||
|-------------------------------- |------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Text-to-Image Latent Diffusion | [](https://huggingface.co/spaces/CompVis/text2img-latent-diffusion) |
|
||||
| Faces generator | [](https://huggingface.co/spaces/CompVis/celeba-latent-diffusion) |
|
||||
| DDPM with different schedulers | [](https://huggingface.co/spaces/fusing/celeba-diffusion) |
|
||||
| Conditional generation from sketch | [](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface/diffuse-the-rest) |
|
||||
| Composable diffusion | [](https://huggingface.co/spaces/Shuang59/Composable-Diffusion) |
|
||||
|
||||
## Definitions
|
||||
|
||||
**Models**: Neural network that models $p_\theta(\mathbf{x}_{t-1}|\mathbf{x}_t)$ (see image below) and is trained end-to-end to *denoise* a noisy input to an image.
|
||||
*Examples*: UNet, Conditioned UNet, 3D UNet, Transformer UNet
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/10695622/174349667-04e9e485-793b-429a-affe-096e8199ad5b.png" width="800"/>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<em> Figure from DDPM paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239). </em>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
|
||||
**Schedulers**: Algorithm class for both **inference** and **training**.
|
||||
The class provides functionality to compute previous image according to alpha, beta schedule as well as predict noise for training. Also known as **Samplers**.
|
||||
*Examples*: [DDPM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239), [DDIM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502), [PNDM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09778), [DEIS](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.13902)
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/10695622/174349706-53d58acc-a4d1-4cda-b3e8-432d9dc7ad38.png" width="800"/>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<em> Sampling and training algorithms. Figure from DDPM paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239). </em>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Diffusion Pipeline**: End-to-end pipeline that includes multiple diffusion models, possible text encoders, ...
|
||||
*Examples*: Glide, Latent-Diffusion, Imagen, DALL-E 2
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/10695622/174348898-481bd7c2-5457-4830-89bc-f0907756f64c.jpeg" width="550"/>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<em> Figure from ImageGen (https://imagen.research.google/). </em>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Philosophy
|
||||
|
||||
- Readability and clarity is preferred over highly optimized code. A strong importance is put on providing readable, intuitive and elementary code design. *E.g.*, the provided [schedulers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers) are separated from the provided [models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models) and provide well-commented code that can be read alongside the original paper.
|
||||
- Diffusers is **modality independent** and focuses on providing pretrained models and tools to build systems that generate **continuous outputs**, *e.g.* vision and audio.
|
||||
- Diffusion models and schedulers are provided as concise, elementary building blocks. In contrast, diffusion pipelines are a collection of end-to-end diffusion systems that can be used out-of-the-box, should stay as close as possible to their original implementation and can include components of another library, such as text-encoders. Examples for diffusion pipelines are [Glide](https://github.com/openai/glide-text2im) and [Latent Diffusion](https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
## In the works
|
||||
|
||||
For the first release, 🤗 Diffusers focuses on text-to-image diffusion techniques. However, diffusers can be used for much more than that! Over the upcoming releases, we'll be focusing on:
|
||||
|
||||
- Diffusers for audio
|
||||
- Diffusers for reinforcement learning (initial work happening in https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/105).
|
||||
- Diffusers for video generation
|
||||
- Diffusers for molecule generation (initial work happening in https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/54)
|
||||
|
||||
A few pipeline components are already being worked on, namely:
|
||||
|
||||
- BDDMPipeline for spectrogram-to-sound vocoding
|
||||
- GLIDEPipeline to support OpenAI's GLIDE model
|
||||
- Grad-TTS for text to audio generation / conditional audio generation
|
||||
|
||||
We want diffusers to be a toolbox useful for diffusers models in general; if you find yourself limited in any way by the current API, or would like to see additional models, schedulers, or techniques, please open a [GitHub issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues) mentioning what you would like to see.
|
||||
|
||||
## Credits
|
||||
|
||||
This library concretizes previous work by many different authors and would not have been possible without their great research and implementations. We'd like to thank, in particular, the following implementations which have helped us in our development and without which the API could not have been as polished today:
|
||||
|
||||
- @CompVis' latent diffusion models library, available [here](https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion)
|
||||
- @hojonathanho original DDPM implementation, available [here](https://github.com/hojonathanho/diffusion) as well as the extremely useful translation into PyTorch by @pesser, available [here](https://github.com/pesser/pytorch_diffusion)
|
||||
- @ermongroup's DDIM implementation, available [here](https://github.com/ermongroup/ddim)
|
||||
- @ermongroup's DDIM implementation, available [here](https://github.com/ermongroup/ddim).
|
||||
- @yang-song's Score-VE and Score-VP implementations, available [here](https://github.com/yang-song/score_sde_pytorch)
|
||||
|
||||
We also want to thank @heejkoo for the very helpful overview of papers, code and resources on diffusion models, available [here](https://github.com/heejkoo/Awesome-Diffusion-Models) as well as @crowsonkb and @rromb for useful discussions and insights.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -27,6 +27,7 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip && \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
--extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117 && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
@@ -39,4 +40,4 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip && \
|
||||
tensorboard \
|
||||
transformers
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# docstyle-ignore
|
||||
INSTALL_CONTENT = """
|
||||
# Diffusers installation
|
||||
! pip install diffusers transformers datasets accelerate
|
||||
# To install from source instead of the last release, comment the command above and uncomment the following one.
|
||||
# ! pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
notebook_first_cells = [{"type": "code", "content": INSTALL_CONTENT}]
|
||||
@@ -4,77 +4,47 @@
|
||||
- local: quicktour
|
||||
title: Quicktour
|
||||
- local: stable_diffusion
|
||||
title: Effective and efficient diffusion
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion
|
||||
- local: installation
|
||||
title: Installation
|
||||
title: Get started
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: tutorials/tutorial_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/write_own_pipeline
|
||||
title: Understanding models and schedulers
|
||||
- local: tutorials/basic_training
|
||||
title: Train a diffusion model
|
||||
title: Tutorials
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/loading_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/loading
|
||||
title: Load pipelines, models, and schedulers
|
||||
title: Loading Pipelines, Models, and Schedulers
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/schedulers
|
||||
title: Load and compare different schedulers
|
||||
title: Using different Schedulers
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/configuration
|
||||
title: Configuring Pipelines, Models, and Schedulers
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Load and add custom pipelines
|
||||
title: Loading and Adding Custom Pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/kerascv
|
||||
title: Load KerasCV Stable Diffusion checkpoints
|
||||
title: Using KerasCV Stable Diffusion Checkpoints in Diffusers
|
||||
title: Loading & Hub
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/unconditional_image_generation
|
||||
title: Unconditional image generation
|
||||
title: Unconditional Image Generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation
|
||||
title: Text-to-image generation
|
||||
title: Text-to-Image Generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/img2img
|
||||
title: Text-guided image-to-image
|
||||
title: Text-Guided Image-to-Image
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/inpaint
|
||||
title: Text-guided image-inpainting
|
||||
title: Text-Guided Image-Inpainting
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/depth2img
|
||||
title: Text-guided depth-to-image
|
||||
title: Text-Guided Depth-to-Image
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/controlling_generation
|
||||
title: Controlling generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/reusing_seeds
|
||||
title: Improve image quality with deterministic generation
|
||||
title: Reusing seeds for deterministic generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/reproducibility
|
||||
title: Create reproducible pipelines
|
||||
title: Reproducibility
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_examples
|
||||
title: Community Pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/contribute_pipeline
|
||||
title: How to contribute a Pipeline
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/using_safetensors
|
||||
title: Using safetensors
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/stable_diffusion_jax_how_to
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion in JAX/Flax
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/weighted_prompts
|
||||
title: Weighting Prompts
|
||||
title: Pipelines for Inference
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: training/unconditional_training
|
||||
title: Unconditional image generation
|
||||
- local: training/text_inversion
|
||||
title: Textual Inversion
|
||||
- local: training/dreambooth
|
||||
title: DreamBooth
|
||||
- local: training/text2image
|
||||
title: Text-to-image
|
||||
- local: training/lora
|
||||
title: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models (LoRA)
|
||||
- local: training/controlnet
|
||||
title: ControlNet
|
||||
- local: training/instructpix2pix
|
||||
title: InstructPix2Pix Training
|
||||
title: Training
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/rl
|
||||
title: Reinforcement Learning
|
||||
@@ -85,8 +55,6 @@
|
||||
title: Taking Diffusers Beyond Images
|
||||
title: Using Diffusers
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: optimization/opt_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: optimization/fp16
|
||||
title: Memory and Speed
|
||||
- local: optimization/torch2.0
|
||||
@@ -97,24 +65,32 @@
|
||||
title: ONNX
|
||||
- local: optimization/open_vino
|
||||
title: OpenVINO
|
||||
- local: optimization/coreml
|
||||
title: Core ML
|
||||
- local: optimization/mps
|
||||
title: MPS
|
||||
- local: optimization/habana
|
||||
title: Habana Gaudi
|
||||
title: Optimization/Special Hardware
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: training/unconditional_training
|
||||
title: Unconditional Image Generation
|
||||
- local: training/text_inversion
|
||||
title: Textual Inversion
|
||||
- local: training/dreambooth
|
||||
title: Dreambooth
|
||||
- local: training/text2image
|
||||
title: Text-to-image fine-tuning
|
||||
- local: training/lora
|
||||
title: LoRA Support in Diffusers
|
||||
title: Training
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: conceptual/philosophy
|
||||
title: Philosophy
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/controlling_generation
|
||||
title: Controlled generation
|
||||
- local: conceptual/contribution
|
||||
title: How to contribute?
|
||||
- local: conceptual/ethical_guidelines
|
||||
title: Diffusers' Ethical Guidelines
|
||||
- local: conceptual/evaluation
|
||||
title: Evaluating Diffusion Models
|
||||
title: Conceptual Guides
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
@@ -138,8 +114,6 @@
|
||||
title: AltDiffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/audio_diffusion
|
||||
title: Audio Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/audioldm
|
||||
title: AudioLDM
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/cycle_diffusion
|
||||
title: Cycle Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/dance_diffusion
|
||||
@@ -164,8 +138,6 @@
|
||||
title: Score SDE VE
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion
|
||||
title: Semantic Guidance
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/spectrogram_diffusion
|
||||
title: "Spectrogram Diffusion"
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
@@ -195,8 +167,6 @@
|
||||
title: MultiDiffusion Panorama
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/controlnet
|
||||
title: Text-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/model_editing
|
||||
title: Text-to-Image Model Editing
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion 2
|
||||
@@ -204,10 +174,6 @@
|
||||
title: Stable unCLIP
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stochastic_karras_ve
|
||||
title: Stochastic Karras VE
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/text_to_video
|
||||
title: Text-to-Video
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/text_to_video_zero
|
||||
title: Text-to-Video Zero
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/unclip
|
||||
title: UnCLIP
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,8 +12,8 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Schedulers from [`~schedulers.scheduling_utils.SchedulerMixin`] and models from [`ModelMixin`] inherit from [`ConfigMixin`] which conveniently takes care of storing all the parameters that are
|
||||
passed to their respective `__init__` methods in a JSON-configuration file.
|
||||
In Diffusers, schedulers of type [`schedulers.scheduling_utils.SchedulerMixin`], and models of type [`ModelMixin`] inherit from [`ConfigMixin`] which conveniently takes care of storing all parameters that are
|
||||
passed to the respective `__init__` methods in a JSON-configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
## ConfigMixin
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,5 +21,3 @@ passed to their respective `__init__` methods in a JSON-configuration file.
|
||||
- load_config
|
||||
- from_config
|
||||
- save_config
|
||||
- to_json_file
|
||||
- to_json_string
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,11 +28,3 @@ API to load such adapter neural networks via the [`loaders.py` module](https://g
|
||||
### UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin
|
||||
|
||||
### TextualInversionLoaderMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] loaders.TextualInversionLoaderMixin
|
||||
|
||||
### LoraLoaderMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] loaders.LoraLoaderMixin
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,12 +37,6 @@ The models are built on the base class ['ModelMixin'] that is a `torch.nn.module
|
||||
## UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
[[autodoc]] UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
|
||||
## UNet3DConditionOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.unet_3d_condition.UNet3DConditionOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## UNet3DConditionModel
|
||||
[[autodoc]] UNet3DConditionModel
|
||||
|
||||
## DecoderOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.vae.DecoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -64,12 +58,6 @@ The models are built on the base class ['ModelMixin'] that is a `torch.nn.module
|
||||
## Transformer2DModelOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.transformer_2d.Transformer2DModelOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## TransformerTemporalModel
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.transformer_temporal.TransformerTemporalModel
|
||||
|
||||
## Transformer2DModelOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.transformer_temporal.TransformerTemporalModelOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## PriorTransformer
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.prior_transformer.PriorTransformer
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -99,9 +87,3 @@ The models are built on the base class ['ModelMixin'] that is a `torch.nn.module
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxAutoencoderKL
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxAutoencoderKL
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxControlNetOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.controlnet_flax.FlaxControlNetOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxControlNetModel
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxControlNetModel
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# AltDiffusion
|
||||
|
||||
AltDiffusion was proposed in [AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) by Zhongzhi Chen, Guang Liu, Bo-Wen Zhang, Fulong Ye, Qinghong Yang, Ledell Wu.
|
||||
AltDiffusion was proposed in [AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) by Zhongzhi Chen, Guang Liu, Bo-Wen Zhang, Fulong Ye, Qinghong Yang, Ledell Wu
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,11 +28,11 @@ The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips
|
||||
|
||||
- AltDiffusion is conceptually exactly the same as [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion/overview).
|
||||
- AltDiffusion is conceptually exaclty the same as [Stable Diffusion](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
- *Run AltDiffusion*
|
||||
|
||||
AltDiffusion can be tested very easily with the [`AltDiffusionPipeline`], [`AltDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`] and the `"BAAI/AltDiffusion-m9"` checkpoint exactly in the same way it is shown in the [Conditional Image Generation Guide](../../using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation) and the [Image-to-Image Generation Guide](../../using-diffusers/img2img).
|
||||
AltDiffusion can be tested very easily with the [`AltDiffusionPipeline`], [`AltDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`] and the `"BAAI/AltDiffusion-m9"` checkpoint exactly in the same way it is shown in the [Conditional Image Generation Guide](./using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation) and the [Image-to-Image Generation Guide](./using-diffusers/img2img).
|
||||
|
||||
- *How to load and use different schedulers.*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# AudioLDM
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
AudioLDM was proposed in [AudioLDM: Text-to-Audio Generation with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12503) by Haohe Liu et al.
|
||||
|
||||
Inspired by [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview), AudioLDM
|
||||
is a text-to-audio _latent diffusion model (LDM)_ that learns continuous audio representations from [CLAP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/clap)
|
||||
latents. AudioLDM takes a text prompt as input and predicts the corresponding audio. It can generate text-conditional
|
||||
sound effects, human speech and music.
|
||||
|
||||
This pipeline was contributed by [sanchit-gandhi](https://huggingface.co/sanchit-gandhi). The original codebase can be found [here](https://github.com/haoheliu/AudioLDM).
|
||||
|
||||
## Text-to-Audio
|
||||
|
||||
The [`AudioLDMPipeline`] can be used to load pre-trained weights from [cvssp/audioldm](https://huggingface.co/cvssp/audioldm) and generate text-conditional audio outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AudioLDMPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import scipy
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "cvssp/audioldm"
|
||||
pipe = AudioLDMPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Techno music with a strong, upbeat tempo and high melodic riffs"
|
||||
audio = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=10, audio_length_in_s=5.0).audios[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# save the audio sample as a .wav file
|
||||
scipy.io.wavfile.write("techno.wav", rate=16000, data=audio)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Tips
|
||||
|
||||
Prompts:
|
||||
* Descriptive prompt inputs work best: you can use adjectives to describe the sound (e.g. "high quality" or "clear") and make the prompt context specific (e.g., "water stream in a forest" instead of "stream").
|
||||
* It's best to use general terms like 'cat' or 'dog' instead of specific names or abstract objects that the model may not be familiar with.
|
||||
|
||||
Inference:
|
||||
* The _quality_ of the predicted audio sample can be controlled by the `num_inference_steps` argument: higher steps give higher quality audio at the expense of slower inference.
|
||||
* The _length_ of the predicted audio sample can be controlled by varying the `audio_length_in_s` argument.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to load and use different schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
The AudioLDM pipeline uses [`DDIMScheduler`] scheduler by default. But `diffusers` provides many other schedulers
|
||||
that can be used with the AudioLDM pipeline such as [`PNDMScheduler`], [`LMSDiscreteScheduler`], [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`],
|
||||
[`EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler`] etc. We recommend using the [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`] as it's currently the fastest
|
||||
scheduler there is.
|
||||
|
||||
To use a different scheduler, you can either change it via the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`]
|
||||
method, or pass the `scheduler` argument to the `from_pretrained` method of the pipeline. For example, to use the
|
||||
[`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`], you can do the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import AudioLDMPipeline, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipeline = AudioLDMPipeline.from_pretrained("cvssp/audioldm", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
>>> pipeline.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # or
|
||||
>>> dpm_scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_pretrained("cvssp/audioldm", subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
>>> pipeline = AudioLDMPipeline.from_pretrained("cvssp/audioldm", scheduler=dpm_scheduler, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AudioLDMPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AudioLDMPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -19,9 +19,9 @@ components - all of which are needed to have a functioning end-to-end diffusion
|
||||
As an example, [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/blog/stable_diffusion) has three independently trained models:
|
||||
- [Autoencoder](./api/models#vae)
|
||||
- [Conditional Unet](./api/models#UNet2DConditionModel)
|
||||
- [CLIP text encoder](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/v4.27.1/en/model_doc/clip#transformers.CLIPTextModel)
|
||||
- [CLIP text encoder](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/v4.21.2/en/model_doc/clip#transformers.CLIPTextModel)
|
||||
- a scheduler component, [scheduler](./api/scheduler#pndm),
|
||||
- a [CLIPImageProcessor](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/v4.27.1/en/model_doc/clip#transformers.CLIPImageProcessor),
|
||||
- a [CLIPFeatureExtractor](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/v4.21.2/en/model_doc/clip#transformers.CLIPFeatureExtractor),
|
||||
- as well as a [safety checker](./stable_diffusion#safety_checker).
|
||||
All of these components are necessary to run stable diffusion in inference even though they were trained
|
||||
or created independently from each other.
|
||||
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ available a colab notebook to directly try them out.
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|:---:|
|
||||
| [alt_diffusion](./alt_diffusion) | [**AltDiffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation | -
|
||||
| [audio_diffusion](./audio_diffusion) | [**Audio Diffusion**](https://github.com/teticio/audio_diffusion.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [controlnet](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/controlnet) | [**ControlNet with Stable Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/controlnet.ipynb)
|
||||
| [controlnet](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/controlnet) | [**ControlNet with Stable Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1AiR7Q-sBqO88NCyswpfiuwXZc7DfMyKA?usp=sharing)
|
||||
| [cycle_diffusion](./cycle_diffusion) | [**Cycle Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.05559) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [dance_diffusion](./dance_diffusion) | [**Dance Diffusion**](https://github.com/williamberman/diffusers.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [ddpm](./ddpm) | [**Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
@@ -77,13 +77,11 @@ available a colab notebook to directly try them out.
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | **Stable unCLIP** | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | **Stable unCLIP** | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stochastic_karras_ve](./stochastic_karras_ve) | [**Elucidating the Design Space of Diffusion-Based Generative Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00364) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [text_to_video_sd](./api/pipelines/text_to_video) | [Modelscope's Text-to-video-synthesis Model in Open Domain](https://modelscope.cn/models/damo/text-to-video-synthesis/summary) | Text-to-Video Generation |
|
||||
| [unclip](./unclip) | [Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06125) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Image Variations Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Dual Image and Text Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [vq_diffusion](./vq_diffusion) | [Vector Quantized Diffusion Model for Text-to-Image Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.14822) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [text_to_video_zero](./text_to_video_zero) | [Text2Video-Zero: Text-to-Image Diffusion Models are Zero-Shot Video Generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.13439) | Text-to-Video Generation |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Pipelines are simple examples of how to play around with the diffusion systems as described in the corresponding papers.
|
||||
@@ -109,7 +107,7 @@ from the local path.
|
||||
each pipeline, one should look directly into the respective pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: All pipelines have PyTorch's autograd disabled by decorating the `__call__` method with a [`torch.no_grad`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.no_grad.html) decorator because pipelines should
|
||||
not be used for training. If you want to store the gradients during the forward pass, we recommend writing your own pipeline, see also our [community-examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community).
|
||||
not be used for training. If you want to store the gradients during the forward pass, we recommend writing your own pipeline, see also our [community-examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community)
|
||||
|
||||
## Contribution
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -174,7 +172,7 @@ You can also run this example on colab [ shows how to do it step by step. You can also run it in Google Colab [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/pcuenca/diffusers-examples/blob/main/notebooks/stable-diffusion-seeds.ipynb)
|
||||
You can generate your own latents to reproduce results, or tweak your prompt on a specific result you liked. [This notebook](https://github.com/pcuenca/diffusers-examples/blob/main/notebooks/stable-diffusion-seeds.ipynb) shows how to do it step by step. You can also run it in Google Colab [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/pcuenca/diffusers-examples/blob/main/notebooks/stable-diffusion-seeds.ipynb).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### In-painting using Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13227) by Binxin Yang, Shuyang Gu, Bo Zhang, Ting Zhang, Xuejin Chen, Xiaoyan Sun, Dong Chen, Fang Wen.
|
||||
[Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13227) by Binxin Yang, Shuyang Gu, Bo Zhang, Ting Zhang, Xuejin Chen, Xiaoyan Sun, Dong Chen, Fang Wen
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,11 +24,11 @@ The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Colab | Demo
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|:---:|
|
||||
| [pipeline_semantic_stable_diffusion.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion/pipeline_semantic_stable_diffusion.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation* | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ml-research/semantic-image-editing/blob/main/examples/SemanticGuidance.ipynb) | [Coming Soon](https://huggingface.co/AIML-TUDA)
|
||||
| [pipeline_semantic_stable_diffusion.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion/pipeline_semantic_stable_diffusion) | *Text-to-Image Generation* | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ml-research/semantic-image-editing/blob/main/examples/SemanticGuidance.ipynb) | [Coming Soon](https://huggingface.co/AIML-TUDA)
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips
|
||||
|
||||
- The Semantic Guidance pipeline can be used with any [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion/text2img) checkpoint.
|
||||
- The Semantic Guidance pipeline can be used with any [Stable Diffusion](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img) checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
### Run Semantic Guidance
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ out = pipe(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more examples check the Colab notebook.
|
||||
For more examples check the colab notebook.
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionSafePipelineOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.semantic_stable_diffusion.SemanticStableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Multi-instrument Music Synthesis with Spectrogram Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[Spectrogram Diffusion](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.05408) by Curtis Hawthorne, Ian Simon, Adam Roberts, Neil Zeghidour, Josh Gardner, Ethan Manilow, and Jesse Engel.
|
||||
|
||||
An ideal music synthesizer should be both interactive and expressive, generating high-fidelity audio in realtime for arbitrary combinations of instruments and notes. Recent neural synthesizers have exhibited a tradeoff between domain-specific models that offer detailed control of only specific instruments, or raw waveform models that can train on any music but with minimal control and slow generation. In this work, we focus on a middle ground of neural synthesizers that can generate audio from MIDI sequences with arbitrary combinations of instruments in realtime. This enables training on a wide range of transcription datasets with a single model, which in turn offers note-level control of composition and instrumentation across a wide range of instruments. We use a simple two-stage process: MIDI to spectrograms with an encoder-decoder Transformer, then spectrograms to audio with a generative adversarial network (GAN) spectrogram inverter. We compare training the decoder as an autoregressive model and as a Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM) and find that the DDPM approach is superior both qualitatively and as measured by audio reconstruction and Fréchet distance metrics. Given the interactivity and generality of this approach, we find this to be a promising first step towards interactive and expressive neural synthesis for arbitrary combinations of instruments and notes.
|
||||
|
||||
The original codebase of this implementation can be found at [magenta/music-spectrogram-diffusion](https://github.com/magenta/music-spectrogram-diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
## Model
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As depicted above the model takes as input a MIDI file and tokenizes it into a sequence of 5 second intervals. Each tokenized interval then together with positional encodings is passed through the Note Encoder and its representation is concatenated with the previous window's generated spectrogram representation obtained via the Context Encoder. For the initial 5 second window this is set to zero. The resulting context is then used as conditioning to sample the denoised Spectrogram from the MIDI window and we concatenate this spectrogram to the final output as well as use it for the context of the next MIDI window. The process repeats till we have gone over all the MIDI inputs. Finally a MelGAN decoder converts the potentially long spectrogram to audio which is the final result of this pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Colab
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [pipeline_spectrogram_diffusion.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/spectrogram_diffusion/pipeline_spectrogram_diffusion.py) | *Unconditional Audio Generation* | - |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import SpectrogramDiffusionPipeline, MidiProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = SpectrogramDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("google/music-spectrogram-diffusion")
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
processor = MidiProcessor()
|
||||
|
||||
# Download MIDI from: wget http://www.piano-midi.de/midis/beethoven/beethoven_hammerklavier_2.mid
|
||||
output = pipe(processor("beethoven_hammerklavier_2.mid"))
|
||||
|
||||
audio = output.audios[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## SpectrogramDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] SpectrogramDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ Resources:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Demo
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_controlnet.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning* | [Colab Example](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/controlnet.ipynb)
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_controlnet.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning* | [Colab Example](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1AiR7Q-sBqO88NCyswpfiuwXZc7DfMyKA?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -65,12 +65,6 @@ First, we need to install opencv:
|
||||
pip install opencv-contrib-python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let's also install all required Hugging Face libraries:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install diffusers transformers git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we can retrieve the canny edges of the image.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@@ -131,117 +125,10 @@ This should take only around 3-4 seconds on GPU (depending on hardware). The out
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: To see how to run all other ControlNet checkpoints, please have a look at [ControlNet with Stable Diffusion 1.5](#controlnet-with-stable-diffusion-1.5).
|
||||
**Note**: To see how to run all other ControlNet checkpoints, please have a look at [ControlNet with Stable Diffusion 1.5](#controlnet-with-stable-diffusion-1.5)
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- TODO: add space -->
|
||||
|
||||
## Combining multiple conditionings
|
||||
|
||||
Multiple ControlNet conditionings can be combined for a single image generation. Pass a list of ControlNets to the pipeline's constructor and a corresponding list of conditionings to `__call__`.
|
||||
|
||||
When combining conditionings, it is helpful to mask conditionings such that they do not overlap. In the example, we mask the middle of the canny map where the pose conditioning is located.
|
||||
|
||||
It can also be helpful to vary the `controlnet_conditioning_scales` to emphasize one conditioning over the other.
|
||||
|
||||
### Canny conditioning
|
||||
|
||||
The original image:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/landscape.png"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Prepare the conditioning:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
canny_image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/landscape.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
canny_image = np.array(canny_image)
|
||||
|
||||
low_threshold = 100
|
||||
high_threshold = 200
|
||||
|
||||
canny_image = cv2.Canny(canny_image, low_threshold, high_threshold)
|
||||
|
||||
# zero out middle columns of image where pose will be overlayed
|
||||
zero_start = canny_image.shape[1] // 4
|
||||
zero_end = zero_start + canny_image.shape[1] // 2
|
||||
canny_image[:, zero_start:zero_end] = 0
|
||||
|
||||
canny_image = canny_image[:, :, None]
|
||||
canny_image = np.concatenate([canny_image, canny_image, canny_image], axis=2)
|
||||
canny_image = Image.fromarray(canny_image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/blog/controlnet/landscape_canny_masked.png"/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Openpose conditioning
|
||||
|
||||
The original image:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/person.png" width=600/>
|
||||
|
||||
Prepare the conditioning:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from controlnet_aux import OpenposeDetector
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
openpose = OpenposeDetector.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/ControlNet")
|
||||
|
||||
openpose_image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/person.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
openpose_image = openpose(openpose_image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/blog/controlnet/person_pose.png" width=600/>
|
||||
|
||||
### Running ControlNet with multiple conditionings
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline, ControlNetModel, UniPCMultistepScheduler
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
controlnet = [
|
||||
ControlNetModel.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-openpose", torch_dtype=torch.float16),
|
||||
ControlNetModel.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-canny", torch_dtype=torch.float16),
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", controlnet=controlnet, torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = UniPCMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a giant standing in a fantasy landscape, best quality"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "monochrome, lowres, bad anatomy, worst quality, low quality"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(1)
|
||||
|
||||
images = [openpose_image, canny_image]
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
images,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=20,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
|
||||
controlnet_conditioning_scale=[1.0, 0.8],
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
image.save("./multi_controlnet_output.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/blog/controlnet/multi_controlnet_output.png" width=600/>
|
||||
|
||||
## Available checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
ControlNet requires a *control image* in addition to the text-to-image *prompt*.
|
||||
@@ -258,11 +145,10 @@ All checkpoints can be found under the authors' namespace [lllyasviel](https://h
|
||||
|[lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-hed](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-hed)<br/> *Trained with HED edge detection (soft edge)* |A monochrome image with white soft edges on a black background.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/blob/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_bird_hed.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_bird_hed.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_bird_hed_1.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_bird_hed_1.png"/></a> |
|
||||
|[lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-mlsd](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-mlsd)<br/> *Trained with M-LSD line detection* |A monochrome image composed only of white straight lines on a black background.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/blob/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_room_mlsd.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_room_mlsd.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_room_mlsd_0.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_room_mlsd_0.png"/></a>|
|
||||
|[lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-normal](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-normal)<br/> *Trained with normal map* |A [normal mapped](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal_mapping) image.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/blob/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_human_normal.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_human_normal.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_human_normal_1.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_human_normal_1.png"/></a>|
|
||||
|[lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-openpose](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet_openpose)<br/> *Trained with OpenPose bone image* |A [OpenPose bone](https://github.com/CMU-Perceptual-Computing-Lab/openpose) image.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/blob/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_human_openpose.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_human_openpose.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_human_openpose_0.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_human_openpose_0.png"/></a>|
|
||||
|[lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-scribble](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet_scribble)<br/> *Trained with human scribbles* |A hand-drawn monochrome image with white outlines on a black background.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/blob/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_vermeer_scribble.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_vermeer_scribble.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_vermeer_scribble_0.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_vermeer_scribble_0.png"/></a> |
|
||||
|[lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-seg](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet_seg)<br/>*Trained with semantic segmentation* |An [ADE20K](https://groups.csail.mit.edu/vision/datasets/ADE20K/)'s segmentation protocol image.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/blob/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_room_seg.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_room_seg.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_room_seg_1.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_room_seg_1.png"/></a> |
|
||||
|[lllyasviel/sd-controlnet_openpose](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet_openpose)<br/> *Trained with OpenPose bone image* |A [OpenPose bone](https://github.com/CMU-Perceptual-Computing-Lab/openpose) image.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/blob/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_human_openpose.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_human_openpose.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_human_openpose_0.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_human_openpose_0.png"/></a>|
|
||||
|[lllyasviel/sd-controlnet_scribble](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet_scribble)<br/> *Trained with human scribbles* |A hand-drawn monochrome image with white outlines on a black background.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/blob/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_vermeer_scribble.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_vermeer_scribble.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_vermeer_scribble_0.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_vermeer_scribble_0.png"/></a> |
|
||||
|[lllyasviel/sd-controlnet_seg](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet_seg)<br/>*Trained with semantic segmentation* |An [ADE20K](https://groups.csail.mit.edu/vision/datasets/ADE20K/)'s segmentation protocol image.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/blob/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_room_seg.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/control_images/converted/control_room_seg.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_room_seg_1.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/takuma104/controlnet_dev/resolve/main/gen_compare/output_images/diffusers/output_room_seg_1.png"/></a> |
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -272,9 +158,3 @@ All checkpoints can be found under the authors' namespace [lllyasviel](https://h
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxStableDiffusionControlNetPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxStableDiffusionControlNetPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionImageVariationPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[`StableDiffusionImageVariationPipeline`] lets you generate variations from an input image using Stable Diffusion. It uses a fine-tuned version of Stable Diffusion model, trained by [Justin Pinkney](https://www.justinpinkney.com/) (@Buntworthy) at [Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/).
|
||||
[`StableDiffusionImageVariationPipeline`] lets you generate variations from an input image using Stable Diffusion. It uses a fine-tuned version of Stable Diffusion model, trained by [Justin Pinkney](https://www.justinpinkney.com/) (@Buntworthy) at [Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/)
|
||||
|
||||
The original codebase can be found here:
|
||||
[Stable Diffusion Image Variations](https://github.com/LambdaLabsML/lambda-diffusers#stable-diffusion-image-variations)
|
||||
@@ -28,4 +28,4 @@ Available Checkpoints are:
|
||||
- enable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- disable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
@@ -29,8 +29,4 @@ proposed by Chenlin Meng, Yutong He, Yang Song, Jiaming Song, Jiajun Wu, Jun-Yan
|
||||
- enable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- disable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxStableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
@@ -30,8 +30,4 @@ Available checkpoints are:
|
||||
- enable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- disable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxStableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
@@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Editing Implicit Assumptions in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[Editing Implicit Assumptions in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.08084) by Hadas Orgad, Bahjat Kawar, and Yonatan Belinkov.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Text-to-image diffusion models often make implicit assumptions about the world when generating images. While some assumptions are useful (e.g., the sky is blue), they can also be outdated, incorrect, or reflective of social biases present in the training data. Thus, there is a need to control these assumptions without requiring explicit user input or costly re-training. In this work, we aim to edit a given implicit assumption in a pre-trained diffusion model. Our Text-to-Image Model Editing method, TIME for short, receives a pair of inputs: a "source" under-specified prompt for which the model makes an implicit assumption (e.g., "a pack of roses"), and a "destination" prompt that describes the same setting, but with a specified desired attribute (e.g., "a pack of blue roses"). TIME then updates the model's cross-attention layers, as these layers assign visual meaning to textual tokens. We edit the projection matrices in these layers such that the source prompt is projected close to the destination prompt. Our method is highly efficient, as it modifies a mere 2.2% of the model's parameters in under one second. To evaluate model editing approaches, we introduce TIMED (TIME Dataset), containing 147 source and destination prompt pairs from various domains. Our experiments (using Stable Diffusion) show that TIME is successful in model editing, generalizes well for related prompts unseen during editing, and imposes minimal effect on unrelated generations.*
|
||||
|
||||
Resources:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Project Page](https://time-diffusion.github.io/).
|
||||
* [Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.08084).
|
||||
* [Original Code](https://github.com/bahjat-kawar/time-diffusion).
|
||||
* [Demo](https://huggingface.co/spaces/bahjat-kawar/time-diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Demo
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionModelEditingPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_model_editing.py) | *Text-to-Image Model Editing* | [🤗 Space](https://huggingface.co/spaces/bahjat-kawar/time-diffusion)) |
|
||||
|
||||
This pipeline enables editing the diffusion model weights, such that its assumptions on a given concept are changed. The resulting change is expected to take effect in all prompt generations pertaining to the edited concept.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionModelEditingPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_ckpt = "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionModelEditingPipeline.from_pretrained(model_ckpt)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
source_prompt = "A pack of roses"
|
||||
destination_prompt = "A pack of blue roses"
|
||||
pipe.edit_model(source_prompt, destination_prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A field of roses"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
image.save("field_of_roses.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionModelEditingPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StableDiffusionModelEditingPipeline
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- all
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,6 @@ For more details about how Stable Diffusion works and how it differs from the ba
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline](./pix2pix) | **Experimental** – *Text-Based Image Editing * | | [InstructPix2Pix: Learning to Follow Image Editing Instructions](https://huggingface.co/spaces/timbrooks/instruct-pix2pix)
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionAttendAndExcitePipeline](./attend_and_excite) | **Experimental** – *Text-to-Image Generation * | | [Attend-and-Excite: Attention-Based Semantic Guidance for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://huggingface.co/spaces/AttendAndExcite/Attend-and-Excite)
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline](./pix2pix_zero) | **Experimental** – *Text-Based Image Editing * | | [Zero-shot Image-to-Image Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.03027)
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionModelEditingPipeline](./model_editing) | **Experimental** – *Text-to-Image Model Editing * | | [Editing Implicit Assumptions in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.08084)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,26 +14,25 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[Improving Sample Quality of Diffusion Models Using Self-Attention Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.00939) by Susung Hong et al.
|
||||
[Self-Attention Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.00939) by Susung Hong et al.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Denoising diffusion models (DDMs) have attracted attention for their exceptional generation quality and diversity. This success is largely attributed to the use of class- or text-conditional diffusion guidance methods, such as classifier and classifier-free guidance. In this paper, we present a more comprehensive perspective that goes beyond the traditional guidance methods. From this generalized perspective, we introduce novel condition- and training-free strategies to enhance the quality of generated images. As a simple solution, blur guidance improves the suitability of intermediate samples for their fine-scale information and structures, enabling diffusion models to generate higher quality samples with a moderate guidance scale. Improving upon this, Self-Attention Guidance (SAG) uses the intermediate self-attention maps of diffusion models to enhance their stability and efficacy. Specifically, SAG adversarially blurs only the regions that diffusion models attend to at each iteration and guides them accordingly. Our experimental results show that our SAG improves the performance of various diffusion models, including ADM, IDDPM, Stable Diffusion, and DiT. Moreover, combining SAG with conventional guidance methods leads to further improvement.*
|
||||
*Denoising diffusion models (DDMs) have been drawing much attention for their appreciable sample quality and diversity. Despite their remarkable performance, DDMs remain black boxes on which further study is necessary to take a profound step. Motivated by this, we delve into the design of conventional U-shaped diffusion models. More specifically, we investigate the self-attention modules within these models through carefully designed experiments and explore their characteristics. In addition, inspired by the studies that substantiate the effectiveness of the guidance schemes, we present plug-and-play diffusion guidance, namely Self-Attention Guidance (SAG), that can drastically boost the performance of existing diffusion models. Our method, SAG, extracts the intermediate attention map from a diffusion model at every iteration and selects tokens above a certain attention score for masking and blurring to obtain a partially blurred input. Subsequently, we measure the dissimilarity between the predicted noises obtained from feeding the blurred and original input to the diffusion model and leverage it as guidance. With this guidance, we observe apparent improvements in a wide range of diffusion models, e.g., ADM, IDDPM, and Stable Diffusion, and show that the results further improve by combining our method with the conventional guidance scheme. We provide extensive ablation studies to verify our choices.*
|
||||
|
||||
Resources:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Project Page](https://ku-cvlab.github.io/Self-Attention-Guidance).
|
||||
* [Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.00939).
|
||||
* [Original Code](https://github.com/KU-CVLAB/Self-Attention-Guidance).
|
||||
* [Hugging Face Demo](https://huggingface.co/spaces/susunghong/Self-Attention-Guidance).
|
||||
* [Colab Demo](https://colab.research.google.com/github/SusungHong/Self-Attention-Guidance/blob/main/SAG_Stable.ipynb).
|
||||
* [Demo](https://colab.research.google.com/github/SusungHong/Self-Attention-Guidance/blob/main/SAG_Stable.ipynb).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Demo
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionSAGPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_sag.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation* | [🤗 Space](https://huggingface.co/spaces/susunghong/Self-Attention-Guidance) |
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionSAGPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_sag.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation* | [Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/github/SusungHong/Self-Attention-Guidance/blob/main/SAG_Stable.ipynb) |
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -39,7 +39,3 @@ Available Checkpoints are:
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- enable_vae_tiling
|
||||
- disable_vae_tiling
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,15 +28,15 @@ The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips
|
||||
|
||||
- Safe Stable Diffusion may also be used with weights of [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion/text2img).
|
||||
- Safe Stable Diffusion may also be used with weights of [Stable Diffusion](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img).
|
||||
|
||||
### Run Safe Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
Safe Stable Diffusion can be tested very easily with the [`StableDiffusionPipelineSafe`], and the `"AIML-TUDA/stable-diffusion-safe"` checkpoint exactly in the same way it is shown in the [Conditional Image Generation Guide](../../using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation).
|
||||
Safe Stable Diffusion can be tested very easily with the [`StableDiffusionPipelineSafe`], and the `"AIML-TUDA/stable-diffusion-safe"` checkpoint exactly in the same way it is shown in the [Conditional Image Generation Guide](./using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation).
|
||||
|
||||
### Interacting with the Safety Concept
|
||||
|
||||
To check and edit the currently used safety concept, use the `safety_concept` property of [`StableDiffusionPipelineSafe`]:
|
||||
To check and edit the currently used safety concept, use the `safety_concept` property of [`StableDiffusionPipelineSafe`]
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipelineSafe
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ You may use the 4 configurations defined in the [Safe Latent Diffusion paper](ht
|
||||
|
||||
The following configurations are available: `SafetyConfig.WEAK`, `SafetyConfig.MEDIUM`, `SafetyConfig.STRONG`, and `SafetyConfig.MAX`.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to load and use different schedulers
|
||||
### How to load and use different schedulers.
|
||||
|
||||
The safe stable diffusion pipeline uses [`PNDMScheduler`] scheduler by default. But `diffusers` provides many other schedulers that can be used with the stable diffusion pipeline such as [`DDIMScheduler`], [`LMSDiscreteScheduler`], [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`], [`EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler`] etc.
|
||||
To use a different scheduler, you can either change it via the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`] method or pass the `scheduler` argument to the `from_pretrained` method of the pipeline. For example, to use the [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`], you can do the following:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,10 +16,6 @@ Stable unCLIP checkpoints are finetuned from [stable diffusion 2.1](./stable_dif
|
||||
Stable unCLIP also still conditions on text embeddings. Given the two separate conditionings, stable unCLIP can be used
|
||||
for text guided image variation. When combined with an unCLIP prior, it can also be used for full text to image generation.
|
||||
|
||||
To know more about the unCLIP process, check out the following paper:
|
||||
|
||||
[Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06125) by Aditya Ramesh, Prafulla Dhariwal, Alex Nichol, Casey Chu, Mark Chen.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips
|
||||
|
||||
Stable unCLIP takes a `noise_level` as input during inference. `noise_level` determines how much noise is added
|
||||
@@ -28,124 +24,50 @@ we do not add any additional noise to the image embeddings i.e. `noise_level = 0
|
||||
|
||||
### Available checkpoints:
|
||||
|
||||
* Image variation
|
||||
* [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip](https://hf.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip)
|
||||
* [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip-small](https://hf.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip-small)
|
||||
* Text-to-image
|
||||
* [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip-small](https://hf.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip-small)
|
||||
TODO
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-to-Image Generation
|
||||
Stable unCLIP can be leveraged for text-to-image generation by pipelining it with the prior model of KakaoBrain's open source DALL-E 2 replication [Karlo](https://huggingface.co/kakaobrain/karlo-v1-alpha)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import UnCLIPScheduler, DDPMScheduler, StableUnCLIPPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.models import PriorTransformer
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPTokenizer, CLIPTextModelWithProjection
|
||||
|
||||
prior_model_id = "kakaobrain/karlo-v1-alpha"
|
||||
data_type = torch.float16
|
||||
prior = PriorTransformer.from_pretrained(prior_model_id, subfolder="prior", torch_dtype=data_type)
|
||||
|
||||
prior_text_model_id = "openai/clip-vit-large-patch14"
|
||||
prior_tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(prior_text_model_id)
|
||||
prior_text_model = CLIPTextModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(prior_text_model_id, torch_dtype=data_type)
|
||||
prior_scheduler = UnCLIPScheduler.from_pretrained(prior_model_id, subfolder="prior_scheduler")
|
||||
prior_scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_config(prior_scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
stable_unclip_model_id = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip-small"
|
||||
from diffusers import StableUnCLIPPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableUnCLIPPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
stable_unclip_model_id,
|
||||
torch_dtype=data_type,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
prior_tokenizer=prior_tokenizer,
|
||||
prior_text_encoder=prior_text_model,
|
||||
prior=prior,
|
||||
prior_scheduler=prior_scheduler,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
"fusing/stable-unclip-2-1-l", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
) # TODO update model path
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
wave_prompt = "dramatic wave, the Oceans roar, Strong wave spiral across the oceans as the waves unfurl into roaring crests; perfect wave form; perfect wave shape; dramatic wave shape; wave shape unbelievable; wave; wave shape spectacular"
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt=wave_prompt).images
|
||||
images[0].save("waves.png")
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt).images
|
||||
images[0].save("astronaut_horse.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
For text-to-image we use `stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip-small` as it was trained on CLIP ViT-L/14 embedding, the same as the Karlo model prior. [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip](https://hf.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip) was trained on OpenCLIP ViT-H, so we don't recommend its use.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Text guided Image-to-Image Variation
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableUnCLIPImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import StableUnCLIPImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableUnCLIPImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variation="fp16"
|
||||
)
|
||||
"fusing/stable-unclip-2-1-l-img2img", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
) # TODO update model path
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/stable_unclip/tarsila_do_amaral.png"
|
||||
init_image = load_image(url)
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(init_image).images
|
||||
images[0].save("variation_image.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
init_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
init_image = init_image.resize((768, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally, you can also pass a prompt to `pipe` such as:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, trending on artstation"
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(init_image, prompt=prompt).images
|
||||
images[0].save("variation_image_two.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory optimization
|
||||
|
||||
If you are short on GPU memory, you can enable smart CPU offloading so that models that are not needed
|
||||
immediately for a computation can be offloaded to CPU:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableUnCLIPImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableUnCLIPImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variation="fp16"
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Offload to CPU.
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/stable_unclip/tarsila_do_amaral.png"
|
||||
init_image = load_image(url)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(init_image).images
|
||||
images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Further memory optimizations are possible by enabling VAE slicing on the pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableUnCLIPImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableUnCLIPImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1-unclip", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variation="fp16"
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/stable_unclip/tarsila_do_amaral.png"
|
||||
init_image = load_image(url)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(init_image).images
|
||||
images[0]
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt, init_image).images
|
||||
images[0].save("fantasy_landscape.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### StableUnCLIPPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,130 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
This pipeline is for research purposes only.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
# Text-to-video synthesis
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[VideoFusion: Decomposed Diffusion Models for High-Quality Video Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.08320) by Zhengxiong Luo, Dayou Chen, Yingya Zhang, Yan Huang, Liang Wang, Yujun Shen, Deli Zhao, Jingren Zhou, Tieniu Tan.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*A diffusion probabilistic model (DPM), which constructs a forward diffusion process by gradually adding noise to data points and learns the reverse denoising process to generate new samples, has been shown to handle complex data distribution. Despite its recent success in image synthesis, applying DPMs to video generation is still challenging due to high-dimensional data spaces. Previous methods usually adopt a standard diffusion process, where frames in the same video clip are destroyed with independent noises, ignoring the content redundancy and temporal correlation. This work presents a decomposed diffusion process via resolving the per-frame noise into a base noise that is shared among all frames and a residual noise that varies along the time axis. The denoising pipeline employs two jointly-learned networks to match the noise decomposition accordingly. Experiments on various datasets confirm that our approach, termed as VideoFusion, surpasses both GAN-based and diffusion-based alternatives in high-quality video generation. We further show that our decomposed formulation can benefit from pre-trained image diffusion models and well-support text-conditioned video creation.*
|
||||
|
||||
Resources:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Website](https://modelscope.cn/models/damo/text-to-video-synthesis/summary)
|
||||
* [GitHub repository](https://github.com/modelscope/modelscope/)
|
||||
* [🤗 Spaces](https://huggingface.co/spaces/damo-vilab/modelscope-text-to-video-synthesis)
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Demo
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [TextToVideoSDPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/text_to_video_synthesis/pipeline_text_to_video_synth.py) | *Text-to-Video Generation* | [🤗 Spaces](https://huggingface.co/spaces/damo-vilab/modelscope-text-to-video-synthesis)
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
Let's start by generating a short video with the default length of 16 frames (2s at 8 fps):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_video
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16")
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Spiderman is surfing"
|
||||
video_frames = pipe(prompt).frames
|
||||
video_path = export_to_video(video_frames)
|
||||
video_path
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers supports different optimization techniques to improve the latency
|
||||
and memory footprint of a pipeline. Since videos are often more memory-heavy than images,
|
||||
we can enable CPU offloading and VAE slicing to keep the memory footprint at bay.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's generate a video of 8 seconds (64 frames) on the same GPU using CPU offloading and VAE slicing:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_video
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16")
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
# memory optimization
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Darth Vader surfing a wave"
|
||||
video_frames = pipe(prompt, num_frames=64).frames
|
||||
video_path = export_to_video(video_frames)
|
||||
video_path
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It just takes **7 GBs of GPU memory** to generate the 64 video frames using PyTorch 2.0, "fp16" precision and the techniques mentioned above.
|
||||
|
||||
We can also use a different scheduler easily, using the same method we'd use for Stable Diffusion:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_video
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16")
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Spiderman is surfing"
|
||||
video_frames = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=25).frames
|
||||
video_path = export_to_video(video_frames)
|
||||
video_path
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><center>
|
||||
An astronaut riding a horse.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/astr.gif"
|
||||
alt="An astronaut riding a horse."
|
||||
style="width: 300px;" />
|
||||
</center></td>
|
||||
<td ><center>
|
||||
Darth vader surfing in waves.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/vader.gif"
|
||||
alt="Darth vader surfing in waves."
|
||||
style="width: 300px;" />
|
||||
</center></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
## Available checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
* [damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b](https://huggingface.co/damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b/)
|
||||
* [damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b-legacy](https://huggingface.co/damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b-legacy)
|
||||
|
||||
## TextToVideoSDPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TextToVideoSDPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -1,240 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Zero-Shot Text-to-Video Generation
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Text2Video-Zero: Text-to-Image Diffusion Models are Zero-Shot Video Generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.13439) by
|
||||
Levon Khachatryan,
|
||||
Andranik Movsisyan,
|
||||
Vahram Tadevosyan,
|
||||
Roberto Henschel,
|
||||
[Zhangyang Wang](https://www.ece.utexas.edu/people/faculty/atlas-wang), Shant Navasardyan, [Humphrey Shi](https://www.humphreyshi.com).
|
||||
|
||||
Our method Text2Video-Zero enables zero-shot video generation using either
|
||||
1. A textual prompt, or
|
||||
2. A prompt combined with guidance from poses or edges, or
|
||||
3. Video Instruct-Pix2Pix, i.e., instruction-guided video editing.
|
||||
|
||||
Results are temporally consistent and follow closely the guidance and textual prompts.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Recent text-to-video generation approaches rely on computationally heavy training and require large-scale video datasets. In this paper, we introduce a new task of zero-shot text-to-video generation and propose a low-cost approach (without any training or optimization) by leveraging the power of existing text-to-image synthesis methods (e.g., Stable Diffusion), making them suitable for the video domain.
|
||||
Our key modifications include (i) enriching the latent codes of the generated frames with motion dynamics to keep the global scene and the background time consistent; and (ii) reprogramming frame-level self-attention using a new cross-frame attention of each frame on the first frame, to preserve the context, appearance, and identity of the foreground object.
|
||||
Experiments show that this leads to low overhead, yet high-quality and remarkably consistent video generation. Moreover, our approach is not limited to text-to-video synthesis but is also applicable to other tasks such as conditional and content-specialized video generation, and Video Instruct-Pix2Pix, i.e., instruction-guided video editing.
|
||||
As experiments show, our method performs comparably or sometimes better than recent approaches, despite not being trained on additional video data.*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Resources:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Project Page](https://text2video-zero.github.io/)
|
||||
* [Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.13439)
|
||||
* [Original Code](https://github.com/Picsart-AI-Research/Text2Video-Zero)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Demo
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [TextToVideoZeroPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/text_to_video_synthesis/pipeline_text_to_video_zero.py) | *Zero-shot Text-to-Video Generation* | [🤗 Space](https://huggingface.co/spaces/PAIR/Text2Video-Zero)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-To-Video
|
||||
|
||||
To generate a video from prompt, run the following python command
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import imageio
|
||||
from diffusers import TextToVideoZeroPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = TextToVideoZeroPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A panda is playing guitar on times square"
|
||||
result = pipe(prompt=prompt).images
|
||||
result = [(r * 255).astype("uint8") for r in result]
|
||||
imageio.mimsave("video.mp4", result, fps=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
You can change these parameters in the pipeline call:
|
||||
* Motion field strength (see the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.13439), Sect. 3.3.1):
|
||||
* `motion_field_strength_x` and `motion_field_strength_y`. Default: `motion_field_strength_x=12`, `motion_field_strength_y=12`
|
||||
* `T` and `T'` (see the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.13439), Sect. 3.3.1)
|
||||
* `t0` and `t1` in the range `{0, ..., num_inference_steps}`. Default: `t0=45`, `t1=48`
|
||||
* Video length:
|
||||
* `video_length`, the number of frames video_length to be generated. Default: `video_length=8`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-To-Video with Pose Control
|
||||
To generate a video from prompt with additional pose control
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download a demo video
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
|
||||
|
||||
filename = "__assets__/poses_skeleton_gifs/dance1_corr.mp4"
|
||||
repo_id = "PAIR/Text2Video-Zero"
|
||||
video_path = hf_hub_download(repo_type="space", repo_id=repo_id, filename=filename)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. Read video containing extracted pose images
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import imageio
|
||||
|
||||
reader = imageio.get_reader(video_path, "ffmpeg")
|
||||
frame_count = 8
|
||||
pose_images = [Image.fromarray(reader.get_data(i)) for i in range(frame_count)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
To extract pose from actual video, read [ControlNet documentation](./stable_diffusion/controlnet).
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run `StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline` with our custom attention processor
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline, ControlNetModel
|
||||
from diffusers.pipelines.text_to_video_synthesis.pipeline_text_to_video_zero import CrossFrameAttnProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-openpose", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id, controlnet=controlnet, torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# Set the attention processor
|
||||
pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(CrossFrameAttnProcessor(batch_size=2))
|
||||
pipe.controlnet.set_attn_processor(CrossFrameAttnProcessor(batch_size=2))
|
||||
|
||||
# fix latents for all frames
|
||||
latents = torch.randn((1, 4, 64, 64), device="cuda", dtype=torch.float16).repeat(len(pose_images), 1, 1, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Darth Vader dancing in a desert"
|
||||
result = pipe(prompt=[prompt] * len(pose_images), image=pose_images, latents=latents).images
|
||||
imageio.mimsave("video.mp4", result, fps=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-To-Video with Edge Control
|
||||
|
||||
To generate a video from prompt with additional pose control,
|
||||
follow the steps described above for pose-guided generation using [Canny edge ControlNet model](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-canny).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Video Instruct-Pix2Pix
|
||||
|
||||
To perform text-guided video editing (with [InstructPix2Pix](./stable_diffusion/pix2pix)):
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download a demo video
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
|
||||
|
||||
filename = "__assets__/pix2pix video/camel.mp4"
|
||||
repo_id = "PAIR/Text2Video-Zero"
|
||||
video_path = hf_hub_download(repo_type="space", repo_id=repo_id, filename=filename)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Read video from path
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import imageio
|
||||
|
||||
reader = imageio.get_reader(video_path, "ffmpeg")
|
||||
frame_count = 8
|
||||
video = [Image.fromarray(reader.get_data(i)) for i in range(frame_count)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run `StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline` with our custom attention processor
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.pipelines.text_to_video_synthesis.pipeline_text_to_video_zero import CrossFrameAttnProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "timbrooks/instruct-pix2pix"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(CrossFrameAttnProcessor(batch_size=3))
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "make it Van Gogh Starry Night style"
|
||||
result = pipe(prompt=[prompt] * len(video), image=video).images
|
||||
imageio.mimsave("edited_video.mp4", result, fps=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### DreamBooth specialization
|
||||
|
||||
Methods **Text-To-Video**, **Text-To-Video with Pose Control** and **Text-To-Video with Edge Control**
|
||||
can run with custom [DreamBooth](../training/dreambooth) models, as shown below for
|
||||
[Canny edge ControlNet model](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-canny) and
|
||||
[Avatar style DreamBooth](https://huggingface.co/PAIR/text2video-zero-controlnet-canny-avatar) model
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download a demo video
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
|
||||
|
||||
filename = "__assets__/canny_videos_mp4/girl_turning.mp4"
|
||||
repo_id = "PAIR/Text2Video-Zero"
|
||||
video_path = hf_hub_download(repo_type="space", repo_id=repo_id, filename=filename)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Read video from path
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import imageio
|
||||
|
||||
reader = imageio.get_reader(video_path, "ffmpeg")
|
||||
frame_count = 8
|
||||
video = [Image.fromarray(reader.get_data(i)) for i in range(frame_count)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run `StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline` with custom trained DreamBooth model
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline, ControlNetModel
|
||||
from diffusers.pipelines.text_to_video_synthesis.pipeline_text_to_video_zero import CrossFrameAttnProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
# set model id to custom model
|
||||
model_id = "PAIR/text2video-zero-controlnet-canny-avatar"
|
||||
controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-canny", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id, controlnet=controlnet, torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# Set the attention processor
|
||||
pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(CrossFrameAttnProcessor(batch_size=2))
|
||||
pipe.controlnet.set_attn_processor(CrossFrameAttnProcessor(batch_size=2))
|
||||
|
||||
# fix latents for all frames
|
||||
latents = torch.randn((1, 4, 64, 64), device="cuda", dtype=torch.float16).repeat(len(pose_images), 1, 1, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "oil painting of a beautiful girl avatar style"
|
||||
result = pipe(prompt=[prompt] * len(pose_images), image=pose_images, latents=latents).images
|
||||
imageio.mimsave("video.mp4", result, fps=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can filter out some available DreamBooth-trained models with [this link](https://huggingface.co/models?search=dreambooth).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## TextToVideoZeroPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TextToVideoZeroPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips
|
||||
|
||||
- VersatileDiffusion is conceptually very similar as [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion/overview), but instead of providing just a image data stream conditioned on text, VersatileDiffusion provides both a image and text data stream and can be conditioned on both text and image.
|
||||
- VersatileDiffusion is conceptually very similar as [Stable Diffusion](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview), but instead of providing just a image data stream conditioned on text, VersatileDiffusion provides both a image and text data stream and can be conditioned on both text and image.
|
||||
|
||||
### *Run VersatileDiffusion*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models (DDIM)
|
||||
# Denoising diffusion implicit models (DDIM)
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,4 +24,4 @@ The original codebase of this paper can be found here: [ermongroup/ddim](https:/
|
||||
For questions, feel free to contact the author on [tsong.me](https://tsong.me/).
|
||||
|
||||
## DDIMScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DDIMScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DDIMScheduler
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM)
|
||||
# Denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPM)
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,4 +24,4 @@ We present high quality image synthesis results using diffusion probabilistic mo
|
||||
The original paper can be found [here](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502).
|
||||
|
||||
## DDPMScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DDPMScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DDPMScheduler
|
||||
@@ -14,8 +14,8 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Ancestral sampling with Euler method steps. Based on the original [k-diffusion](https://github.com/crowsonkb/k-diffusion/blob/481677d114f6ea445aa009cf5bd7a9cdee909e47/k_diffusion/sampling.py#L72) implementation by Katherine Crowson.
|
||||
Ancestral sampling with Euler method steps. Based on the original (k-diffusion)[https://github.com/crowsonkb/k-diffusion/blob/481677d114f6ea445aa009cf5bd7a9cdee909e47/k_diffusion/sampling.py#L72] implementation by Katherine Crowson.
|
||||
Fast scheduler which often times generates good outputs with 20-30 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
## EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
@@ -10,11 +10,11 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Variance Exploding Stochastic Differential Equation (VE-SDE) scheduler
|
||||
# variance exploding stochastic differential equation (VE-SDE) scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Original paper can be found [here](https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.13456).
|
||||
|
||||
## ScoreSdeVeScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ScoreSdeVeScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ScoreSdeVeScheduler
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Variance Preserving Stochastic Differential Equation (VP-SDE) scheduler
|
||||
# Variance preserving stochastic differential equation (VP-SDE) scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,4 +23,4 @@ Score SDE-VP is under construction.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## ScoreSdeVpScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] schedulers.scheduling_sde_vp.ScoreSdeVpScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] schedulers.scheduling_sde_vp.ScoreSdeVpScheduler
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
UniPC is a training-free framework designed for the fast sampling of diffusion models, which consists of a corrector (UniC) and a predictor (UniP) that share a unified analytical form and support arbitrary orders.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about the method, please refer to the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.04867) and the [code](https://github.com/wl-zhao/UniPC).
|
||||
For more details about the method, please refer to the [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.04867) and the [[code]](https://github.com/wl-zhao/UniPC).
|
||||
|
||||
Fast Sampling of Diffusion Models with Exponential Integrator.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,339 +12,83 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# How to contribute to Diffusers 🧨
|
||||
|
||||
We ❤️ contributions from the open-source community! Everyone is welcome, and all types of participation –not just code– are valued and appreciated. Answering questions, helping others, reaching out, and improving the documentation are all immensely valuable to the community, so don't be afraid and get involved if you're up for it!
|
||||
We ❤️ contributions from the open-source community! Everyone is welcome, and all types of participation –not just code– are valued and appreciated. Answering questions, helping others, reaching out and improving the documentation are all immensely valuable to the community, so don't be afraid and get involved if you're up for it!
|
||||
|
||||
Everyone is encouraged to start by saying 👋 in our public Discord channel. We discuss the latest trends in diffusion models, ask questions, show off personal projects, help each other with contributions, or just hang out ☕. <a href="https://Discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR"><img alt="Join us on Discord" src="https://img.shields.io/Discord/823813159592001537?color=5865F2&logo=Discord&logoColor=white"></a>
|
||||
It also helps us if you spread the word: reference the library from blog posts
|
||||
on the awesome projects it made possible, shout out on Twitter every time it has
|
||||
helped you, or simply star the repo to say "thank you".
|
||||
|
||||
Whichever way you choose to contribute, we strive to be part of an open, welcoming, and kind community. Please, read our [code of conduct](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md) and be mindful to respect it during your interactions. We also recommend you become familiar with the [ethical guidelines](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/ethical_guidelines) that guide our project and ask you to adhere to the same principles of transparency and responsibility.
|
||||
We encourage everyone to start by saying 👋 in our public Discord channel. We discuss the hottest trends about diffusion models, ask questions, show-off personal projects, help each other with contributions, or just hang out ☕. <a href="https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR"><img alt="Join us on Discord" src="https://img.shields.io/discord/823813159592001537?color=5865F2&logo=discord&logoColor=white"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
Whichever way you choose to contribute, we strive to be part of an open, welcoming and kind community. Please, read our [code of conduct](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md) and be mindful to respect it during your interactions.
|
||||
|
||||
We enormously value feedback from the community, so please do not be afraid to speak up if you believe you have valuable feedback that can help improve the library - every message, comment, issue, and pull request (PR) is read and considered.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
You can contribute in many ways ranging from answering questions on issues to adding new diffusion models to
|
||||
the core library.
|
||||
You can contribute in so many ways! Just to name a few:
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we give an overview of different ways to contribute, ranked by difficulty in ascending order. All of them are valuable to the community.
|
||||
* Fixing outstanding issues with the existing code.
|
||||
* Implementing [new diffusion pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines#contribution), [new schedulers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers) or [new models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models).
|
||||
* [Contributing to the examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples).
|
||||
* [Contributing to the documentation](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source).
|
||||
* Submitting issues related to bugs or desired new features.
|
||||
|
||||
* 1. Asking and answering questions on [the Diffusers discussion forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers) or on [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR).
|
||||
* 2. Opening new issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose)
|
||||
* 3. Answering issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues)
|
||||
* 4. Fix a simple issue, marked by the "Good first issue" label, see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22).
|
||||
* 5. Contribute to the [documentation](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source).
|
||||
* 6. Contribute a [Community Pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3Acommunity-examples)
|
||||
* 7. Contribute to the [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples).
|
||||
* 8. Fix a more difficult issue, marked by the "Good second issue" label, see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22).
|
||||
* 9. Add a new pipeline, model, or scheduler, see ["New Pipeline/Model"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22) and ["New scheduler"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22) issues. For this contribution, please have a look at [Design Philosophy](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/PHILOSOPHY.md).
|
||||
*All are equally valuable to the community.*
|
||||
|
||||
As said before, **all contributions are valuable to the community**.
|
||||
In the following, we will explain each contribution a bit more in detail.
|
||||
### Browse GitHub issues for suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
For all contributions 4.-9. you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in [Opening a pull requst](#how-to-open-a-pr)
|
||||
If you need inspiration, you can look out for [issues](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues) you'd like to tackle to contribute to the library. There are a few filters that can be helpful:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Asking and answering questions on the Diffusers discussion forum or on the Diffusers Discord
|
||||
- See [Good first issues](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22) for general opportunities to contribute and getting started with the codebase.
|
||||
- See [New pipeline/model](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22) to contribute exciting new diffusion models or diffusion pipelines.
|
||||
- See [New scheduler](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22) to work on new samplers and schedulers.
|
||||
|
||||
Any question or comment related to the Diffusers library can be asked on the [discussion forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/) or on [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR). Such questions and comments include (but are not limited to):
|
||||
- Reports of training or inference experiments in an attempt to share knowledge
|
||||
- Presentation of personal projects
|
||||
- Questions to non-official training examples
|
||||
- Project proposals
|
||||
- General feedback
|
||||
- Paper summaries
|
||||
- Asking for help on personal projects that build on top of the Diffusers library
|
||||
- General questions
|
||||
- Ethical questions regarding diffusion models
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
|
||||
Every question that is asked on the forum or on Discord actively encourages the community to publicly
|
||||
share knowledge and might very well help a beginner in the future that has the same question you're
|
||||
having. Please do pose any questions you might have.
|
||||
In the same spirit, you are of immense help to the community by answering such questions because this way you are publicly documenting knowledge for everybody to learn from.
|
||||
## Submitting a new issue or feature request
|
||||
|
||||
**Please** keep in mind that the more effort you put into asking or answering a question, the higher
|
||||
the quality of the publicly documented knowledge. In the same way, well-posed and well-answered questions create a high-quality knowledge database accessible to everybody, while badly posed questions or answers reduce the overall quality of the public knowledge database.
|
||||
In short, a high quality question or answer is *precise*, *concise*, *relevant*, *easy-to-understand*, *accesible*, and *well-formated/well-posed*. For more information, please have a look through the [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue) section.
|
||||
Do your best to follow these guidelines when submitting an issue or a feature
|
||||
request. It will make it easier for us to come back to you quickly and with good
|
||||
feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE about channels**:
|
||||
[*The forum*](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) is much better indexed by search engines, such as Google. Posts are ranked by popularity rather than chronologically. Hence, it's easier to look up questions and answers that we posted some time ago.
|
||||
In addition, questions and answers posted in the forum can easily be linked to.
|
||||
In contrast, *Discord* has a chat-like format that invites fast back-and-forth communication.
|
||||
While it will most likely take less time for you to get an answer to your question on Discord, your
|
||||
question won't be visible anymore over time. Also, it's much harder to find information that was posted a while back on Discord. We therefore strongly recommend using the forum for high-quality questions and answers in an attempt to create long-lasting knowledge for the community. If discussions on Discord lead to very interesting answers and conclusions, we recommend posting the results on the forum to make the information more available for future readers.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Opening new issues on the GitHub issues tab
|
||||
### Did you find a bug?
|
||||
|
||||
The 🧨 Diffusers library is robust and reliable thanks to the users who notify us of
|
||||
the problems they encounter. So thank you for reporting an issue.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember, GitHub issues are reserved for technical questions directly related to the Diffusers library, bug reports, feature requests, or feedback on the library design.
|
||||
First, we would really appreciate it if you could **make sure the bug was not
|
||||
already reported** (use the search bar on GitHub under Issues).
|
||||
|
||||
In a nutshell, this means that everything that is **not** related to the **code of the Diffusers library** (including the documentation) should **not** be asked on GitHub, but rather on either the [forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) or [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR).
|
||||
### Do you want to implement a new diffusion pipeline / diffusion model?
|
||||
|
||||
**Please consider the following guidelines when opening a new issue**:
|
||||
- Make sure you have searched whether your issue has already been asked before (use the search bar on GitHub under Issues).
|
||||
- Please never report a new issue on another (related) issue. If another issue is highly related, please
|
||||
open a new issue nevertheless and link to the related issue.
|
||||
- Make sure your issue is written in English. Please use one of the great, free online translation services, such as [DeepL](https://www.deepl.com/translator) to translate from your native language to English if you are not comfortable in English.
|
||||
- Check whether your issue might be solved by updating to the newest Diffusers version. Before posting your issue, please make sure that `python -c "import diffusers; print(diffusers.__version__)"` is higher or matches the latest Diffusers version.
|
||||
- Remember that the more effort you put into opening a new issue, the higher the quality of your answer will be and the better the overall quality of the Diffusers issues.
|
||||
Awesome! Please provide the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
New issues usually include the following.
|
||||
* Short description of the diffusion pipeline and link to the paper;
|
||||
* Link to the implementation if it is open-source;
|
||||
* Link to the model weights if they are available.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.1. Reproducible, minimal bug reports.
|
||||
If you are willing to contribute the model yourself, let us know so we can best
|
||||
guide you.
|
||||
|
||||
A bug report should always have a reproducible code snippet and be as minimal and concise as possible.
|
||||
This means in more detail:
|
||||
- Narrow the bug down as much as you can, **do not just dump your whole code file**
|
||||
- Format your code
|
||||
- Do not include any external libraries except for Diffusers depending on them.
|
||||
- **Always** provide all necessary information about your environment; for this, you can run: `diffusers-cli env` in your shell and copy-paste the displayed information to the issue.
|
||||
- Explain the issue. If the reader doesn't know what the issue is and why it is an issue, she cannot solve it.
|
||||
- **Always** make sure the reader can reproduce your issue with as little effort as possible. If your code snippet cannot be run because of missing libraries or undefined variables, the reader cannot help you. Make sure your reproducible code snippet is as minimal as possible and can be copy-pasted into a simple Python shell.
|
||||
- If in order to reproduce your issue a model and/or dataset is required, make sure the reader has access to that model or dataset. You can always upload your model or dataset to the [Hub](https://huggingface.co) to make it easily downloadable. Try to keep your model and dataset as small as possible, to make the reproduction of your issue as effortless as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, please have a look through the [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue) section.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a bug report [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.2. Feature requests.
|
||||
### Do you want a new feature (that is not a model)?
|
||||
|
||||
A world-class feature request addresses the following points:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Motivation first:
|
||||
* Is it related to a problem/frustration with the library? If so, please explain
|
||||
why. Providing a code snippet that demonstrates the problem is best.
|
||||
* Is it related to something you would need for a project? We'd love to hear
|
||||
about it!
|
||||
* Is it something you worked on and think could benefit the community?
|
||||
Awesome! Tell us what problem it solved for you.
|
||||
* Is it related to a problem/frustration with the library? If so, please explain
|
||||
why. Providing a code snippet that demonstrates the problem is best.
|
||||
* Is it related to something you would need for a project? We'd love to hear
|
||||
about it!
|
||||
* Is it something you worked on and think could benefit the community?
|
||||
Awesome! Tell us what problem it solved for you.
|
||||
2. Write a *full paragraph* describing the feature;
|
||||
3. Provide a **code snippet** that demonstrates its future use;
|
||||
4. In case this is related to a paper, please attach a link;
|
||||
5. Attach any additional information (drawings, screenshots, etc.) you think may help.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a feature request [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feature_request.md&title=).
|
||||
If your issue is well written we're already 80% of the way there by the time you
|
||||
post it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.3 Feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
Feedback about the library design and why it is good or not good helps the core maintainers immensely to build a user-friendly library. To understand the philosophy behind the current design philosophy, please have a look [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy). If you feel like a certain design choice does not fit with the current design philosophy, please explain why and how it should be changed. If a certain design choice follows the design philosophy too much, hence restricting use cases, explain why and how it should be changed.
|
||||
If a certain design choice is very useful for you, please also leave a note as this is great feedback for future design decisions.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open an issue about feedback [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.4 Technical questions.
|
||||
|
||||
Technical questions are mainly about why certain code of the library was written in a certain way, or what a certain part of the code does. Please make sure to link to the code in question and please provide detail on
|
||||
why this part of the code is difficult to understand.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open an issue about a technical question [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&template=bug-report.yml).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.5 Proposal to add a new model, scheduler, or pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
If the diffusion model community released a new model, pipeline, or scheduler that you would like to see in the Diffusers library, please provide the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
* Short description of the diffusion pipeline, model, or scheduler and link to the paper or public release.
|
||||
* Link to any of its open-source implementation.
|
||||
* Link to the model weights if they are available.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are willing to contribute to the model yourself, let us know so we can best guide you. Also, don't forget
|
||||
to tag the original author of the component (model, scheduler, pipeline, etc.) by GitHub handle if you can find it.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a request for a model/pipeline/scheduler [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=New+model%2Fpipeline%2Fscheduler&template=new-model-addition.yml).
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Answering issues on the GitHub issues tab
|
||||
|
||||
Answering issues on GitHub might require some technical knowledge of Diffusers, but we encourage everybody to give it a try even if you are not 100% certain that your answer is correct.
|
||||
Some tips to give a high-quality answer to an issue:
|
||||
- Be as concise and minimal as possible
|
||||
- Stay on topic. An answer to the issue should concern the issue and only the issue.
|
||||
- Provide links to code, papers, or other sources that prove or encourage your point.
|
||||
- Answer in code. If a simple code snippet is the answer to the issue or shows how the issue can be solved, please provide a fully reproducible code snippet.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, many issues tend to be simply off-topic, duplicates of other issues, or irrelevant. It is of great
|
||||
help to the maintainers if you can answer such issues, encouraging the author of the issue to be
|
||||
more precise, provide the link to a duplicated issue or redirect them to [the forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) or [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)
|
||||
|
||||
If you have verified that the issued bug report is correct and requires a correction in the source code,
|
||||
please have a look at the next sections.
|
||||
|
||||
For all of the following contributions, you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in the [Opening a pull requst](#how-to-open-a-pr) section.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Fixing a `Good first issue`
|
||||
|
||||
*Good first issues* are marked by the [Good first issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22) label. Usually, the issue already
|
||||
explains how a potential solution should look so that it is easier to fix.
|
||||
If the issue hasn't been closed and you would like to try to fix this issue, you can just leave a message "I would like to try this issue.". There are usually three scenarios:
|
||||
- a.) The issue description already proposes a fix. In this case and if the solution makes sense to you, you can open a PR or draft PR to fix it.
|
||||
- b.) The issue description does not propose a fix. In this case, you can ask what a proposed fix could look like and someone from the Diffusers team should answer shortly. If you have a good idea of how to fix it, feel free to directly open a PR.
|
||||
- c.) There is already an open PR to fix the issue, but the issue hasn't been closed yet. If the PR has gone stale, you can simply open a new PR and link to the stale PR. PRs often go stale if the original contributor who wanted to fix the issue suddenly cannot find the time anymore to proceed. This often happens in open-source and is very normal. In this case, the community will be very happy if you give it a new try and leverage the knowledge of the existing PR. If there is already a PR and it is active, you can help the author by giving suggestions, reviewing the PR or even asking whether you can contribute to the PR.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Contribute to the documentation
|
||||
|
||||
A good library **always** has good documentation! The official documentation is often one of the first points of contact for new users of the library, and therefore contributing to the documentation is a **highly
|
||||
valuable contribution**.
|
||||
|
||||
Contributing to the library can have many forms:
|
||||
|
||||
- Correcting spelling or grammatical errors.
|
||||
- Correct incorrect formatting of the docstring. If you see that the official documentation is weirdly displayed or a link is broken, we are very happy if you take some time to correct it.
|
||||
- Correct the shape or dimensions of a docstring input or output tensor.
|
||||
- Clarify documentation that is hard to understand or incorrect.
|
||||
- Update outdated code examples.
|
||||
- Translating the documentation to another language.
|
||||
|
||||
Anything displayed on [the official Diffusers doc page](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index) is part of the official documentation and can be corrected, adjusted in the respective [documentation source](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source).
|
||||
|
||||
Please have a look at [this page](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs) on how to verify changes made to the documentation locally.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[Pipelines](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/overview) are usually the first point of contact between the Diffusers library and the user.
|
||||
Pipelines are examples of how to use Diffusers [models](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models) and [schedulers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/schedulers/overview).
|
||||
We support two types of pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
- Official Pipelines
|
||||
- Community Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Both official and community pipelines follow the same design and consist of the same type of components.
|
||||
|
||||
Official pipelines are tested and maintained by the core maintainers of Diffusers. Their code
|
||||
resides in [src/diffusers/pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines).
|
||||
In contrast, community pipelines are contributed and maintained purely by the **community** and are **not** tested.
|
||||
They reside in [examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) and while they can be accessed via the [PyPI diffusers package](https://pypi.org/project/diffusers/), their code is not part of the PyPI distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
The reason for the distinction is that the core maintainers of the Diffusers library cannot maintain and test all
|
||||
possible ways diffusion models can be used for inference, but some of them may be of interest to the community.
|
||||
Officially released diffusion pipelines,
|
||||
such as Stable Diffusion are added to the core src/diffusers/pipelines package which ensures
|
||||
high quality of maintenance, no backward-breaking code changes, and testing.
|
||||
More bleeding edge pipelines should be added as community pipelines. If usage for a community pipeline is high, the pipeline can be moved to the official pipelines upon request from the community. This is one of the ways we strive to be a community-driven library.
|
||||
|
||||
To add a community pipeline, one should add a <name-of-the-community>.py file to [examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) and adapt the [examples/community/README.md](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community/README.md) to include an example of the new pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
An example can be seen [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/2400).
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipeline PRs are only checked at a superficial level and ideally they should be maintained by their original authors.
|
||||
|
||||
Contributing a community pipeline is a great way to understand how Diffusers models and schedulers work. Having contributed a community pipeline is usually the first stepping stone to contributing an official pipeline to the
|
||||
core package.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Contribute to training examples
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers examples are a collection of training scripts that reside in [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples).
|
||||
|
||||
We support two types of training examples:
|
||||
|
||||
- Official training examples
|
||||
- Research training examples
|
||||
|
||||
Research training examples are located in [examples/research_projects](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects) whereas official training examples include all folders under [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples) except the `research_projects` and `community` folders.
|
||||
The official training examples are maintained by the Diffusers' core maintainers whereas the research training examples are maintained by the community.
|
||||
This is because of the same reasons put forward in [6. Contribute a community pipeline](#contribute-a-community-pipeline) for official pipelines vs. community pipelines: It is not feasible for the core maintainers to maintain all possible training methods for diffusion models.
|
||||
If the Diffusers core maintainers and the community consider a certain training paradigm to be too experimental or not popular enough, the corresponding training code should be put in the `research_projects` folder and maintained by the author.
|
||||
|
||||
Both official training and research examples consist of a directory that contains one or more training scripts, a requirements.txt file, and a README.md file. In order for the user to make use of the
|
||||
training examples, it is required to clone the repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
as well as to install all additional dependencies required for training:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install -r /examples/<your-example-folder>/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore when adding an example, the `requirements.txt` file shall define all pip dependencies required for your training example so that once all those are installed, the user can run the example's training script. See, for example, the [DreamBooth `requirements.txt` file](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/requirements.txt).
|
||||
|
||||
Training examples of the Diffusers library should adhere to the following philosophy:
|
||||
- All the code necessary to run the examples should be found in a single Python file
|
||||
- One should be able to run the example from the command line with `python <your-example>.py --args`
|
||||
- Examples should be kept simple and serve as **an example** on how to use Diffusers for training. The purpose of example scripts is **not** to create state-of-the-art diffusion models, but rather to reproduce known training schemes without adding too much custom logic. As a byproduct of this point, our examples also strive to serve as good educational materials.
|
||||
|
||||
To contribute an example, it is highly recommended to look at already existing examples such as [dreambooth](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py) to get an idea of how they should look like.
|
||||
We strongly advise contributors to make use of the [Accelerate library](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate) as it's tightly integrated
|
||||
with Diffusers.
|
||||
Once an example script works, please make sure to add a comprehensive `README.md` that states how to use the example exactly. This README should include:
|
||||
- An example command on how to run the example script as shown [here e.g.](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#running-locally-with-pytorch).
|
||||
- A link to some training results (logs, models, ...) that show what the user can expect as shown [here e.g.](https://api.wandb.ai/report/patrickvonplaten/xm6cd5q5).
|
||||
- If you are adding a non-official/research training example, **please don't forget** to add a sentence that you are maintaining this training example which includes your git handle as shown [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/intel_opts#diffusers-examples-with-intel-optimizations).
|
||||
|
||||
If you are contributing to the official training examples, please also make sure to add a test to [examples/test_examples.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/test_examples.py). This is not necessary for non-official training examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Fixing a `Good second issue`
|
||||
|
||||
*Good second issues* are marked by the [Good second issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22) label. Good second issues are
|
||||
usually more complicated to solve than [Good first issues](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22).
|
||||
The issue description usually gives less guidance on how to fix the issue and requires
|
||||
a decent understanding of the library by the interested contributor.
|
||||
If you are interested in tackling a second good issue, feel free to open a PR to fix it and link the PR to the issue. If you see that a PR has already been opened for this issue but did not get merged, have a look to understand why it wasn't merged and try to open an improved PR.
|
||||
Good second issues are usually more difficult to get merged compared to good first issues, so don't hesitate to ask for help from the core maintainers. If your PR is almost finished the core maintainers can also jump into your PR and commit to it in order to get it merged.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Adding pipelines, models, schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines, models, and schedulers are the most important pieces of the Diffusers library.
|
||||
They provide easy access to state-of-the-art diffusion technologies and thus allow the community to
|
||||
build powerful generative AI applications.
|
||||
|
||||
By adding a new model, pipeline, or scheduler you might enable a new powerful use case for any of the user interfaces relying on Diffusers which can be of immense value for the whole generative AI ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers has a couple of open feature requests for all three components - feel free to gloss over them
|
||||
if you don't know yet what specific component you would like to add:
|
||||
- [Model or pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22)
|
||||
- [Scheduler](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22)
|
||||
|
||||
Before adding any of the three components, it is strongly recommended that you give the [Philosophy guide](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22) a read to better understand the design of any of the three components. Please be aware that
|
||||
we cannot merge model, scheduler, or pipeline additions that strongly diverge from our design philosophy
|
||||
as it will lead to API inconsistencies. If you fundamentally disagree with a design choice, please
|
||||
open a [Feedback issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=) instead so that it can be discussed whether a certain design
|
||||
pattern/design choice shall be changed everywhere in the library and whether we shall update our design philosophy. Consistency across the library is very important for us.
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure to add links to the original codebase/paper to the PR and ideally also ping the
|
||||
original author directly on the PR so that they can follow the progress and potentially help with questions.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are unsure or stuck in the PR, don't hesitate to leave a message to ask for a first review or help.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to write a good issue
|
||||
|
||||
**The better your issue is written, the higher the chances that it will be quickly resolved.**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Make sure that you've used the correct template for your issue. You can pick between *Bug Report*, *Feature Request*, *Feedback about API Design*, *New model/pipeline/scheduler addition*, *Forum*, or a blank issue. Make sure to pick the correct one when opening [a new issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose).
|
||||
2. **Be precise**: Give your issue a fitting title. Try to formulate your issue description as simple as possible. The more precise you are when submitting an issue, the less time it takes to understand the issue and potentially solve it. Make sure to open an issue for one issue only and not for multiple issues. If you found multiple issues, simply open multiple issues. If your issue is a bug, try to be as precise as possible about what bug it is - you should not just write "Error in diffusers".
|
||||
3. **Reproducibility**: No reproducible code snippet == no solution. If you encounter a bug, maintainers **have to be able to reproduce** it. Make sure that you include a code snippet that can be copy-pasted into a Python interpreter to reproduce the issue. Make sure that your code snippet works, *i.e.* that there are no missing imports or missing links to images, ... Your issue should contain an error message **and** a code snippet that can be copy-pasted without any changes to reproduce the exact same error message. If your issue is using local model weights or local data that cannot be accessed by the reader, the issue cannot be solved. If you cannot share your data or model, try to make a dummy model or dummy data.
|
||||
4. **Minimalistic**: Try to help the reader as much as you can to understand the issue as quickly as possible by staying as concise as possible. Remove all code / all information that is irrelevant to the issue. If you have found a bug, try to create the easiest code example you can to demonstrate your issue, do not just dump your whole workflow into the issue as soon as you have found a bug. E.g., if you train a model and get an error at some point during the training, you should first try to understand what part of the training code is responsible for the error and try to reproduce it with a couple of lines. Try to use dummy data instead of full datasets.
|
||||
5. Add links. If you are referring to a certain naming, method, or model make sure to provide a link so that the reader can better understand what you mean. If you are referring to a specific PR or issue, make sure to link it to your issue. Do not assume that the reader knows what you are talking about. The more links you add to your issue the better.
|
||||
6. Formatting. Make sure to nicely format your issue by formatting code into Python code syntax, and error messages into normal code syntax. See the [official GitHub formatting docs](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/writing-on-github/getting-started-with-writing-and-formatting-on-github/basic-writing-and-formatting-syntax) for more information.
|
||||
7. Think of your issue not as a ticket to be solved, but rather as a beautiful entry to a well-written encyclopedia. Every added issue is a contribution to publicly available knowledge. By adding a nicely written issue you not only make it easier for maintainers to solve your issue, but you are helping the whole community to better understand a certain aspect of the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to write a good PR
|
||||
|
||||
1. Be a chameleon. Understand existing design patterns and syntax and make sure your code additions flow seamlessly into the existing code base. Pull requests that significantly diverge from existing design patterns or user interfaces will not be merged.
|
||||
2. Be laser focused. A pull request should solve one problem and one problem only. Make sure to not fall into the trap of "also fixing another problem while we're adding it". It is much more difficult to review pull requests that solve multiple, unrelated problems at once.
|
||||
3. If helpful, try to add a code snippet that displays an example of how your addition can be used.
|
||||
4. The title of your pull request should be a summary of its contribution.
|
||||
5. If your pull request addresses an issue, please mention the issue number in
|
||||
the pull request description to make sure they are linked (and people
|
||||
consulting the issue know you are working on it);
|
||||
6. To indicate a work in progress please prefix the title with `[WIP]`. These
|
||||
are useful to avoid duplicated work, and to differentiate it from PRs ready
|
||||
to be merged;
|
||||
7. Try to formulate and format your text as explained in [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue).
|
||||
8. Make sure existing tests pass;
|
||||
9. Add high-coverage tests. No quality testing = no merge.
|
||||
- If you are adding new `@slow` tests, make sure they pass using
|
||||
`RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest tests/test_my_new_model.py`.
|
||||
CircleCI does not run the slow tests, but GitHub actions does every night!
|
||||
10. All public methods must have informative docstrings that work nicely with markdown. See `[pipeline_latent_diffusion.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/latent_diffusion/pipeline_latent_diffusion.py)` for an example.
|
||||
11. Due to the rapidly growing repository, it is important to make sure that no files that would significantly weigh down the repository are added. This includes images, videos, and other non-text files. We prefer to leverage a hf.co hosted `dataset` like
|
||||
[`hf-internal-testing`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing) or [huggingface/documentation-images](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images) to place these files.
|
||||
If an external contribution, feel free to add the images to your PR and ask a Hugging Face member to migrate your images
|
||||
to this dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to open a PR
|
||||
## Start contributing! (Pull Requests)
|
||||
|
||||
Before writing code, we strongly advise you to search through the existing PRs or
|
||||
issues to make sure that nobody is already working on the same thing. If you are
|
||||
@@ -355,98 +99,144 @@ You will need basic `git` proficiency to be able to contribute to
|
||||
manual. Type `git --help` in a shell and enjoy. If you prefer books, [Pro
|
||||
Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2) is a very good reference.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow these steps to start contributing ([supported Python versions](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/setup.py#L244)):
|
||||
Follow these steps to start contributing ([supported Python versions](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/setup.py#L212)):
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) by
|
||||
clicking on the 'Fork' button on the repository's page. This creates a copy of the code
|
||||
under your GitHub user account.
|
||||
clicking on the 'Fork' button on the repository's page. This creates a copy of the code
|
||||
under your GitHub user account.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Clone your fork to your local disk, and add the base repository as a remote:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git clone git@github.com:<your Github handle>/diffusers.git
|
||||
$ cd diffusers
|
||||
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git clone git@github.com:<your Github handle>/diffusers.git
|
||||
$ cd diffusers
|
||||
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Create a new branch to hold your development changes:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git checkout -b a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git checkout -b a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Do not** work on the `main` branch.
|
||||
**Do not** work on the `main` branch.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Set up a development environment by running the following command in a virtual environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pip install -e ".[dev]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pip install -e ".[dev]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have already cloned the repo, you might need to `git pull` to get the most recent changes in the
|
||||
library.
|
||||
(If Diffusers was already installed in the virtual environment, remove
|
||||
it with `pip uninstall diffusers` before reinstalling it in editable
|
||||
mode with the `-e` flag.)
|
||||
|
||||
To run the full test suite, you might need the additional dependency on `transformers` and `datasets` which requires a separate source
|
||||
install:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
|
||||
$ cd transformers
|
||||
$ pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/huggingface/datasets
|
||||
$ cd datasets
|
||||
$ pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have already cloned that repo, you might need to `git pull` to get the most recent changes in the `datasets`
|
||||
library.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Develop the features on your branch.
|
||||
|
||||
As you work on the features, you should make sure that the test suite
|
||||
passes. You should run the tests impacted by your changes like this:
|
||||
As you work on the features, you should make sure that the test suite
|
||||
passes. You should run the tests impacted by your changes like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pytest tests/<TEST_TO_RUN>.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pytest tests/<TEST_TO_RUN>.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also run the full suite with the following command, but it takes
|
||||
a beefy machine to produce a result in a decent amount of time now that
|
||||
Diffusers has grown a lot. Here is the command for it:
|
||||
You can also run the full suite with the following command, but it takes
|
||||
a beefy machine to produce a result in a decent amount of time now that
|
||||
Diffusers has grown a lot. Here is the command for it:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make test
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers relies on `black` and `isort` to format its source code
|
||||
consistently. After you make changes, apply automatic style corrections and code verifications
|
||||
that can't be automated in one go with:
|
||||
For more information about tests, check out the
|
||||
[dedicated documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/testing)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make style
|
||||
```
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers relies on `black` and `isort` to format its source code
|
||||
consistently. After you make changes, apply automatic style corrections and code verifications
|
||||
that can't be automated in one go with:
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers also uses `ruff` and a few custom scripts to check for coding mistakes. Quality
|
||||
control runs in CI, however, you can also run the same checks with:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make style
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make quality
|
||||
```
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers also uses `ruff` and a few custom scripts to check for coding mistakes. Quality
|
||||
control runs in CI, however you can also run the same checks with:
|
||||
|
||||
Once you're happy with your changes, add changed files using `git add` and
|
||||
make a commit with `git commit` to record your changes locally:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ make quality
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git add modified_file.py
|
||||
$ git commit
|
||||
```
|
||||
Once you're happy with your changes, add changed files using `git add` and
|
||||
make a commit with `git commit` to record your changes locally:
|
||||
|
||||
It is a good idea to sync your copy of the code with the original
|
||||
repository regularly. This way you can quickly account for changes:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git add modified_file.py
|
||||
$ git commit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git pull upstream main
|
||||
```
|
||||
It is a good idea to sync your copy of the code with the original
|
||||
repository regularly. This way you can quickly account for changes:
|
||||
|
||||
Push the changes to your account using:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git fetch upstream
|
||||
$ git rebase upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git push -u origin a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
Push the changes to your account using:
|
||||
|
||||
6. Once you are satisfied, go to the
|
||||
webpage of your fork on GitHub. Click on 'Pull request' to send your changes
|
||||
to the project maintainers for review.
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git push -u origin a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Once you are satisfied (**and the checklist below is happy too**), go to the
|
||||
webpage of your fork on GitHub. Click on 'Pull request' to send your changes
|
||||
to the project maintainers for review.
|
||||
|
||||
7. It's ok if maintainers ask you for changes. It happens to core contributors
|
||||
too! So everyone can see the changes in the Pull request, work in your local
|
||||
branch and push the changes to your fork. They will automatically appear in
|
||||
the pull request.
|
||||
too! So everyone can see the changes in the Pull request, work in your local
|
||||
branch and push the changes to your fork. They will automatically appear in
|
||||
the pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Checklist
|
||||
|
||||
1. The title of your pull request should be a summary of its contribution;
|
||||
2. If your pull request addresses an issue, please mention the issue number in
|
||||
the pull request description to make sure they are linked (and people
|
||||
consulting the issue know you are working on it);
|
||||
3. To indicate a work in progress please prefix the title with `[WIP]`. These
|
||||
are useful to avoid duplicated work, and to differentiate it from PRs ready
|
||||
to be merged;
|
||||
4. Make sure existing tests pass;
|
||||
5. Add high-coverage tests. No quality testing = no merge.
|
||||
- If you are adding new `@slow` tests, make sure they pass using
|
||||
`RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest tests/test_my_new_model.py`.
|
||||
- If you are adding a new tokenizer, write tests, and make sure
|
||||
`RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest tests/test_tokenization_{your_model_name}.py` passes.
|
||||
CircleCI does not run the slow tests, but GitHub actions does every night!
|
||||
6. All public methods must have informative docstrings that work nicely with sphinx. See `[pipeline_latent_diffusion.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/latent_diffusion/pipeline_latent_diffusion.py)` for an example.
|
||||
7. Due to the rapidly growing repository, it is important to make sure that no files that would significantly weigh down the repository are added. This includes images, videos and other non-text files. We prefer to leverage a hf.co hosted `dataset` like
|
||||
the ones hosted on [`hf-internal-testing`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing) in which to place these files and reference or [huggingface/documentation-images](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images).
|
||||
If an external contribution, feel free to add the images to your PR and ask a Hugging Face member to migrate your images
|
||||
to this dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tests
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -496,3 +286,6 @@ $ git push --set-upstream origin your-branch-for-syncing
|
||||
### Style guide
|
||||
|
||||
For documentation strings, 🧨 Diffusers follows the [google style](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**This guide was heavily inspired by the awesome [scikit-learn guide to contributing](https://github.com/scikit-learn/scikit-learn/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md).**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,8 +44,6 @@ The team works daily to make the technical and non-technical tools available to
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Safe Stable Diffusion**](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe): It mitigates the well-known issue that models, like Stable Diffusion, that are trained on unfiltered, web-crawled datasets tend to suffer from inappropriate degeneration. Related paper: [Safe Latent Diffusion: Mitigating Inappropriate Degeneration in Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105).
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Safety Checker**](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py): It checks and compares the class probability of a set of hard-coded harmful concepts in the embedding space against an image after it has been generated. The harmful concepts are intentionally hidden to prevent reverse engineering of the checker.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Staged released on the Hub**: in particularly sensitive situations, access to some repositories should be restricted. This staged release is an intermediary step that allows the repository’s authors to have more control over its use.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Licensing**: [OpenRAILs](https://huggingface.co/blog/open_rail), a new type of licensing, allow us to ensure free access while having a set of restrictions that ensure more responsible use.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,565 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Evaluating Diffusion Models
|
||||
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/evaluation.ipynb">
|
||||
<img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Evaluation of generative models like [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/stable_diffusion) is subjective in nature. But as practitioners and researchers, we often have to make careful choices amongst many different possibilities. So, when working with different generative models (like GANs, Diffusion, etc.), how do we choose one over the other?
|
||||
|
||||
Qualitative evaluation of such models can be error-prone and might incorrectly influence a decision.
|
||||
However, quantitative metrics don't necessarily correspond to image quality. So, usually, a combination
|
||||
of both qualitative and quantitative evaluations provides a stronger signal when choosing one model
|
||||
over the other.
|
||||
|
||||
In this document, we provide a non-exhaustive overview of qualitative and quantitative methods to evaluate Diffusion models. For quantitative methods, we specifically focus on how to implement them alongside `diffusers`.
|
||||
|
||||
The methods shown in this document can also be used to evaluate different [noise schedulers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/schedulers/overview) keeping the underlying generation model fixed.
|
||||
|
||||
## Scenarios
|
||||
|
||||
We cover Diffusion models with the following pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
- Text-guided image generation (such as the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img)).
|
||||
- Text-guided image generation, additionally conditioned on an input image (such as the [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img), and [`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix)).
|
||||
- Class-conditioned image generation models (such as the [`DiTPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/dit)).
|
||||
|
||||
## Qualitative Evaluation
|
||||
|
||||
Qualitative evaluation typically involves human assessment of generated images. Quality is measured across aspects such as compositionality, image-text alignment, and spatial relations. Common prompts provide a degree of uniformity for subjective metrics. DrawBench and PartiPrompts are prompt datasets used for qualitative benchmarking. DrawBench and PartiPrompts were introduced by [Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/) and [Parti](https://parti.research.google/) respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
From the [official Parti website](https://parti.research.google/):
|
||||
|
||||
> PartiPrompts (P2) is a rich set of over 1600 prompts in English that we release as part of this work. P2 can be used to measure model capabilities across various categories and challenge aspects.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PartiPrompts has the following columns:
|
||||
|
||||
- Prompt
|
||||
- Category of the prompt (such as “Abstract”, “World Knowledge”, etc.)
|
||||
- Challenge reflecting the difficulty (such as “Basic”, “Complex”, “Writing & Symbols”, etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
These benchmarks allow for side-by-side human evaluation of different image generation models. Let’s see how we can use `diffusers` on a couple of PartiPrompts.
|
||||
|
||||
Below we show some prompts sampled across different challenges: Basic, Complex, Linguistic Structures, Imagination, and Writing & Symbols. Here we are using PartiPrompts as a [dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/nateraw/parti-prompts).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
# prompts = load_dataset("nateraw/parti-prompts", split="train")
|
||||
# prompts = prompts.shuffle()
|
||||
# sample_prompts = [prompts[i]["Prompt"] for i in range(5)]
|
||||
|
||||
# Fixing these sample prompts in the interest of reproducibility.
|
||||
sample_prompts = [
|
||||
"a corgi",
|
||||
"a hot air balloon with a yin-yang symbol, with the moon visible in the daytime sky",
|
||||
"a car with no windows",
|
||||
"a cube made of porcupine",
|
||||
'The saying "BE EXCELLENT TO EACH OTHER" written on a red brick wall with a graffiti image of a green alien wearing a tuxedo. A yellow fire hydrant is on a sidewalk in the foreground.',
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can use these prompts to generate some images using Stable Diffusion ([v1-4 checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4)):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
seed = 0
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(sample_prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We can also set `num_images_per_prompt` accordingly to compare different images for the same prompt. Running the same pipeline but with a different checkpoint ([v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)), yields:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once several images are generated from all the prompts using multiple models (under evaluation), these results are presented to human evaluators for scoring. For
|
||||
more details on the DrawBench and PartiPrompts benchmarks, refer to their respective papers.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
It is useful to look at some inference samples while a model is training to measure the
|
||||
training progress. In our [training scripts](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/), we support this utility with additional support for
|
||||
logging to TensorBoard and Weights & Biases.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Quantitative Evaluation
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we will walk you through how to evaluate three different diffusion pipelines using:
|
||||
|
||||
- CLIP score
|
||||
- CLIP directional similarity
|
||||
- FID
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-guided image generation
|
||||
|
||||
[CLIP score](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08718) measures the compatibility of image-caption pairs. Higher CLIP scores imply higher compatibility 🔼. The CLIP score is a quantitative measurement of the qualitative concept "compatibility". Image-caption pair compatibility can also be thought of as the semantic similarity between the image and the caption. CLIP score was found to have high correlation with human judgement.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's first load a [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model_ckpt = "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
sd_pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_ckpt, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generate some images with multiple prompts:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompts = [
|
||||
"a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars",
|
||||
"A high tech solarpunk utopia in the Amazon rainforest",
|
||||
"A pikachu fine dining with a view to the Eiffel Tower",
|
||||
"A mecha robot in a favela in expressionist style",
|
||||
"an insect robot preparing a delicious meal",
|
||||
"A small cabin on top of a snowy mountain in the style of Disney, artstation",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
|
||||
print(images.shape)
|
||||
# (6, 512, 512, 3)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And then, we calculate the CLIP score.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from torchmetrics.functional.multimodal import clip_score
|
||||
from functools import partial
|
||||
|
||||
clip_score_fn = partial(clip_score, model_name_or_path="openai/clip-vit-base-patch16")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def calculate_clip_score(images, prompts):
|
||||
images_int = (images * 255).astype("uint8")
|
||||
clip_score = clip_score_fn(torch.from_numpy(images_int).permute(0, 3, 1, 2), prompts).detach()
|
||||
return round(float(clip_score), 4)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sd_clip_score = calculate_clip_score(images, prompts)
|
||||
print(f"CLIP score: {sd_clip_score}")
|
||||
# CLIP score: 35.7038
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, we generated one image per prompt. If we generated multiple images per prompt, we would have to take the average score from the generated images per prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, if we wanted to compare two checkpoints compatible with the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] we should pass a generator while calling the pipeline. First, we generate images with a
|
||||
fixed seed with the [v1-4 Stable Diffusion checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
seed = 0
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we load the [v1-5 checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) to generate images:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model_ckpt_1_5 = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
sd_pipeline_1_5 = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_ckpt_1_5, torch_dtype=weight_dtype).to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
images_1_5 = sd_pipeline_1_5(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And finally, we compare their CLIP scores:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
sd_clip_score_1_4 = calculate_clip_score(images, prompts)
|
||||
print(f"CLIP Score with v-1-4: {sd_clip_score_1_4}")
|
||||
# CLIP Score with v-1-4: 34.9102
|
||||
|
||||
sd_clip_score_1_5 = calculate_clip_score(images_1_5, prompts)
|
||||
print(f"CLIP Score with v-1-5: {sd_clip_score_1_5}")
|
||||
# CLIP Score with v-1-5: 36.2137
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It seems like the [v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) checkpoint performs better than its predecessor. Note, however, that the number of prompts we used to compute the CLIP scores is quite low. For a more practical evaluation, this number should be way higher, and the prompts should be diverse.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
By construction, there are some limitations in this score. The captions in the training dataset
|
||||
were crawled from the web and extracted from `alt` and similar tags associated an image on the internet.
|
||||
They are not necessarily representative of what a human being would use to describe an image. Hence we
|
||||
had to "engineer" some prompts here.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Image-conditioned text-to-image generation
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, we condition the generation pipeline with an input image as well as a text prompt. Let's take the [`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`], as an example. It takes an edit instruction as an input prompt and an input image to be edited.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is one example:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
One strategy to evaluate such a model is to measure the consistency of the change between the two images (in [CLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip) space) with the change between the two image captions (as shown in [CLIP-Guided Domain Adaptation of Image Generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.00946)). This is referred to as the "**CLIP directional similarity**".
|
||||
|
||||
- Caption 1 corresponds to the input image (image 1) that is to be edited.
|
||||
- Caption 2 corresponds to the edited image (image 2). It should reflect the edit instruction.
|
||||
|
||||
Following is a pictorial overview:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We have prepared a mini dataset to implement this metric. Let's first load the dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("sayakpaul/instructpix2pix-demo", split="train")
|
||||
dataset.features
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
{'input': Value(dtype='string', id=None),
|
||||
'edit': Value(dtype='string', id=None),
|
||||
'output': Value(dtype='string', id=None),
|
||||
'image': Image(decode=True, id=None)}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here we have:
|
||||
|
||||
- `input` is a caption corresponding to the `image`.
|
||||
- `edit` denotes the edit instruction.
|
||||
- `output` denotes the modified caption reflecting the `edit` instruction.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look at a sample.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
idx = 0
|
||||
print(f"Original caption: {dataset[idx]['input']}")
|
||||
print(f"Edit instruction: {dataset[idx]['edit']}")
|
||||
print(f"Modified caption: {dataset[idx]['output']}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
Original caption: 2. FAROE ISLANDS: An archipelago of 18 mountainous isles in the North Atlantic Ocean between Norway and Iceland, the Faroe Islands has 'everything you could hope for', according to Big 7 Travel. It boasts 'crystal clear waterfalls, rocky cliffs that seem to jut out of nowhere and velvety green hills'
|
||||
Edit instruction: make the isles all white marble
|
||||
Modified caption: 2. WHITE MARBLE ISLANDS: An archipelago of 18 mountainous white marble isles in the North Atlantic Ocean between Norway and Iceland, the White Marble Islands has 'everything you could hope for', according to Big 7 Travel. It boasts 'crystal clear waterfalls, rocky cliffs that seem to jut out of nowhere and velvety green hills'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And here is the image:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
dataset[idx]["image"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We will first edit the images of our dataset with the edit instruction and compute the directional similarity.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's first load the [`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
instruct_pix2pix_pipeline = StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"timbrooks/instruct-pix2pix", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to(device)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we perform the edits:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def edit_image(input_image, instruction):
|
||||
image = instruct_pix2pix_pipeline(
|
||||
instruction,
|
||||
image=input_image,
|
||||
output_type="numpy",
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
input_images = []
|
||||
original_captions = []
|
||||
modified_captions = []
|
||||
edited_images = []
|
||||
|
||||
for idx in range(len(dataset)):
|
||||
input_image = dataset[idx]["image"]
|
||||
edit_instruction = dataset[idx]["edit"]
|
||||
edited_image = edit_image(input_image, edit_instruction)
|
||||
|
||||
input_images.append(np.array(input_image))
|
||||
original_captions.append(dataset[idx]["input"])
|
||||
modified_captions.append(dataset[idx]["output"])
|
||||
edited_images.append(edited_image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To measure the directional similarity, we first load CLIP's image and text encoders:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
CLIPTokenizer,
|
||||
CLIPTextModelWithProjection,
|
||||
CLIPVisionModelWithProjection,
|
||||
CLIPImageProcessor,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
clip_id = "openai/clip-vit-large-patch14"
|
||||
tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(clip_id)
|
||||
text_encoder = CLIPTextModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(clip_id).to(device)
|
||||
image_processor = CLIPImageProcessor.from_pretrained(clip_id)
|
||||
image_encoder = CLIPVisionModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(clip_id).to(device)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that we are using a particular CLIP checkpoint, i.e., `openai/clip-vit-large-patch14`. This is because the Stable Diffusion pre-training was performed with this CLIP variant. For more details, refer to the [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix#diffusers.StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline.text_encoder).
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we prepare a PyTorch `nn.Module` to compute directional similarity:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
import torch.nn.functional as F
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DirectionalSimilarity(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, tokenizer, text_encoder, image_processor, image_encoder):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
|
||||
self.text_encoder = text_encoder
|
||||
self.image_processor = image_processor
|
||||
self.image_encoder = image_encoder
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_image(self, image):
|
||||
image = self.image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")["pixel_values"]
|
||||
return {"pixel_values": image.to(device)}
|
||||
|
||||
def tokenize_text(self, text):
|
||||
inputs = self.tokenizer(
|
||||
text,
|
||||
max_length=self.tokenizer.model_max_length,
|
||||
padding="max_length",
|
||||
truncation=True,
|
||||
return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
)
|
||||
return {"input_ids": inputs.input_ids.to(device)}
|
||||
|
||||
def encode_image(self, image):
|
||||
preprocessed_image = self.preprocess_image(image)
|
||||
image_features = self.image_encoder(**preprocessed_image).image_embeds
|
||||
image_features = image_features / image_features.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
|
||||
return image_features
|
||||
|
||||
def encode_text(self, text):
|
||||
tokenized_text = self.tokenize_text(text)
|
||||
text_features = self.text_encoder(**tokenized_text).text_embeds
|
||||
text_features = text_features / text_features.norm(dim=1, keepdim=True)
|
||||
return text_features
|
||||
|
||||
def compute_directional_similarity(self, img_feat_one, img_feat_two, text_feat_one, text_feat_two):
|
||||
sim_direction = F.cosine_similarity(img_feat_two - img_feat_one, text_feat_two - text_feat_one)
|
||||
return sim_direction
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, image_one, image_two, caption_one, caption_two):
|
||||
img_feat_one = self.encode_image(image_one)
|
||||
img_feat_two = self.encode_image(image_two)
|
||||
text_feat_one = self.encode_text(caption_one)
|
||||
text_feat_two = self.encode_text(caption_two)
|
||||
directional_similarity = self.compute_directional_similarity(
|
||||
img_feat_one, img_feat_two, text_feat_one, text_feat_two
|
||||
)
|
||||
return directional_similarity
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's put `DirectionalSimilarity` to use now.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
dir_similarity = DirectionalSimilarity(tokenizer, text_encoder, image_processor, image_encoder)
|
||||
scores = []
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(len(input_images)):
|
||||
original_image = input_images[i]
|
||||
original_caption = original_captions[i]
|
||||
edited_image = edited_images[i]
|
||||
modified_caption = modified_captions[i]
|
||||
|
||||
similarity_score = dir_similarity(original_image, edited_image, original_caption, modified_caption)
|
||||
scores.append(float(similarity_score.detach().cpu()))
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"CLIP directional similarity: {np.mean(scores)}")
|
||||
# CLIP directional similarity: 0.0797976553440094
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Like the CLIP Score, the higher the CLIP directional similarity, the better it is.
|
||||
|
||||
It should be noted that the `StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline` exposes two arguments, namely, `image_guidance_scale` and `guidance_scale` that let you control the quality of the final edited image. We encourage you to experiment with these two arguments and see the impact of that on the directional similarity.
|
||||
|
||||
We can extend the idea of this metric to measure how similar the original image and edited version are. To do that, we can just do `F.cosine_similarity(img_feat_two, img_feat_one)`. For these kinds of edits, we would still want the primary semantics of the images to be preserved as much as possible, i.e., a high similarity score.
|
||||
|
||||
We can use these metrics for similar pipelines such as the [`StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero#diffusers.StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Both CLIP score and CLIP direction similarity rely on the CLIP model, which can make the evaluations biased.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
***Extending metrics like IS, FID (discussed later), or KID can be difficult*** when the model under evaluation was pre-trained on a large image-captioning dataset (such as the [LAION-5B dataset](https://laion.ai/blog/laion-5b/)). This is because underlying these metrics is an InceptionNet (pre-trained on the ImageNet-1k dataset) used for extracting intermediate image features. The pre-training dataset of Stable Diffusion may have limited overlap with the pre-training dataset of InceptionNet, so it is not a good candidate here for feature extraction.
|
||||
|
||||
***Using the above metrics helps evaluate models that are class-conditioned. For example, [DiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview). It was pre-trained being conditioned on the ImageNet-1k classes.***
|
||||
|
||||
### Class-conditioned image generation
|
||||
|
||||
Class-conditioned generative models are usually pre-trained on a class-labeled dataset such as [ImageNet-1k](https://huggingface.co/datasets/imagenet-1k). Popular metrics for evaluating these models include Fréchet Inception Distance (FID), Kernel Inception Distance (KID), and Inception Score (IS). In this document, we focus on FID ([Heusel et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.08500)). We show how to compute it with the [`DiTPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/dit), which uses the [DiT model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.09748) under the hood.
|
||||
|
||||
FID aims to measure how similar are two datasets of images. As per [this resource](https://mmgeneration.readthedocs.io/en/latest/quick_run.html#fid):
|
||||
|
||||
> Fréchet Inception Distance is a measure of similarity between two datasets of images. It was shown to correlate well with the human judgment of visual quality and is most often used to evaluate the quality of samples of Generative Adversarial Networks. FID is calculated by computing the Fréchet distance between two Gaussians fitted to feature representations of the Inception network.
|
||||
|
||||
These two datasets are essentially the dataset of real images and the dataset of fake images (generated images in our case). FID is usually calculated with two large datasets. However, for this document, we will work with two mini datasets.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's first download a few images from the ImageNet-1k training set:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from zipfile import ZipFile
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def download(url, local_filepath):
|
||||
r = requests.get(url)
|
||||
with open(local_filepath, "wb") as f:
|
||||
f.write(r.content)
|
||||
return local_filepath
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dummy_dataset_url = "https://hf.co/datasets/sayakpaul/sample-datasets/resolve/main/sample-imagenet-images.zip"
|
||||
local_filepath = download(dummy_dataset_url, dummy_dataset_url.split("/")[-1])
|
||||
|
||||
with ZipFile(local_filepath, "r") as zipper:
|
||||
zipper.extractall(".")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
dataset_path = "sample-imagenet-images"
|
||||
image_paths = sorted([os.path.join(dataset_path, x) for x in os.listdir(dataset_path)])
|
||||
|
||||
real_images = [np.array(Image.open(path).convert("RGB")) for path in image_paths]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These are 10 images from the following Imagenet-1k classes: "cassette_player", "chain_saw" (x2), "church", "gas_pump" (x3), "parachute" (x2), and "tench".
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/evaluation_diffusion_models/real-images.png" alt="real-images"><br>
|
||||
<em>Real images.</em>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Now that the images are loaded, let's apply some lightweight pre-processing on them to use them for FID calculation.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from torchvision.transforms import functional as F
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_image(image):
|
||||
image = torch.tensor(image).unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
image = image.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) / 255.0
|
||||
return F.center_crop(image, (256, 256))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
real_images = torch.cat([preprocess_image(image) for image in real_images])
|
||||
print(real_images.shape)
|
||||
# torch.Size([10, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We now load the [`DiTPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/dit) to generate images conditioned on the above-mentioned classes.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiTPipeline, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
dit_pipeline = DiTPipeline.from_pretrained("facebook/DiT-XL-2-256", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
dit_pipeline.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(dit_pipeline.scheduler.config)
|
||||
dit_pipeline = dit_pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
words = [
|
||||
"cassette player",
|
||||
"chainsaw",
|
||||
"chainsaw",
|
||||
"church",
|
||||
"gas pump",
|
||||
"gas pump",
|
||||
"gas pump",
|
||||
"parachute",
|
||||
"parachute",
|
||||
"tench",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
class_ids = dit_pipeline.get_label_ids(words)
|
||||
output = dit_pipeline(class_labels=class_ids, generator=generator, output_type="numpy")
|
||||
|
||||
fake_images = output.images
|
||||
fake_images = torch.tensor(fake_images)
|
||||
fake_images = fake_images.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
print(fake_images.shape)
|
||||
# torch.Size([10, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can compute the FID using [`torchmetrics`](https://torchmetrics.readthedocs.io/).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from torchmetrics.image.fid import FrechetInceptionDistance
|
||||
|
||||
fid = FrechetInceptionDistance(normalize=True)
|
||||
fid.update(real_images, real=True)
|
||||
fid.update(fake_images, real=False)
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"FID: {float(fid.compute())}")
|
||||
# FID: 177.7147216796875
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The lower the FID, the better it is. Several things can influence FID here:
|
||||
|
||||
- Number of images (both real and fake)
|
||||
- Randomness induced in the diffusion process
|
||||
- Number of inference steps in the diffusion process
|
||||
- The scheduler being used in the diffusion process
|
||||
|
||||
For the last two points, it is, therefore, a good practice to run the evaluation across different seeds and inference steps, and then report an average result.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
FID results tend to be fragile as they depend on a lot of factors:
|
||||
|
||||
* The specific Inception model used during computation.
|
||||
* The implementation accuracy of the computation.
|
||||
* The image format (not the same if we start from PNGs vs JPGs).
|
||||
|
||||
Keeping that in mind, FID is often most useful when comparing similar runs, but it is
|
||||
hard to reproduce paper results unless the authors carefully disclose the FID
|
||||
measurement code.
|
||||
|
||||
These points apply to other related metrics too, such as KID and IS.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
As a final step, let's visually inspect the `fake_images`.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/evaluation_diffusion_models/fake-images.png" alt="fake-images"><br>
|
||||
<em>Fake images.</em>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
@@ -60,17 +60,17 @@ Let's walk through more in-detail design decisions for each class.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines are designed to be easy to use (therefore do not follow [*Simple over easy*](#simple-over-easy) 100%), are not feature complete, and should loosely be seen as examples of how to use [models](#models) and [schedulers](#schedulers) for inference.
|
||||
Pipelines are designed to be easy to use (therefore do not follow [*Simple over easy*](#simple-over-easy) 100%)), are not feature complete, and should loosely be seen as examples of how to use [models](#models) and [schedulers](#schedulers) for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Pipelines follow the single-file policy. All pipelines can be found in individual directories under src/diffusers/pipelines. One pipeline folder corresponds to one diffusion paper/project/release. Multiple pipeline files can be gathered in one pipeline folder, as it’s done for [`src/diffusers/pipelines/stable-diffusion`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion). If pipelines share similar functionality, one can make use of the [#Copied from mechanism](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/125d783076e5bd9785beb05367a2d2566843a271/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_img2img.py#L251).
|
||||
- Pipelines all inherit from [`DiffusionPipeline`].
|
||||
- Pipelines all inherit from [`DiffusionPipeline`]
|
||||
- Every pipeline consists of different model and scheduler components, that are documented in the [`model_index.json` file](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/blob/main/model_index.json), are accessible under the same name as attributes of the pipeline and can be shared between pipelines with [`DiffusionPipeline.components`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/diffusion_pipeline#diffusers.DiffusionPipeline.components) function.
|
||||
- Every pipeline should be loadable via the [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/diffusion_pipeline#diffusers.DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained) function.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be used **only** for inference.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be very readable, self-explanatory, and easy to tweak.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be designed to build on top of each other and be easy to integrate into higher-level APIs.
|
||||
- Pipelines are **not** intended to be feature-complete user interfaces. For future complete user interfaces one should rather have a look at [InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI), [Diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers), and [lama-cleaner](https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner).
|
||||
- Pipelines are **not** intended to be feature-complete user interfaces. For future complete user interfaces one should rather have a look at [InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI), [Diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers), and [lama-cleaner](https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner)
|
||||
- Every pipeline should have one and only one way to run it via a `__call__` method. The naming of the `__call__` arguments should be shared across all pipelines.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be named after the task they are intended to solve.
|
||||
- In almost all cases, novel diffusion pipelines shall be implemented in a new pipeline folder/file.
|
||||
@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Schedulers all inherit from `SchedulerMixin` and `ConfigMixin`.
|
||||
- Schedulers can be easily swapped out with the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/configuration#diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config) method as explained in detail [here](./using-diffusers/schedulers.mdx).
|
||||
- Every scheduler has to have a `set_num_inference_steps`, and a `step` function. `set_num_inference_steps(...)` has to be called before every denoising process, *i.e.* before `step(...)` is called.
|
||||
- Every scheduler exposes the timesteps to be "looped over" via a `timesteps` attribute, which is an array of timesteps the model will be called upon.
|
||||
- Every scheduler exposes the timesteps to be "looped over" via a `timesteps` attribute, which is an array of timesteps the model will be called upon
|
||||
- The `step(...)` function takes a predicted model output and the "current" sample (x_t) and returns the "previous", slightly more denoised sample (x_t-1).
|
||||
- Given the complexity of diffusion schedulers, the `step` function does not expose all the complexity and can be a bit of a "black box".
|
||||
- In almost all cases, novel schedulers shall be implemented in a new scheduling file.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,78 +16,61 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
# Diffusers
|
||||
# 🧨 Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is the go-to library for state-of-the-art pretrained diffusion models for generating images, audio, and even 3D structures of molecules. Whether you're looking for a simple inference solution or want to train your own diffusion model, 🤗 Diffusers is a modular toolbox that supports both. Our library is designed with a focus on [usability over performance](conceptual/philosophy#usability-over-performance), [simple over easy](conceptual/philosophy#simple-over-easy), and [customizability over abstractions](conceptual/philosophy#tweakable-contributorfriendly-over-abstraction).
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers provides pretrained vision and audio diffusion models, and serves as a modular toolbox for inference and training.
|
||||
|
||||
The library has three main components:
|
||||
More precisely, 🤗 Diffusers offers:
|
||||
|
||||
- State-of-the-art [diffusion pipelines](api/pipelines/overview) for inference with just a few lines of code.
|
||||
- Interchangeable [noise schedulers](api/schedulers/overview) for balancing trade-offs between generation speed and quality.
|
||||
- Pretrained [models](api/models) that can be used as building blocks, and combined with schedulers, for creating your own end-to-end diffusion systems.
|
||||
- State-of-the-art diffusion pipelines that can be run in inference with just a couple of lines of code (see [**Using Diffusers**](./using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation)) or have a look at [**Pipelines**](#pipelines) to get an overview of all supported pipelines and their corresponding papers.
|
||||
- Various noise schedulers that can be used interchangeably for the preferred speed vs. quality trade-off in inference. For more information see [**Schedulers**](./api/schedulers/overview).
|
||||
- Multiple types of models, such as UNet, can be used as building blocks in an end-to-end diffusion system. See [**Models**](./api/models) for more details
|
||||
- Training examples to show how to train the most popular diffusion model tasks. For more information see [**Training**](./training/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="mt-10">
|
||||
<div class="w-full flex flex-col space-y-4 md:space-y-0 md:grid md:grid-cols-2 md:gap-y-4 md:gap-x-5">
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./tutorials/tutorial_overview"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-blue-400 to-blue-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Tutorials</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">Learn the fundamental skills you need to start generating outputs, build your own diffusion system, and train a diffusion model. We recommend starting here if you're using 🤗 Diffusers for the first time!</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./using-diffusers/loading_overview"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-indigo-400 to-indigo-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">How-to guides</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">Practical guides for helping you load pipelines, models, and schedulers. You'll also learn how to use pipelines for specific tasks, control how outputs are generated, optimize for inference speed, and different training techniques.</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./conceptual/philosophy"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-pink-400 to-pink-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Conceptual guides</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">Understand why the library was designed the way it was, and learn more about the ethical guidelines and safety implementations for using the library.</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./api/models"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-purple-400 to-purple-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Reference</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">Technical descriptions of how 🤗 Diffusers classes and methods work.</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
## 🧨 Diffusers Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported pipelines
|
||||
The following table summarizes all officially supported pipelines, their corresponding paper, and if
|
||||
available a colab notebook to directly try them out.
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Paper/Repository | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [alt_diffusion](./api/pipelines/alt_diffusion) | [AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [audio_diffusion](./api/pipelines/audio_diffusion) | [Audio Diffusion](https://github.com/teticio/audio-diffusion.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [controlnet](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/controlnet) | [Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [cycle_diffusion](./api/pipelines/cycle_diffusion) | [Unifying Diffusion Models' Latent Space, with Applications to CycleDiffusion and Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.05559) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [dance_diffusion](./api/pipelines/dance_diffusion) | [Dance Diffusion](https://github.com/williamberman/diffusers.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [ddpm](./api/pipelines/ddpm) | [Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [ddim](./api/pipelines/ddim) | [Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion_uncond](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [paint_by_example](./api/pipelines/paint_by_example) | [Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13227) | Image-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [pndm](./api/pipelines/pndm) | [Pseudo Numerical Methods for Diffusion Models on Manifolds](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09778) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_ve](./api/pipelines/score_sde_ve) | [Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_vp](./api/pipelines/score_sde_vp) | [Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [semantic_stable_diffusion](./api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion) | [Semantic Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12247) | Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_text2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_img2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_inpaint](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/inpaint) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_panorama](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/panorama) | [MultiDiffusion](https://multidiffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Panorama Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix) | [InstructPix2Pix: Learning to Follow Image Editing Instructions](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09800) | Text-Guided Image Editing|
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix_zero](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero) | [Zero-shot Image-to-Image Translation](https://pix2pixzero.github.io/) | Text-Guided Image Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_attend_and_excite](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/attend_and_excite) | [Attend-and-Excite: Attention-Based Semantic Guidance for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13826) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_self_attention_guidance](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/self_attention_guidance) | [Improving Sample Quality of Diffusion Models Using Self-Attention Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.00939) | Text-to-Image Generation Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_image_variation](./stable_diffusion/image_variation) | [Stable Diffusion Image Variations](https://github.com/LambdaLabsML/lambda-diffusers#stable-diffusion-image-variations) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_latent_upscale](./stable_diffusion/latent_upscale) | [Stable Diffusion Latent Upscaler](https://twitter.com/StabilityAI/status/1590531958815064065) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_model_editing](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/model_editing) | [Editing Implicit Assumptions in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://time-diffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Image Model Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Depth-Conditional Stable Diffusion](https://github.com/Stability-AI/stablediffusion#depth-conditional-stable-diffusion) | Depth-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_safe](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe) | [Safe Stable Diffusion](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105) | Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | Stable unCLIP | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | Stable unCLIP | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stochastic_karras_ve](./api/pipelines/stochastic_karras_ve) | [Elucidating the Design Space of Diffusion-Based Generative Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00364) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [text_to_video_sd](./api/pipelines/text_to_video) | [Modelscope's Text-to-video-synthesis Model in Open Domain](https://modelscope.cn/models/damo/text-to-video-synthesis/summary) | Text-to-Video Generation |
|
||||
| [unclip](./api/pipelines/unclip) | [Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06125)(implementation by [kakaobrain](https://github.com/kakaobrain/karlo)) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Image Variations Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Dual Image and Text Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [vq_diffusion](./api/pipelines/vq_diffusion) | [Vector Quantized Diffusion Model for Text-to-Image Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.14822) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| Pipeline | Paper | Tasks | Colab
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|:---:|
|
||||
| [alt_diffusion](./api/pipelines/alt_diffusion) | [**AltDiffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [audio_diffusion](./api/pipelines/audio_diffusion) | [**Audio Diffusion**](https://github.com/teticio/audio-diffusion.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/teticio/audio-diffusion/blob/master/notebooks/audio_diffusion_pipeline.ipynb)
|
||||
| [controlnet](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/controlnet) | [**ControlNet with Stable Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1AiR7Q-sBqO88NCyswpfiuwXZc7DfMyKA?usp=sharing)
|
||||
| [cycle_diffusion](./api/pipelines/cycle_diffusion) | [**Cycle Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.05559) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [dance_diffusion](./api/pipelines/dance_diffusion) | [**Dance Diffusion**](https://github.com/williamberman/diffusers.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [ddpm](./api/pipelines/ddpm) | [**Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [ddim](./api/pipelines/ddim) | [**Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [**High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [**High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion_uncond](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond) | [**High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [paint_by_example](./api/pipelines/paint_by_example) | [**Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13227) | Image-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [pndm](./api/pipelines/pndm) | [**Pseudo Numerical Methods for Diffusion Models on Manifolds**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09778) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_ve](./api/pipelines/score_sde_ve) | [**Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations**](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_vp](./api/pipelines/score_sde_vp) | [**Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations**](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [semantic_stable_diffusion](./api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion) | [**Semantic Guidance**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12247) | Text-Guided Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ml-research/semantic-image-editing/blob/main/examples/SemanticGuidance.ipynb)
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_text2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img) | [**Stable Diffusion**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-to-Image Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/training_example.ipynb)
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_img2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) | [**Stable Diffusion**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/image_2_image_using_diffusers.ipynb)
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_inpaint](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/inpaint) | [**Stable Diffusion**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/in_painting_with_stable_diffusion_using_diffusers.ipynb)
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_panorama](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/panorama) | [**MultiDiffusion**](https://multidiffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Panorama Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix) | [**InstructPix2Pix**](https://github.com/timothybrooks/instruct-pix2pix) | Text-Guided Image Editing|
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix_zero](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero) | [**Zero-shot Image-to-Image Translation**](https://pix2pixzero.github.io/) | Text-Guided Image Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_attend_and_excite](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/attend_and_excite) | [**Attend and Excite for Stable Diffusion**](https://attendandexcite.github.io/Attend-and-Excite/) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_self_attention_guidance](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/self_attention_guidance) | [**Self-Attention Guidance**](https://ku-cvlab.github.io/Self-Attention-Guidance) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_image_variation](./stable_diffusion/image_variation) | [**Stable Diffusion Image Variations**](https://github.com/LambdaLabsML/lambda-diffusers#stable-diffusion-image-variations) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_latent_upscale](./stable_diffusion/latent_upscale) | [**Stable Diffusion Latent Upscaler**](https://twitter.com/StabilityAI/status/1590531958815064065) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Stable Diffusion 2**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Stable Diffusion 2**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Depth-Conditional Stable Diffusion**](https://github.com/Stability-AI/stablediffusion#depth-conditional-stable-diffusion) | Depth-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Stable Diffusion 2**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_safe](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe) | [**Safe Stable Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105) | Text-Guided Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ml-research/safe-latent-diffusion/blob/main/examples/Safe%20Latent%20Diffusion.ipynb)
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | **Stable unCLIP** | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | **Stable unCLIP** | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stochastic_karras_ve](./api/pipelines/stochastic_karras_ve) | [**Elucidating the Design Space of Diffusion-Based Generative Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00364) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [unclip](./api/pipelines/unclip) | [Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06125) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Image Variations Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Dual Image and Text Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [vq_diffusion](./api/pipelines/vq_diffusion) | [Vector Quantized Diffusion Model for Text-to-Image Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.14822) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Pipelines are simple examples of how to play around with the diffusion systems as described in the corresponding papers.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,167 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# How to run Stable Diffusion with Core ML
|
||||
|
||||
[Core ML](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coreml) is the model format and machine learning library supported by Apple frameworks. If you are interested in running Stable Diffusion models inside your macOS or iOS/iPadOS apps, this guide will show you how to convert existing PyTorch checkpoints into the Core ML format and use them for inference with Python or Swift.
|
||||
|
||||
Core ML models can leverage all the compute engines available in Apple devices: the CPU, the GPU, and the Apple Neural Engine (or ANE, a tensor-optimized accelerator available in Apple Silicon Macs and modern iPhones/iPads). Depending on the model and the device it's running on, Core ML can mix and match compute engines too, so some portions of the model may run on the CPU while others run on GPU, for example.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You can also run the `diffusers` Python codebase on Apple Silicon Macs using the `mps` accelerator built into PyTorch. This approach is explained in depth in [the mps guide](mps), but it is not compatible with native apps.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion Core ML Checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion weights (or checkpoints) are stored in the PyTorch format, so you need to convert them to the Core ML format before we can use them inside native apps.
|
||||
|
||||
Thankfully, Apple engineers developed [a conversion tool](https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion#-converting-models-to-core-ml) based on `diffusers` to convert the PyTorch checkpoints to Core ML.
|
||||
|
||||
Before you convert a model, though, take a moment to explore the Hugging Face Hub – chances are the model you're interested in is already available in Core ML format:
|
||||
|
||||
- the [Apple](https://huggingface.co/apple) organization includes Stable Diffusion versions 1.4, 1.5, 2.0 base, and 2.1 base
|
||||
- [coreml](https://huggingface.co/coreml) organization includes custom DreamBoothed and finetuned models
|
||||
- use this [filter](https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=text-to-image&library=coreml&p=2&sort=likes) to return all available Core ML checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
If you can't find the model you're interested in, we recommend you follow the instructions for [Converting Models to Core ML](https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion#-converting-models-to-core-ml) by Apple.
|
||||
|
||||
## Selecting the Core ML Variant to Use
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion models can be converted to different Core ML variants intended for different purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
- The type of attention blocks used. The attention operation is used to "pay attention" to the relationship between different areas in the image representations and to understand how the image and text representations are related. Attention is compute- and memory-intensive, so different implementations exist that consider the hardware characteristics of different devices. For Core ML Stable Diffusion models, there are two attention variants:
|
||||
* `split_einsum` ([introduced by Apple](https://machinelearning.apple.com/research/neural-engine-transformers)) is optimized for ANE devices, which is available in modern iPhones, iPads and M-series computers.
|
||||
* The "original" attention (the base implementation used in `diffusers`) is only compatible with CPU/GPU and not ANE. It can be *faster* to run your model on CPU + GPU using `original` attention than ANE. See [this performance benchmark](https://huggingface.co/blog/fast-mac-diffusers#performance-benchmarks) as well as some [additional measures provided by the community](https://github.com/huggingface/swift-coreml-diffusers/issues/31) for additional details.
|
||||
|
||||
- The supported inference framework.
|
||||
* `packages` are suitable for Python inference. This can be used to test converted Core ML models before attempting to integrate them inside native apps, or if you want to explore Core ML performance but don't need to support native apps. For example, an application with a web UI could perfectly use a Python Core ML backend.
|
||||
* `compiled` models are required for Swift code. The `compiled` models in the Hub split the large UNet model weights into several files for compatibility with iOS and iPadOS devices. This corresponds to the [`--chunk-unet` conversion option](https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion#-converting-models-to-core-ml). If you want to support native apps, then you need to select the `compiled` variant.
|
||||
|
||||
The official Core ML Stable Diffusion [models](https://huggingface.co/apple/coreml-stable-diffusion-v1-4/tree/main) include these variants, but the community ones may vary:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
coreml-stable-diffusion-v1-4
|
||||
├── README.md
|
||||
├── original
|
||||
│ ├── compiled
|
||||
│ └── packages
|
||||
└── split_einsum
|
||||
├── compiled
|
||||
└── packages
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can download and use the variant you need as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
## Core ML Inference in Python
|
||||
|
||||
Install the following libraries to run Core ML inference in Python:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Download the Model Checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
To run inference in Python, use one of the versions stored in the `packages` folders because the `compiled` ones are only compatible with Swift. You may choose whether you want to use `original` or `split_einsum` attention.
|
||||
|
||||
This is how you'd download the `original` attention variant from the Hub to a directory called `models`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "apple/coreml-stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
variant = "original/packages"
|
||||
|
||||
model_path = Path("./models") / (repo_id.split("/")[-1] + "_" + variant.replace("/", "_"))
|
||||
snapshot_download(repo_id, allow_patterns=f"{variant}/*", local_dir=model_path, local_dir_use_symlinks=False)
|
||||
print(f"Model downloaded at {model_path}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference[[python-inference]]
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have downloaded a snapshot of the model, you can test it using Apple's Python script.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python -m python_coreml_stable_diffusion.pipeline --prompt "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars" -i models/coreml-stable-diffusion-v1-4_original_packages -o </path/to/output/image> --compute-unit CPU_AND_GPU --seed 93
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`<output-mlpackages-directory>` should point to the checkpoint you downloaded in the step above, and `--compute-unit` indicates the hardware you want to allow for inference. It must be one of the following options: `ALL`, `CPU_AND_GPU`, `CPU_ONLY`, `CPU_AND_NE`. You may also provide an optional output path, and a seed for reproducibility.
|
||||
|
||||
The inference script assumes you're using the original version of the Stable Diffusion model, `CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4`. If you use another model, you *have* to specify its Hub id in the inference command line, using the `--model-version` option. This works for models already supported and custom models you trained or fine-tuned yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you want to use [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python -m python_coreml_stable_diffusion.pipeline --prompt "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars" --compute-unit ALL -o output --seed 93 -i models/coreml-stable-diffusion-v1-5_original_packages --model-version runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Core ML inference in Swift
|
||||
|
||||
Running inference in Swift is slightly faster than in Python because the models are already compiled in the `mlmodelc` format. This is noticeable on app startup when the model is loaded but shouldn’t be noticeable if you run several generations afterward.
|
||||
|
||||
### Download
|
||||
|
||||
To run inference in Swift on your Mac, you need one of the `compiled` checkpoint versions. We recommend you download them locally using Python code similar to the previous example, but with one of the `compiled` variants:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "apple/coreml-stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
variant = "original/compiled"
|
||||
|
||||
model_path = Path("./models") / (repo_id.split("/")[-1] + "_" + variant.replace("/", "_"))
|
||||
snapshot_download(repo_id, allow_patterns=f"{variant}/*", local_dir=model_path, local_dir_use_symlinks=False)
|
||||
print(f"Model downloaded at {model_path}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference[[swift-inference]]
|
||||
|
||||
To run inference, please clone Apple's repo:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion
|
||||
cd ml-stable-diffusion
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And then use Apple's command line tool, [Swift Package Manager](https://www.swift.org/package-manager/#):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
swift run StableDiffusionSample --resource-path models/coreml-stable-diffusion-v1-4_original_compiled --compute-units all "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You have to specify in `--resource-path` one of the checkpoints downloaded in the previous step, so please make sure it contains compiled Core ML bundles with the extension `.mlmodelc`. The `--compute-units` has to be one of these values: `all`, `cpuOnly`, `cpuAndGPU`, `cpuAndNeuralEngine`.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, please refer to the [instructions in Apple's repo](https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Diffusers Features
|
||||
|
||||
The Core ML models and inference code don't support many of the features, options, and flexibility of 🧨 Diffusers. These are some of the limitations to keep in mind:
|
||||
|
||||
- Core ML models are only suitable for inference. They can't be used for training or fine-tuning.
|
||||
- Only two schedulers have been ported to Swift, the default one used by Stable Diffusion and `DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`, which we ported to Swift from our `diffusers` implementation. We recommend you use `DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`, since it produces the same quality in about half the steps.
|
||||
- Negative prompts, classifier-free guidance scale, and image-to-image tasks are available in the inference code. Advanced features such as depth guidance, ControlNet, and latent upscalers are not available yet.
|
||||
|
||||
Apple's [conversion and inference repo](https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion) and our own [swift-coreml-diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/swift-coreml-diffusers) repos are intended as technology demonstrators to enable other developers to build upon.
|
||||
|
||||
If you feel strongly about any missing features, please feel free to open a feature request or, better yet, a contribution PR :)
|
||||
|
||||
## Native Diffusers Swift app
|
||||
|
||||
One easy way to run Stable Diffusion on your own Apple hardware is to use [our open-source Swift repo](https://github.com/huggingface/swift-coreml-diffusers), based on `diffusers` and Apple's conversion and inference repo. You can study the code, compile it with [Xcode](https://developer.apple.com/xcode/) and adapt it for your own needs. For your convenience, there's also a [standalone Mac app in the App Store](https://apps.apple.com/app/diffusers/id1666309574), so you can play with it without having to deal with the code or IDE. If you are a developer and have determined that Core ML is the best solution to build your Stable Diffusion app, then you can use the rest of this guide to get started with your project. We can't wait to see what you'll build :)
|
||||
@@ -19,6 +19,7 @@ We'll discuss how the following settings impact performance and memory.
|
||||
| | Latency | Speedup |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------- |
|
||||
| original | 9.50s | x1 |
|
||||
| cuDNN auto-tuner | 9.37s | x1.01 |
|
||||
| fp16 | 3.61s | x2.63 |
|
||||
| channels last | 3.30s | x2.88 |
|
||||
| traced UNet | 3.21s | x2.96 |
|
||||
@@ -30,6 +31,18 @@ We'll discuss how the following settings impact performance and memory.
|
||||
steps.
|
||||
</em>
|
||||
|
||||
## Enable cuDNN auto-tuner
|
||||
|
||||
[NVIDIA cuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) supports many algorithms to compute a convolution. Autotuner runs a short benchmark and selects the kernel with the best performance on a given hardware for a given input size.
|
||||
|
||||
Since we’re using **convolutional networks** (other types currently not supported), we can enable cuDNN autotuner before launching the inference by setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Use tf32 instead of fp32 (on Ampere and later CUDA devices)
|
||||
|
||||
On Ampere and later CUDA devices matrix multiplications and convolutions can use the TensorFloat32 (TF32) mode for faster but slightly less accurate computations. By default PyTorch enables TF32 mode for convolutions but not matrix multiplications, and unless a network requires full float32 precision we recommend enabling this setting for matrix multiplications, too. It can significantly speed up computations with typically negligible loss of numerical accuracy. You can read more about it [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/v4.18.0/en/performance#tf32). All you need to do is to add this before your inference:
|
||||
@@ -45,10 +58,7 @@ torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
|
||||
To save more GPU memory and get more speed, you can load and run the model weights directly in half precision. This involves loading the float16 version of the weights, which was saved to a branch named `fp16`, and telling PyTorch to use the `float16` type when loading them:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
@@ -75,13 +85,13 @@ For even additional memory savings, you can use a sliced version of attention th
|
||||
each head which can save a significant amount of memory.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To perform the attention computation sequentially over each head, you only need to invoke [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_attention_slicing`] in your pipeline before inference, like here:
|
||||
To perform the attention computation sequentially over each head, you only need to invoke [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_attention_slicing`] in your pipeline before inference, like here:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
@@ -211,7 +221,7 @@ image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
Full-model offloading is an alternative that moves whole models to the GPU, instead of handling each model's constituent _modules_. This results in a negligible impact on inference time (compared with moving the pipeline to `cuda`), while still providing some memory savings.
|
||||
|
||||
In this scenario, only one of the main components of the pipeline (typically: text encoder, unet and vae)
|
||||
will be in the GPU while the others wait in the CPU. Components like the UNet that run for multiple iterations will stay on GPU until they are no longer needed.
|
||||
will be in the GPU while the others wait in the CPU. Compoments like the UNet that run for multiple iterations will stay on GPU until they are no longer needed.
|
||||
|
||||
This feature can be enabled by invoking `enable_model_cpu_offload()` on the pipeline, as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -405,10 +415,10 @@ To leverage it just make sure you have:
|
||||
- Cuda available
|
||||
- [Installed the xformers library](xformers).
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,8 +16,8 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
- Optimum Habana 1.4 or later, [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/habana/installation) is how to install it.
|
||||
- SynapseAI 1.8.
|
||||
- Optimum Habana 1.3 or later, [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/habana/installation) is how to install it.
|
||||
- SynapseAI 1.7.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference Pipeline
|
||||
@@ -62,9 +62,9 @@ For more information, check out Optimum Habana's [documentation](https://hugging
|
||||
|
||||
## Benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the latencies for Habana first-generation Gaudi and Gaudi2 with the [Habana/stable-diffusion](https://huggingface.co/Habana/stable-diffusion) Gaudi configuration (mixed precision bf16/fp32):
|
||||
Here are the latencies for Habana Gaudi 1 and Gaudi 2 with the [Habana/stable-diffusion](https://huggingface.co/Habana/stable-diffusion) Gaudi configuration (mixed precision bf16/fp32):
|
||||
|
||||
| | Latency (batch size = 1) | Throughput (batch size = 8) |
|
||||
| ---------------------- |:------------------------:|:---------------------------:|
|
||||
| first-generation Gaudi | 4.29s | 0.283 images/s |
|
||||
| Gaudi2 | 1.54s | 0.904 images/s |
|
||||
| | Latency | Batch size |
|
||||
| ------- |:-------:|:----------:|
|
||||
| Gaudi 1 | 4.37s | 4/8 |
|
||||
| Gaudi 2 | 1.19s | 4/8 |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,25 +19,20 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
- Mac computer with Apple silicon (M1/M2) hardware.
|
||||
- macOS 12.6 or later (13.0 or later recommended).
|
||||
- arm64 version of Python.
|
||||
- PyTorch 2.0 (recommended) or 1.13 (minimum version supported for `mps`). You can install it with `pip` or `conda` using the instructions in https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/.
|
||||
- PyTorch 1.13. You can install it with `pip` or `conda` using the instructions in https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
The snippet below demonstrates how to use the `mps` backend using the familiar `to()` interface to move the Stable Diffusion pipeline to your M1 or M2 device.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
**If you are using PyTorch 1.13** you need to "prime" the pipeline using an additional one-time pass through it. This is a temporary workaround for a weird issue we detected: the first inference pass produces slightly different results than subsequent ones. You only need to do this pass once, and it's ok to use just one inference step and discard the result.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
We strongly recommend you use PyTorch 2 or better, as it solves a number of problems like the one described in the previous tip.
|
||||
We recommend to "prime" the pipeline using an additional one-time pass through it. This is a temporary workaround for a weird issue we have detected: the first inference pass produces slightly different results than subsequent ones. You only need to do this pass once, and it's ok to use just one inference step and discard the result.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
# make sure you're logged in with `huggingface-cli login`
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("mps")
|
||||
|
||||
# Recommended if your computer has < 64 GB of RAM
|
||||
@@ -45,7 +40,7 @@ pipe.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
|
||||
# First-time "warmup" pass if PyTorch version is 1.13 (see explanation above)
|
||||
# First-time "warmup" pass (see explanation above)
|
||||
_ = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Results match those from the CPU device after the warmup pass.
|
||||
@@ -56,7 +51,7 @@ image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
M1/M2 performance is very sensitive to memory pressure. The system will automatically swap if it needs to, but performance will degrade significantly when it does.
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend you use _attention slicing_ to reduce memory pressure during inference and prevent swapping, particularly if your computer has less than 64 GB of system RAM, or if you generate images at non-standard resolutions larger than 512 × 512 pixels. Attention slicing performs the costly attention operation in multiple steps instead of all at once. It usually has a performance impact of ~20% in computers without universal memory, but we have observed _better performance_ in most Apple Silicon computers, unless you have 64 GB or more.
|
||||
We recommend you use _attention slicing_ to reduce memory pressure during inference and prevent swapping, particularly if your computer has lass than 64 GB of system RAM, or if you generate images at non-standard resolutions larger than 512 × 512 pixels. Attention slicing performs the costly attention operation in multiple steps instead of all at once. It usually has a performance impact of ~20% in computers without universal memory, but we have observed _better performance_ in most Apple Silicon computers, unless you have 64 GB or more.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
@@ -64,4 +59,5 @@ pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
|
||||
## Known Issues
|
||||
|
||||
- As mentioned above, we are investigating a strange [first-time inference issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/372).
|
||||
- Generating multiple prompts in a batch [crashes or doesn't work reliably](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/363). We believe this is related to the [`mps` backend in PyTorch](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/84039). This is being resolved, but for now we recommend to iterate instead of batching.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,53 +13,30 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# How to use the ONNX Runtime for inference
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 [Optimum](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum) provides a Stable Diffusion pipeline compatible with ONNX Runtime.
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers provides a Stable Diffusion pipeline compatible with the ONNX Runtime. This allows you to run Stable Diffusion on any hardware that supports ONNX (including CPUs), and where an accelerated version of PyTorch is not available.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Install 🤗 Optimum with the following command for ONNX Runtime support:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install optimum["onnxruntime"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
- TODO
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion Inference
|
||||
|
||||
To load an ONNX model and run inference with the ONNX Runtime, you need to replace [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] with `ORTStableDiffusionPipeline`. In case you want to load
|
||||
a PyTorch model and convert it to the ONNX format on-the-fly, you can set `export=True`.
|
||||
The snippet below demonstrates how to use the ONNX runtime. You need to use `StableDiffusionOnnxPipeline` instead of `StableDiffusionPipeline`. You also need to download the weights from the `onnx` branch of the repository, and indicate the runtime provider you want to use.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from optimum.onnxruntime import ORTStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
# make sure you're logged in with `huggingface-cli login`
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionOnnxPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionOnnxPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
revision="onnx",
|
||||
provider="CUDAExecutionProvider",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = ORTStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, export=True)
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
pipe.save_pretrained("./onnx-stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to export the pipeline in the ONNX format offline and later use it for inference,
|
||||
you can use the [`optimum-cli export`](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/main/en/exporters/onnx/usage_guides/export_a_model#exporting-a-model-to-onnx-using-the-cli) command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
optimum-cli export onnx --model runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5 sd_v15_onnx/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then perform inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from optimum.onnxruntime import ORTStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "sd_v15_onnx"
|
||||
pipe = ORTStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that we didn't have to specify `export=True` above.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find more examples in [optimum documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Known Issues
|
||||
|
||||
- Generating multiple prompts in a batch seems to take too much memory. While we look into it, you may need to iterate instead of batching.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,30 +10,6 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# OpenVINO
|
||||
|
||||
# How to use OpenVINO for inference
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 [Optimum](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-intel) provides a Stable Diffusion pipeline compatible with OpenVINO. You can now easily perform inference with OpenVINO Runtime on a variety of Intel processors ([see](https://docs.openvino.ai/latest/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_Supported_Devices.html) the full list of supported devices).
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Install 🤗 Optimum Intel with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install optimum["openvino"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion Inference
|
||||
|
||||
To load an OpenVINO model and run inference with OpenVINO Runtime, you need to replace `StableDiffusionPipeline` with `OVStableDiffusionPipeline`. In case you want to load a PyTorch model and convert it to the OpenVINO format on-the-fly, you can set `export=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from optimum.intel.openvino import OVStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = OVStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, export=True)
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can find more examples (such as static reshaping and model compilation) in [optimum documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/intel/inference#export-and-inference-of-stable-diffusion-models).
|
||||
Under construction 🚧
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Generating high-quality outputs is computationally intensive, especially during each iterative step where you go from a noisy output to a less noisy output. One of 🧨 Diffuser's goal is to make this technology widely accessible to everyone, which includes enabling fast inference on consumer and specialized hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
This section will cover tips and tricks - like half-precision weights and sliced attention - for optimizing inference speed and reducing memory-consumption. You can also learn how to speed up your PyTorch code with [`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html) or [ONNX Runtime](https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/), and enable memory-efficient attention with [xFormers](https://facebookresearch.github.io/xformers/). There are also guides for running inference on specific hardware like Apple Silicon, and Intel or Habana processors.
|
||||
@@ -18,10 +18,11 @@ Starting from version `0.13.0`, Diffusers supports the latest optimization from
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
To benefit from the accelerated attention implementation and `torch.compile`, you just need to install the latest versions of PyTorch 2.0 from `pip`, and make sure you are on diffusers 0.13.0 or later. As explained below, `diffusers` automatically uses the attention optimizations (but not `torch.compile`) when available.
|
||||
To benefit from the accelerated transformers implementation and `torch.compile`, we will need to install the nightly version of PyTorch, as the stable version is yet to be released. The first step is to install CUDA 11.7 or CUDA 11.8,
|
||||
as PyTorch 2.0 does not support the previous versions. Once CUDA is installed, torch nightly can be installed using:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade torch torchvision diffusers
|
||||
pip install --pre torch torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu117
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Using accelerated transformers and torch.compile.
|
||||
@@ -35,9 +36,9 @@ pip install --upgrade torch torchvision diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
@@ -48,10 +49,10 @@ pip install --upgrade torch torchvision diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnProcessor2_0
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.models.cross_attention import AttnProcessor2_0
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnProcessor2_0())
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
@@ -68,9 +69,11 @@ pip install --upgrade torch torchvision diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to(
|
||||
"cuda"
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.unet = torch.compile(pipe.unet)
|
||||
|
||||
batch_size = 10
|
||||
@@ -86,9 +89,10 @@ pip install --upgrade torch torchvision diffusers
|
||||
## Benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
We conducted a simple benchmark on different GPUs to compare vanilla attention, xFormers, `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention` and `torch.compile+torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention`.
|
||||
For the benchmark we used the [stable-diffusion-v1-4](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) model with 50 steps. The `xFormers` benchmark is done using the `torch==1.13.1` version, while the accelerated transformers optimizations are tested using nightly versions of PyTorch 2.0. The tables below summarize the results we got.
|
||||
For the benchmark we used the the [stable-diffusion-v1-4](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) model with 50 steps. The `xFormers` benchmark is done using the `torch==1.13.1` version, while the accelerated transformers optimizations are tested using nightly versions of PyTorch 2.0. The tables below summarize the results we got.
|
||||
|
||||
The `Speed over xformers` columns denote the speed-up gained over `xFormers` using the `torch.compile+torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention`.
|
||||
|
||||
Please refer to [our featured blog post in the PyTorch site](https://pytorch.org/blog/accelerated-diffusers-pt-20/) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### FP16 benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -99,14 +103,10 @@ ___The time reported is in seconds.___
|
||||
|
||||
| GPU | Batch Size | Vanilla Attention | xFormers | PyTorch2.0 SDPA | SDPA + torch.compile | Speed over xformers (%) |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| A100 | 1 | 2.69 | 2.7 | 1.98 | 2.47 | 8.52 |
|
||||
| A100 | 2 | 3.21 | 3.04 | 2.38 | 2.78 | 8.55 |
|
||||
| A100 | 4 | 5.27 | 3.91 | 3.89 | 3.53 | 9.72 |
|
||||
| A100 | 8 | 9.74 | 7.03 | 7.04 | 6.62 | 5.83 |
|
||||
| A100 | 10 | 12.02 | 8.7 | 8.67 | 8.45 | 2.87 |
|
||||
| A100 | 16 | 18.95 | 13.57 | 13.55 | 13.20 | 2.73 |
|
||||
| A100 | 32 (1) | OOM | 26.56 | 26.68 | 25.85 | 2.67 |
|
||||
| A100 | 64 | | 52.51 | 53.03 | 50.93 | 3.01 |
|
||||
| A100 | 10 | 12.02 | 8.7 | 8.79 | 7.89 | 9.31 |
|
||||
| A100 | 16 | 18.95 | 13.57 | 13.67 | 12.25 | 9.73 |
|
||||
| A100 | 32 (1) | OOM | 26.56 | 26.68 | 24.08 | 9.34 |
|
||||
| A100 | 64 | | 52.51 | 53.03 | 47.81 | 8.95 |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| A10 | 4 | 13.94 | 9.81 | 10.01 | 9.35 | 4.69 |
|
||||
| A10 | 8 | 27.09 | 19 | 19.53 | 18.33 | 3.53 |
|
||||
@@ -125,28 +125,25 @@ ___The time reported is in seconds.___
|
||||
| V100 | 10 | OOM | 19.52 | 19.28 | 18.18 | 6.86 |
|
||||
| V100 | 16 | OOM | 30.29 | 29.84 | 28.22 | 6.83 |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| 3090 | 1 | 2.94 | 2.5 | 2.42 | 2.33 | 6.80 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 4 | 10.04 | 7.82 | 7.72 | 7.38 | 5.63 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 8 | 19.27 | 14.97 | 14.88 | 14.15 | 5.48 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 10| 24.08 | 18.7 | 18.62 | 18.12 | 3.10 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 16 | OOM | 29.06 | 28.88 | 28.2 | 2.96 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 32 (1) | | 58.05 | 57.42 | 56.28 | 3.05 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 64 (1) | | 126.54 | 114.27 | 112.21 | 11.32 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 4 | 10.04 | 7.82 | 7.89 | 7.47 | 4.48 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 8 | 19.27 | 14.97 | 15.04 | 14.22 | 5.01 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 10| 24.08 | 18.7 | 18.7 | 17.69 | 5.40 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 16 | OOM | 29.06 | 29.06 | 28.2 | 2.96 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 32 (1) | | 58.05 | 58 | 54.88 | 5.46 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 64 (1) | | 126.54 | 126.03 | 117.33 | 7.28 |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 1 | 2.7 | 2.26 | 2.19 | 2.12 | 6.19 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 4 | 9.07 | 7.14 | 7.00 | 6.71 | 6.02 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 8 | 17.51 | 13.65 | 13.53 | 12.94 | 5.20 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 10 (2) | 21.79 | 16.85 | 16.77 | 16.44 | 2.43 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 16 | OOM | 26.1 | 26.04 | 25.53 | 2.18 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 32 (1) | | 51.78 | 51.71 | 50.91 | 1.68 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 64 (1) | | 112.02 | 102.78 | 100.89 | 9.94 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 4 | 9.07 | 7.14 | 7.15 | 6.81 | 4.62 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 8 | 17.51 | 13.65 | 13.72 | 12.99 | 4.84 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 10 (2) | 21.79 | 16.85 | 16.93 | 16.02 | 4.93 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 16 | OOM | 26.1 | 26.28 | 25.46 | 2.45 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 32 (1) | | 51.78 | 52.04 | 49.15 | 5.08 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 64 (1) | | 112.02 | 112.33 | 103.91 | 7.24 |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| 4090 | 1 | 4.47 | 3.98 | 1.28 | 1.21 | 69.60 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 4 | 10.48 | 8.37 | 3.76 | 3.56 | 57.47 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 8 | 14.33 | 10.22 | 7.43 | 6.99 | 31.60 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 16 | | 17.07 | 14.98 | 14.58 | 14.59 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 32 (1) | | 39.03 | 30.18 | 29.49 | 24.44 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 64 (1) | | 77.29 | 61.34 | 59.96 | 22.42 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 4 | 10.48 | 8.37 | 8.32 | 8.01 | 4.30 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 8 | 14.33 | 10.22 | 10.42 | 9.78 | 4.31 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 16 | | 17.07 | 17.46 | 17.15 | -0.47 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 32 (1) | | 39.03 | 39.86 | 37.97 | 2.72 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 64 (1) | | 77.29 | 79.44 | 77.67 | -0.49 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -158,13 +155,11 @@ Using `torch.compile` in addition to the accelerated transformers implementation
|
||||
|
||||
| GPU | Batch Size | Vanilla Attention | xFormers | PyTorch2.0 SDPA | SDPA + torch.compile | Speed over xformers (%) | Speed over vanilla (%) |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| A100 | 1 | 4.97 | 3.86 | 2.6 | 2.86 | 25.91 | 42.45 |
|
||||
| A100 | 2 | 9.03 | 6.76 | 4.41 | 4.21 | 37.72 | 53.38 |
|
||||
| A100 | 4 | 16.70 | 12.42 | 7.94 | 7.54 | 39.29 | 54.85 |
|
||||
| A100 | 10 | OOM | 29.93 | 18.70 | 18.46 | 38.32 | |
|
||||
| A100 | 16 | | 47.08 | 29.41 | 29.04 | 38.32 | |
|
||||
| A100 | 32 | | 92.89 | 57.55 | 56.67 | 38.99 | |
|
||||
| A100 | 64 | | 185.3 | 114.8 | 112.98 | 39.03 | |
|
||||
| A100 | 4 | 16.56 | 12.42 | 12.2 | 11.84 | 4.67 | 28.50 |
|
||||
| A100 | 10 | OOM | 29.93 | 29.44 | 28.5 | 4.78 | |
|
||||
| A100 | 16 | | 47.08 | 46.27 | 44.8 | 4.84 | |
|
||||
| A100 | 32 | | 92.89 | 91.34 | 88.35 | 4.89 | |
|
||||
| A100 | 64 | | 185.3 | 182.71 | 176.48 | 4.76 | |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| A10 | 1 | 10.59 | 8.81 | 7.51 | 7.35 | 16.57 | 30.59 |
|
||||
| A10 | 4 | 34.77 | 27.63 | 22.77 | 22.07 | 20.12 | 36.53 |
|
||||
@@ -184,27 +179,30 @@ Using `torch.compile` in addition to the accelerated transformers implementation
|
||||
| V100 | 8 | | 43.95 | 43.37 | 42.25 | 3.87 | |
|
||||
| V100 | 16 | | 84.99 | 84.73 | 82.55 | 2.87 | |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| 3090 | 1 | 7.09 | 6.78 | 5.34 | 5.35 | 21.09 | 24.54 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 4 | 22.69 | 21.45 | 18.56 | 18.18 | 15.24 | 19.88 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 8 | | 42.59 | 36.68 | 35.61 | 16.39 | |
|
||||
| 3090 | 16 | | 85.35 | 72.93 | 70.18 | 17.77 | |
|
||||
| 3090 | 32 (1) | | 162.05 | 143.46 | 138.67 | 14.43 | |
|
||||
| 3090 | 1 | 7.09 | 6.78 | 6.11 | 6.03 | 11.06 | 14.95 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 4 | 22.69 | 21.45 | 18.67 | 18.09 | 15.66 | 20.27 |
|
||||
| 3090 | 8 | | 42.59 | 36.75 | 35.59 | 16.44 | |
|
||||
| 3090 | 16 | | 85.35 | 72.37 | 70.25 | 17.69 | |
|
||||
| 3090 | 32 (1) | | 162.05 | 138.99 | 134.53 | 16.98 | |
|
||||
| 3090 | 48 | | 241.91 | 207.75 | | 14.12 | |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 1 | 6.45 | 6.19 | 4.99 | 4.89 | 21.00 | 24.19 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 4 | 20.32 | 19.31 | 17.02 | 16.48 | 14.66 | 18.90 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 8 | | 37.93 | 33.21 | 32.24 | 15.00 | |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 16 | | 75.37 | 66.63 | 64.5 | 14.42 | |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 32 (1) | | 142.55 | 128.89 | 124.92 | 12.37 | |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 1 | 6.45 | 6.19 | 5.64 | 5.49 | 11.31 | 14.88 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 4 | 20.32 | 19.31 | 16.9 | 16.37 | 15.23 | 19.44 |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 8 (2) | | 37.93 | 33.05 | 31.99 | 15.66 | |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 16 | | 75.37 | 65.25 | 64.32 | 14.66 | |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 32 (1) | | 142.55 | 124.44 | 120.74 | 15.30 | |
|
||||
| 3090 Ti | 48 | | 213.19 | 186.55 | | 12.50 | |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| 4090 | 1 | 5.54 | 4.99 | 2.66 | 2.58 | 48.30 | 53.43 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 4 | 13.67 | 11.4 | 8.81 | 8.46 | 25.79 | 38.11 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 8 | | 19.79 | 17.55 | 16.62 | 16.02 | |
|
||||
| 4090 | 16 | | 38.62 | 35.65 | 34.07 | 11.78 | |
|
||||
| 4090 | 32 (1) | | 76.57 | 69.48 | 65.35 | 14.65 | |
|
||||
| 4090 | 48 | | 114.44 | 106.3 | | 7.11 | |
|
||||
| 4090 | 1 | 5.54 | 4.99 | 4.51 | 4.44 | 11.02 | 19.86 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 4 | 13.67 | 11.4 | 10.3 | 9.84 | 13.68 | 28.02 |
|
||||
| 4090 | 8 | | 19.79 | 17.13 | 16.19 | 18.19 | |
|
||||
| 4090 | 16 | | 38.62 | 33.14 | 32.31 | 16.34 | |
|
||||
| 4090 | 32 (1) | | 76.57 | 65.96 | 62.05 | 18.96 | |
|
||||
| 4090 | 48 | | 114.44 | 98.78 | | 13.68 | |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
(1) Batch Size >= 32 requires enable_vae_slicing() because of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/81665.
|
||||
This is required for PyTorch 1.13.1, and also for PyTorch 2.0 and large batch sizes.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about how this benchmark was run, please refer to [this PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/2303) and to [the blog post](https://pytorch.org/blog/accelerated-diffusers-pt-20/).
|
||||
(1) Batch Size >= 32 requires enable_vae_slicing() because of https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/81665
|
||||
This is required for PyTorch 1.13.1, and also for PyTorch 2.0 and batch size of 64
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about how this benchmark was run, please refer to [this PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/2303).
|
||||
@@ -10,25 +10,10 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
# Quicktour
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusion models are trained to denoise random Gaussian noise step-by-step to generate a sample of interest, such as an image or audio. This has sparked a tremendous amount of interest in generative AI, and you have probably seen examples of diffusion generated images on the internet. 🧨 Diffusers is a library aimed at making diffusion models widely accessible to everyone.
|
||||
|
||||
Whether you're a developer or an everyday user, this quicktour will introduce you to 🧨 Diffusers and help you get up and generating quickly! There are three main components of the library to know about:
|
||||
|
||||
* The [`DiffusionPipeline`] is a high-level end-to-end class designed to rapidly generate samples from pretrained diffusion models for inference.
|
||||
* Popular pretrained [model](./api/models) architectures and modules that can be used as building blocks for creating diffusion systems.
|
||||
* Many different [schedulers](./api/schedulers/overview) - algorithms that control how noise is added for training, and how to generate denoised images during inference.
|
||||
|
||||
The quicktour will show you how to use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] for inference, and then walk you through how to combine a model and scheduler to replicate what's happening inside the [`DiffusionPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The quicktour is a simplified version of the introductory 🧨 Diffusers [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/diffusers_intro.ipynb) to help you get started quickly. If you want to learn more about 🧨 Diffusers goal, design philosophy, and additional details about it's core API, check out the notebook!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
Get up and running with 🧨 Diffusers quickly!
|
||||
Whether you're a developer or an everyday user, this quick tour will help you get started and show you how to use [`DiffusionPipeline`] for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, make sure you have all the necessary libraries installed:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,32 +21,32 @@ Before you begin, make sure you have all the necessary libraries installed:
|
||||
pip install --upgrade diffusers accelerate transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- [🤗 Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index) speeds up model loading for inference and training.
|
||||
- [🤗 Transformers](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index) is required to run the most popular diffusion models, such as [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview).
|
||||
- [`accelerate`](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index) speeds up model loading for inference and training
|
||||
- [`transformers`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index) is required to run the most popular diffusion models, such as [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview)
|
||||
|
||||
## DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] is the easiest way to use a pretrained diffusion system for inference. It is an end-to-end system containing the model and the scheduler. You can use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] out-of-the-box for many tasks. Take a look at the table below for some supported tasks, and for a complete list of supported tasks, check out the [🧨 Diffusers Summary](./api/pipelines/overview#diffusers-summary) table.
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] is the easiest way to use a pre-trained diffusion system for inference. You can use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] out-of-the-box for many tasks across different modalities. Take a look at the table below for some supported tasks:
|
||||
|
||||
| **Task** | **Description** | **Pipeline**
|
||||
|------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------|
|
||||
| Unconditional Image Generation | generate an image from Gaussian noise | [unconditional_image_generation](./using-diffusers/unconditional_image_generation) |
|
||||
| Unconditional Image Generation | generate an image from gaussian noise | [unconditional_image_generation](./using-diffusers/unconditional_image_generation) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Image Generation | generate an image given a text prompt | [conditional_image_generation](./using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Image-to-Image Translation | adapt an image guided by a text prompt | [img2img](./using-diffusers/img2img) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Image-Inpainting | fill the masked part of an image given the image, the mask and a text prompt | [inpaint](./using-diffusers/inpaint) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Depth-to-Image Translation | adapt parts of an image guided by a text prompt while preserving structure via depth estimation | [depth2img](./using-diffusers/depth2img) |
|
||||
|
||||
Start by creating an instance of a [`DiffusionPipeline`] and specify which pipeline checkpoint you would like to download.
|
||||
You can use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] for any [checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads) stored on the Hugging Face Hub.
|
||||
In this quicktour, you'll load the [`stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) checkpoint for text-to-image generation.
|
||||
For more in-detail information on how diffusion pipelines function for the different tasks, please have a look at the [**Using Diffusers**](./using-diffusers/overview) section.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
As an example, start by creating an instance of [`DiffusionPipeline`] and specify which pipeline checkpoint you would like to download.
|
||||
You can use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] for any [Diffusers' checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads).
|
||||
In this guide though, you'll use [`DiffusionPipeline`] for text-to-image generation with [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
For [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion) models, please carefully read the [license](https://huggingface.co/spaces/CompVis/stable-diffusion-license) first before running the model. 🧨 Diffusers implements a [`safety_checker`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py) to prevent offensive or harmful content, but the model's improved image generation capabilities can still produce potentially harmful content.
|
||||
For [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion), please carefully read its [license](https://huggingface.co/spaces/CompVis/stable-diffusion-license) before running the model.
|
||||
This is due to the improved image generation capabilities of the model and the potentially harmful content that could be produced with it.
|
||||
Please, head over to your stable diffusion model of choice, *e.g.* [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), and read the license.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Load the model with the [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method:
|
||||
You can load the model as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -69,245 +54,77 @@ Load the model with the [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method:
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] downloads and caches all modeling, tokenization, and scheduling components. You'll see that the Stable Diffusion pipeline is composed of the [`UNet2DConditionModel`] and [`PNDMScheduler`] among other things:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pipeline
|
||||
StableDiffusionPipeline {
|
||||
"_class_name": "StableDiffusionPipeline",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.13.1",
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"scheduler": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"PNDMScheduler"
|
||||
],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"unet": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"UNet2DConditionModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"vae": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"AutoencoderKL"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We strongly recommend running the pipeline on a GPU because the model consists of roughly 1.4 billion parameters.
|
||||
You can move the generator object to a GPU, just like you would in PyTorch:
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] downloads and caches all modeling, tokenization, and scheduling components.
|
||||
Because the model consists of roughly 1.4 billion parameters, we strongly recommend running it on GPU.
|
||||
You can move the generator object to GPU, just like you would in PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can pass a text prompt to the `pipeline` to generate an image, and then access the denoised image. By default, the image output is wrapped in a [`PIL.Image`](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/Image.html?highlight=image#the-image-class) object.
|
||||
Now you can use the `pipeline` on your text prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> image = pipeline("An image of a squirrel in Picasso style").images[0]
|
||||
>>> image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/image_of_squirrel_painting.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
The output is by default wrapped into a [PIL Image object](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/Image.html?highlight=image#the-image-class).
|
||||
|
||||
Save the image by calling `save`:
|
||||
You can save the image by simply calling:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> image.save("image_of_squirrel_painting.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Local pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the pipeline locally. The only difference is you need to download the weights first:
|
||||
**Note**: You can also use the pipeline locally by downloading the weights via:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git lfs install
|
||||
git clone https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then load the saved weights into the pipeline:
|
||||
and then loading the saved weights into the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can run the pipeline as you would in the section above.
|
||||
Running the pipeline is then identical to the code above as it's the same model architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
### Swapping schedulers
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> generator.to("cuda")
|
||||
>>> image = generator("An image of a squirrel in Picasso style").images[0]
|
||||
>>> image.save("image_of_squirrel_painting.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Different schedulers come with different denoising speeds and quality trade-offs. The best way to find out which one works best for you is to try them out! One of the main features of 🧨 Diffusers is to allow you to easily switch between schedulers. For example, to replace the default [`PNDMScheduler`] with the [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`], load it with the [`~diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config`] method:
|
||||
Diffusion systems can be used with multiple different [schedulers](./api/schedulers/overview) each with their
|
||||
pros and cons. By default, Stable Diffusion runs with [`PNDMScheduler`], but it's very simple to
|
||||
use a different scheduler. *E.g.* if you would instead like to use the [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`] scheduler,
|
||||
you could use it as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import EulerDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
>>> pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # change scheduler to Euler
|
||||
>>> pipeline.scheduler = EulerDiscreteScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Try generating an image with the new scheduler and see if you notice a difference!
|
||||
For more in-detail information on how to change between schedulers, please refer to the [Using Schedulers](./using-diffusers/schedulers) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
In the next section, you'll take a closer look at the components - the model and scheduler - that make up the [`DiffusionPipeline`] and learn how to use these components to generate an image of a cat.
|
||||
[Stability AI's](https://stability.ai/) Stable Diffusion model is an impressive image generation model
|
||||
and can do much more than just generating images from text. We have dedicated a whole documentation page,
|
||||
just for Stable Diffusion [here](./conceptual/stable_diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
## Models
|
||||
If you want to know how to optimize Stable Diffusion to run on less memory, higher inference speeds, on specific hardware, such as Mac, or with [ONNX Runtime](https://onnxruntime.ai/), please have a look at our
|
||||
optimization pages:
|
||||
|
||||
Most models take a noisy sample, and at each timestep it predicts the *noise residual* (other models learn to predict the previous sample directly or the velocity or [`v-prediction`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/5e5ce13e2f89ac45a0066cb3f369462a3cf1d9ef/src/diffusers/schedulers/scheduling_ddim.py#L110)), the difference between a less noisy image and the input image. You can mix and match models to create other diffusion systems.
|
||||
- [Optimized PyTorch on GPU](./optimization/fp16)
|
||||
- [Mac OS with PyTorch](./optimization/mps)
|
||||
- [ONNX](./optimization/onnx)
|
||||
- [OpenVINO](./optimization/open_vino)
|
||||
|
||||
Models are initiated with the [`~ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] method which also locally caches the model weights so it is faster the next time you load the model. For the quicktour, you'll load the [`UNet2DModel`], a basic unconditional image generation model with a checkpoint trained on cat images:
|
||||
If you want to fine-tune or train your diffusion model, please have a look at the [**training section**](./training/overview)
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import UNet2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> repo_id = "google/ddpm-cat-256"
|
||||
>>> model = UNet2DModel.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To access the model parameters, call `model.config`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model.config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The model configuration is a 🧊 frozen 🧊 dictionary, which means those parameters can't be changed after the model is created. This is intentional and ensures that the parameters used to define the model architecture at the start remain the same, while other parameters can still be adjusted during inference.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the most important parameters are:
|
||||
|
||||
* `sample_size`: the height and width dimension of the input sample.
|
||||
* `in_channels`: the number of input channels of the input sample.
|
||||
* `down_block_types` and `up_block_types`: the type of down- and upsampling blocks used to create the UNet architecture.
|
||||
* `block_out_channels`: the number of output channels of the downsampling blocks; also used in reverse order for the number of input channels of the upsampling blocks.
|
||||
* `layers_per_block`: the number of ResNet blocks present in each UNet block.
|
||||
|
||||
To use the model for inference, create the image shape with random Gaussian noise. It should have a `batch` axis because the model can receive multiple random noises, a `channel` axis corresponding to the number of input channels, and a `sample_size` axis for the height and width of the image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> noisy_sample = torch.randn(1, model.config.in_channels, model.config.sample_size, model.config.sample_size)
|
||||
>>> noisy_sample.shape
|
||||
torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For inference, pass the noisy image to the model and a `timestep`. The `timestep` indicates how noisy the input image is, with more noise at the beginning and less at the end. This helps the model determine its position in the diffusion process, whether it is closer to the start or the end. Use the `sample` method to get the model output:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... noisy_residual = model(sample=noisy_sample, timestep=2).sample
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To generate actual examples though, you'll need a scheduler to guide the denoising process. In the next section, you'll learn how to couple a model with a scheduler.
|
||||
|
||||
## Schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
Schedulers manage going from a noisy sample to a less noisy sample given the model output - in this case, it is the `noisy_residual`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers is a toolbox for building diffusion systems. While the [`DiffusionPipeline`] is a convenient way to get started with a pre-built diffusion system, you can also choose your own model and scheduler components separately to build a custom diffusion system.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For the quicktour, you'll instantiate the [`DDPMScheduler`] with it's [`~diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config`] method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DDPMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_config(repo_id)
|
||||
>>> scheduler
|
||||
DDPMScheduler {
|
||||
"_class_name": "DDPMScheduler",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.13.1",
|
||||
"beta_end": 0.02,
|
||||
"beta_schedule": "linear",
|
||||
"beta_start": 0.0001,
|
||||
"clip_sample": true,
|
||||
"clip_sample_range": 1.0,
|
||||
"num_train_timesteps": 1000,
|
||||
"prediction_type": "epsilon",
|
||||
"trained_betas": null,
|
||||
"variance_type": "fixed_small"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Notice how the scheduler is instantiated from a configuration. Unlike a model, a scheduler does not have trainable weights and is parameter-free!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the most important parameters are:
|
||||
|
||||
* `num_train_timesteps`: the length of the denoising process or in other words, the number of timesteps required to process random Gaussian noise into a data sample.
|
||||
* `beta_schedule`: the type of noise schedule to use for inference and training.
|
||||
* `beta_start` and `beta_end`: the start and end noise values for the noise schedule.
|
||||
|
||||
To predict a slightly less noisy image, pass the following to the scheduler's [`~diffusers.DDPMScheduler.step`] method: model output, `timestep`, and current `sample`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> less_noisy_sample = scheduler.step(model_output=noisy_residual, timestep=2, sample=noisy_sample).prev_sample
|
||||
>>> less_noisy_sample.shape
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `less_noisy_sample` can be passed to the next `timestep` where it'll get even less noisier! Let's bring it all together now and visualize the entire denoising process.
|
||||
|
||||
First, create a function that postprocesses and displays the denoised image as a `PIL.Image`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import PIL.Image
|
||||
>>> import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def display_sample(sample, i):
|
||||
... image_processed = sample.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
|
||||
... image_processed = (image_processed + 1.0) * 127.5
|
||||
... image_processed = image_processed.numpy().astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
... image_pil = PIL.Image.fromarray(image_processed[0])
|
||||
... display(f"Image at step {i}")
|
||||
... display(image_pil)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To speed up the denoising process, move the input and model to a GPU:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model.to("cuda")
|
||||
>>> noisy_sample = noisy_sample.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now create a denoising loop that predicts the residual of the less noisy sample, and computes the less noisy sample with the scheduler:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
>>> sample = noisy_sample
|
||||
|
||||
>>> for i, t in enumerate(tqdm.tqdm(scheduler.timesteps)):
|
||||
... # 1. predict noise residual
|
||||
... with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... residual = model(sample, t).sample
|
||||
|
||||
... # 2. compute less noisy image and set x_t -> x_t-1
|
||||
... sample = scheduler.step(residual, t, sample).prev_sample
|
||||
|
||||
... # 3. optionally look at image
|
||||
... if (i + 1) % 50 == 0:
|
||||
... display_sample(sample, i + 1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sit back and watch as a cat is generated from nothing but noise! 😻
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/diffusion-quicktour.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
Hopefully you generated some cool images with 🧨 Diffusers in this quicktour! For your next steps, you can:
|
||||
|
||||
* Train or finetune a model to generate your own images in the [training](./tutorials/basic_training) tutorial.
|
||||
* See example official and community [training or finetuning scripts](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples#-diffusers-examples) for a variety of use cases.
|
||||
* Learn more about loading, accessing, changing and comparing schedulers in the [Using different Schedulers](./using-diffusers/schedulers) guide.
|
||||
* Explore prompt engineering, speed and memory optimizations, and tips and tricks for generating higher quality images with the [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion) guide.
|
||||
* Dive deeper into speeding up 🧨 Diffusers with guides on [optimized PyTorch on a GPU](./optimization/fp16), and inference guides for running [Stable Diffusion on Apple Silicon (M1/M2)](./optimization/mps) and [ONNX Runtime](./optimization/onnx).
|
||||
Finally, please be considerate when distributing generated images publicly 🤗.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,271 +1,333 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# The Stable Diffusion Guide 🎨
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/sd_101_guide.ipynb">
|
||||
<img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Intro
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion is a [Latent Diffusion model](https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion) developed by researchers from the Machine Vision and Learning group at LMU Munich, *a.k.a* CompVis.
|
||||
Model checkpoints were publicly released at the end of August 2022 by a collaboration of Stability AI, CompVis, and Runway with support from EleutherAI and LAION. For more information, you can check out [the official blog post](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release).
|
||||
|
||||
Since its public release the community has done an incredible job at working together to make the stable diffusion checkpoints **faster**, **more memory efficient**, and **more performant**.
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers offers a simple API to run stable diffusion with all memory, computing, and quality improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
This notebook walks you through the improvements one-by-one so you can best leverage [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] for **inference**.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prompt Engineering 🎨
|
||||
|
||||
When running *Stable Diffusion* in inference, we usually want to generate a certain type, or style of image and then improve upon it. Improving upon a previously generated image means running inference over and over again with a different prompt and potentially a different seed until we are happy with our generation.
|
||||
|
||||
So to begin with, it is most important to speed up stable diffusion as much as possible to generate as many pictures as possible in a given amount of time.
|
||||
|
||||
This can be done by both improving the **computational efficiency** (speed) and the **memory efficiency** (GPU RAM).
|
||||
|
||||
Let's start by looking into computational efficiency first.
|
||||
|
||||
Throughout the notebook, we will focus on [runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5):
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's load the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
## Speed Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We aim at generating a beautiful photograph of an *old warrior chief* and will later try to find the best prompt to generate such a photograph. For now, let's keep the prompt simple:
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
prompt = "portrait photo of a old warrior chief"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To begin with, we should make sure we run inference on GPU, so let's move the pipeline to GPU, just like you would with any PyTorch module.
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To generate an image, you should use the [~`StableDiffusionPipeline.__call__`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
To make sure we can reproduce more or less the same image in every call, let's make use of the generator. See the documentation on reproducibility [here](./conceptual/reproducibility) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's take a spin on it.
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cool, this now took roughly 30 seconds on a T4 GPU (you might see faster inference if your allocated GPU is better than a T4).
|
||||
|
||||
The default run we did above used full float32 precision and ran the default number of inference steps (50). The easiest speed-ups come from switching to float16 (or half) precision and simply running fewer inference steps. Let's load the model now in float16 instead.
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And we can again call the pipeline to generate an image.
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cool, this is almost three times as fast for arguably the same image quality.
|
||||
|
||||
We strongly suggest always running your pipelines in float16 as so far we have very rarely seen degradations in quality because of it.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let's see if we need to use 50 inference steps or whether we could use significantly fewer. The number of inference steps is associated with the denoising scheduler we use. Choosing a more efficient scheduler could help us decrease the number of steps.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's have a look at all the schedulers the stable diffusion pipeline is compatible with.
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
pipe.scheduler.compatibles
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_singlestep.DPMSolverSinglestepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_lms_discrete.LMSDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_heun_discrete.HeunDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_pndm.PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_discrete.EulerDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_ancestral_discrete.EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_multistep.DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddpm.DDPMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddim.DDIMScheduler]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Cool, that's a lot of schedulers.
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers is constantly adding a bunch of novel schedulers/samplers that can be used with Stable Diffusion. For more information, we recommend taking a look at the official documentation [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/schedulers/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
Alright, right now Stable Diffusion is using the `PNDMScheduler` which usually requires around 50 inference steps. However, other schedulers such as `DPMSolverMultistepScheduler` or `DPMSolverSinglestepScheduler` seem to get away with just 20 to 25 inference steps. Let's try them out.
|
||||
|
||||
You can set a new scheduler by making use of the [from_config](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/configuration#diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config) function.
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's try to reduce the number of inference steps to just 20.
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, generator=generator, num_inference_steps=20).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The image now does look a little different, but it's arguably still of equally high quality. We now cut inference time to just 4 seconds though 😍.
|
||||
|
||||
## Memory Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
Less memory used in generation indirectly implies more speed, since we're often trying to maximize how many images we can generate per second. Usually, the more images per inference run, the more images per second too.
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
The easiest way to see how many images we can generate at once is to simply try it out, and see when we get a *"Out-of-memory (OOM)"* error.
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Effective and efficient diffusion
|
||||
We can run batched inference by simply passing a list of prompts and generators. Let's define a quick function that generates a batch for us.
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
def get_inputs(batch_size=1):
|
||||
generator = [torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(i) for i in range(batch_size)]
|
||||
prompts = batch_size * [prompt]
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 20
|
||||
|
||||
Getting the [`DiffusionPipeline`] to generate images in a certain style or include what you want can be tricky. Often times, you have to run the [`DiffusionPipeline`] several times before you end up with an image you're happy with. But generating something out of nothing is a computationally intensive process, especially if you're running inference over and over again.
|
||||
return {"prompt": prompts, "generator": generator, "num_inference_steps": num_inference_steps}
|
||||
```
|
||||
This function returns a list of prompts and a list of generators, so we can reuse the generator that produced a result we like.
|
||||
|
||||
This is why it's important to get the most *computational* (speed) and *memory* (GPU RAM) efficiency from the pipeline to reduce the time between inference cycles so you can iterate faster.
|
||||
We also need a method that allows us to easily display a batch of images.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial walks you through how to generate faster and better with the [`DiffusionPipeline`].
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
Begin by loading the [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) model:
|
||||
def image_grid(imgs, rows=2, cols=2):
|
||||
w, h = imgs[0].size
|
||||
grid = Image.new('RGB', size=(cols*w, rows*h))
|
||||
|
||||
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
|
||||
grid.paste(img, box=(i%cols*w, i//cols*h))
|
||||
return grid
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
Cool, let's see how much memory we can use starting with `batch_size=4`.
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
images = pipe(**get_inputs(batch_size=4)).images
|
||||
image_grid(images)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The example prompt you'll use is a portrait of an old warrior chief, but feel free to use your own prompt:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "portrait photo of a old warrior chief"
|
||||
```
|
||||
Going over a batch_size of 4 will error out in this notebook (assuming we are running it on a T4 GPU). Also, we can see we only generate slightly more images per second (3.75s/image) compared to 4s/image previously.
|
||||
|
||||
## Speed
|
||||
However, the community has found some nice tricks to improve the memory constraints further. After stable diffusion was released, the community found improvements within days and shared them freely over GitHub - open-source at its finest! I believe the original idea came from [this](https://github.com/basujindal/stable-diffusion/pull/117) GitHub thread.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
By far most of the memory is taken up by the cross-attention layers. Instead of running this operation in batch, one can run it sequentially to save a significant amount of memory.
|
||||
|
||||
💡 If you don't have access to a GPU, you can use one for free from a GPU provider like [Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/)!
|
||||
It can easily be enabled by calling `enable_attention_slicing` as is documented [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img#diffusers.StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_attention_slicing).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
pipe.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
One of the simplest ways to speed up inference is to place the pipeline on a GPU the same way you would with any PyTorch module:
|
||||
Great, now that attention slicing is enabled, let's try to double the batch size again, going for `batch_size=8`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
images = pipe(**get_inputs(batch_size=8)).images
|
||||
image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To make sure you can use the same image and improve on it, use a [`Generator`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html) and set a seed for [reproducibility](./using-diffusers/reproducibility):
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Nice, it works. However, the speed gain is again not very big (it might however be much more significant on other GPUs).
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can generate an image:
|
||||
We're at roughly 3.5 seconds per image 🔥 which is probably the fastest we can be with a simple T4 without sacrificing quality.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
Next, let's look into how to improve the quality!
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_1.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
## Quality Improvements
|
||||
|
||||
This process took ~30 seconds on a T4 GPU (it might be faster if your allocated GPU is better than a T4). By default, the [`DiffusionPipeline`] runs inference with full `float32` precision for 50 inference steps. You can speed this up by switching to a lower precision like `float16` or running fewer inference steps.
|
||||
Now that our image generation pipeline is blazing fast, let's try to get maximum image quality.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's start by loading the model in `float16` and generate an image:
|
||||
First of all, image quality is extremely subjective, so it's difficult to make general claims here.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
The most obvious step to take to improve quality is to use *better checkpoints*. Since the release of Stable Diffusion, many improved versions have been released, which are summarized here:
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
- *Official Release - 22 Aug 2022*: [Stable-Diffusion 1.4](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4)
|
||||
- *20 October 2022*: [Stable-Diffusion 1.5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)
|
||||
- *24 Nov 2022*: [Stable-Diffusion 2.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-0)
|
||||
- *7 Dec 2022*: [Stable-Diffusion 2.1](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1)
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_2.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
Newer versions don't necessarily mean better image quality with the same parameters. People mentioned that *2.0* is slightly worse than *1.5* for certain prompts, but given the right prompt engineering *2.0* and *2.1* seem to be better.
|
||||
|
||||
This time, it only took ~11 seconds to generate the image, which is almost 3x faster than before!
|
||||
Overall, we strongly recommend just trying the models out and reading up on advice online (e.g. it has been shown that using negative prompts is very important for 2.0 and 2.1 to get the highest possible quality. See for example [this nice blog post](https://minimaxir.com/2022/11/stable-diffusion-negative-prompt/).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
Additionally, the community has started fine-tuning many of the above versions on certain styles with some of them having an extremely high quality and gaining a lot of traction.
|
||||
|
||||
💡 We strongly suggest always running your pipelines in `float16`, and so far, we've rarely seen any degradation in output quality.
|
||||
We recommend having a look at all [diffusers checkpoints sorted by downloads and trying out the different checkpoints](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
For the following, we will stick to v1.5 for simplicity.
|
||||
|
||||
Another option is to reduce the number of inference steps. Choosing a more efficient scheduler could help decrease the number of steps without sacrificing output quality. You can find which schedulers are compatible with the current model in the [`DiffusionPipeline`] by calling the `compatibles` method:
|
||||
Next, we can also try to optimize single components of the pipeline, e.g. switching out the latent decoder. For more details on how the whole Stable Diffusion pipeline works, please have a look at [this blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/stable_diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler.compatibles
|
||||
[
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_lms_discrete.LMSDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_unipc_multistep.UniPCMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_k_dpm_2_discrete.KDPM2DiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_deis_multistep.DEISMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_discrete.EulerDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_multistep.DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddpm.DDPMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_singlestep.DPMSolverSinglestepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_k_dpm_2_ancestral_discrete.KDPM2AncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_heun_discrete.HeunDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_pndm.PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_ancestral_discrete.EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddim.DDIMScheduler,
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
Let's load [stabilityai's newest auto-decoder](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1).
|
||||
|
||||
The Stable Diffusion model uses the [`PNDMScheduler`] by default which usually requires ~50 inference steps, but more performant schedulers like [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`], require only ~20 or 25 inference steps. Use the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`] method to load a new scheduler:
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoencoderKL
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained("stabilityai/sd-vae-ft-mse", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Now we can set it to the vae of the pipeline to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
Now set the `num_inference_steps` to 20:
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
pipe.vae = vae
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=generator, num_inference_steps=20).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
Let's run the same prompt as before to compare quality.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_3.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
images = pipe(**get_inputs(batch_size=8)).images
|
||||
image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Great, you've managed to cut the inference time to just 4 seconds! ⚡️
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Memory
|
||||
Seems like the difference is only very minor, but the new generations are arguably a bit *sharper*.
|
||||
|
||||
The other key to improving pipeline performance is consuming less memory, which indirectly implies more speed, since you're often trying to maximize the number of images generated per second. The easiest way to see how many images you can generate at once is to try out different batch sizes until you get an `OutOfMemoryError` (OOM).
|
||||
Cool, finally, let's look a bit into prompt engineering.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a function that'll generate a batch of images from a list of prompts and `Generators`. Make sure to assign each `Generator` a seed so you can reuse it if it produces a good result.
|
||||
Our goal was to generate a photo of an old warrior chief. Let's now try to bring a bit more color into the photos and make the look more impressive.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def get_inputs(batch_size=1):
|
||||
generator = [torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(i) for i in range(batch_size)]
|
||||
prompts = batch_size * [prompt]
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 20
|
||||
Originally our prompt was "*portrait photo of an old warrior chief*".
|
||||
|
||||
return {"prompt": prompts, "generator": generator, "num_inference_steps": num_inference_steps}
|
||||
```
|
||||
To improve the prompt, it often helps to add cues that could have been used online to save high-quality photos, as well as add more details.
|
||||
Essentially, when doing prompt engineering, one has to think:
|
||||
|
||||
You'll also need a function that'll display each batch of images:
|
||||
- How was the photo or similar photos of the one I want probably stored on the internet?
|
||||
- What additional detail can I give that steers the models into the style that I want?
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from PIL import image
|
||||
Cool, let's add more details.
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
prompt += ", tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
def image_grid(imgs, rows=2, cols=2):
|
||||
w, h = imgs[0].size
|
||||
grid = Image.new("RGB", size=(cols * w, rows * h))
|
||||
and let's also add some cues that usually help to generate higher quality images.
|
||||
|
||||
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
|
||||
grid.paste(img, box=(i % cols * w, i // cols * h))
|
||||
return grid
|
||||
```
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
prompt += " 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta"
|
||||
prompt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Start with `batch_size=4` and see how much memory you've consumed:
|
||||
Cool, let's now try this prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
images = pipeline(**get_inputs(batch_size=4)).images
|
||||
image_grid(images)
|
||||
```
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
images = pipe(**get_inputs(batch_size=8)).images
|
||||
image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Unless you have a GPU with more RAM, the code above probably returned an `OOM` error! Most of the memory is taken up by the cross-attention layers. Instead of running this operation in a batch, you can run it sequentially to save a significant amount of memory. All you have to do is configure the pipeline to use the [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_attention_slicing`] function:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
```
|
||||
Pretty impressive! We got some very high-quality image generations there. The 2nd image is my personal favorite, so I'll re-use this seed and see whether I can tweak the prompts slightly by using "oldest warrior", "old", "", and "young" instead of "old".
|
||||
|
||||
Now try increasing the `batch_size` to 8!
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
prompts = [
|
||||
"portrait photo of the oldest warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
"portrait photo of a old warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
"portrait photo of a warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
"portrait photo of a young warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
images = pipeline(**get_inputs(batch_size=8)).images
|
||||
image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
generator = [torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(1) for _ in range(len(prompts))] # 1 because we want the 2nd image
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_5.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt=prompts, generator=generator, num_inference_steps=25).images
|
||||
image_grid(images)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Whereas before you couldn't even generate a batch of 4 images, now you can generate a batch of 8 images at ~3.5 seconds per image! This is probably the fastest you can go on a T4 GPU without sacrificing quality.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Quality
|
||||
The first picture looks nice! The eye movement slightly changed and looks nice. This finished up our 101-guide on how to use Stable Diffusion 🤗.
|
||||
|
||||
In the last two sections, you learned how to optimize the speed of your pipeline by using `fp16`, reducing the number of inference steps by using a more performant scheduler, and enabling attention slicing to reduce memory consumption. Now you're going to focus on how to improve the quality of generated images.
|
||||
For more information on optimization or other guides, I recommend taking a look at the following:
|
||||
|
||||
### Better checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
The most obvious step is to use better checkpoints. The Stable Diffusion model is a good starting point, and since its official launch, several improved versions have also been released. However, using a newer version doesn't automatically mean you'll get better results. You'll still have to experiment with different checkpoints yourself, and do a little research (such as using [negative prompts](https://minimaxir.com/2022/11/stable-diffusion-negative-prompt/)) to get the best results.
|
||||
|
||||
As the field grows, there are more and more high-quality checkpoints finetuned to produce certain styles. Try exploring the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads) and [Diffusers Gallery](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-projects/diffusers-gallery) to find one you're interested in!
|
||||
|
||||
### Better pipeline components
|
||||
|
||||
You can also try replacing the current pipeline components with a newer version. Let's try loading the latest [autodecoder](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1/tree/main/vae) from Stability AI into the pipeline, and generate some images:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoencoderKL
|
||||
|
||||
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained("stabilityai/sd-vae-ft-mse", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.vae = vae
|
||||
images = pipeline(**get_inputs(batch_size=8)).images
|
||||
image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_6.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### Better prompt engineering
|
||||
|
||||
The text prompt you use to generate an image is super important, so much so that it is called *prompt engineering*. Some considerations to keep during prompt engineering are:
|
||||
|
||||
- How is the image or similar images of the one I want to generate stored on the internet?
|
||||
- What additional detail can I give that steers the model towards the style I want?
|
||||
|
||||
With this in mind, let's improve the prompt to include color and higher quality details:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt += ", tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes"
|
||||
prompt += " 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generate a batch of images with the new prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
images = pipeline(**get_inputs(batch_size=8)).images
|
||||
image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_7.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Pretty impressive! Let's tweak the second image - corresponding to the `Generator` with a seed of `1` - a bit more by adding some text about the age of the subject:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prommpts = [
|
||||
"portrait photo of the oldest warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
"portrait photo of a old warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
"portrait photo of a warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
"portrait photo of a young warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
generator = [torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(1) for _ in range(len(prompts))]
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt=prompts, generator=generator, num_inference_steps=25).images
|
||||
image_grid(images)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_8.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, you learned how to optimize a [`DiffusionPipeline`] for computational and memory efficiency as well as improving the quality of generated outputs. If you're interested in making your pipeline even faster, take a look at the following resources:
|
||||
|
||||
- Enable [xFormers](./optimization/xformers) memory efficient attention mechanism for faster speed and reduced memory consumption.
|
||||
- Learn how in [PyTorch 2.0](./optimization/torch2.0), [`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.compile.html) can yield 2-9% faster inference speed.
|
||||
- Many optimization techniques for inference are also included in this memory and speed [guide](./optimization/fp16), such as memory offloading.
|
||||
- [Blog post about Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/blog/stable_diffusion): In-detail blog post explaining Stable Diffusion.
|
||||
- [FlashAttention](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/optimization/xformers): XFormers flash attention can optimize your model even further with more speed and memory improvements.
|
||||
- [Dreambooth](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/training/dreambooth) - Quickly customize the model by fine-tuning it.
|
||||
- [General info on Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview) - Info on other tasks that are powered by Stable Diffusion.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,290 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# ControlNet
|
||||
|
||||
[Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) (ControlNet) by Lvmin Zhang and Maneesh Agrawala.
|
||||
|
||||
This example is based on the [training example in the original ControlNet repository](https://github.com/lllyasviel/ControlNet/blob/main/docs/train.md). It trains a ControlNet to fill circles using a [small synthetic dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/fusing/fill50k).
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing the dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the scripts, make sure to install the library's training dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
To successfully run the latest versions of the example scripts, we highly recommend **installing from source** and keeping the installation up to date. We update the example scripts frequently and install example-specific requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To do this, execute the following steps in a new virtual environment:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
cd diffusers
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then navigate into the example folder and run:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And initialize an [🤗Accelerate](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/) environment with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or for a default 🤗Accelerate configuration without answering questions about your environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config default
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell like a notebook:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Circle filling dataset
|
||||
|
||||
The original dataset is hosted in the ControlNet [repo](https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/ControlNet/blob/main/training/fill50k.zip), but we re-uploaded it [here](https://huggingface.co/datasets/fusing/fill50k) to be compatible with 🤗 Datasets so that it can handle the data loading within the training script.
|
||||
|
||||
Our training examples use [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) because that is what the original set of ControlNet models was trained on. However, ControlNet can be trained to augment any compatible Stable Diffusion model (such as [`CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4`](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4)) or [`stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1`](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1).
|
||||
|
||||
## Training
|
||||
|
||||
Download the following images to condition our training with:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
wget https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/controlnet_training/conditioning_image_1.png
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/controlnet_training/conditioning_image_2.png
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_DIR="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path to save model"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_controlnet.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--dataset_name=fusing/fill50k \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-5 \
|
||||
--validation_image "./conditioning_image_1.png" "./conditioning_image_2.png" \
|
||||
--validation_prompt "red circle with blue background" "cyan circle with brown floral background" \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This default configuration requires ~38GB VRAM.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the training script logs outputs to tensorboard. Pass `--report_to wandb` to use Weights &
|
||||
Biases.
|
||||
|
||||
Gradient accumulation with a smaller batch size can be used to reduce training requirements to ~20 GB VRAM.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_DIR="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path to save model"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_controlnet.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--dataset_name=fusing/fill50k \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-5 \
|
||||
--validation_image "./conditioning_image_1.png" "./conditioning_image_2.png" \
|
||||
--validation_prompt "red circle with blue background" "cyan circle with brown floral background" \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Example results
|
||||
|
||||
#### After 300 steps with batch size 8
|
||||
|
||||
| | |
|
||||
|-------------------|:-------------------------:|
|
||||
| | red circle with blue background |
|
||||
 |  |
|
||||
| | cyan circle with brown floral background |
|
||||
 |  |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### After 6000 steps with batch size 8:
|
||||
|
||||
| | |
|
||||
|-------------------|:-------------------------:|
|
||||
| | red circle with blue background |
|
||||
 |  |
|
||||
| | cyan circle with brown floral background |
|
||||
 |  |
|
||||
|
||||
## Training on a 16 GB GPU
|
||||
|
||||
Enable the following optimizations to train on a 16GB GPU:
|
||||
|
||||
- Gradient checkpointing
|
||||
- bitsandbyte's 8-bit optimizer (take a look at the [installation]((https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes#requirements--installation) instructions if you don't already have it installed)
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can launch the training script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_DIR="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path to save model"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_controlnet.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--dataset_name=fusing/fill50k \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-5 \
|
||||
--validation_image "./conditioning_image_1.png" "./conditioning_image_2.png" \
|
||||
--validation_prompt "red circle with blue background" "cyan circle with brown floral background" \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=4 \
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing \
|
||||
--use_8bit_adam
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Training on a 12 GB GPU
|
||||
|
||||
Enable the following optimizations to train on a 12GB GPU:
|
||||
- Gradient checkpointing
|
||||
- bitsandbyte's 8-bit optimizer (take a look at the [installation]((https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes#requirements--installation) instructions if you don't already have it installed)
|
||||
- xFormers (take a look at the [installation](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/training/optimization/xformers) instructions if you don't already have it installed)
|
||||
- set gradients to `None`
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_DIR="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path to save model"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_controlnet.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--dataset_name=fusing/fill50k \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-5 \
|
||||
--validation_image "./conditioning_image_1.png" "./conditioning_image_2.png" \
|
||||
--validation_prompt "red circle with blue background" "cyan circle with brown floral background" \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=4 \
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing \
|
||||
--use_8bit_adam \
|
||||
--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention \
|
||||
--set_grads_to_none
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When using `enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention`, please make sure to install `xformers` by `pip install xformers`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Training on an 8 GB GPU
|
||||
|
||||
We have not exhaustively tested DeepSpeed support for ControlNet. While the configuration does
|
||||
save memory, we have not confirmed whether the configuration trains successfully. You will very likely
|
||||
have to make changes to the config to have a successful training run.
|
||||
|
||||
Enable the following optimizations to train on a 8GB GPU:
|
||||
- Gradient checkpointing
|
||||
- bitsandbyte's 8-bit optimizer (take a look at the [installation]((https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes#requirements--installation) instructions if you don't already have it installed)
|
||||
- xFormers (take a look at the [installation](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/training/optimization/xformers) instructions if you don't already have it installed)
|
||||
- set gradients to `None`
|
||||
- DeepSpeed stage 2 with parameter and optimizer offloading
|
||||
- fp16 mixed precision
|
||||
|
||||
[DeepSpeed](https://www.deepspeed.ai/) can offload tensors from VRAM to either
|
||||
CPU or NVME. This requires significantly more RAM (about 25 GB).
|
||||
|
||||
You'll have to configure your environment with `accelerate config` to enable DeepSpeed stage 2.
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration file should look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
deepspeed_config:
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps: 4
|
||||
offload_optimizer_device: cpu
|
||||
offload_param_device: cpu
|
||||
zero3_init_flag: false
|
||||
zero_stage: 2
|
||||
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
See [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/usage_guides/deepspeed) for more DeepSpeed configuration options.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Changing the default Adam optimizer to DeepSpeed's Adam
|
||||
`deepspeed.ops.adam.DeepSpeedCPUAdam` gives a substantial speedup but
|
||||
it requires a CUDA toolchain with the same version as PyTorch. 8-bit optimizer
|
||||
does not seem to be compatible with DeepSpeed at the moment.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_DIR="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path to save model"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_controlnet.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--dataset_name=fusing/fill50k \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--validation_image "./conditioning_image_1.png" "./conditioning_image_2.png" \
|
||||
--validation_prompt "red circle with blue background" "cyan circle with brown floral background" \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=4 \
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing \
|
||||
--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention \
|
||||
--set_grads_to_none \
|
||||
--mixed_precision fp16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
The trained model can be run with the [`StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline`].
|
||||
Set `base_model_path` and `controlnet_path` to the values `--pretrained_model_name_or_path` and
|
||||
`--output_dir` were respectively set to in the training script.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline, ControlNetModel, UniPCMultistepScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
base_model_path = "path to model"
|
||||
controlnet_path = "path to controlnet"
|
||||
|
||||
controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained(controlnet_path, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
base_model_path, controlnet=controlnet, torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# speed up diffusion process with faster scheduler and memory optimization
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = UniPCMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
# remove following line if xformers is not installed
|
||||
pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
control_image = load_image("./conditioning_image_1.png")
|
||||
prompt = "pale golden rod circle with old lace background"
|
||||
|
||||
# generate image
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=20, generator=generator, image=control_image).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
image.save("./output.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -10,67 +10,55 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# DreamBooth
|
||||
# DreamBooth fine-tuning example
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
[DreamBooth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.12242) is a method to personalize text-to-image models like Stable Diffusion given just a few (3-5) images of a subject. It allows the model to generate contextualized images of the subject in different scenes, poses, and views.
|
||||
[DreamBooth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.12242) is a method to personalize text-to-image models like stable diffusion given just a few (3~5) images of a subject.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
<small>Dreambooth examples from the <a href="https://dreambooth.github.io">project's blog.</a></small>
|
||||
_Dreambooth examples from the [project's blog](https://dreambooth.github.io)._
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to finetune DreamBooth with the [`CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4`](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) model for various GPU sizes, and with Flax. All the training scripts for DreamBooth used in this guide can be found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth) if you're interested in digging deeper and seeing how things work.
|
||||
The [Dreambooth training script](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth) shows how to implement this training procedure on a pre-trained Stable Diffusion model.
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the scripts, make sure you install the library's training dependencies. We also recommend installing 🧨 Diffusers from the `main` GitHub branch:
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Dreambooth fine-tuning is very sensitive to hyperparameters and easy to overfit. We recommend you take a look at our [in-depth analysis](https://huggingface.co/blog/dreambooth) with recommended settings for different subjects, and go from there.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Training locally
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing the dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the scripts, make sure to install the library's training dependencies. We also recommend to install `diffusers` from the `main` github branch.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
pip install -U -r diffusers/examples/dreambooth/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
xFormers is not part of the training requirements, but we recommend you [install](../optimization/xformers) it if you can because it could make your training faster and less memory intensive.
|
||||
xFormers is not part of the training requirements, but [we recommend you install it if you can](../optimization/xformers). It could make your training faster and less memory intensive.
|
||||
|
||||
After all the dependencies have been set up, initialize a [🤗 Accelerate](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/) environment with:
|
||||
After all dependencies have been set up you can configure a [🤗 Accelerate](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/) environment with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To setup a default 🤗 Accelerate environment without choosing any configurations:
|
||||
In this example we'll use model version `v1-4`, so please visit [its card](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) and carefully read the license before proceeding.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config default
|
||||
```
|
||||
The command below will download and cache the model weights from the Hub because we use the model's Hub id `CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4`. You may also clone the repo locally and use the local path in your system where the checkout was saved.
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
### Dog toy example
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
In this example we'll use [these images](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1BO_dyz-p65qhBRRMRA4TbZ8qW4rB99JZ) to add a new concept to Stable Diffusion using the Dreambooth process. They will be our training data. Please, download them and place them somewhere in your system.
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Finetuning
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
DreamBooth finetuning is very sensitive to hyperparameters and easy to overfit. We recommend you take a look at our [in-depth analysis](https://huggingface.co/blog/dreambooth) with recommended settings for different subjects to help you choose the appropriate hyperparameters.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Let's try DreamBooth with a [few images of a dog](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1BO_dyz-p65qhBRRMRA4TbZ8qW4rB99JZ); download and save them to a directory and then set the `INSTANCE_DIR` environment variable to that path:
|
||||
Then you can launch the training script using:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="path_to_training_images"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path_to_saved_model"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can launch the training script (you can find the full training script [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py)) with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
@@ -84,44 +72,13 @@ accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=400
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
If you have access to TPUs or want to train even faster, you can try out the [Flax training script](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth_flax.py). The Flax training script doesn't support gradient checkpointing or gradient accumulation, so you'll need a GPU with at least 30GB of memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the script, make sure you have the requirements installed:
|
||||
### Training with a prior-preserving loss
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -U -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
Prior preservation is used to avoid overfitting and language-drift. Please, refer to the paper to learn more about it if you are interested. For prior preservation, we use other images of the same class as part of the training process. The nice thing is that we can generate those images using the Stable Diffusion model itself! The training script will save the generated images to a local path we specify.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can launch the training script with the following command:
|
||||
According to the paper, it's recommended to generate `num_epochs * num_samples` images for prior preservation. 200-300 works well for most cases.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="duongna/stable-diffusion-v1-4-flax"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="path-to-instance-images"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path-to-save-model"
|
||||
|
||||
python train_dreambooth_flax.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--instance_prompt="a photo of sks dog" \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=5e-6 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=400
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Finetuning with prior-preserving loss
|
||||
|
||||
Prior preservation is used to avoid overfitting and language-drift (check out the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.12242) to learn more if you're interested). For prior preservation, you use other images of the same class as part of the training process. The nice thing is that you can generate those images using the Stable Diffusion model itself! The training script will save the generated images to a local path you specify.
|
||||
|
||||
The authors recommend generating `num_epochs * num_samples` images for prior preservation. In most cases, 200-300 images work well.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="path_to_training_images"
|
||||
@@ -145,125 +102,32 @@ accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--num_class_images=200 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=800
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="duongna/stable-diffusion-v1-4-flax"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="path-to-instance-images"
|
||||
export CLASS_DIR="path-to-class-images"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path-to-save-model"
|
||||
|
||||
python train_dreambooth_flax.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
--class_data_dir=$CLASS_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--with_prior_preservation --prior_loss_weight=1.0 \
|
||||
--instance_prompt="a photo of sks dog" \
|
||||
--class_prompt="a photo of dog" \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=5e-6 \
|
||||
--num_class_images=200 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=800
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
### Saving checkpoints while training
|
||||
|
||||
## Finetuning the text encoder and UNet
|
||||
|
||||
The script also allows you to finetune the `text_encoder` along with the `unet`. In our experiments (check out the [Training Stable Diffusion with DreamBooth using 🧨 Diffusers](https://huggingface.co/blog/dreambooth) post for more details), this yields much better results, especially when generating images of faces.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Training the text encoder requires additional memory and it won't fit on a 16GB GPU. You'll need at least 24GB VRAM to use this option.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Pass the `--train_text_encoder` argument to the training script to enable finetuning the `text_encoder` and `unet`:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="path_to_training_images"
|
||||
export CLASS_DIR="path_to_class_images"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path_to_saved_model"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--train_text_encoder \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
--class_data_dir=$CLASS_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--with_prior_preservation --prior_loss_weight=1.0 \
|
||||
--instance_prompt="a photo of sks dog" \
|
||||
--class_prompt="a photo of dog" \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--use_8bit_adam
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing \
|
||||
--learning_rate=2e-6 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler="constant" \
|
||||
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--num_class_images=200 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=800
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="duongna/stable-diffusion-v1-4-flax"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="path-to-instance-images"
|
||||
export CLASS_DIR="path-to-class-images"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path-to-save-model"
|
||||
|
||||
python train_dreambooth_flax.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--train_text_encoder \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
--class_data_dir=$CLASS_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--with_prior_preservation --prior_loss_weight=1.0 \
|
||||
--instance_prompt="a photo of sks dog" \
|
||||
--class_prompt="a photo of dog" \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=2e-6 \
|
||||
--num_class_images=200 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=800
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Finetuning with LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models (LoRA), a fine-tuning technique for accelerating training large models, on DreamBooth. For more details, take a look at the [LoRA training](./lora#dreambooth) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
## Saving checkpoints while training
|
||||
|
||||
It's easy to overfit while training with Dreambooth, so sometimes it's useful to save regular checkpoints during the training process. One of the intermediate checkpoints might actually work better than the final model! Pass the following argument to the training script to enable saving checkpoints:
|
||||
It's easy to overfit while training with Dreambooth, so sometimes it's useful to save regular checkpoints during the process. One of the intermediate checkpoints might work better than the final model! To use this feature you need to pass the following argument to the training script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=500
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This saves the full training state in subfolders of your `output_dir`. Subfolder names begin with the prefix `checkpoint-`, followed by the number of steps performed so far; for example, `checkpoint-1500` would be a checkpoint saved after 1500 training steps.
|
||||
This will save the full training state in subfolders of your `output_dir`. Subfolder names begin with the prefix `checkpoint-`, and then the number of steps performed so far; for example: `checkpoint-1500` would be a checkpoint saved after 1500 training steps.
|
||||
|
||||
### Resume training from a saved checkpoint
|
||||
#### Resuming training from a saved checkpoint
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to resume training from any of the saved checkpoints, you can pass the argument `--resume_from_checkpoint` to the script and specify the name of the checkpoint you want to use. You can also use the special string `"latest"` to resume from the last saved checkpoint (the one with the largest number of steps). For example, the following would resume training from the checkpoint saved after 1500 steps:
|
||||
If you want to resume training from any of the saved checkpoints, you can pass the argument `--resume_from_checkpoint` and then indicate the name of the checkpoint you want to use. You can also use the special string `"latest"` to resume from the last checkpoint saved (i.e., the one with the largest number of steps). For example, the following would resume training from the checkpoint saved after 1500 steps:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--resume_from_checkpoint="checkpoint-1500"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is a good opportunity to tweak some of your hyperparameters if you wish.
|
||||
This would be a good opportunity to tweak some of your hyperparameters if you wish.
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference from a saved checkpoint
|
||||
#### Performing inference using a saved checkpoint
|
||||
|
||||
Saved checkpoints are stored in a format suitable for resuming training. They not only include the model weights, but also the state of the optimizer, data loaders, and learning rate.
|
||||
Saved checkpoints are stored in a format suitable for resuming training. They not only include the model weights, but also the state of the optimizer, data loaders and learning rate.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have **`"accelerate>=0.16.0"`** installed, use the following code to run
|
||||
**Note**: If you have installed `"accelerate>=0.16.0"` you can use the following code to run
|
||||
inference from an intermediate checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@@ -286,7 +150,7 @@ pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.save_pretrained("dreambooth-pipeline")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have **`"accelerate<0.16.0"`** installed, you need to convert it to an inference pipeline first:
|
||||
If you have installed `"accelerate<0.16.0"` you need to first convert it to an inference pipeline. This is how you could do it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
@@ -315,37 +179,15 @@ pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
pipeline.save_pretrained("dreambooth-pipeline")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Optimizations for different GPU sizes
|
||||
### Training on a 16GB GPU
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on your hardware, there are a few different ways to optimize DreamBooth on GPUs from 16GB to just 8GB!
|
||||
|
||||
### xFormers
|
||||
|
||||
[xFormers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers) is a toolbox for optimizing Transformers, and it includes a [memory-efficient attention](https://facebookresearch.github.io/xformers/components/ops.html#module-xformers.ops) mechanism that is used in 🧨 Diffusers. You'll need to [install xFormers](./optimization/xformers) and then add the following argument to your training script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
xFormers is not available in Flax.
|
||||
|
||||
### Set gradients to none
|
||||
|
||||
Another way you can lower your memory footprint is to [set the gradients](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.optim.Optimizer.zero_grad.html) to `None` instead of zero. However, this may change certain behaviors, so if you run into any issues, try removing this argument. Add the following argument to your training script to set the gradients to `None`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--set_grads_to_none
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 16GB GPU
|
||||
|
||||
With the help of gradient checkpointing and [bitsandbytes](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes) 8-bit optimizer, it's possible to train DreamBooth on a 16GB GPU. Make sure you have bitsandbytes installed:
|
||||
With the help of gradient checkpointing and the 8-bit optimizer from [bitsandbytes](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes), it's possible to train dreambooth on a 16GB GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install bitsandbytes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then pass the `--use_8bit_adam` option to the training script:
|
||||
Then pass the `--use_8bit_adam` option to the training script.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
@@ -372,18 +214,25 @@ accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=800
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 12GB GPU
|
||||
### Fine-tune the text encoder in addition to the UNet
|
||||
|
||||
To run DreamBooth on a 12GB GPU, you'll need to enable gradient checkpointing, the 8-bit optimizer, xFormers, and set the gradients to `None`:
|
||||
The script also allows to fine-tune the `text_encoder` along with the `unet`. It has been observed experimentally that this gives much better results, especially on faces. Please, refer to [our blog](https://huggingface.co/blog/dreambooth) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable this option, pass the `--train_text_encoder` argument to the training script.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
Training the text encoder requires additional memory, so training won't fit on a 16GB GPU. You'll need at least 24GB VRAM to use this option.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="path-to-instance-images"
|
||||
export CLASS_DIR="path-to-class-images"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path-to-save-model"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="path_to_training_images"
|
||||
export CLASS_DIR="path_to_class_images"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path_to_saved_model"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--train_text_encoder \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
--class_data_dir=$CLASS_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
@@ -392,10 +241,8 @@ accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--class_prompt="a photo of dog" \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=1 --gradient_checkpointing \
|
||||
--use_8bit_adam \
|
||||
--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention \
|
||||
--set_grads_to_none \
|
||||
--use_8bit_adam
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing \
|
||||
--learning_rate=2e-6 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler="constant" \
|
||||
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
@@ -403,25 +250,19 @@ accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=800
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 8 GB GPU
|
||||
### Training on a 8 GB GPU:
|
||||
|
||||
For 8GB GPUs, you'll need the help of [DeepSpeed](https://www.deepspeed.ai/) to offload some
|
||||
tensors from the VRAM to either the CPU or NVME, enabling training with less GPU memory.
|
||||
Using [DeepSpeed](https://www.deepspeed.ai/) it's even possible to offload some
|
||||
tensors from VRAM to either CPU or NVME, allowing training to proceed with less GPU memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command to configure your 🤗 Accelerate environment:
|
||||
DeepSpeed needs to be enabled with `accelerate config`. During configuration,
|
||||
answer yes to "Do you want to use DeepSpeed?". Combining DeepSpeed stage 2, fp16
|
||||
mixed precision, and offloading both the model parameters and the optimizer state to CPU, it's
|
||||
possible to train on under 8 GB VRAM. The drawback is that this requires more system RAM (about 25 GB). See [the DeepSpeed documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/usage_guides/deepspeed) for more configuration options.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
During configuration, confirm that you want to use DeepSpeed. Now it's possible to train on under 8GB VRAM by combining DeepSpeed stage 2, fp16 mixed precision, and offloading the model parameters and the optimizer state to the CPU. The drawback is that this requires more system RAM, about 25 GB. See [the DeepSpeed documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/usage_guides/deepspeed) for more configuration options.
|
||||
|
||||
You should also change the default Adam optimizer to DeepSpeed's optimized version of Adam
|
||||
[`deepspeed.ops.adam.DeepSpeedCPUAdam`](https://deepspeed.readthedocs.io/en/latest/optimizers.html#adam-cpu) for a substantial speedup. Enabling `DeepSpeedCPUAdam` requires your system's CUDA toolchain version to be the same as the one installed with PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
8-bit optimizers don't seem to be compatible with DeepSpeed at the moment.
|
||||
|
||||
Launch training with the following command:
|
||||
Changing the default Adam optimizer to DeepSpeed's special version of Adam
|
||||
`deepspeed.ops.adam.DeepSpeedCPUAdam` gives a substantial speedup, but enabling
|
||||
it requires the system's CUDA toolchain version to be the same as the one installed with PyTorch. 8-bit optimizers don't seem to be compatible with DeepSpeed at the moment.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
@@ -451,17 +292,18 @@ accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have trained a model, specify the path to where the model is saved, and use it for inference in the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]. Make sure your prompts include the special `identifier` used during training (`sks` in the previous examples).
|
||||
Once you have trained a model, inference can be done using the `StableDiffusionPipeline`, by simply indicating the path where the model was saved. Make sure that your prompts include the special `identifier` used during training (`sks` in the previous examples).
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: If you have installed `"accelerate>=0.16.0"` you can use the following code to run
|
||||
inference from an intermediate checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have **`"accelerate>=0.16.0"`** installed, you can use the following code to run
|
||||
inference from an intermediate checkpoint:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "path_to_saved_model"
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A photo of sks dog in a bucket"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=50, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
@@ -469,4 +311,4 @@ image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=50, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
image.save("dog-bucket.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You may also run inference from any of the [saved training checkpoints](#inference-from-a-saved-checkpoint).
|
||||
You may also run inference from [any of the saved training checkpoints](#performing-inference-using-a-saved-checkpoint).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,181 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# InstructPix2Pix
|
||||
|
||||
[InstructPix2Pix](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09800) is a method to fine-tune text-conditioned diffusion models such that they can follow an edit instruction for an input image. Models fine-tuned using this method take the following as inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/evaluation_diffusion_models/edit-instruction.png" alt="instructpix2pix-inputs" width=600/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
The output is an "edited" image that reflects the edit instruction applied on the input image:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/output-gs%407-igs%401-steps%4050.png" alt="instructpix2pix-output" width=600/>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
The `train_instruct_pix2pix.py` script shows how to implement the training procedure and adapt it for Stable Diffusion.
|
||||
|
||||
***Disclaimer: Even though `train_instruct_pix2pix.py` implements the InstructPix2Pix
|
||||
training procedure while being faithful to the [original implementation](https://github.com/timothybrooks/instruct-pix2pix) we have only tested it on a [small-scale dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/fusing/instructpix2pix-1000-samples). This can impact the end results. For better results, we recommend longer training runs with a larger dataset. [Here](https://huggingface.co/datasets/timbrooks/instructpix2pix-clip-filtered) you can find a large dataset for InstructPix2Pix training.***
|
||||
|
||||
## Running locally with PyTorch
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing the dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the scripts, make sure to install the library's training dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
**Important**
|
||||
|
||||
To make sure you can successfully run the latest versions of the example scripts, we highly recommend **installing from source** and keeping the install up to date as we update the example scripts frequently and install some example-specific requirements. To do this, execute the following steps in a new virtual environment:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
cd diffusers
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then cd in the example folder and run
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And initialize an [🤗Accelerate](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/) environment with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or for a default accelerate configuration without answering questions about your environment
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config default
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell e.g. a notebook
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Toy example
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned before, we'll use a [small toy dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/fusing/instructpix2pix-1000-samples) for training. The dataset
|
||||
is a smaller version of the [original dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/timbrooks/instructpix2pix-clip-filtered) used in the InstructPix2Pix paper.
|
||||
|
||||
Configure environment variables such as the dataset identifier and the Stable Diffusion
|
||||
checkpoint:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export DATASET_ID="fusing/instructpix2pix-1000-samples"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can launch training:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_instruct_pix2pix.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--dataset_name=$DATASET_ID \
|
||||
--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention \
|
||||
--resolution=256 --random_flip \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=4 --gradient_accumulation_steps=4 --gradient_checkpointing \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=15000 \
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=5000 --checkpoints_total_limit=1 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=5e-05 --max_grad_norm=1 --lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--conditioning_dropout_prob=0.05 \
|
||||
--mixed_precision=fp16 \
|
||||
--seed=42
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, we support performing validation inference to monitor training progress
|
||||
with Weights and Biases. You can enable this feature with `report_to="wandb"`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_instruct_pix2pix.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--dataset_name=$DATASET_ID \
|
||||
--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention \
|
||||
--resolution=256 --random_flip \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=4 --gradient_accumulation_steps=4 --gradient_checkpointing \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=15000 \
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=5000 --checkpoints_total_limit=1 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=5e-05 --max_grad_norm=1 --lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--conditioning_dropout_prob=0.05 \
|
||||
--mixed_precision=fp16 \
|
||||
--val_image_url="https://hf.co/datasets/diffusers/diffusers-images-docs/resolve/main/mountain.png" \
|
||||
--validation_prompt="make the mountains snowy" \
|
||||
--seed=42 \
|
||||
--report_to=wandb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend this type of validation as it can be useful for model debugging. Note that you need `wandb` installed to use this. You can install `wandb` by running `pip install wandb`.
|
||||
|
||||
[Here](https://wandb.ai/sayakpaul/instruct-pix2pix/runs/ctr3kovq), you can find an example training run that includes some validation samples and the training hyperparameters.
|
||||
|
||||
***Note: In the original paper, the authors observed that even when the model is trained with an image resolution of 256x256, it generalizes well to bigger resolutions such as 512x512. This is likely because of the larger dataset they used during training.***
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Once training is complete, we can perform inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "your_model_id" # <- replace this
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/sayakpaul/sample-datasets/resolve/main/test_pix2pix_4.png"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def download_image(url):
|
||||
image = PIL.Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
image = PIL.ImageOps.exif_transpose(image)
|
||||
image = image.convert("RGB")
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
image = download_image(url)
|
||||
prompt = "wipe out the lake"
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 20
|
||||
image_guidance_scale = 1.5
|
||||
guidance_scale = 10
|
||||
|
||||
edited_image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps,
|
||||
image_guidance_scale=image_guidance_scale,
|
||||
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
edited_image.save("edited_image.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
An example model repo obtained using this training script can be found
|
||||
here - [sayakpaul/instruct-pix2pix](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/instruct-pix2pix).
|
||||
|
||||
We encourage you to play with the following three parameters to control
|
||||
speed and quality during performance:
|
||||
|
||||
* `num_inference_steps`
|
||||
* `image_guidance_scale`
|
||||
* `guidance_scale`
|
||||
|
||||
Particularly, `image_guidance_scale` and `guidance_scale` can have a profound impact
|
||||
on the generated ("edited") image (see [here](https://twitter.com/RisingSayak/status/1628392199196151808?s=20) for an example).
|
||||
@@ -10,151 +10,54 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models (LoRA)
|
||||
# LoRA Support in Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
Diffusers supports LoRA for faster fine-tuning of Stable Diffusion, allowing greater memory efficiency and easier portability.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
Low-Rank Adaption of Large Language Models was first introduced by Microsoft in
|
||||
[LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685) by *Edward J. Hu, Yelong Shen, Phillip Wallis, Zeyuan Allen-Zhu, Yuanzhi Li, Shean Wang, Lu Wang, Weizhu Chen*.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, LoRA is only supported for the attention layers of the [`UNet2DConditionalModel`].
|
||||
In a nutshell, LoRA allows adapting pretrained models by adding pairs of rank-decomposition weight matrices (called **update matrices**)
|
||||
to existing weights and **only** training those newly added weights. This has a couple of advantages:
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
[Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models (LoRA)](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685) is a training method that accelerates the training of large models while consuming less memory. It adds pairs of rank-decomposition weight matrices (called **update matrices**) to existing weights, and **only** trains those newly added weights. This has a couple of advantages:
|
||||
|
||||
- Previous pretrained weights are kept frozen so the model is not as prone to [catastrophic forgetting](https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1611835114).
|
||||
- Previous pretrained weights are kept frozen so that the model is not so prone to [catastrophic forgetting](https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1611835114).
|
||||
- Rank-decomposition matrices have significantly fewer parameters than the original model, which means that trained LoRA weights are easily portable.
|
||||
- LoRA matrices are generally added to the attention layers of the original model. 🧨 Diffusers provides the [`~diffusers.loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.load_attn_procs`] method to load the LoRA weights into a model's attention layers. You can control the extent to which the model is adapted toward new training images via a `scale` parameter.
|
||||
- The greater memory-efficiency allows you to run fine-tuning on consumer GPUs like the Tesla T4, RTX 3080 or even the RTX 2080 Ti! GPUs like the T4 are free and readily accessible in Kaggle or Google Colab notebooks.
|
||||
- LoRA matrices are generally added to the attention layers of the original model and they control to which extent the model is adapted toward new training images via a `scale` parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
**__Note that the usage of LoRA is not just limited to attention layers. In the original LoRA work, the authors found out that just amending
|
||||
the attention layers of a language model is sufficient to obtain good downstream performance with great efficiency. This is why, it's common
|
||||
to just add the LoRA weights to the attention layers of a model.__**
|
||||
|
||||
[cloneofsimo](https://github.com/cloneofsimo) was the first to try out LoRA training for Stable Diffusion in the popular [lora](https://github.com/cloneofsimo/lora) GitHub repository.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 LoRA is not only limited to attention layers. The authors found that amending
|
||||
the attention layers of a language model is sufficient to obtain good downstream performance with great efficiency. This is why it's common to just add the LoRA weights to the attention layers of a model. Check out the [Using LoRA for efficient Stable Diffusion fine-tuning](https://huggingface.co/blog/lora) blog for more information about how LoRA works!
|
||||
LoRA allows us to achieve greater memory efficiency since the pretrained weights are kept frozen and only the LoRA weights are trained, thereby
|
||||
allowing us to run fine-tuning on consumer GPUs like Tesla T4, RTX 3080 or even RTX 2080 Ti! One can get access to GPUs like T4 in the free
|
||||
tiers of Kaggle Kernels and Google Colab Notebooks.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
[cloneofsimo](https://github.com/cloneofsimo) was the first to try out LoRA training for Stable Diffusion in the popular [lora](https://github.com/cloneofsimo/lora) GitHub repository. 🧨 Diffusers now supports finetuning with LoRA for [text-to-image generation](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/text_to_image#training-with-lora) and [DreamBooth](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#training-with-low-rank-adaptation-of-large-language-models-lora). This guide will show you how to do both.
|
||||
## Getting started with LoRA for fine-tuning
|
||||
|
||||
If you'd like to store or share your model with the community, login to your Hugging Face account (create [one](hf.co/join) if you don't have one already):
|
||||
Stable Diffusion can be fine-tuned in different ways:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
```
|
||||
* [Textual inversion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/training/text_inversion)
|
||||
* [DreamBooth](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/training/dreambooth)
|
||||
* [Text2Image fine-tuning](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/training/text2image)
|
||||
|
||||
## Text-to-image
|
||||
We provide two end-to-end examples that show how to run fine-tuning with LoRA:
|
||||
|
||||
Finetuning a model like Stable Diffusion, which has billions of parameters, can be slow and difficult. With LoRA, it is much easier and faster to finetune a diffusion model. It can run on hardware with as little as 11GB of GPU RAM without resorting to tricks such as 8-bit optimizers.
|
||||
* [DreamBooth](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#training-with-low-rank-adaptation-of-large-language-models-lora)
|
||||
* [Text2Image](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/text_to_image#training-with-lora)
|
||||
|
||||
### Training[[text-to-image-training]]
|
||||
|
||||
Let's finetune [`stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) on the [Pokémon BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions) dataset to generate your own Pokémon.
|
||||
|
||||
To start, make sure you have the `MODEL_NAME` and `DATASET_NAME` environment variables set. The `OUTPUT_DIR` and `HUB_MODEL_ID` variables are optional and specify where to save the model to on the Hub:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="/sddata/finetune/lora/pokemon"
|
||||
export HUB_MODEL_ID="pokemon-lora"
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are some flags to be aware of before you start training:
|
||||
|
||||
* `--push_to_hub` stores the trained LoRA embeddings on the Hub.
|
||||
* `--report_to=wandb` reports and logs the training results to your Weights & Biases dashboard (as an example, take a look at this [report](https://wandb.ai/pcuenq/text2image-fine-tune/runs/b4k1w0tn?workspace=user-pcuenq)).
|
||||
* `--learning_rate=1e-04`, you can afford to use a higher learning rate than you normally would with LoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you're ready to launch the training (you can find the full training script [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/text_to_image/train_text_to_image_lora.py)):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image_lora.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--dataset_name=$DATASET_NAME \
|
||||
--dataloader_num_workers=8 \
|
||||
--resolution=512 --center_crop --random_flip \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=4 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=15000 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-04 \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm=1 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler="cosine" --lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--output_dir=${OUTPUT_DIR} \
|
||||
--push_to_hub \
|
||||
--hub_model_id=${HUB_MODEL_ID} \
|
||||
--report_to=wandb \
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=500 \
|
||||
--validation_prompt="A pokemon with blue eyes." \
|
||||
--seed=1337
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference[[text-to-image-inference]]
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use the model for inference by loading the base model in the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] and then the [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_base = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_base, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
>>> pipe.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Load the LoRA weights from your finetuned model *on top of the base model weights*, and then move the pipeline to a GPU for faster inference. When you merge the LoRA weights with the frozen pretrained model weights, you can optionally adjust how much of the weights to merge with the `scale` parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 A `scale` value of `0` is the same as not using your LoRA weights and you're only using the base model weights, and a `scale` value of `1` means you're only using the fully finetuned LoRA weights. Values between `0` and `1` interpolates between the two weights.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pipe.unet.load_attn_procs(model_path)
|
||||
>>> pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
# use half the weights from the LoRA finetuned model and half the weights from the base model
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image = pipe(
|
||||
... "A pokemon with blue eyes.", num_inference_steps=25, guidance_scale=7.5, cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 0.5}
|
||||
... ).images[0]
|
||||
# use the weights from the fully finetuned LoRA model
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image = pipe("A pokemon with blue eyes.", num_inference_steps=25, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
>>> image.save("blue_pokemon.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## DreamBooth
|
||||
|
||||
[DreamBooth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.12242) is a finetuning technique for personalizing a text-to-image model like Stable Diffusion to generate photorealistic images of a subject in different contexts, given a few images of the subject. However, DreamBooth is very sensitive to hyperparameters and it is easy to overfit. Some important hyperparameters to consider include those that affect the training time (learning rate, number of training steps), and inference time (number of steps, scheduler type).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Take a look at the [Training Stable Diffusion with DreamBooth using 🧨 Diffusers](https://huggingface.co/blog/dreambooth) blog for an in-depth analysis of DreamBooth experiments and recommended settings.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Training[[dreambooth-training]]
|
||||
|
||||
Let's finetune [`stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) with DreamBooth and LoRA with some 🐶 [dog images](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1BO_dyz-p65qhBRRMRA4TbZ8qW4rB99JZ). Download and save these images to a directory.
|
||||
|
||||
To start, make sure you have the `MODEL_NAME` and `INSTANCE_DIR` (path to directory containing images) environment variables set. The `OUTPUT_DIR` variables is optional and specifies where to save the model to on the Hub:
|
||||
If you want to perform DreamBooth training with LoRA, for instance, you would run:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="path-to-instance-images"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path-to-save-model"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are some flags to be aware of before you start training:
|
||||
|
||||
* `--push_to_hub` stores the trained LoRA embeddings on the Hub.
|
||||
* `--report_to=wandb` reports and logs the training results to your Weights & Biases dashboard (as an example, take a look at this [report](https://wandb.ai/pcuenq/text2image-fine-tune/runs/b4k1w0tn?workspace=user-pcuenq)).
|
||||
* `--learning_rate=1e-04`, you can afford to use a higher learning rate than you normally would with LoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you're ready to launch the training (you can find the full training script [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth_lora.py)):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch train_dreambooth_lora.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
@@ -175,40 +78,101 @@ accelerate launch train_dreambooth_lora.py \
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference[[dreambooth-inference]]
|
||||
A similar process can be followed to fully fine-tune Stable Diffusion on a custom dataset using the
|
||||
`examples/text_to_image/train_text_to_image_lora.py` script.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use the model for inference by loading the base model in the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_base = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_base, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Load the LoRA weights from your finetuned DreamBooth model *on top of the base model weights*, and then move the pipeline to a GPU for faster inference. When you merge the LoRA weights with the frozen pretrained model weights, you can optionally adjust how much of the weights to merge with the `scale` parameter:
|
||||
Refer to the respective examples linked above to learn more.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 A `scale` value of `0` is the same as not using your LoRA weights and you're only using the base model weights, and a `scale` value of `1` means you're only using the fully finetuned LoRA weights. Values between `0` and `1` interpolates between the two weights.
|
||||
When using LoRA we can use a much higher learning rate (typically 1e-4 as opposed to ~1e-6) compared to non-LoRA Dreambooth fine-tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
But there is no free lunch. For the given dataset and expected generation quality, you'd still need to experiment with
|
||||
different hyperparameters. Here are some important ones:
|
||||
|
||||
* Training time
|
||||
* Learning rate
|
||||
* Number of training steps
|
||||
* Inference time
|
||||
* Number of steps
|
||||
* Scheduler type
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, you can follow [this blog](https://huggingface.co/blog/dreambooth) that documents some of our experimental
|
||||
findings for performing DreamBooth training of Stable Diffusion.
|
||||
|
||||
When fine-tuning, the LoRA update matrices are only added to the attention layers. To enable this, we added new weight
|
||||
loading functionalities. Their details are available [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/loaders).
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming you used the `examples/text_to_image/train_text_to_image_lora.py` to fine-tune Stable Diffusion on the [Pokemon
|
||||
dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions), you can perform inference like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model_path = "sayakpaul/sd-model-finetuned-lora-t4"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.unet.load_attn_procs(model_path)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A pokemon with blue eyes."
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
image.save("pokemon.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some example images you can expect:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pokemon-collage.png"/>
|
||||
|
||||
[`sayakpaul/sd-model-finetuned-lora-t4`](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/sd-model-finetuned-lora-t4) contains [LoRA fine-tuned update matrices](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/sd-model-finetuned-lora-t4/blob/main/pytorch_lora_weights.bin)
|
||||
which is only 3 MBs in size. During inference, the pre-trained Stable Diffusion checkpoints are loaded alongside these update
|
||||
matrices and then they are combined to run inference.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the [`huggingface_hub`](https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface_hub) library to retrieve the base model
|
||||
from [`sayakpaul/sd-model-finetuned-lora-t4`](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/sd-model-finetuned-lora-t4) like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pipe.unet.load_attn_procs(model_path)
|
||||
>>> pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
# use half the weights from the LoRA finetuned model and half the weights from the base model
|
||||
from huggingface_hub.repocard import RepoCard
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image = pipe(
|
||||
... "A picture of a sks dog in a bucket.",
|
||||
... num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
... guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
... cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 0.5},
|
||||
... ).images[0]
|
||||
# use the weights from the fully finetuned LoRA model
|
||||
card = RepoCard.load("sayakpaul/sd-model-finetuned-lora-t4")
|
||||
base_model = card.data.to_dict()["base_model"]
|
||||
# 'CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image = pipe("A picture of a sks dog in a bucket.", num_inference_steps=25, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
>>> image.save("bucket-dog.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
And then you can use `pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(base_model, torch_dtype=torch.float16)`.
|
||||
|
||||
This is especially useful when you don't want to hardcode the base model identifier during initializing the `StableDiffusionPipeline`.
|
||||
|
||||
Inference for DreamBooth training remains the same. Check
|
||||
[this section](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#inference-1) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Merging LoRA with original model
|
||||
|
||||
When performing inference, you can merge the trained LoRA weights with the frozen pre-trained model weights, to interpolate between the original model's inference result (as if no fine-tuning had occurred) and the fully fine-tuned version.
|
||||
|
||||
You can adjust the merging ratio with a parameter called α (alpha) in the paper, or `scale` in our implementation. You can tweak it with the following code, that passes `scale` as `cross_attention_kwargs` in the pipeline call:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model_path = "sayakpaul/sd-model-finetuned-lora-t4"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.unet.load_attn_procs(model_path)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A pokemon with blue eyes."
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30, guidance_scale=7.5, cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 0.5}).images[0]
|
||||
image.save("pokemon.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A value of `0` is the same as _not_ using the LoRA weights, whereas `1` means only the LoRA fine-tuned weights will be used. Values between 0 and 1 will interpolate between the two versions.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Known limitations
|
||||
|
||||
* Currently, we only support LoRA for the attention layers of [`UNet2DConditionModel`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/models#diffusers.UNet2DConditionModel).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +38,6 @@ Training examples show how to pretrain or fine-tune diffusion models for a varie
|
||||
- [Text Inversion](./text_inversion)
|
||||
- [Dreambooth](./dreambooth)
|
||||
- [LoRA Support](./lora)
|
||||
- [ControlNet](./controlnet)
|
||||
|
||||
If possible, please [install xFormers](../optimization/xformers) for memory efficient attention. This could help make your training faster and less memory intensive.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,8 +47,6 @@ If possible, please [install xFormers](../optimization/xformers) for memory effi
|
||||
| [**Text-to-Image fine-tuning**](./text2image) | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [**Textual Inversion**](./text_inversion) | ✅ | - | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/sd_textual_inversion_training.ipynb)
|
||||
| [**Dreambooth**](./dreambooth) | ✅ | - | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/sd_dreambooth_training.ipynb)
|
||||
| [**Training with LoRA**](./lora) | ✅ | - | - |
|
||||
| [**ControlNet**](./controlnet) | ✅ | ✅ | - |
|
||||
|
||||
## Community
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,15 +11,20 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Text-to-image
|
||||
# Stable Diffusion text-to-image fine-tuning
|
||||
|
||||
The [`train_text_to_image.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/text_to_image) script shows how to fine-tune the stable diffusion model on your own dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The text-to-image fine-tuning script is experimental. It's easy to overfit and run into issues like catastrophic forgetting. We recommend you explore different hyperparameters to get the best results on your dataset.
|
||||
The text-to-image fine-tuning script is experimental. It's easy to overfit and run into issues like catastrophic forgetting. We recommend to explore different hyperparameters to get the best results on your dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Text-to-image models like Stable Diffusion generate an image from a text prompt. This guide will show you how to finetune the [`CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4`](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) model on your own dataset with PyTorch and Flax. All the training scripts for text-to-image finetuning used in this guide can be found in this [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/text_to_image) if you're interested in taking a closer look.
|
||||
|
||||
## Running locally
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing the dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the scripts, make sure to install the library's training dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,63 +33,56 @@ pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
pip install -U -r requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And initialize an [🤗 Accelerate](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/) environment with:
|
||||
And initialize an [🤗Accelerate](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/) environment with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You need to accept the model license before downloading or using the weights. In this example we'll use model version `v1-4`, so you'll need to visit [its card](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4), read the license and tick the checkbox if you agree.
|
||||
|
||||
You have to be a registered user in 🤗 Hugging Face Hub, and you'll also need to use an access token for the code to work. For more information on access tokens, please refer to [this section of the documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-tokens).
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command to authenticate your token
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have already cloned the repo, then you won't need to go through these steps. Instead, you can pass the path to your local checkout to the training script and it will be loaded from there.
|
||||
|
||||
## Hardware requirements
|
||||
### Hardware Requirements for Fine-tuning
|
||||
|
||||
Using `gradient_checkpointing` and `mixed_precision`, it should be possible to finetune the model on a single 24GB GPU. For higher `batch_size`'s and faster training, it's better to use GPUs with more than 30GB of GPU memory. You can also use JAX/Flax for fine-tuning on TPUs or GPUs, which will be covered [below](#flax-jax-finetuning).
|
||||
Using `gradient_checkpointing` and `mixed_precision` it should be possible to fine tune the model on a single 24GB GPU. For higher `batch_size` and faster training it's better to use GPUs with more than 30GB of GPU memory. You can also use JAX / Flax for fine-tuning on TPUs or GPUs, see [below](#flax-jax-finetuning) for details.
|
||||
|
||||
You can reduce your memory footprint even more by enabling memory efficient attention with xFormers. Make sure you have [xFormers installed](./optimization/xformers) and pass the `--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention` flag to the training script.
|
||||
### Fine-tuning Example
|
||||
|
||||
xFormers is not available for Flax.
|
||||
The following script will launch a fine-tuning run using [Justin Pinkneys' captioned Pokemon dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions), available in Hugging Face Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
## Upload model to Hub
|
||||
|
||||
Store your model on the Hub by adding the following argument to the training script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
export dataset_name="lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_text_to_image.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--dataset_name=$dataset_name \
|
||||
--use_ema \
|
||||
--resolution=512 --center_crop --random_flip \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=4 \
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing \
|
||||
--mixed_precision="fp16" \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=15000 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-05 \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm=1 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler="constant" --lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--output_dir="sd-pokemon-model"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Save and load checkpoints
|
||||
To run on your own training files you need to prepare the dataset according to the format required by `datasets`. You can upload your dataset to the Hub, or you can prepare a local folder with your files. [This documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/v2.4.0/en/image_load#imagefolder-with-metadata) explains how to do it.
|
||||
|
||||
It is a good idea to regularly save checkpoints in case anything happens during training. To save a checkpoint, pass the following argument to the training script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=500
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Every 500 steps, the full training state is saved in a subfolder in the `output_dir`. The checkpoint has the format `checkpoint-` followed by the number of steps trained so far. For example, `checkpoint-1500` is a checkpoint saved after 1500 training steps.
|
||||
|
||||
To load a checkpoint to resume training, pass the argument `--resume_from_checkpoint` to the training script and specify the checkpoint you want to resume from. For example, the following argument resumes training from the checkpoint saved after 1500 training steps:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--resume_from_checkpoint="checkpoint-1500"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Fine-tuning
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Launch the [PyTorch training script](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/text_to_image/train_text_to_image.py) for a fine-tuning run on the [Pokémon BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions) dataset like this:
|
||||
|
||||
<literalinclude>
|
||||
{"path": "../../../../examples/text_to_image/README.md",
|
||||
"language": "bash",
|
||||
"start-after": "accelerate_snippet_start",
|
||||
"end-before": "accelerate_snippet_end",
|
||||
"dedent": 0}
|
||||
</literalinclude>
|
||||
|
||||
To finetune on your own dataset, prepare the dataset according to the format required by 🤗 [Datasets](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/index). You can [upload your dataset to the Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/image_dataset#upload-dataset-to-the-hub), or you can [prepare a local folder with your files](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/image_dataset#imagefolder).
|
||||
|
||||
Modify the script if you want to use custom loading logic. We left pointers in the code in the appropriate places to help you. 🤗 The example script below shows how to finetune on a local dataset in `TRAIN_DIR` and where to save the model to in `OUTPUT_DIR`:
|
||||
You should modify the script if you wish to use custom loading logic. We have left pointers in the code in the appropriate places :)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
@@ -106,19 +104,25 @@ accelerate launch train_text_to_image.py \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler="constant" --lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--output_dir=${OUTPUT_DIR}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
With Flax, it's possible to train a Stable Diffusion model faster on TPUs and GPUs thanks to [@duongna211](https://github.com/duongna21). This is very efficient on TPU hardware but works great on GPUs too. The Flax training script doesn't support features like gradient checkpointing or gradient accumulation yet, so you'll need a GPU with at least 30GB of memory or a TPU v3.
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the script, make sure you have the requirements installed:
|
||||
Once training is finished the model will be saved to the `OUTPUT_DIR` specified in the command. To load the fine-tuned model for inference, just pass that path to `StableDiffusionPipeline`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -U -r requirements_flax.txt
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_path = "path_to_saved_model"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_path, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt="yoda").images[0]
|
||||
image.save("yoda-pokemon.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can launch the [Flax training script](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/text_to_image/train_text_to_image_flax.py) like this:
|
||||
### Flax / JAX fine-tuning
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
Thanks to [@duongna211](https://github.com/duongna21) it's possible to fine-tune Stable Diffusion using Flax! This is very efficient on TPU hardware but works great on GPUs too. You can use the [Flax training script](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/text_to_image/train_text_to_image_flax.py) like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export dataset_name="lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -132,99 +136,3 @@ python train_text_to_image_flax.py \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm=1 \
|
||||
--output_dir="sd-pokemon-model"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To finetune on your own dataset, prepare the dataset according to the format required by 🤗 [Datasets](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/index). You can [upload your dataset to the Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/image_dataset#upload-dataset-to-the-hub), or you can [prepare a local folder with your files](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/image_dataset#imagefolder).
|
||||
|
||||
Modify the script if you want to use custom loading logic. We left pointers in the code in the appropriate places to help you. 🤗 The example script below shows how to finetune on a local dataset in `TRAIN_DIR`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="duongna/stable-diffusion-v1-4-flax"
|
||||
export TRAIN_DIR="path_to_your_dataset"
|
||||
|
||||
python train_text_to_image_flax.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--train_data_dir=$TRAIN_DIR \
|
||||
--resolution=512 --center_crop --random_flip \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--mixed_precision="fp16" \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=15000 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-05 \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm=1 \
|
||||
--output_dir="sd-pokemon-model"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Training with Min-SNR weighting
|
||||
|
||||
We support training with the Min-SNR weighting strategy proposed in [Efficient Diffusion Training via Min-SNR Weighting Strategy](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.09556) which helps to achieve faster convergence
|
||||
by rebalancing the loss. In order to use it, one needs to set the `--snr_gamma` argument. The recommended
|
||||
value when using it is 5.0.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find [this project on Weights and Biases](https://wandb.ai/sayakpaul/text2image-finetune-minsnr) that compares the loss surfaces of the following setups:
|
||||
|
||||
* Training without the Min-SNR weighting strategy
|
||||
* Training with the Min-SNR weighting strategy (`snr_gamma` set to 5.0)
|
||||
* Training with the Min-SNR weighting strategy (`snr_gamma` set to 1.0)
|
||||
|
||||
For our small Pokemons dataset, the effects of Min-SNR weighting strategy might not appear to be pronounced, but for larger datasets, we believe the effects will be more pronounced.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, note that in this example, we either predict `epsilon` (i.e., the noise) or the `v_prediction`. For both of these cases, the formulation of the Min-SNR weighting strategy that we have used holds.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Training with Min-SNR weighting strategy is only supported in PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models (LoRA), a fine-tuning technique for accelerating training large models, for fine-tuning text-to-image models. For more details, take a look at the [LoRA training](lora#text-to-image) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can load the fine-tuned model for inference by passing the model path or model name on the Hub to the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_path = "path_to_saved_model"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_path, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt="yoda").images[0]
|
||||
image.save("yoda-pokemon.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import jax
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from flax.jax_utils import replicate
|
||||
from flax.training.common_utils import shard
|
||||
from diffusers import FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_path = "path_to_saved_model"
|
||||
pipe, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_path, dtype=jax.numpy.bfloat16)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "yoda pokemon"
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 50
|
||||
|
||||
num_samples = jax.device_count()
|
||||
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
|
||||
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
# shard inputs and rng
|
||||
params = replicate(params)
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.split(prng_seed, jax.device_count())
|
||||
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
|
||||
images = pipeline.numpy_to_pil(np.asarray(images.reshape((num_samples,) + images.shape[-3:])))
|
||||
image.save("yoda-pokemon.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,85 +14,74 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Textual Inversion
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
[Textual Inversion](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.01618) is a technique for capturing novel concepts from a small number of example images. While the technique was originally demonstrated with a [latent diffusion model](https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion), it has since been applied to other model variants like [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/conceptual/stable_diffusion). The learned concepts can be used to better control the images generated from text-to-image pipelines. It learns new "words" in the text encoder's embedding space, which are used within text prompts for personalized image generation.
|
||||
Textual Inversion is a technique for capturing novel concepts from a small number of example images in a way that can later be used to control text-to-image pipelines. It does so by learning new 'words' in the embedding space of the pipeline's text encoder. These special words can then be used within text prompts to achieve very fine-grained control of the resulting images.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
<small>By using just 3-5 images you can teach new concepts to a model such as Stable Diffusion for personalized image generation <a href="https://github.com/rinongal/textual_inversion">(image source)</a>.</small>
|
||||
_By using just 3-5 images you can teach new concepts to a model such as Stable Diffusion for personalized image generation ([image source](https://github.com/rinongal/textual_inversion))._
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to train a [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) model with Textual Inversion. All the training scripts for Textual Inversion used in this guide can be found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/textual_inversion) if you're interested in taking a closer look at how things work under the hood.
|
||||
This technique was introduced in [An Image is Worth One Word: Personalizing Text-to-Image Generation using Textual Inversion](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.01618). The paper demonstrated the concept using a [latent diffusion model](https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion) but the idea has since been applied to other variants such as [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/conceptual/stable_diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
There is a community-created collection of trained Textual Inversion models in the [Stable Diffusion Textual Inversion Concepts Library](https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library) which are readily available for inference. Over time, this'll hopefully grow into a useful resource as more concepts are added!
|
||||
## How It Works
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
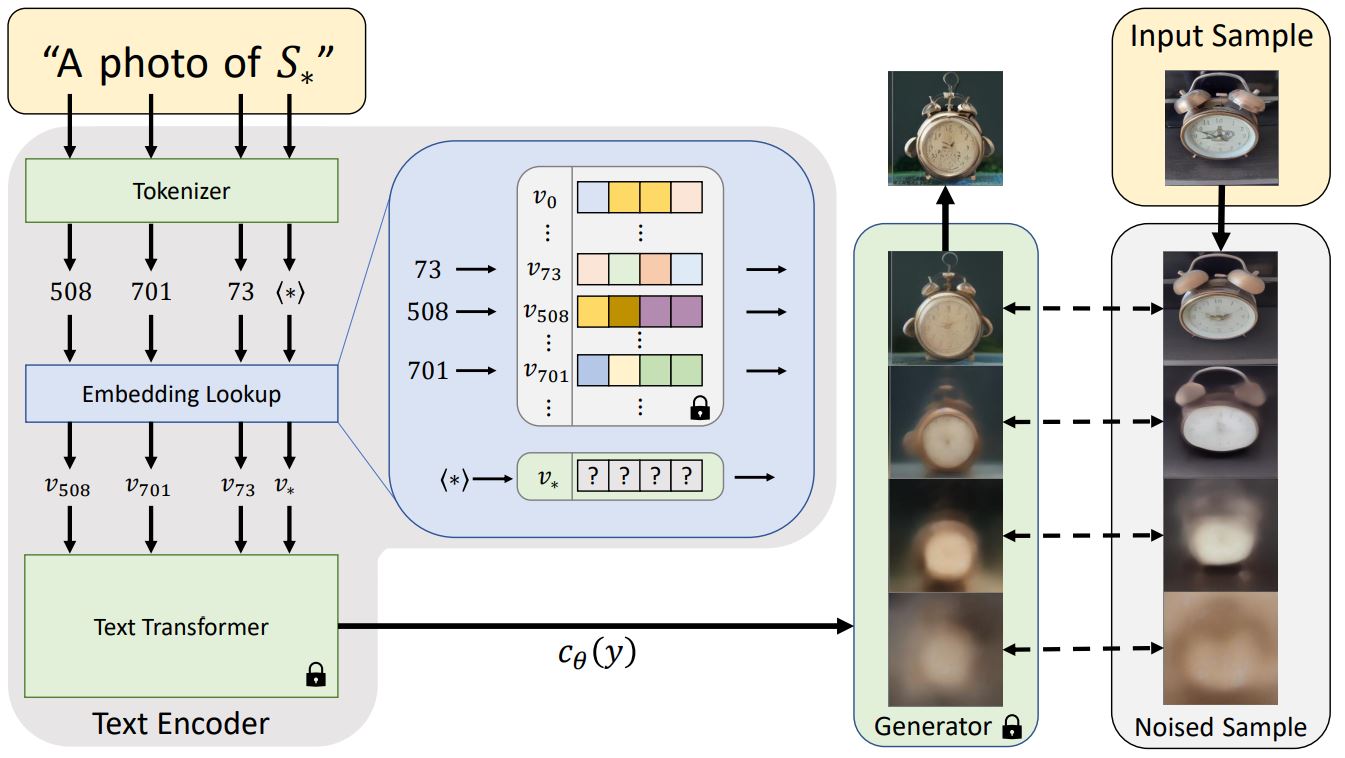
|
||||
_Architecture Overview from the [textual inversion blog post](https://textual-inversion.github.io/)_
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, make sure you install the library's training dependencies:
|
||||
Before a text prompt can be used in a diffusion model, it must first be processed into a numerical representation. This typically involves tokenizing the text, converting each token to an embedding and then feeding those embeddings through a model (typically a transformer) whose output will be used as the conditioning for the diffusion model.
|
||||
|
||||
Textual inversion learns a new token embedding (v* in the diagram above). A prompt (that includes a token which will be mapped to this new embedding) is used in conjunction with a noised version of one or more training images as inputs to the generator model, which attempts to predict the denoised version of the image. The embedding is optimized based on how well the model does at this task - an embedding that better captures the object or style shown by the training images will give more useful information to the diffusion model and thus result in a lower denoising loss. After many steps (typically several thousand) with a variety of prompt and image variants the learned embedding should hopefully capture the essence of the new concept being taught.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
To train your own textual inversions, see the [example script here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/textual_inversion).
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a notebook for training:
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/sd_textual_inversion_training.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
And one for inference:
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/stable_conceptualizer_inference.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to using concepts you have trained yourself, there is a community-created collection of trained textual inversions in the new [Stable Diffusion public concepts library](https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library) which you can also use from the inference notebook above. Over time this will hopefully grow into a useful resource as more examples are added.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example: Running locally
|
||||
|
||||
The `textual_inversion.py` script [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/textual_inversion) shows how to implement the training procedure and adapt it for stable diffusion.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing the dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the scripts, make sure to install the library's training dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install diffusers accelerate transformers
|
||||
pip install diffusers[training] accelerate transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After all the dependencies have been set up, initialize a [🤗Accelerate](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/) environment with:
|
||||
And initialize an [🤗Accelerate](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/) environment with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To setup a default 🤗 Accelerate environment without choosing any configurations:
|
||||
|
||||
### Cat toy example
|
||||
|
||||
You need to accept the model license before downloading or using the weights. In this example we'll use model version `v1-4`, so you'll need to visit [its card](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4), read the license and tick the checkbox if you agree.
|
||||
|
||||
You have to be a registered user in 🤗 Hugging Face Hub, and you'll also need to use an access token for the code to work. For more information on access tokens, please refer to [this section of the documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-tokens).
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command to authenticate your token
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config default
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
If you have already cloned the repo, then you won't need to go through these steps.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
```
|
||||
Now let's get our dataset.Download 3-4 images from [here](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1fmJMs25nxS_rSNqS5hTcRdLem_YQXbq5) and save them in a directory. This will be our training data.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you try and [install xFormers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/training/optimization/xformers) to reduce your memory footprint with xFormers memory-efficient attention. Once you have xFormers installed, add the `--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention` argument to the training script. xFormers is not supported for Flax.
|
||||
And launch the training using
|
||||
|
||||
## Upload model to Hub
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to store your model on the Hub, add the following argument to the training script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Save and load checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
It is often a good idea to regularly save checkpoints of your model during training. This way, you can resume training from a saved checkpoint if your training is interrupted for any reason. To save a checkpoint, pass the following argument to the training script to save the full training state in a subfolder in `output_dir` every 500 steps:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=500
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To resume training from a saved checkpoint, pass the following argument to the training script and the specific checkpoint you'd like to resume from:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--resume_from_checkpoint="checkpoint-1500"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Finetuning
|
||||
|
||||
For your training dataset, download these [images of a cat statue](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1fmJMs25nxS_rSNqS5hTcRdLem_YQXbq5) and store them in a directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Set the `MODEL_NAME` environment variable to the model repository id, and the `DATA_DIR` environment variable to the path of the directory containing the images. Now you can launch the [training script](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/textual_inversion/textual_inversion.py):
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 A full training run takes ~1 hour on one V100 GPU. While you're waiting for the training to complete, feel free to check out [how Textual Inversion works](#how-it-works) in the section below if you're curious!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export DATA_DIR="path-to-dir-containing-images"
|
||||
@@ -111,142 +100,23 @@ accelerate launch textual_inversion.py \
|
||||
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--output_dir="textual_inversion_cat"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
If you have access to TPUs, try out the [Flax training script](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/textual_inversion/textual_inversion_flax.py) to train even faster (this'll also work for GPUs). With the same configuration settings, the Flax training script should be at least 70% faster than the PyTorch training script! ⚡️
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, make sure you install the Flax specific dependencies:
|
||||
A full training run takes ~1 hour on one V100 GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -U -r requirements_flax.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can launch the [training script](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/textual_inversion/textual_inversion_flax.py):
|
||||
### Inference
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="duongna/stable-diffusion-v1-4-flax"
|
||||
export DATA_DIR="path-to-dir-containing-images"
|
||||
Once you have trained a model using above command, the inference can be done simply using the `StableDiffusionPipeline`. Make sure to include the `placeholder_token` in your prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
python textual_inversion_flax.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--train_data_dir=$DATA_DIR \
|
||||
--learnable_property="object" \
|
||||
--placeholder_token="<cat-toy>" --initializer_token="toy" \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=3000 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=5.0e-04 --scale_lr \
|
||||
--output_dir="textual_inversion_cat"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
### Intermediate logging
|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in following along with your model training progress, you can save the generated images from the training process. Add the following arguments to the training script to enable intermediate logging:
|
||||
|
||||
- `validation_prompt`, the prompt used to generate samples (this is set to `None` by default and intermediate logging is disabled)
|
||||
- `num_validation_images`, the number of sample images to generate
|
||||
- `validation_steps`, the number of steps before generating `num_validation_images` from the `validation_prompt`
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--validation_prompt="A <cat-toy> backpack"
|
||||
--num_validation_images=4
|
||||
--validation_steps=100
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have trained a model, you can use it for inference with the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
The textual inversion script will by default only save the textual inversion embedding vector(s) that have
|
||||
been added to the text encoder embedding matrix and consequently been trained.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 The community has created a large library of different textual inversion embedding vectors, called [sd-concepts-library](https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library).
|
||||
Instead of training textual inversion embeddings from scratch you can also see whether a fitting textual inversion embedding has already been added to the libary.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To load the textual inversion embeddings you first need to load the base model that was used when training
|
||||
your textual inversion embedding vectors. Here we assume that [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)
|
||||
was used as a base model so we load it first:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
model_id = "path-to-your-trained-model"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we need to load the textual inversion embedding vector which can be done via the [`TextualInversionLoaderMixin.load_textual_inversion`]
|
||||
function. Here we'll load the embeddings of the "<cat-toy>" example from before.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe.load_textual_inversion("sd-concepts-library/cat-toy")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can run the pipeline making sure that the placeholder token `<cat-toy>` is used in our prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "A <cat-toy> backpack"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=50).images[0]
|
||||
image.save("cat-backpack.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The function [`TextualInversionLoaderMixin.load_textual_inversion`] can not only
|
||||
load textual embedding vectors saved in Diffusers' format, but also embedding vectors
|
||||
saved in [Automatic1111](https://github.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui) format.
|
||||
To do so, you can first download an embedding vector from [civitAI](https://civitai.com/models/3036?modelVersionId=8387)
|
||||
and then load it locally:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe.load_textual_inversion("./charturnerv2.pt")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
Currently there is no `load_textual_inversion` function for Flax so one has to make sure the textual inversion
|
||||
embedding vector is saved as part of the model after training.
|
||||
|
||||
The model can then be run just like any other Flax model:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import jax
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from flax.jax_utils import replicate
|
||||
from flax.training.common_utils import shard
|
||||
from diffusers import FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_path = "path-to-your-trained-model"
|
||||
pipe, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_path, dtype=jax.numpy.bfloat16)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A <cat-toy> backpack"
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 50
|
||||
|
||||
num_samples = jax.device_count()
|
||||
prompt = num_samples * [prompt]
|
||||
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=50, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# shard inputs and rng
|
||||
params = replicate(params)
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.split(prng_seed, jax.device_count())
|
||||
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
|
||||
images = pipeline.numpy_to_pil(np.asarray(images.reshape((num_samples,) + images.shape[-3:])))
|
||||
image.save("cat-backpack.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## How it works
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
<small>Architecture overview from the Textual Inversion <a href="https://textual-inversion.github.io/">blog post.</a></small>
|
||||
|
||||
Usually, text prompts are tokenized into an embedding before being passed to a model, which is often a transformer. Textual Inversion does something similar, but it learns a new token embedding, `v*`, from a special token `S*` in the diagram above. The model output is used to condition the diffusion model, which helps the diffusion model understand the prompt and new concepts from just a few example images.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this, Textual Inversion uses a generator model and noisy versions of the training images. The generator tries to predict less noisy versions of the images, and the token embedding `v*` is optimized based on how well the generator does. If the token embedding successfully captures the new concept, it gives more useful information to the diffusion model and helps create clearer images with less noise. This optimization process typically occurs after several thousand steps of exposure to a variety of prompt and image variants.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,79 +10,29 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Unconditional image generation
|
||||
# Unconditional Image-Generation
|
||||
|
||||
Unconditional image generation is not conditioned on any text or images, unlike text- or image-to-image models. It only generates images that resemble its training data distribution.
|
||||
In this section, we explain how one can train an unconditional image generation diffusion
|
||||
model. "Unconditional" because the model is not conditioned on any context to generate an image - once trained the model will simply generate images that resemble its training data
|
||||
distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://stevhliu-ddpm-butterflies-128.hf.space"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="550"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
## Installing the dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to train an unconditional image generation model on existing datasets as well as your own custom dataset. All the training scripts for unconditional image generation can be found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/unconditional_image_generation) if you're interested in learning more about the training details.
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the script, make sure you install the library's training dependencies:
|
||||
Before running the scripts, make sure to install the library's training dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install diffusers[training] accelerate datasets
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, initialize an 🤗 [Accelerate](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/) environment with:
|
||||
And initialize an [🤗Accelerate](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/) environment with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To setup a default 🤗 Accelerate environment without choosing any configurations:
|
||||
## Unconditional Flowers
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config default
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Upload model to Hub
|
||||
|
||||
You can upload your model on the Hub by adding the following argument to the training script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Save and load checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
It is a good idea to regularly save checkpoints in case anything happens during training. To save a checkpoint, pass the following argument to the training script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=500
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The full training state is saved in a subfolder in the `output_dir` every 500 steps, which allows you to load a checkpoint and resume training if you pass the `--resume_from_checkpoint` argument to the training script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--resume_from_checkpoint="checkpoint-1500"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Finetuning
|
||||
|
||||
You're ready to launch the [training script](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/unconditional_image_generation/train_unconditional.py) now! Specify the dataset name to finetune on with the `--dataset_name` argument and then save it to the path in `--output_dir`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 A full training run takes 2 hours on 4xV100 GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to finetune on the [Oxford Flowers](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggan/flowers-102-categories) dataset:
|
||||
The command to train a DDPM UNet model on the Oxford Flowers dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch train_unconditional.py \
|
||||
@@ -97,12 +47,15 @@ accelerate launch train_unconditional.py \
|
||||
--mixed_precision=no \
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
An example trained model: https://huggingface.co/anton-l/ddpm-ema-flowers-64
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26864830/180248660-a0b143d0-b89a-42c5-8656-2ebf6ece7e52.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
A full training run takes 2 hours on 4xV100 GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
Or if you want to train your model on the [Pokemon](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggan/pokemon) dataset:
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26864830/180248660-a0b143d0-b89a-42c5-8656-2ebf6ece7e52.png" width="700" />
|
||||
|
||||
## Unconditional Pokemon
|
||||
|
||||
The command to train a DDPM UNet model on the Pokemon dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch train_unconditional.py \
|
||||
@@ -117,29 +70,26 @@ accelerate launch train_unconditional.py \
|
||||
--mixed_precision=no \
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
An example trained model: https://huggingface.co/anton-l/ddpm-ema-pokemon-64
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26864830/180248200-928953b4-db38-48db-b0c6-8b740fe6786f.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
A full training run takes 2 hours on 4xV100 GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Finetuning with your own data
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26864830/180248200-928953b4-db38-48db-b0c6-8b740fe6786f.png" width="700" />
|
||||
|
||||
There are two ways to finetune a model on your own dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
- provide your own folder of images to the `--train_data_dir` argument
|
||||
- upload your dataset to the Hub and pass the dataset repository id to the `--dataset_name` argument.
|
||||
## Using your own data
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
To use your own dataset, there are 2 ways:
|
||||
- you can either provide your own folder as `--train_data_dir`
|
||||
- or you can upload your dataset to the hub (possibly as a private repo, if you prefer so), and simply pass the `--dataset_name` argument.
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Learn more about how to create an image dataset for training in the [Create an image dataset](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/image_dataset) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
**Note**: If you want to create your own training dataset please have a look at [this document](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/image_process#image-datasets).
|
||||
|
||||
Below, we explain both in more detail.
|
||||
|
||||
### Provide the dataset as a folder
|
||||
|
||||
If you provide your own dataset as a folder, the script expects the following directory structure:
|
||||
If you provide your own folders with images, the script expects the following directory structure:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
data_dir/xxx.png
|
||||
@@ -147,7 +97,7 @@ data_dir/xxy.png
|
||||
data_dir/[...]/xxz.png
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pass the path to the folder containing the images to the `--train_data_dir` argument and launch the training:
|
||||
In other words, the script will take care of gathering all images inside the folder. You can then run the script like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch train_unconditional.py \
|
||||
@@ -155,17 +105,11 @@ accelerate launch train_unconditional.py \
|
||||
<other-arguments>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Internally, the script uses the [`ImageFolder`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/image_load#imagefolder) to automatically build a dataset from the folder.
|
||||
Internally, the script will use the [`ImageFolder`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/v2.0.0/en/image_process#imagefolder) feature which will automatically turn the folders into 🤗 Dataset objects.
|
||||
|
||||
### Upload your data to the Hub
|
||||
### Upload your data to the hub, as a (possibly private) repo
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 For more details and context about creating and uploading a dataset to the Hub, take a look at the [Image search with 🤗 Datasets](https://huggingface.co/blog/image-search-datasets) post.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To upload your dataset to the Hub, you can start by creating one with the [`ImageFolder`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/image_load#imagefolder) feature, which creates an `image` column containing the PIL-encoded images, from 🤗 Datasets:
|
||||
It's very easy (and convenient) to upload your image dataset to the hub using the [`ImageFolder`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/v2.0.0/en/image_process#imagefolder) feature available in 🤗 Datasets. Simply do the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
@@ -188,7 +132,9 @@ dataset = load_dataset(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can use the [`~datasets.Dataset.push_to_hub`] method to upload it to the Hub:
|
||||
`ImageFolder` will create an `image` column containing the PIL-encoded images.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, push it to the hub!
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# assuming you have ran the huggingface-cli login command in a terminal
|
||||
@@ -198,4 +144,6 @@ dataset.push_to_hub("name_of_your_dataset")
|
||||
dataset.push_to_hub("name_of_your_dataset", private=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now train your model by simply setting the `--dataset_name` argument to the name of your dataset on the Hub.
|
||||
and that's it! You can now train your model by simply setting the `--dataset_name` argument to the name of your dataset on the hub.
|
||||
|
||||
More on this can also be found in [this blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/image-search-datasets).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,415 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
# Train a diffusion model
|
||||
|
||||
Unconditional image generation is a popular application of diffusion models that generates images that look like those in the dataset used for training. Typically, the best results are obtained from finetuning a pretrained model on a specific dataset. You can find many of these checkpoints on the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/search/full-text?q=unconditional-image-generation&type=model), but if you can't find one you like, you can always train your own!
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will teach you how to train a [`UNet2DModel`] from scratch on a subset of the [Smithsonian Butterflies](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggan/smithsonian_butterflies_subset) dataset to generate your own 🦋 butterflies 🦋.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 This training tutorial is based on the [Training with 🧨 Diffusers](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/training_example.ipynb) notebook. For additional details and context about diffusion models like how they work, check out the notebook!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, make sure you have 🤗 Datasets installed to load and preprocess image datasets, and 🤗 Accelerate, to simplify training on any number of GPUs. The following command will also install [TensorBoard](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard) to visualize training metrics (you can also use [Weights & Biases](https://docs.wandb.ai/) to track your training).
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
!pip install diffusers[training]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We encourage you to share your model with the community, and in order to do that, you'll need to login to your Hugging Face account (create one [here](https://hf.co/join) if you don't already have one!). You can login from a notebook and enter your token when prompted:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
>>> notebook_login()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or login in from the terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Since the model checkpoints are quite large, install [Git-LFS](https://git-lfs.com/) to version these large files:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
!sudo apt -qq install git-lfs
|
||||
!git config --global credential.helper store
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Training configuration
|
||||
|
||||
For convenience, create a `TrainingConfig` class containing the training hyperparameters (feel free to adjust them):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> @dataclass
|
||||
... class TrainingConfig:
|
||||
... image_size = 128 # the generated image resolution
|
||||
... train_batch_size = 16
|
||||
... eval_batch_size = 16 # how many images to sample during evaluation
|
||||
... num_epochs = 50
|
||||
... gradient_accumulation_steps = 1
|
||||
... learning_rate = 1e-4
|
||||
... lr_warmup_steps = 500
|
||||
... save_image_epochs = 10
|
||||
... save_model_epochs = 30
|
||||
... mixed_precision = "fp16" # `no` for float32, `fp16` for automatic mixed precision
|
||||
... output_dir = "ddpm-butterflies-128" # the model name locally and on the HF Hub
|
||||
|
||||
... push_to_hub = True # whether to upload the saved model to the HF Hub
|
||||
... hub_private_repo = False
|
||||
... overwrite_output_dir = True # overwrite the old model when re-running the notebook
|
||||
... seed = 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = TrainingConfig()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Load the dataset
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily load the [Smithsonian Butterflies](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggan/smithsonian_butterflies_subset) dataset with the 🤗 Datasets library:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config.dataset_name = "huggan/smithsonian_butterflies_subset"
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset(config.dataset_name, split="train")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 You can find additional datasets from the [HugGan Community Event](https://huggingface.co/huggan) or you can use your own dataset by creating a local [`ImageFolder`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/image_dataset#imagefolder). Set `config.dataset_name` to the repository id of the dataset if it is from the HugGan Community Event, or `imagefolder` if you're using your own images.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Datasets uses the [`~datasets.Image`] feature to automatically decode the image data and load it as a [`PIL.Image`](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/Image.html) which we can visualize:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 4, figsize=(16, 4))
|
||||
>>> for i, image in enumerate(dataset[:4]["image"]):
|
||||
... axs[i].imshow(image)
|
||||
... axs[i].set_axis_off()
|
||||
>>> fig.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/butterflies_ds.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
The images are all different sizes though, so you'll need to preprocess them first:
|
||||
|
||||
* `Resize` changes the image size to the one defined in `config.image_size`.
|
||||
* `RandomHorizontalFlip` augments the dataset by randomly mirroring the images.
|
||||
* `Normalize` is important to rescale the pixel values into a [-1, 1] range, which is what the model expects.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from torchvision import transforms
|
||||
|
||||
>>> preprocess = transforms.Compose(
|
||||
... [
|
||||
... transforms.Resize((config.image_size, config.image_size)),
|
||||
... transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
|
||||
... transforms.ToTensor(),
|
||||
... transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5]),
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets' [`~datasets.Dataset.set_transform`] method to apply the `preprocess` function on the fly during training:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def transform(examples):
|
||||
... images = [preprocess(image.convert("RGB")) for image in examples["image"]]
|
||||
... return {"images": images}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset.set_transform(transform)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to visualize the images again to confirm that they've been resized. Now you're ready to wrap the dataset in a [DataLoader](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/data#torch.utils.data.DataLoader) for training!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> train_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=config.train_batch_size, shuffle=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a UNet2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
Pretrained models in 🧨 Diffusers are easily created from their model class with the parameters you want. For example, to create a [`UNet2DModel`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import UNet2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = UNet2DModel(
|
||||
... sample_size=config.image_size, # the target image resolution
|
||||
... in_channels=3, # the number of input channels, 3 for RGB images
|
||||
... out_channels=3, # the number of output channels
|
||||
... layers_per_block=2, # how many ResNet layers to use per UNet block
|
||||
... block_out_channels=(128, 128, 256, 256, 512, 512), # the number of output channels for each UNet block
|
||||
... down_block_types=(
|
||||
... "DownBlock2D", # a regular ResNet downsampling block
|
||||
... "DownBlock2D",
|
||||
... "DownBlock2D",
|
||||
... "DownBlock2D",
|
||||
... "AttnDownBlock2D", # a ResNet downsampling block with spatial self-attention
|
||||
... "DownBlock2D",
|
||||
... ),
|
||||
... up_block_types=(
|
||||
... "UpBlock2D", # a regular ResNet upsampling block
|
||||
... "AttnUpBlock2D", # a ResNet upsampling block with spatial self-attention
|
||||
... "UpBlock2D",
|
||||
... "UpBlock2D",
|
||||
... "UpBlock2D",
|
||||
... "UpBlock2D",
|
||||
... ),
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is often a good idea to quickly check the sample image shape matches the model output shape:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> sample_image = dataset[0]["images"].unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
>>> print("Input shape:", sample_image.shape)
|
||||
Input shape: torch.Size([1, 3, 128, 128])
|
||||
|
||||
>>> print("Output shape:", model(sample_image, timestep=0).sample.shape)
|
||||
Output shape: torch.Size([1, 3, 128, 128])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Great! Next, you'll need a scheduler to add some noise to the image.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
The scheduler behaves differently depending on whether you're using the model for training or inference. During inference, the scheduler generates image from the noise. During training, the scheduler takes a model output - or a sample - from a specific point in the diffusion process and applies noise to the image according to a *noise schedule* and an *update rule*.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look at the [`DDPMScheduler`] and use the `add_noise` method to add some random noise to the `sample_image` from before:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from PIL import Image
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DDPMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> noise_scheduler = DDPMScheduler(num_train_timesteps=1000)
|
||||
>>> noise = torch.randn(sample_image.shape)
|
||||
>>> timesteps = torch.LongTensor([50])
|
||||
>>> noisy_image = noise_scheduler.add_noise(sample_image, noise, timesteps)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> Image.fromarray(((noisy_image.permute(0, 2, 3, 1) + 1.0) * 127.5).type(torch.uint8).numpy()[0])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/noisy_butterfly.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
The training objective of the model is to predict the noise added to the image. The loss at this step can be calculated by:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch.nn.functional as F
|
||||
|
||||
>>> noise_pred = model(noisy_image, timesteps).sample
|
||||
>>> loss = F.mse_loss(noise_pred, noise)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Train the model
|
||||
|
||||
By now, you have most of the pieces to start training the model and all that's left is putting everything together.
|
||||
|
||||
First, you'll need an optimizer and a learning rate scheduler:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers.optimization import get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup
|
||||
|
||||
>>> optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=config.learning_rate)
|
||||
>>> lr_scheduler = get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup(
|
||||
... optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
... num_warmup_steps=config.lr_warmup_steps,
|
||||
... num_training_steps=(len(train_dataloader) * config.num_epochs),
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, you'll need a way to evaluate the model. For evaluation, you can use the [`DDPMPipeline`] to generate a batch of sample images and save it as a grid:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DDPMPipeline
|
||||
>>> import math
|
||||
>>> import os
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def make_grid(images, rows, cols):
|
||||
... w, h = images[0].size
|
||||
... grid = Image.new("RGB", size=(cols * w, rows * h))
|
||||
... for i, image in enumerate(images):
|
||||
... grid.paste(image, box=(i % cols * w, i // cols * h))
|
||||
... return grid
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def evaluate(config, epoch, pipeline):
|
||||
... # Sample some images from random noise (this is the backward diffusion process).
|
||||
... # The default pipeline output type is `List[PIL.Image]`
|
||||
... images = pipeline(
|
||||
... batch_size=config.eval_batch_size,
|
||||
... generator=torch.manual_seed(config.seed),
|
||||
... ).images
|
||||
|
||||
... # Make a grid out of the images
|
||||
... image_grid = make_grid(images, rows=4, cols=4)
|
||||
|
||||
... # Save the images
|
||||
... test_dir = os.path.join(config.output_dir, "samples")
|
||||
... os.makedirs(test_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
... image_grid.save(f"{test_dir}/{epoch:04d}.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can wrap all these components together in a training loop with 🤗 Accelerate for easy TensorBoard logging, gradient accumulation, and mixed precision training. To upload the model to the Hub, write a function to get your repository name and information and then push it to the Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 The training loop below may look intimidating and long, but it'll be worth it later when you launch your training in just one line of code! If you can't wait and want to start generating images, feel free to copy and run the code below. You can always come back and examine the training loop more closely later, like when you're waiting for your model to finish training. 🤗
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
>>> from huggingface_hub import HfFolder, Repository, whoami
|
||||
>>> from tqdm.auto import tqdm
|
||||
>>> from pathlib import Path
|
||||
>>> import os
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def get_full_repo_name(model_id: str, organization: str = None, token: str = None):
|
||||
... if token is None:
|
||||
... token = HfFolder.get_token()
|
||||
... if organization is None:
|
||||
... username = whoami(token)["name"]
|
||||
... return f"{username}/{model_id}"
|
||||
... else:
|
||||
... return f"{organization}/{model_id}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def train_loop(config, model, noise_scheduler, optimizer, train_dataloader, lr_scheduler):
|
||||
... # Initialize accelerator and tensorboard logging
|
||||
... accelerator = Accelerator(
|
||||
... mixed_precision=config.mixed_precision,
|
||||
... gradient_accumulation_steps=config.gradient_accumulation_steps,
|
||||
... log_with="tensorboard",
|
||||
... logging_dir=os.path.join(config.output_dir, "logs"),
|
||||
... )
|
||||
... if accelerator.is_main_process:
|
||||
... if config.push_to_hub:
|
||||
... repo_name = get_full_repo_name(Path(config.output_dir).name)
|
||||
... repo = Repository(config.output_dir, clone_from=repo_name)
|
||||
... elif config.output_dir is not None:
|
||||
... os.makedirs(config.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
... accelerator.init_trackers("train_example")
|
||||
|
||||
... # Prepare everything
|
||||
... # There is no specific order to remember, you just need to unpack the
|
||||
... # objects in the same order you gave them to the prepare method.
|
||||
... model, optimizer, train_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
... model, optimizer, train_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
... )
|
||||
|
||||
... global_step = 0
|
||||
|
||||
... # Now you train the model
|
||||
... for epoch in range(config.num_epochs):
|
||||
... progress_bar = tqdm(total=len(train_dataloader), disable=not accelerator.is_local_main_process)
|
||||
... progress_bar.set_description(f"Epoch {epoch}")
|
||||
|
||||
... for step, batch in enumerate(train_dataloader):
|
||||
... clean_images = batch["images"]
|
||||
... # Sample noise to add to the images
|
||||
... noise = torch.randn(clean_images.shape).to(clean_images.device)
|
||||
... bs = clean_images.shape[0]
|
||||
|
||||
... # Sample a random timestep for each image
|
||||
... timesteps = torch.randint(
|
||||
... 0, noise_scheduler.config.num_train_timesteps, (bs,), device=clean_images.device
|
||||
... ).long()
|
||||
|
||||
... # Add noise to the clean images according to the noise magnitude at each timestep
|
||||
... # (this is the forward diffusion process)
|
||||
... noisy_images = noise_scheduler.add_noise(clean_images, noise, timesteps)
|
||||
|
||||
... with accelerator.accumulate(model):
|
||||
... # Predict the noise residual
|
||||
... noise_pred = model(noisy_images, timesteps, return_dict=False)[0]
|
||||
... loss = F.mse_loss(noise_pred, noise)
|
||||
... accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
... accelerator.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), 1.0)
|
||||
... optimizer.step()
|
||||
... lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
... optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
|
||||
... progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
... logs = {"loss": loss.detach().item(), "lr": lr_scheduler.get_last_lr()[0], "step": global_step}
|
||||
... progress_bar.set_postfix(**logs)
|
||||
... accelerator.log(logs, step=global_step)
|
||||
... global_step += 1
|
||||
|
||||
... # After each epoch you optionally sample some demo images with evaluate() and save the model
|
||||
... if accelerator.is_main_process:
|
||||
... pipeline = DDPMPipeline(unet=accelerator.unwrap_model(model), scheduler=noise_scheduler)
|
||||
|
||||
... if (epoch + 1) % config.save_image_epochs == 0 or epoch == config.num_epochs - 1:
|
||||
... evaluate(config, epoch, pipeline)
|
||||
|
||||
... if (epoch + 1) % config.save_model_epochs == 0 or epoch == config.num_epochs - 1:
|
||||
... if config.push_to_hub:
|
||||
... repo.push_to_hub(commit_message=f"Epoch {epoch}", blocking=True)
|
||||
... else:
|
||||
... pipeline.save_pretrained(config.output_dir)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Phew, that was quite a bit of code! But you're finally ready to launch the training with 🤗 Accelerate's [`~accelerate.notebook_launcher`] function. Pass the function the training loop, all the training arguments, and the number of processes (you can change this value to the number of GPUs available to you) to use for training:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import notebook_launcher
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = (config, model, noise_scheduler, optimizer, train_dataloader, lr_scheduler)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> notebook_launcher(train_loop, args, num_processes=1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once training is complete, take a look at the final 🦋 images 🦋 generated by your diffusion model!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import glob
|
||||
|
||||
>>> sample_images = sorted(glob.glob(f"{config.output_dir}/samples/*.png"))
|
||||
>>> Image.open(sample_images[-1])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/butterflies_final.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
Unconditional image generation is one example of a task that can be trained. You can explore other tasks and training techniques by visiting the [🧨 Diffusers Training Examples](./training/overview) page. Here are some examples of what you can learn:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Textual Inversion](./training/text_inversion), an algorithm that teaches a model a specific visual concept and integrates it into the generated image.
|
||||
* [DreamBooth](./training/dreambooth), a technique for generating personalized images of a subject given several input images of the subject.
|
||||
* [Guide](./training/text2image) to finetuning a Stable Diffusion model on your own dataset.
|
||||
* [Guide](./training/lora) to using LoRA, a memory-efficient technique for finetuning really large models faster.
|
||||
@@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Welcome to 🧨 Diffusers! If you're new to diffusion models and generative AI, and want to learn more, then you've come to the right place. These beginner-friendly tutorials are designed to provide a gentle introduction to diffusion models and help you understand the library fundamentals - the core components and how 🧨 Diffusers is meant to be used.
|
||||
|
||||
You'll learn how to use a pipeline for inference to rapidly generate things, and then deconstruct that pipeline to really understand how to use the library as a modular toolbox for building your own diffusion systems. In the next lesson, you'll learn how to train your own diffusion model to generate what you want.
|
||||
|
||||
After completing the tutorials, you'll have gained the necessary skills to start exploring the library on your own and see how to use it for your own projects and applications.
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to join our community on [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/JfAtkvEtRb) or the [forums](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) to connect and collaborate with other users and developers!
|
||||
|
||||
Let's start diffusing! 🧨
|
||||
@@ -10,27 +10,22 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Conditional image generation
|
||||
# Conditional Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] is the easiest way to use a pre-trained diffusion system for inference
|
||||
|
||||
Conditional image generation allows you to generate images from a text prompt. The text is converted into embeddings which are used to condition the model to generate an image from noise.
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] is the easiest way to use a pre-trained diffusion system for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
Start by creating an instance of [`DiffusionPipeline`] and specify which pipeline [checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads) you would like to download.
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, you'll use [`DiffusionPipeline`] for text-to-image generation with [Latent Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/ldm-text2im-large-256):
|
||||
Start by creating an instance of [`DiffusionPipeline`] and specify which pipeline checkpoint you would like to download.
|
||||
You can use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] for any [Diffusers' checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads).
|
||||
In this guide though, you'll use [`DiffusionPipeline`] for text-to-image generation with [Latent Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/ldm-text2im-large-256):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> generator = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("CompVis/ldm-text2im-large-256")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] downloads and caches all modeling, tokenization, and scheduling components.
|
||||
Because the model consists of roughly 1.4 billion parameters, we strongly recommend running it on a GPU.
|
||||
You can move the generator object to a GPU, just like you would in PyTorch:
|
||||
Because the model consists of roughly 1.4 billion parameters, we strongly recommend running it on GPU.
|
||||
You can move the generator object to GPU, just like you would in PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> generator.to("cuda")
|
||||
@@ -42,19 +37,10 @@ Now you can use the `generator` on your text prompt:
|
||||
>>> image = generator("An image of a squirrel in Picasso style").images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The output is by default wrapped into a [`PIL.Image`](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/Image.html?highlight=image#the-image-class) object.
|
||||
The output is by default wrapped into a [PIL Image object](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/Image.html?highlight=image#the-image-class).
|
||||
|
||||
You can save the image by calling:
|
||||
You can save the image by simply calling:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> image.save("image_of_squirrel_painting.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Try out the Spaces below, and feel free to play around with the guidance scale parameter to see how it affects the image quality!
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://stabilityai-stable-diffusion.hf.space"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="500"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
21
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/configuration.mdx
Normal file
21
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/configuration.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
The handling of configurations in Diffusers is with the `ConfigMixin` class.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ConfigMixin
|
||||
|
||||
Under further construction 🚧, open a [PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/compare) if you want to contribute!
|
||||
@@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self):
|
||||
image = torch.randn(
|
||||
(1, self.unet.config.in_channels, self.unet.config.sample_size, self.unet.config.sample_size),
|
||||
(1, self.unet.in_channels, self.unet.sample_size, self.unet.sample_size),
|
||||
)
|
||||
timestep = 1
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -108,7 +108,7 @@ class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self):
|
||||
image = torch.randn(
|
||||
(1, self.unet.config.in_channels, self.unet.config.sample_size, self.unet.config.sample_size),
|
||||
(1, self.unet.in_channels, self.unet.sample_size, self.unet.sample_size),
|
||||
)
|
||||
timestep = 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Controlled generation
|
||||
# Controlling generation of diffusion models
|
||||
|
||||
Controlling outputs generated by diffusion models has been long pursued by the community and is now an active research topic. In many popular diffusion models, subtle changes in inputs, both images and text prompts, can drastically change outputs. In an ideal world we want to be able to control how semantics are preserved and changed.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,7 +36,6 @@ Unless otherwise mentioned, these are techniques that work with existing models
|
||||
8. [DreamBooth](#dreambooth)
|
||||
9. [Textual Inversion](#textual-inversion)
|
||||
10. [ControlNet](#controlnet)
|
||||
11. [Prompt Weighting](#prompt-weighting)
|
||||
|
||||
## Instruct Pix2Pix
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -63,7 +62,7 @@ Next, we generate image captions for the concept that shall be edited and for th
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Pix2Pix Zero is the first model that allows "zero-shot" image editing. This means that the model
|
||||
can edit an image in less than a minute on a consumer GPU as shown [here](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero#usage-example).
|
||||
can edit an image in less than a minute on a consumer GPU as shown [here](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero#usage-example)
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -159,9 +158,3 @@ depth maps, and semantic segmentations.
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/controlnet) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prompt Weighting
|
||||
|
||||
Prompt weighting is a simple technique that puts more attention weight on certain parts of the text
|
||||
input.
|
||||
|
||||
For a more in-detail explanation and examples, see [here](../using-diffusers/weighted_prompts).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -45,11 +45,11 @@ The following code requires roughly 12GB of GPU RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPImageProcessor, CLIPModel
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor, CLIPModel
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPImageProcessor.from_pretrained("laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K")
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained("laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K")
|
||||
clip_model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ is safe 🔒. Make sure to check out the code online before loading & running it
|
||||
|
||||
## Loading official community pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipelines are summarized in the [community examples folder](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community).
|
||||
Community pipelines are summarized in the [community examples folder](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community)
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, you need to pass both the *repo id* from where you wish to load the weights as well as the `custom_pipeline` argument. Here the `custom_pipeline` argument should consist simply of the filename of the community pipeline excluding the `.py` suffix, *e.g.* `clip_guided_stable_diffusion`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -50,11 +50,11 @@ and passing pipeline modules directly.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPImageProcessor, CLIPModel
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor, CLIPModel
|
||||
|
||||
clip_model_id = "laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K"
|
||||
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPImageProcessor.from_pretrained(clip_model_id)
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(clip_model_id)
|
||||
clip_model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained(clip_model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
@@ -89,9 +89,7 @@ class MyPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def __call__(self, batch_size: int = 1, num_inference_steps: int = 50):
|
||||
# Sample gaussian noise to begin loop
|
||||
image = torch.randn(
|
||||
(batch_size, self.unet.config.in_channels, self.unet.config.sample_size, self.unet.config.sample_size)
|
||||
)
|
||||
image = torch.randn((batch_size, self.unet.in_channels, self.unet.sample_size, self.unet.sample_size))
|
||||
|
||||
image = image.to(self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,13 +10,9 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Text-guided depth-to-image generation
|
||||
# Text-Guided Image-to-Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
The [`StableDiffusionDepth2ImgPipeline`] lets you pass a text prompt and an initial image to condition the generation of new images. In addition, you can also pass a `depth_map` to preserve the image structure. If no `depth_map` is provided, the pipeline automatically predicts the depth via an integrated [depth-estimation model](https://github.com/isl-org/MiDaS).
|
||||
|
||||
Start by creating an instance of the [`StableDiffusionDepth2ImgPipeline`]:
|
||||
The [`StableDiffusionDepth2ImgPipeline`] lets you pass a text prompt and an initial image to condition the generation of new images as well as a `depth_map` to preserve the images' structure. If no `depth_map` is provided, the pipeline will automatically predict the depth via an integrated depth-estimation model.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -29,28 +25,11 @@ pipe = StableDiffusionDepth2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-depth",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now pass your prompt to the pipeline. You can also pass a `negative_prompt` to prevent certain words from guiding how an image is generated:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
|
||||
init_image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
prompt = "two tigers"
|
||||
n_prompt = "bad, deformed, ugly, bad anatomy"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, negative_prompt=n_prompt, strength=0.7).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| Input | Output |
|
||||
|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| <img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/coco-cats.png" width="500"/> | <img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/depth2img-tigers.png" width="500"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
Play around with the Spaces below and see if you notice a difference between generated images with and without a depth map!
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://radames-stable-diffusion-depth2img.hf.space"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="500"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,90 +10,36 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Text-guided image-to-image generation
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
# Text-Guided Image-to-Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
The [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`] lets you pass a text prompt and an initial image to condition the generation of new images.
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, make sure you have all the necessary libraries installed:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
!pip install diffusers transformers ftfy accelerate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Get started by creating a [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`] with a pretrained Stable Diffusion model like [`nitrosocke/Ghibli-Diffusion`](https://huggingface.co/nitrosocke/Ghibli-Diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
# load the pipeline
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained("nitrosocke/Ghibli-Diffusion", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to(
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to(
|
||||
device
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Download and preprocess an initial image so you can pass it to the pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# let's download an initial image
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
init_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
init_image.thumbnail((768, 768))
|
||||
init_image
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, trending on artstation"
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, strength=0.75, guidance_scale=7.5).images
|
||||
|
||||
images[0].save("fantasy_landscape.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
You can also run this example on colab [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/image_2_image_using_diffusers.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/YiYiXu/test-doc-assets/resolve/main/image_2_image_using_diffusers_cell_8_output_0.jpeg"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 `strength` is a value between 0.0 and 1.0 that controls the amount of noise added to the input image. Values that approach 1.0 allow for lots of variations but will also produce images that are not semantically consistent with the input.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Define the prompt (for this checkpoint finetuned on Ghibli-style art, you need to prefix the prompt with the `ghibli style` tokens) and run the pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "ghibli style, a fantasy landscape with castles"
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device=device).manual_seed(1024)
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, strength=0.75, guidance_scale=7.5, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/ghibli-castles.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
You can also try experimenting with a different scheduler to see how that affects the output:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import LMSDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
lms = LMSDiscreteScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = lms
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device=device).manual_seed(1024)
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, strength=0.75, guidance_scale=7.5, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lms-ghibli.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the Spaces below, and try generating images with different values for `strength`. You'll notice that using lower values for `strength` produces images that are more similar to the original image.
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to also switch the scheduler to the [`LMSDiscreteScheduler`] and see how that affects the output.
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://stevhliu-ghibli-img2img.hf.space"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="500"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,13 +10,9 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Text-guided image-inpainting
|
||||
# Text-Guided Image-Inpainting
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
The [`StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline`] allows you to edit specific parts of an image by providing a mask and a text prompt. It uses a version of Stable Diffusion, like [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting) specifically trained for inpainting tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
Get started by loading an instance of the [`StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline`]:
|
||||
The [`StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline`] lets you edit specific parts of an image by providing a mask and a text prompt. It uses a version of Stable Diffusion specifically trained for in-painting tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
@@ -26,16 +22,7 @@ from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Download an image and a mask of a dog which you'll eventually replace:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def download_image(url):
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
return PIL.Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
@@ -46,31 +33,24 @@ mask_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = download_image(img_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
mask_image = download_image(mask_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can create a prompt to replace the mask with something else:
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "Face of a yellow cat, high resolution, sitting on a park bench"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`image` | `mask_image` | `prompt` | output |
|
||||
`image` | `mask_image` | `prompt` | **Output** |
|
||||
:-------------------------:|:-------------------------:|:-------------------------:|-------------------------:|
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo.png" alt="drawing" width="250"/> | <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo_mask.png" alt="drawing" width="250"/> | ***Face of a yellow cat, high resolution, sitting on a park bench*** | <img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/in_paint/yellow_cat_sitting_on_a_park_bench.png" alt="drawing" width="250"/> |
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo.png" alt="drawing" width="250"/> | <img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo_mask.png" alt="drawing" width="250"/> | ***Face of a yellow cat, high resolution, sitting on a park bench*** | <img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/patrickvonplaten/images/resolve/main/test.png" alt="drawing" width="250"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can also run this example on colab [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/in_painting_with_stable_diffusion_using_diffusers.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
A previous experimental implementation of inpainting used a different, lower-quality process. To ensure backwards compatibility, loading a pretrained pipeline that doesn't contain the new model will still apply the old inpainting method.
|
||||
|
||||
A previous experimental implementation of in-painting used a different, lower-quality process. To ensure backwards compatibility, loading a pretrained pipeline that doesn't contain the new model will still apply the old in-painting method.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the Spaces below to try out image inpainting yourself!
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://runwayml-stable-diffusion-inpainting.hf.space"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="500"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -97,7 +97,7 @@ Note that we're not specifying the UNet weights here since the UNet is not fine-
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
And that's it! You now have your fine-tuned KerasCV Stable Diffusion model in Diffusers 🧨.
|
||||
And that's it! You now have your fine-tuned KerasCV Stable Diffusion model in Diffusers 🧨
|
||||
|
||||
## Using the Converted Model in Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -176,4 +176,4 @@ more details. For inference-specific optimizations, refer [here](https://hugging
|
||||
|
||||
## Known Limitations
|
||||
|
||||
* Only Stable Diffusion v1 checkpoints are supported for conversion in this tool.
|
||||
* Only Stable Diffusion v1 checkpoints are supported for conversion in this tool.
|
||||
@@ -10,28 +10,20 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Load pipelines, models, and schedulers
|
||||
# Loading
|
||||
|
||||
Having an easy way to use a diffusion system for inference is essential to 🧨 Diffusers. Diffusion systems often consist of multiple components like parameterized models, tokenizers, and schedulers that interact in complex ways. That is why we designed the [`DiffusionPipeline`] to wrap the complexity of the entire diffusion system into an easy-to-use API, while remaining flexible enough to be adapted for other use cases, such as loading each component individually as building blocks to assemble your own diffusion system.
|
||||
A core premise of the diffusers library is to make diffusion models **as accessible as possible**.
|
||||
Accessibility is therefore achieved by providing an API to load complete diffusion pipelines as well as individual components with a single line of code.
|
||||
|
||||
Everything you need for inference or training is accessible with the `from_pretrained()` method.
|
||||
In the following we explain in-detail how to easily load:
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to load:
|
||||
- *Complete Diffusion Pipelines* via the [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`]
|
||||
- *Diffusion Models* via [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`]
|
||||
- *Schedulers* via [`SchedulerMixin.from_pretrained`]
|
||||
|
||||
- pipelines from the Hub and locally
|
||||
- different components into a pipeline
|
||||
- checkpoint variants such as different floating point types or non-exponential mean averaged (EMA) weights
|
||||
- models and schedulers
|
||||
## Loading pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
## Diffusion Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Skip to the [DiffusionPipeline explained](#diffusionpipeline-explained) section if you interested in learning in more detail about how the [`DiffusionPipeline`] class works.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] class is the simplest and most generic way to load any diffusion model from the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers). The [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method automatically detects the correct pipeline class from the checkpoint, downloads and caches all the required configuration and weight files, and returns a pipeline instance ready for inference.
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] class is the easiest way to access any diffusion model that is [available on the Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers). Let's look at an example on how to download [Runway's Stable Diffusion model](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -40,7 +32,10 @@ repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also load a checkpoint with it's specific pipeline class. The example above loaded a Stable Diffusion model; to get the same result, use the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] class:
|
||||
Here [`DiffusionPipeline`] automatically detects the correct pipeline (*i.e.* [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]), downloads and caches all required configuration and weight files (if not already done so), and finally returns a pipeline instance, called `pipe`.
|
||||
The pipeline instance can then be called using [`StableDiffusionPipeline.__call__`] (i.e., `pipe("image of a astronaut riding a horse")`) for text-to-image generation.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of using the generic [`DiffusionPipeline`] class for loading, you can also load the appropriate pipeline class directly. The code snippet above yields the same instance as when doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -49,7 +44,10 @@ repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A checkpoint (such as [`CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4`](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) or [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)) may also be used for more than one task, like text-to-image or image-to-image. To differentiate what task you want to use the checkpoint for, you have to load it directly with it's corresponding task-specific pipeline class:
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Many checkpoints, such as [CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) and [runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) can be used for multiple tasks, *e.g.* *text-to-image* or *image-to-image*.
|
||||
If you want to use those checkpoints for a task that is different from the default one, you have to load it directly from the corresponding task-specific pipeline class:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
@@ -58,16 +56,82 @@ repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Local pipeline
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To load a diffusion pipeline locally, use [`git-lfs`](https://git-lfs.github.com/) to manually download the checkpoint (in this case, [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)) to your local disk. This creates a local folder, `./stable-diffusion-v1-5`, on your disk:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
Diffusion pipelines like `StableDiffusionPipeline` or `StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline` consist of multiple components. These components can be both parameterized models, such as `"unet"`, `"vae"` and `"text_encoder"`, tokenizers or schedulers.
|
||||
These components often interact in complex ways with each other when using the pipeline in inference, *e.g.* for [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] the inference call is explained [here](https://huggingface.co/blog/stable_diffusion#how-does-stable-diffusion-work).
|
||||
The purpose of the [pipeline classes](./api/overview#diffusers-summary) is to wrap the complexity of these diffusion systems and give the user an easy-to-use API while staying flexible for customization, as will be shown later.
|
||||
|
||||
<!---
|
||||
THE FOLLOWING CAN BE UNCOMMENTED ONCE WE HAVE NEW MODELS WITH ACCESS REQUIREMENT
|
||||
|
||||
# Loading pipelines that require access request
|
||||
|
||||
Due to the capabilities of diffusion models to generate extremely realistic images, there is a certain danger that such models might be misused for unwanted applications, *e.g.* generating pornography or violent images.
|
||||
In order to minimize the possibility of such unsolicited use cases, some of the most powerful diffusion models require users to acknowledge a license before being able to use the model. If the user does not agree to the license, the pipeline cannot be downloaded.
|
||||
If you try to load [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) the same way as done previously:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
it will only work if you have both *click-accepted* the license on [the model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) and are logged into the Hugging Face Hub. Otherwise you will get an error message
|
||||
such as the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
OSError: runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5 is not a local folder and is not a valid model identifier listed on 'https://huggingface.co/models'
|
||||
If this is a private repository, make sure to pass a token having permission to this repo with `use_auth_token` or log in with `huggingface-cli login`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, we need to make sure to *click-accept* the license. You can do this by simply visiting
|
||||
the [model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) and clicking on "Agree and access repository":
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/huggingface/diffusers/main/docs/source/imgs/access_request.png" width="400"/>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Second, you need to login with your access token:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
before trying to load the model. Or alternatively, you can pass [your access token](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-tokens#user-access-tokens) directly via the flag `use_auth_token`. In this case you do **not** need
|
||||
to run `huggingface-cli login` before:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, use_auth_token="<your-access-token>")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The final option to use pipelines that require access without having to rely on the Hugging Face Hub is to load the pipeline locally as explained in the next section.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
### Loading pipelines locally
|
||||
|
||||
If you prefer to have complete control over the pipeline and its corresponding files or, as said before, if you want to use pipelines that require an access request without having to be connected to the Hugging Face Hub,
|
||||
we recommend loading pipelines locally.
|
||||
|
||||
To load a diffusion pipeline locally, you first need to manually download the whole folder structure on your local disk and then pass a local path to the [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`]. Let's again look at an example for
|
||||
[Runway's Stable Diffusion Diffusion model](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5).
|
||||
|
||||
First, you should make use of [`git-lfs`](https://git-lfs.github.com/) to download the whole folder structure that has been uploaded to the [model repository](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git lfs install
|
||||
git clone https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then pass the local path to [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
The command above will create a local folder called `./stable-diffusion-v1-5` on your disk.
|
||||
Now, all you have to do is to simply pass the local folder path to `from_pretrained`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -76,29 +140,17 @@ repo_id = "./stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method won't download any files from the Hub when it detects a local path, but this also means it won't download and cache the latest changes to a checkpoint.
|
||||
If `repo_id` is a local path, as it is the case here, [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] will automatically detect it and therefore not try to download any files from the Hub.
|
||||
While we usually recommend to load weights directly from the Hub to be certain to stay up to date with the newest changes, loading pipelines locally should be preferred if one
|
||||
wants to stay anonymous, self-contained applications, etc...
|
||||
|
||||
### Swap components in a pipeline
|
||||
### Loading customized pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize the default components of any pipeline with another compatible component. Customization is important because:
|
||||
Advanced users that want to load customized versions of diffusion pipelines can do so by swapping any of the default components, *e.g.* the scheduler, with other scheduler classes.
|
||||
A classical use case of this functionality is to swap the scheduler. [Stable Diffusion v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) uses the [`PNDMScheduler`] by default which is generally not the most performant scheduler. Since the release
|
||||
of stable diffusion, multiple improved schedulers have been published. To use those, the user has to manually load their preferred scheduler and pass it into [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`].
|
||||
|
||||
- Changing the scheduler is important for exploring the trade-off between generation speed and quality.
|
||||
- Different components of a model are typically trained independently and you can swap out a component with a better-performing one.
|
||||
- During finetuning, usually only some components - like the UNet or text encoder - are trained.
|
||||
|
||||
To find out which schedulers are compatible for customization, you can use the `compatibles` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
stable_diffusion.scheduler.compatibles
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's use the [`SchedulerMixin.from_pretrained`] method to replace the default [`PNDMScheduler`] with a more performant scheduler, [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`]. The `subfolder="scheduler"` argument is required to load the scheduler configuration from the correct [subfolder](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main/scheduler) of the pipeline repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can pass the new [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`] instance to the `scheduler` argument in [`DiffusionPipeline`]:
|
||||
*E.g.* to use [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`] or [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`] to have a better quality vs. generation speed trade-off for inference, one could load them as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, EulerDiscreteScheduler, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
@@ -106,24 +158,31 @@ from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, EulerDiscreteScheduler, DPMSolverMultis
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = EulerDiscreteScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
# or
|
||||
# scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, scheduler=scheduler)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Safety checker
|
||||
Three things are worth paying attention to here.
|
||||
- First, the scheduler is loaded with [`SchedulerMixin.from_pretrained`]
|
||||
- Second, the scheduler is loaded with a function argument, called `subfolder="scheduler"` as the configuration of stable diffusion's scheduling is defined in a [subfolder of the official pipeline repository](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main/scheduler)
|
||||
- Third, the scheduler instance can simply be passed with the `scheduler` keyword argument to [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`]. This works because the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] defines its scheduler with the `scheduler` attribute. It's not possible to use a different name, such as `sampler=scheduler` since `sampler` is not a defined keyword for [`StableDiffusionPipeline.__init__`]
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusion models like Stable Diffusion can generate harmful content, which is why 🧨 Diffusers has a [safety checker](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py) to check generated outputs against known hardcoded NSFW content. If you'd like to disable the safety checker for whatever reason, pass `None` to the `safety_checker` argument:
|
||||
Not only the scheduler components can be customized for diffusion pipelines; in theory, all components of a pipeline can be customized. In practice, however, it often only makes sense to switch out a component that has **compatible** alternatives to what the pipeline expects.
|
||||
Many scheduler classes are compatible with each other as can be seen [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/0dd8c6b4dbab4069de9ed1cafb53cbd495873879/src/diffusers/schedulers/scheduling_ddim.py#L112). This is not always the case for other components, such as the `"unet"`.
|
||||
|
||||
One special case that can also be customized is the `"safety_checker"` of stable diffusion. If you believe the safety checker doesn't serve you any good, you can simply disable it by passing `None`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, EulerDiscreteScheduler, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, safety_checker=None)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Reuse components across pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
You can also reuse the same components in multiple pipelines to avoid loading the weights into RAM twice. Use the [`~DiffusionPipeline.components`] method to save the components:
|
||||
Another common use case is to reuse the same components in multiple pipelines, *e.g.* the weights and configurations of [`"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) can be used for both [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] and [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`] and we might not want to
|
||||
use the exact same weights into RAM twice. In this case, customizing all the input instances would help us
|
||||
to only load the weights into RAM once:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
@@ -132,92 +191,349 @@ model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion_txt2img = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
components = stable_diffusion_txt2img.components
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can pass the `components` to another pipeline without reloading the weights into RAM:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# weights are not reloaded into RAM
|
||||
stable_diffusion_img2img = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline(**components)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also pass the components individually to the pipeline if you want more flexibility over which components to reuse or disable. For example, to reuse the same components in the text-to-image pipeline, except for the safety checker and feature extractor, in the image-to-image pipeline:
|
||||
Note how the above code snippet makes use of [`DiffusionPipeline.components`].
|
||||
|
||||
### Loading variants
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusion Pipeline checkpoints can offer variants of the "main" diffusion pipeline checkpoint.
|
||||
Such checkpoint variants are usually variations of the checkpoint that have advantages for specific use-cases and that are so similar to the "main" checkpoint that they **should not** be put in a new checkpoint.
|
||||
A variation of a checkpoint has to have **exactly** the same serialization format and **exactly** the same model structure, including all weights having the same tensor shapes.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of variations are different floating point types and non-ema weights. I.e. "fp16", "bf16", and "no_ema" are common variations.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Let's first talk about whats **not** checkpoint variant,
|
||||
|
||||
Checkpoint variants do **not** include different serialization formats (such as [safetensors](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/using-diffusers/using_safetensors)) as weights in different serialization formats are
|
||||
identical to the weights of the "main" checkpoint, just loaded in a different framework.
|
||||
|
||||
Also variants do not correspond to different model structures, *e.g.* [stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) is not a variant of [stable-diffusion-2-0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2) since the model structure is different (Stable Diffusion 1-5 uses a different `CLIPTextModel` compared to Stable Diffusion 2.0).
|
||||
|
||||
Pipeline checkpoints that are identical in model structure, but have been trained on different datasets, trained with vastly different training setups and thus correspond to different official releases (such as [Stable Diffusion v1-4](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) and [Stable Diffusion v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)) should probably be stored in individual repositories instead of as variations of eachother.
|
||||
|
||||
#### So what are checkpoint variants then?
|
||||
|
||||
Checkpoint variants usually consist of the checkpoint stored in "*low-precision, low-storage*" dtype so that less bandwith is required to download them, or of *non-exponential-averaged* weights that shall be used when continuing fine-tuning from the checkpoint.
|
||||
Both use cases have clear advantages when their weights are considered variants: they share the same serialization format as the reference weights, and they correspond to a specialization of the "main" checkpoint which does not warrant a new model repository.
|
||||
A checkpoint stored in [torch's half-precision / float16 format](https://pytorch.org/blog/accelerating-training-on-nvidia-gpus-with-pytorch-automatic-mixed-precision/) requires only half the bandwith and storage when downloading the checkpoint,
|
||||
**but** cannot be used when continuing training or when running the checkpoint on CPU.
|
||||
Similarly the *non-exponential-averaged* (or non-EMA) version of the checkpoint should be used when continuing fine-tuning of the model checkpoint, **but** should not be used when using the checkpoint for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
#### How to save and load variants
|
||||
|
||||
Saving a diffusion pipeline as a variant can be done by providing [`DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`] with the `variant` argument.
|
||||
The `variant` extends the weight name by the provided variation, by changing the default weight name from `diffusion_pytorch_model.bin` to `diffusion_pytorch_model.{variant}.bin` or from `diffusion_pytorch_model.safetensors` to `diffusion_pytorch_model.{variant}.safetensors`. By doing so, one creates a variant of the pipeline checkpoint that can be loaded **instead** of the "main" pipeline checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's have a look at how we could create a float16 variant of a pipeline. First, we load
|
||||
the "main" variant of a checkpoint (stored in `float32` precision) into mixed precision format, using `torch_dtype=torch.float16`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion_txt2img = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
stable_diffusion_img2img = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline(
|
||||
vae=stable_diffusion_txt2img.vae,
|
||||
text_encoder=stable_diffusion_txt2img.text_encoder,
|
||||
tokenizer=stable_diffusion_txt2img.tokenizer,
|
||||
unet=stable_diffusion_txt2img.unet,
|
||||
scheduler=stable_diffusion_txt2img.scheduler,
|
||||
safety_checker=None,
|
||||
feature_extractor=None,
|
||||
requires_safety_checker=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Checkpoint variants
|
||||
Now all model components of the pipeline are stored in half-precision dtype. We can now save the
|
||||
pipeline under a `"fp16"` variant as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
A checkpoint variant is usually a checkpoint where it's weights are:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipe.save_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="fp16")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Stored in a different floating point type for lower precision and lower storage, such as [`torch.float16`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html#data-types), because it only requires half the bandwidth and storage to download. You can't use this variant if you're continuing training or using a CPU.
|
||||
- Non-exponential mean averaged (EMA) weights which shouldn't be used for inference. You should use these to continue finetuning a model.
|
||||
If we don't save into an existing `stable-diffusion-v1-5` folder the new folder would look as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
stable-diffusion-v1-5
|
||||
├── feature_extractor
|
||||
│ └── preprocessor_config.json
|
||||
├── model_index.json
|
||||
├── safety_checker
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ └── pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
├── scheduler
|
||||
│ └── scheduler_config.json
|
||||
├── text_encoder
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ └── pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
├── tokenizer
|
||||
│ ├── merges.txt
|
||||
│ ├── special_tokens_map.json
|
||||
│ ├── tokenizer_config.json
|
||||
│ └── vocab.json
|
||||
├── unet
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ └── diffusion_pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
└── vae
|
||||
├── config.json
|
||||
└── diffusion_pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As one can see, all model files now have a `.fp16.bin` extension instead of just `.bin`.
|
||||
The variant now has to be loaded by also passing a `variant="fp16"` to [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`], e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="fp16", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
works just fine, while:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
throws an Exception:
|
||||
```
|
||||
OSError: Error no file named diffusion_pytorch_model.bin found in directory ./stable-diffusion-v1-45/vae since we **only** stored the model
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is expected as we don't have any "non-variant" checkpoint files saved locally.
|
||||
However, the whole idea of pipeline variants is that they can co-exist with the "main" variant,
|
||||
so one would typically also save the "main" variant in the same folder. Let's do this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
pipe.save_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and upload the pipeline to the Hub under [diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants](https://huggingface.co/diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants).
|
||||
The file structure [on the Hub](https://huggingface.co/diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants/tree/main) now looks as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
├── feature_extractor
|
||||
│ └── preprocessor_config.json
|
||||
├── model_index.json
|
||||
├── safety_checker
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ ├── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
│ └── pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
├── scheduler
|
||||
│ └── scheduler_config.json
|
||||
├── text_encoder
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ ├── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
│ └── pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
├── tokenizer
|
||||
│ ├── merges.txt
|
||||
│ ├── special_tokens_map.json
|
||||
│ ├── tokenizer_config.json
|
||||
│ └── vocab.json
|
||||
├── unet
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ ├── diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
│ ├── diffusion_pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
└── vae
|
||||
├── config.json
|
||||
├── diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
└── diffusion_pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can now both download the "main" and the "fp16" variant from the Hub. Both:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants", variant="fp16")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
works.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 When the checkpoints have identical model structures, but they were trained on different datasets and with a different training setup, they should be stored in separate repositories instead of variations (for example, [`stable-diffusion-v1-4`] and [`stable-diffusion-v1-5`]).
|
||||
Note that Diffusers never downloads more checkpoints than needed. E.g. when downloading
|
||||
the "main" variant, none of the "fp16.bin" files are downloaded and cached.
|
||||
Only when the user specifies `variant="fp16"` are those files downloaded and cached.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Otherwise, a variant is **identical** to the original checkpoint. They have exactly the same serialization format (like [Safetensors](./using-diffusers/using_safetensors)), model structure, and weights have identical tensor shapes.
|
||||
Finally, there are cases where only some of the checkpoint files of the pipeline are of a certain
|
||||
variation. E.g. it's usually only the UNet checkpoint that has both a *exponential-mean-averaged* (EMA) and a *non-exponential-mean-averaged* (non-EMA) version. All other model components, e.g. the text encoder, safety checker or variational auto-encoder usually don't have such a variation.
|
||||
In such a case, one would upload just the UNet's checkpoint file with a `non_ema` version format (as done [here](https://huggingface.co/diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants/blob/main/unet/diffusion_pytorch_model.non_ema.bin)) and upon calling:
|
||||
|
||||
| **checkpoint type** | **weight name** | **argument for loading weights** |
|
||||
|---------------------|-------------------------------------|----------------------------------|
|
||||
| original | diffusion_pytorch_model.bin | |
|
||||
| floating point | diffusion_pytorch_model.fp16.bin | `variant`, `torch_dtype` |
|
||||
| non-EMA | diffusion_pytorch_model.non_ema.bin | `variant` |
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants", variant="non_ema")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are two important arguments to know for loading variants:
|
||||
the model will use only the "non_ema" checkpoint variant if it is available - otherwise it'll load the
|
||||
"main" variation. In the above example, `variant="non_ema"` would therefore download the following file structure:
|
||||
|
||||
- `torch_dtype` defines the floating point precision of the loaded checkpoints. For example, if you want to save bandwidth by loading a `fp16` variant, you should specify `torch_dtype=torch.float16` to *convert the weights* to `fp16`. Otherwise, the `fp16` weights are converted to the default `fp32` precision. You can also load the original checkpoint without defining the `variant` argument, and convert it to `fp16` with `torch_dtype=torch.float16`. In this case, the default `fp32` weights are downloaded first, and then they're converted to `fp16` after loading.
|
||||
```
|
||||
├── feature_extractor
|
||||
│ └── preprocessor_config.json
|
||||
├── model_index.json
|
||||
├── safety_checker
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ ├── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
├── scheduler
|
||||
│ └── scheduler_config.json
|
||||
├── text_encoder
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ ├── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
├── tokenizer
|
||||
│ ├── merges.txt
|
||||
│ ├── special_tokens_map.json
|
||||
│ ├── tokenizer_config.json
|
||||
│ └── vocab.json
|
||||
├── unet
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ └── diffusion_pytorch_model.non_ema.bin
|
||||
└── vae
|
||||
├── config.json
|
||||
├── diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `variant` defines which files should be loaded from the repository. For example, if you want to load a `non_ema` variant from the [`diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants`](https://huggingface.co/diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants/tree/main/unet) repository, you should specify `variant="non_ema"` to download the `non_ema` files.
|
||||
In a nutshell, using `variant="{variant}"` will download all files that match the `{variant}` and if for a model component such a file variant is not present it will download the "main" variant. If neither a "main" or `{variant}` variant is available, an error will the thrown.
|
||||
|
||||
### How does loading work?
|
||||
|
||||
As a class method, [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] is responsible for two things:
|
||||
- Download the latest version of the folder structure required to run the `repo_id` with `diffusers` and cache them. If the latest folder structure is available in the local cache, [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] will simply reuse the cache and **not** re-download the files.
|
||||
- Load the cached weights into the _correct_ pipeline class – one of the [officially supported pipeline classes](./api/overview#diffusers-summary) - and return an instance of the class. The _correct_ pipeline class is thereby retrieved from the `model_index.json` file.
|
||||
|
||||
The underlying folder structure of diffusion pipelines correspond 1-to-1 to their corresponding class instances, *e.g.* [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] for [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)
|
||||
This can be better understood by looking at an example. Let's load a pipeline class instance `pipe` and print it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
# load fp16 variant
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="fp16", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
# load non_ema variant
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="non_ema")
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
print(pipe)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To save a checkpoint stored in a different floating point type or as a non-EMA variant, use the [`DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`] method and specify the `variant` argument. You should try and save a variant to the same folder as the original checkpoint, so you can load both from the same folder:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
# save as fp16 variant
|
||||
stable_diffusion.save_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="fp16")
|
||||
# save as non-ema variant
|
||||
stable_diffusion.save_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="non_ema")
|
||||
*Output*:
|
||||
```
|
||||
StableDiffusionPipeline {
|
||||
"feature_extractor": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPFeatureExtractor"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"safety_checker": [
|
||||
"stable_diffusion",
|
||||
"StableDiffusionSafetyChecker"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"scheduler": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"PNDMScheduler"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"text_encoder": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPTextModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"tokenizer": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPTokenizer"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"unet": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"UNet2DConditionModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"vae": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"AutoencoderKL"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't save the variant to an existing folder, you must specify the `variant` argument otherwise it'll throw an `Exception` because it can't find the original checkpoint:
|
||||
First, we see that the official pipeline is the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], and second we see that the `StableDiffusionPipeline` consists of 7 components:
|
||||
- `"feature_extractor"` of class `CLIPFeatureExtractor` as defined [in `transformers`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/model_doc/clip#transformers.CLIPFeatureExtractor).
|
||||
- `"safety_checker"` as defined [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/e55687e1e15407f60f32242027b7bb8170e58266/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py#L32).
|
||||
- `"scheduler"` of class [`PNDMScheduler`].
|
||||
- `"text_encoder"` of class `CLIPTextModel` as defined [in `transformers`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/model_doc/clip#transformers.CLIPTextModel).
|
||||
- `"tokenizer"` of class `CLIPTokenizer` as defined [in `transformers`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/model_doc/clip#transformers.CLIPTokenizer).
|
||||
- `"unet"` of class [`UNet2DConditionModel`].
|
||||
- `"vae"` of class [`AutoencoderKL`].
|
||||
|
||||
Let's now compare the pipeline instance to the folder structure of the model repository `runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`. Looking at the folder structure of [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main) on the Hub and excluding model and saving format variants, we can see it matches 1-to-1 the printed out instance of `StableDiffusionPipeline` above:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 👎 this won't work
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
# 👍 this works
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"./stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="fp16", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── feature_extractor
|
||||
│ └── preprocessor_config.json
|
||||
├── model_index.json
|
||||
├── safety_checker
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ └── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
├── scheduler
|
||||
│ └── scheduler_config.json
|
||||
├── text_encoder
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ └── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
├── tokenizer
|
||||
│ ├── merges.txt
|
||||
│ ├── special_tokens_map.json
|
||||
│ ├── tokenizer_config.json
|
||||
│ └── vocab.json
|
||||
├── unet
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ ├── diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
└── vae
|
||||
├── config.json
|
||||
├── diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Each attribute of the instance of `StableDiffusionPipeline` has its configuration and possibly weights defined in a subfolder that is called **exactly** like the class attribute (`"feature_extractor"`, `"safety_checker"`, `"scheduler"`, `"text_encoder"`, `"tokenizer"`, `"unet"`, `"vae"`). Importantly, every pipeline expects a `model_index.json` file that tells the `DiffusionPipeline` both:
|
||||
- which pipeline class should be loaded, and
|
||||
- what sub-classes from which library are stored in which subfolders
|
||||
|
||||
In the case of `runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5` the `model_index.json` is therefore defined as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
"_class_name": "StableDiffusionPipeline",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.6.0",
|
||||
"feature_extractor": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPFeatureExtractor"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"safety_checker": [
|
||||
"stable_diffusion",
|
||||
"StableDiffusionSafetyChecker"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"scheduler": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"PNDMScheduler"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"text_encoder": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPTextModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"tokenizer": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPTokenizer"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"unet": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"UNet2DConditionModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"vae": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"AutoencoderKL"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `_class_name` tells `DiffusionPipeline` which pipeline class should be loaded.
|
||||
- `_diffusers_version` can be useful to know under which `diffusers` version this model was created.
|
||||
- Every component of the pipeline is then defined under the form:
|
||||
```
|
||||
"name" : [
|
||||
"library",
|
||||
"class"
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
- The `"name"` field corresponds both to the name of the subfolder in which the configuration and weights are stored as well as the attribute name of the pipeline class (as can be seen [here](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main/bert) and [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/cd502b25cf0debac6f98d27a6638ef95208d1ea2/src/diffusers/pipelines/latent_diffusion/pipeline_latent_diffusion.py#L42)
|
||||
- The `"library"` field corresponds to the name of the library, *e.g.* `diffusers` or `transformers` from which the `"class"` should be loaded
|
||||
- The `"class"` field corresponds to the name of the class, *e.g.* [`CLIPTokenizer`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/model_doc/clip#transformers.CLIPTokenizer) or [`UNet2DConditionModel`]
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
TODO(Patrick) - Make sure to uncomment this part as soon as things are deprecated.
|
||||
@@ -246,11 +562,15 @@ instead.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## Models
|
||||
## Loading models
|
||||
|
||||
Models are loaded from the [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] method, which downloads and caches the latest version of the model weights and configurations. If the latest files are available in the local cache, [`~ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] reuses files in the cache instead of redownloading them.
|
||||
Models as defined under [src/diffusers/models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models) can be loaded via the [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] function. The API is very similar the [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] and works in the same way:
|
||||
- Download the latest version of the model weights and configuration with `diffusers` and cache them. If the latest files are available in the local cache, [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] will simply reuse the cache and **not** re-download the files.
|
||||
- Load the cached weights into the _defined_ model class - one of [the existing model classes](./api/models) - and return an instance of the class.
|
||||
|
||||
Models can be loaded from a subfolder with the `subfolder` argument. For example, the model weights for `runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5` are stored in the [`unet`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main/unet) subfolder:
|
||||
In constrast to [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`], models rely on fewer files that usually don't require a folder structure, but just a `diffusion_pytorch_model.bin` and `config.json` file.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's look at an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
@@ -259,7 +579,19 @@ repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
model = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="unet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or directly from a repository's [directory](https://huggingface.co/google/ddpm-cifar10-32/tree/main):
|
||||
Note how we have to define the `subfolder="unet"` argument to tell [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] that the model weights are located in a [subfolder of the repository](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main/unet).
|
||||
|
||||
As explained in [Loading customized pipelines]("./using-diffusers/loading#loading-customized-pipelines"), one can pass a loaded model to a diffusion pipeline, via [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, unet=model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If the model files can be found directly at the root level, which is usually only the case for some very simple diffusion models, such as [`google/ddpm-cifar10-32`](https://huggingface.co/google/ddpm-cifar10-32), we don't
|
||||
need to pass a `subfolder` argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import UNet2DModel
|
||||
@@ -268,21 +600,35 @@ repo_id = "google/ddpm-cifar10-32"
|
||||
model = UNet2DModel.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also load and save model variants by specifying the `variant` argument in [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] and [`ModelMixin.save_pretrained`]:
|
||||
As motivated in [How to save and load variants?](#how-to-save-and-load-variants), models can load and
|
||||
save variants. To load a model variant, one should pass the `variant` function argument to [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`]. Analogous, to save a model variant, one should pass the `variant` function argument to [`ModelMixin.save_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
|
||||
model = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", subfolder="unet", variant="non-ema")
|
||||
model.save_pretrained("./local-unet", variant="non-ema")
|
||||
model = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants", subfolder="unet", variant="non_ema"
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.save_pretrained("./local-unet", variant="non_ema")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Schedulers
|
||||
## Loading schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
Schedulers are loaded from the [`SchedulerMixin.from_pretrained`] method, and unlike models, schedulers are **not parameterized** or **trained**; they are defined by a configuration file.
|
||||
Schedulers rely on [`SchedulerMixin.from_pretrained`]. Schedulers are **not parameterized** or **trained**, but instead purely defined by a configuration file.
|
||||
For consistency, we use the same method name as we do for models or pipelines, but no weights are loaded in this case.
|
||||
|
||||
Loading schedulers does not consume any significant amount of memory and the same configuration file can be used for a variety of different schedulers.
|
||||
For example, the following schedulers are compatible with [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] which means you can load the same scheduler configuration file in any of these classes:
|
||||
In constrast to pipelines or models, loading schedulers does not consume any significant amount of memory and the same configuration file can often be used for a variety of different schedulers.
|
||||
For example, all of:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`DDPMScheduler`]
|
||||
- [`DDIMScheduler`]
|
||||
- [`PNDMScheduler`]
|
||||
- [`LMSDiscreteScheduler`]
|
||||
- [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`]
|
||||
- [`EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler`]
|
||||
- [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`]
|
||||
|
||||
are compatible with [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] and therefore the same scheduler configuration file can be loaded in any of those classes:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -306,155 +652,6 @@ euler_anc = EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="
|
||||
euler = EulerDiscreteScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
dpm = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
|
||||
# replace `dpm` with any of `ddpm`, `ddim`, `pndm`, `lms`, `euler_anc`, `euler`
|
||||
# replace `dpm` with any of `ddpm`, `ddim`, `pndm`, `lms`, `euler`, `euler_anc`
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, scheduler=dpm)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## DiffusionPipeline explained
|
||||
|
||||
As a class method, [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] is responsible for two things:
|
||||
|
||||
- Download the latest version of the folder structure required for inference and cache it. If the latest folder structure is available in the local cache, [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] reuses the cache and won't redownload the files.
|
||||
- Load the cached weights into the correct pipeline [class](./api/pipelines/overview#diffusers-summary) - retrieved from the `model_index.json` file - and return an instance of it.
|
||||
|
||||
The pipelines underlying folder structure corresponds directly with their class instances. For example, the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] corresponds to the folder structure in [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
print(pipeline)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You'll see pipeline is an instance of [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], which consists of seven components:
|
||||
|
||||
- `"feature_extractor"`: a [`~transformers.CLIPFeatureExtractor`] from 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- `"safety_checker"`: a [component](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/e55687e1e15407f60f32242027b7bb8170e58266/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py#L32) for screening against harmful content.
|
||||
- `"scheduler"`: an instance of [`PNDMScheduler`].
|
||||
- `"text_encoder"`: a [`~transformers.CLIPTextModel`] from 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- `"tokenizer"`: a [`~transformers.CLIPTokenizer`] from 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- `"unet"`: an instance of [`UNet2DConditionModel`].
|
||||
- `"vae"` an instance of [`AutoencoderKL`].
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
StableDiffusionPipeline {
|
||||
"feature_extractor": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPImageProcessor"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"safety_checker": [
|
||||
"stable_diffusion",
|
||||
"StableDiffusionSafetyChecker"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"scheduler": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"PNDMScheduler"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"text_encoder": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPTextModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"tokenizer": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPTokenizer"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"unet": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"UNet2DConditionModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"vae": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"AutoencoderKL"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Compare the components of the pipeline instance to the [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) folder structure, and you'll see there is a separate folder for each of the components in the repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── feature_extractor
|
||||
│ └── preprocessor_config.json
|
||||
├── model_index.json
|
||||
├── safety_checker
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ └── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
├── scheduler
|
||||
│ └── scheduler_config.json
|
||||
├── text_encoder
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ └── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
├── tokenizer
|
||||
│ ├── merges.txt
|
||||
│ ├── special_tokens_map.json
|
||||
│ ├── tokenizer_config.json
|
||||
│ └── vocab.json
|
||||
├── unet
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ ├── diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
└── vae
|
||||
├── config.json
|
||||
├── diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can access each of the components of the pipeline as an attribute to view its configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.tokenizer
|
||||
CLIPTokenizer(
|
||||
name_or_path="/root/.cache/huggingface/hub/models--runwayml--stable-diffusion-v1-5/snapshots/39593d5650112b4cc580433f6b0435385882d819/tokenizer",
|
||||
vocab_size=49408,
|
||||
model_max_length=77,
|
||||
is_fast=False,
|
||||
padding_side="right",
|
||||
truncation_side="right",
|
||||
special_tokens={
|
||||
"bos_token": AddedToken("<|startoftext|>", rstrip=False, lstrip=False, single_word=False, normalized=True),
|
||||
"eos_token": AddedToken("<|endoftext|>", rstrip=False, lstrip=False, single_word=False, normalized=True),
|
||||
"unk_token": AddedToken("<|endoftext|>", rstrip=False, lstrip=False, single_word=False, normalized=True),
|
||||
"pad_token": "<|endoftext|>",
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Every pipeline expects a `model_index.json` file that tells the [`DiffusionPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
- which pipeline class to load from `_class_name`
|
||||
- which version of 🧨 Diffusers was used to create the model in `_diffusers_version`
|
||||
- what components from which library are stored in the subfolders (`name` corresponds to the component and subfolder name, `library` corresponds to the name of the library to load the class from, and `class` corresponds to the class name)
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"_class_name": "StableDiffusionPipeline",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.6.0",
|
||||
"feature_extractor": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPImageProcessor"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"safety_checker": [
|
||||
"stable_diffusion",
|
||||
"StableDiffusionSafetyChecker"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"scheduler": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"PNDMScheduler"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"text_encoder": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPTextModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"tokenizer": [
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"CLIPTokenizer"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"unet": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"UNet2DConditionModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"vae": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"AutoencoderKL"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers offers many pipelines, models, and schedulers for generative tasks. To make loading these components as simple as possible, we provide a single and unified method - `from_pretrained()` - that loads any of these components from either the Hugging Face [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads) or your local machine. Whenever you load a pipeline or model, the latest files are automatically downloaded and cached so you can quickly reuse them next time without redownloading the files.
|
||||
|
||||
This section will show you everything you need to know about loading pipelines, how to load different components in a pipeline, how to load checkpoint variants, and how to load community pipelines. You'll also learn how to load schedulers and compare the speed and quality trade-offs of using different schedulers. Finally, you'll see how to convert and load KerasCV checkpoints so you can use them in PyTorch with 🧨 Diffusers.
|
||||
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
A pipeline is an end-to-end class that provides a quick and easy way to use a diffusion system for inference by bundling independently trained models and schedulers together. Certain combinations of models and schedulers define specific pipeline types, like [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] or [`StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline`], with specific capabilities. All pipeline types inherit from the base [`DiffusionPipeline`] class; pass it any checkpoint, and it'll automatically detect the pipeline type and load the necessary components.
|
||||
|
||||
This section introduces you to some of the tasks supported by our pipelines such as unconditional image generation and different techniques and variations of text-to-image generation. You'll also learn how to gain more control over the generation process by setting a seed for reproducibility and weighting prompts to adjust the influence certain words in the prompt has over the output. Finally, you'll see how you can create a community pipeline for a custom task like generating images from speech.
|
||||
@@ -10,26 +10,26 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Create reproducible pipelines
|
||||
# Reproducibility
|
||||
|
||||
Reproducibility is important for testing, replicating results, and can even be used to [improve image quality](reusing_seeds). However, the randomness in diffusion models is a desired property because it allows the pipeline to generate different images every time it is run. While you can't expect to get the exact same results across platforms, you can expect results to be reproducible across releases and platforms within a certain tolerance range. Even then, tolerance varies depending on the diffusion pipeline and checkpoint.
|
||||
Before reading about reproducibility for Diffusers, it is strongly recommended to take a look at
|
||||
[PyTorch's statement about reproducibility](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html).
|
||||
|
||||
This is why it's important to understand how to control sources of randomness in diffusion models.
|
||||
PyTorch states that
|
||||
> *completely reproducible results are not guaranteed across PyTorch releases, individual commits, or different platforms.*
|
||||
While one can never expect the same results across platforms, one can expect results to be reproducible
|
||||
across releases, platforms, etc... within a certain tolerance. However, this tolerance strongly varies
|
||||
depending on the diffusion pipeline and checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 We strongly recommend reading PyTorch's [statement about reproducibility](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html):
|
||||
|
||||
> Completely reproducible results are not guaranteed across PyTorch releases, individual commits, or different platforms. Furthermore, results may not be reproducible between CPU and GPU executions, even when using identical seeds.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
In the following, we show how to best control sources of randomness for diffusion models.
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
During inference, pipelines rely heavily on random sampling operations which include creating the
|
||||
Gaussian noise tensors to denoise and adding noise to the scheduling step.
|
||||
During inference, diffusion pipelines heavily rely on random sampling operations, such as the creating the
|
||||
gaussian noise tensors to be denoised and adding noise to the scheduling step.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the tensor values in the [`DDIMPipeline`] after two inference steps:
|
||||
Let's have a look at an example. We run the [DDIM pipeline](./api/pipelines/ddim.mdx)
|
||||
for just two inference steps and return a numpy tensor to look into the numerical values of the output.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DDIMPipeline
|
||||
@@ -45,15 +45,11 @@ image = ddim(num_inference_steps=2, output_type="np").images
|
||||
print(np.abs(image).sum())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Running the code above prints one value, but if you run it again you get a different value. What is going on here?
|
||||
|
||||
Every time the pipeline is run, [`torch.randn`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.randn.html) uses a different random seed to create Gaussian noise which is denoised stepwise. This leads to a different result each time it is run, which is great for diffusion pipelines since it generates a different random image each time.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you need to reliably generate the same image, that'll depend on whether you're running the pipeline on a CPU or GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
### CPU
|
||||
|
||||
To generate reproducible results on a CPU, you'll need to use a PyTorch [`Generator`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.randn.html) and set a seed:
|
||||
Running the above prints a value of 1464.2076, but running it again prints a different
|
||||
value of 1495.1768. What is going on here? Every time the pipeline is run, gaussian noise
|
||||
is created and step-wise denoised. To create the gaussian noise with [`torch.randn`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.randn.html), a different random seed is taken every time, thus leading to a different result.
|
||||
This is a desired property of diffusion pipelines, as it means that the pipeline can create a different random image every time it is run. In many cases, one would like to generate the exact same image of a certain
|
||||
run, for which case an instance of a [PyTorch generator](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.randn.html) has to be passed:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -73,22 +69,28 @@ image = ddim(num_inference_steps=2, output_type="np", generator=generator).image
|
||||
print(np.abs(image).sum())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now when you run the code above, it always prints a value of `1491.1711` no matter what because the `Generator` object with the seed is passed to all the random functions of the pipeline.
|
||||
Running the above always prints a value of 1491.1711 - also upon running it again because we
|
||||
define the generator object to be passed to all random functions of the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
If you run this code example on your specific hardware and PyTorch version, you should get a similar, if not the same, result.
|
||||
If you run this code snippet on your specific hardware and version, you should get a similar, if not the same, result.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 It might be a bit unintuitive at first to pass `Generator` objects to the pipeline instead of
|
||||
It might be a bit unintuitive at first to pass `generator` objects to the pipelines instead of
|
||||
just integer values representing the seed, but this is the recommended design when dealing with
|
||||
probabilistic models in PyTorch as `Generator`'s are *random states* that can be
|
||||
probabilistic models in PyTorch as generators are *random states* that are advanced and can thus be
|
||||
passed to multiple pipelines in a sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### GPU
|
||||
Great! Now, we know how to write reproducible pipelines, but it gets a bit trickier since the above example only runs on the CPU. How do we also achieve reproducibility on GPU?
|
||||
In short, one should not expect full reproducibility across different hardware when running pipelines on GPU
|
||||
as matrix multiplications are less deterministic on GPU than on CPU and diffusion pipelines tend to require
|
||||
a lot of matrix multiplications. Let's see what we can do to keep the randomness within limits across
|
||||
different GPU hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
Writing a reproducible pipeline on a GPU is a bit trickier, and full reproducibility across different hardware is not guaranteed because matrix multiplication - which diffusion pipelines require a lot of - is less deterministic on a GPU than a CPU. For example, if you run the same code example above on a GPU:
|
||||
To achieve maximum speed performance, it is recommended to create the generator directly on GPU when running
|
||||
the pipeline on GPU:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -109,11 +111,12 @@ image = ddim(num_inference_steps=2, output_type="np", generator=generator).image
|
||||
print(np.abs(image).sum())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The result is not the same even though you're using an identical seed because the GPU uses a different random number generator than the CPU.
|
||||
Running the above now prints a value of 1389.8634 - even though we're using the exact same seed!
|
||||
This is unfortunate as it means we cannot reproduce the results we achieved on GPU, also on CPU.
|
||||
Nevertheless, it should be expected since the GPU uses a different random number generator than the CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
To circumvent this problem, 🧨 Diffusers has a [`randn_tensor`](#diffusers.utils.randn_tensor) function for creating random noise on the CPU, and then moving the tensor to a GPU if necessary. The `randn_tensor` function is used everywhere inside the pipeline, allowing the user to **always** pass a CPU `Generator` even if the pipeline is run on a GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
You'll see the results are much closer now!
|
||||
To circumvent this problem, we created a [`randn_tensor`](#diffusers.utils.randn_tensor) function, which can create random noise
|
||||
on the CPU and then move the tensor to GPU if necessary. The function is used everywhere inside the pipelines allowing the user to **always** pass a CPU generator even if the pipeline is run on GPU:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -126,7 +129,7 @@ model_id = "google/ddpm-cifar10-32"
|
||||
ddim = DDIMPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
ddim.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# create a generator for reproducibility; notice you don't place it on the GPU!
|
||||
# create a generator for reproducibility
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
|
||||
# run pipeline for just two steps and return numpy tensor
|
||||
@@ -134,18 +137,23 @@ image = ddim(num_inference_steps=2, output_type="np", generator=generator).image
|
||||
print(np.abs(image).sum())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Running the above now prints a value of 1491.1713, much closer to the value of 1491.1711 when
|
||||
the pipeline is fully run on the CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 If reproducibility is important, we recommend always passing a CPU generator.
|
||||
The performance loss is often neglectable, and you'll generate much more similar
|
||||
values than if the pipeline had been run on a GPU.
|
||||
As a consequence, we recommend always passing a CPU generator if Reproducibility is important.
|
||||
The loss of performance is often neglectable, but one can be sure to generate much more similar
|
||||
values than if the pipeline would have been run on CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, for more complex pipelines such as [`UnCLIPPipeline`], these are often extremely
|
||||
susceptible to precision error propagation. Don't expect similar results across
|
||||
different GPU hardware or PyTorch versions. In this case, you'll need to run
|
||||
exactly the same hardware and PyTorch version for full reproducibility.
|
||||
Finally, we noticed that more complex pipelines, such as [`UnCLIPPipeline`] are often extremely
|
||||
susceptible to precision error propagation and thus one cannot expect even similar results across
|
||||
different GPU hardware or PyTorch versions. In such cases, one has to make sure to run
|
||||
exactly the same hardware and PyTorch version for full Reproducibility.
|
||||
|
||||
## randn_tensor
|
||||
## Randomness utilities
|
||||
|
||||
### randn_tensor
|
||||
[[autodoc]] diffusers.utils.randn_tensor
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,17 +10,23 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Improve image quality with deterministic generation
|
||||
# Re-using seeds for fast prompt engineering
|
||||
|
||||
A common way to improve the quality of generated images is with *deterministic batch generation*, generate a batch of images and select one image to improve with a more detailed prompt in a second round of inference. The key is to pass a list of [`torch.Generator`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html#generator)'s to the pipeline for batched image generation, and tie each `Generator` to a seed so you can reuse it for an image.
|
||||
A common use case when generating images is to generate a batch of images, select one image and improve it with a better, more detailed prompt in a second run.
|
||||
To do this, one needs to make each generated image of the batch deterministic.
|
||||
Images are generated by denoising gaussian random noise which can be instantiated by passing a [torch generator](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html#generator).
|
||||
|
||||
Let's use [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) for example, and generate several versions of the following prompt:
|
||||
Now, for batched generation, we need to make sure that every single generated image in the batch is tied exactly to one seed. In 🧨 Diffusers, this can be achieved by not passing one `generator`, but a list
|
||||
of `generators` to the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's go through an example using [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5).
|
||||
We want to generate several versions of the prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "Labrador in the style of Vermeer"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Instantiate a pipeline with [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] and place it on a GPU (if available):
|
||||
Let's load the pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -29,7 +35,7 @@ Instantiate a pipeline with [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] and place it o
|
||||
>>> pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, define four different `Generator`'s and assign each `Generator` a seed (`0` to `3`) so you can reuse a `Generator` later for a specific image:
|
||||
Now, let's define 4 different generators, since we would like to reproduce a certain image. We'll use seeds `0` to `3` to create our generators.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +43,7 @@ Now, define four different `Generator`'s and assign each `Generator` a seed (`0`
|
||||
>>> generator = [torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(i) for i in range(4)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generate the images and have a look:
|
||||
Let's generate 4 images:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> images = pipe(prompt, generator=generator, num_images_per_prompt=4).images
|
||||
@@ -46,14 +52,18 @@ Generate the images and have a look:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In this example, you'll improve upon the first image - but in reality, you can use any image you want (even the image with double sets of eyes!). The first image used the `Generator` with seed `0`, so you'll reuse that `Generator` for the second round of inference. To improve the quality of the image, add some additional text to the prompt:
|
||||
Ok, the last images has some double eyes, but the first image looks good!
|
||||
Let's try to make the prompt a bit better **while keeping the first seed**
|
||||
so that the images are similar to the first image.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = [prompt + t for t in [", highly realistic", ", artsy", ", trending", ", colorful"]]
|
||||
generator = [torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(0) for i in range(4)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create four generators with seed `0`, and generate another batch of images, all of which should look like the first image from the previous round!
|
||||
We create 4 generators with seed `0`, which is the first seed we used before.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's run the pipeline again.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> images = pipe(prompt, generator=generator).images
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
# Schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusion pipelines are inherently a collection of diffusion models and schedulers that are partly independent from each other. This means that one is able to switch out parts of the pipeline to better customize
|
||||
a pipeline to one's use case. The best example of this is the [Schedulers](../api/schedulers/overview.mdx).
|
||||
a pipeline to one's use case. The best example of this are the [Schedulers](../api/schedulers/overview.mdx).
|
||||
|
||||
Whereas diffusion models usually simply define the forward pass from noise to a less noisy sample,
|
||||
schedulers define the whole denoising process, *i.e.*:
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ schedulers define the whole denoising process, *i.e.*:
|
||||
They can be quite complex and often define a trade-off between **denoising speed** and **denoising quality**.
|
||||
It is extremely difficult to measure quantitatively which scheduler works best for a given diffusion pipeline, so it is often recommended to simply try out which works best.
|
||||
|
||||
The following paragraphs show how to do so with the 🧨 Diffusers library.
|
||||
The following paragraphs shows how to do so with the 🧨 Diffusers library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Load pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,250 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# 🧨 Stable Diffusion in JAX / Flax !
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Hugging Face [Diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) supports Flax since version `0.5.1`! This allows for super fast inference on Google TPUs, such as those available in Colab, Kaggle or Google Cloud Platform.
|
||||
|
||||
This notebook shows how to run inference using JAX / Flax. If you want more details about how Stable Diffusion works or want to run it in GPU, please refer to [this notebook](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/stable_diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure you are using a TPU backend. If you are running this notebook in Colab, select `Runtime` in the menu above, then select the option "Change runtime type" and then select `TPU` under the `Hardware accelerator` setting.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that JAX is not exclusive to TPUs, but it shines on that hardware because each TPU server has 8 TPU accelerators working in parallel.
|
||||
|
||||
## Setup
|
||||
|
||||
First make sure diffusers is installed.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
!pip install jax==0.3.25 jaxlib==0.3.25 flax transformers ftfy
|
||||
!pip install diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import jax.tools.colab_tpu
|
||||
|
||||
jax.tools.colab_tpu.setup_tpu()
|
||||
import jax
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
num_devices = jax.device_count()
|
||||
device_type = jax.devices()[0].device_kind
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"Found {num_devices} JAX devices of type {device_type}.")
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
"TPU" in device_type
|
||||
), "Available device is not a TPU, please select TPU from Edit > Notebook settings > Hardware accelerator"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python out
|
||||
Found 8 JAX devices of type Cloud TPU.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we import all the dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import jax
|
||||
import jax.numpy as jnp
|
||||
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from jax import pmap
|
||||
from flax.jax_utils import replicate
|
||||
from flax.training.common_utils import shard
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
from diffusers import FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Model Loading
|
||||
|
||||
TPU devices support `bfloat16`, an efficient half-float type. We'll use it for our tests, but you can also use `float32` to use full precision instead.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
dtype = jnp.bfloat16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Flax is a functional framework, so models are stateless and parameters are stored outside them. Loading the pre-trained Flax pipeline will return both the pipeline itself and the model weights (or parameters). We are using a `bf16` version of the weights, which leads to type warnings that you can safely ignore.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
revision="bf16",
|
||||
dtype=dtype,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Since TPUs usually have 8 devices working in parallel, we'll replicate our prompt as many times as devices we have. Then we'll perform inference on the 8 devices at once, each responsible for generating one image. Thus, we'll get 8 images in the same amount of time it takes for one chip to generate a single one.
|
||||
|
||||
After replicating the prompt, we obtain the tokenized text ids by invoking the `prepare_inputs` function of the pipeline. The length of the tokenized text is set to 77 tokens, as required by the configuration of the underlying CLIP Text model.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "A cinematic film still of Morgan Freeman starring as Jimi Hendrix, portrait, 40mm lens, shallow depth of field, close up, split lighting, cinematic"
|
||||
prompt = [prompt] * jax.device_count()
|
||||
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompt)
|
||||
prompt_ids.shape
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python out
|
||||
(8, 77)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Replication and parallelization
|
||||
|
||||
Model parameters and inputs have to be replicated across the 8 parallel devices we have. The parameters dictionary is replicated using `flax.jax_utils.replicate`, which traverses the dictionary and changes the shape of the weights so they are repeated 8 times. Arrays are replicated using `shard`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
p_params = replicate(params)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
|
||||
prompt_ids.shape
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python out
|
||||
(8, 1, 77)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That shape means that each one of the `8` devices will receive as an input a `jnp` array with shape `(1, 77)`. `1` is therefore the batch size per device. In TPUs with sufficient memory, it could be larger than `1` if we wanted to generate multiple images (per chip) at once.
|
||||
|
||||
We are almost ready to generate images! We just need to create a random number generator to pass to the generation function. This is the standard procedure in Flax, which is very serious and opinionated about random numbers – all functions that deal with random numbers are expected to receive a generator. This ensures reproducibility, even when we are training across multiple distributed devices.
|
||||
|
||||
The helper function below uses a seed to initialize a random number generator. As long as we use the same seed, we'll get the exact same results. Feel free to use different seeds when exploring results later in the notebook.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def create_key(seed=0):
|
||||
return jax.random.PRNGKey(seed)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We obtain a rng and then "split" it 8 times so each device receives a different generator. Therefore, each device will create a different image, and the full process is reproducible.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rng = create_key(0)
|
||||
rng = jax.random.split(rng, jax.device_count())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
JAX code can be compiled to an efficient representation that runs very fast. However, we need to ensure that all inputs have the same shape in subsequent calls; otherwise, JAX will have to recompile the code, and we wouldn't be able to take advantage of the optimized speed.
|
||||
|
||||
The Flax pipeline can compile the code for us if we pass `jit = True` as an argument. It will also ensure that the model runs in parallel in the 8 available devices.
|
||||
|
||||
The first time we run the following cell it will take a long time to compile, but subequent calls (even with different inputs) will be much faster. For example, it took more than a minute to compile in a TPU v2-8 when I tested, but then it takes about **`7s`** for future inference runs.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
%%time
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, p_params, rng, jit=True)[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python out
|
||||
CPU times: user 56.2 s, sys: 42.5 s, total: 1min 38s
|
||||
Wall time: 1min 29s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The returned array has shape `(8, 1, 512, 512, 3)`. We reshape it to get rid of the second dimension and obtain 8 images of `512 × 512 × 3` and then convert them to PIL.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
images = images.reshape((images.shape[0] * images.shape[1],) + images.shape[-3:])
|
||||
images = pipeline.numpy_to_pil(images)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Visualization
|
||||
|
||||
Let's create a helper function to display images in a grid.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def image_grid(imgs, rows, cols):
|
||||
w, h = imgs[0].size
|
||||
grid = Image.new("RGB", size=(cols * w, rows * h))
|
||||
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
|
||||
grid.paste(img, box=(i % cols * w, i // cols * h))
|
||||
return grid
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
image_grid(images, 2, 4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Using different prompts
|
||||
|
||||
We don't have to replicate the _same_ prompt in all the devices. We can do whatever we want: generate 2 prompts 4 times each, or even generate 8 different prompts at once. Let's do that!
|
||||
|
||||
First, we'll refactor the input preparation code into a handy function:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompts = [
|
||||
"Labrador in the style of Hokusai",
|
||||
"Painting of a squirrel skating in New York",
|
||||
"HAL-9000 in the style of Van Gogh",
|
||||
"Times Square under water, with fish and a dolphin swimming around",
|
||||
"Ancient Roman fresco showing a man working on his laptop",
|
||||
"Close-up photograph of young black woman against urban background, high quality, bokeh",
|
||||
"Armchair in the shape of an avocado",
|
||||
"Clown astronaut in space, with Earth in the background",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt_ids = pipeline.prepare_inputs(prompts)
|
||||
prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, p_params, rng, jit=True).images
|
||||
images = images.reshape((images.shape[0] * images.shape[1],) + images.shape[-3:])
|
||||
images = pipeline.numpy_to_pil(images)
|
||||
|
||||
image_grid(images, 2, 4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## How does parallelization work?
|
||||
|
||||
We said before that the `diffusers` Flax pipeline automatically compiles the model and runs it in parallel on all available devices. We'll now briefly look inside that process to show how it works.
|
||||
|
||||
JAX parallelization can be done in multiple ways. The easiest one revolves around using the `jax.pmap` function to achieve single-program, multiple-data (SPMD) parallelization. It means we'll run several copies of the same code, each on different data inputs. More sophisticated approaches are possible, we invite you to go over the [JAX documentation](https://jax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html) and the [`pjit` pages](https://jax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/jax-101/08-pjit.html?highlight=pjit) to explore this topic if you are interested!
|
||||
|
||||
`jax.pmap` does two things for us:
|
||||
- Compiles (or `jit`s) the code, as if we had invoked `jax.jit()`. This does not happen when we call `pmap`, but the first time the pmapped function is invoked.
|
||||
- Ensures the compiled code runs in parallel in all the available devices.
|
||||
|
||||
To show how it works we `pmap` the `_generate` method of the pipeline, which is the private method that runs generates images. Please, note that this method may be renamed or removed in future releases of `diffusers`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
p_generate = pmap(pipeline._generate)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After we use `pmap`, the prepared function `p_generate` will conceptually do the following:
|
||||
* Invoke a copy of the underlying function `pipeline._generate` in each device.
|
||||
* Send each device a different portion of the input arguments. That's what sharding is used for. In our case, `prompt_ids` has shape `(8, 1, 77, 768)`. This array will be split in `8` and each copy of `_generate` will receive an input with shape `(1, 77, 768)`.
|
||||
|
||||
We can code `_generate` completely ignoring the fact that it will be invoked in parallel. We just care about our batch size (`1` in this example) and the dimensions that make sense for our code, and don't have to change anything to make it work in parallel.
|
||||
|
||||
The same way as when we used the pipeline call, the first time we run the following cell it will take a while, but then it will be much faster.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
%%time
|
||||
images = p_generate(prompt_ids, p_params, rng)
|
||||
images = images.block_until_ready()
|
||||
images.shape
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python out
|
||||
CPU times: user 1min 15s, sys: 18.2 s, total: 1min 34s
|
||||
Wall time: 1min 15s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
images.shape
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python out
|
||||
(8, 1, 512, 512, 3)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We use `block_until_ready()` to correctly measure inference time, because JAX uses asynchronous dispatch and returns control to the Python loop as soon as it can. You don't need to use that in your code; blocking will occur automatically when you want to use the result of a computation that has not yet been materialized.
|
||||
@@ -10,60 +10,43 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Unconditional image generation
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Unconditional image generation is a relatively straightforward task. The model only generates images - without any additional context like text or an image - resembling the training data it was trained on.
|
||||
# Unconditional Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] is the easiest way to use a pre-trained diffusion system for inference.
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] is the easiest way to use a pre-trained diffusion system for inference
|
||||
|
||||
Start by creating an instance of [`DiffusionPipeline`] and specify which pipeline checkpoint you would like to download.
|
||||
You can use any of the 🧨 Diffusers [checkpoints](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads) from the Hub (the checkpoint you'll use generates images of butterflies).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Want to train your own unconditional image generation model? Take a look at the training [guide](training/unconditional_training) to learn how to generate your own images.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, you'll use [`DiffusionPipeline`] for unconditional image generation with [DDPM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239):
|
||||
You can use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] for any [Diffusers' checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads).
|
||||
In this guide though, you'll use [`DiffusionPipeline`] for unconditional image generation with [DDPM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> generator = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("anton-l/ddpm-butterflies-128")
|
||||
>>> generator = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-celebahq-256")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] downloads and caches all modeling, tokenization, and scheduling components.
|
||||
Because the model consists of roughly 1.4 billion parameters, we strongly recommend running it on a GPU.
|
||||
You can move the generator object to a GPU, just like you would in PyTorch:
|
||||
Because the model consists of roughly 1.4 billion parameters, we strongly recommend running it on GPU.
|
||||
You can move the generator object to GPU, just like you would in PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> generator.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use the `generator` to generate an image:
|
||||
Now you can use the `generator` on your text prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> image = generator().images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The output is by default wrapped into a [`PIL.Image`](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/Image.html?highlight=image#the-image-class) object.
|
||||
The output is by default wrapped into a [PIL Image object](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/Image.html?highlight=image#the-image-class).
|
||||
|
||||
You can save the image by calling:
|
||||
You can save the image by simply calling:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> image.save("generated_image.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Try out the Spaces below, and feel free to play around with the inference steps parameter to see how it affects the image quality!
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://stevhliu-ddpm-butterflies-128.hf.space"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="500"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -75,9 +75,9 @@ And we're equipped with dealing with it.
|
||||
Then in order to use the model, even before the branch gets accepted by the original author you can do:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1", revision="refs/pr/22")
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1", revision="refs/pr/22")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or you can test it directly online with this [space](https://huggingface.co/spaces/diffusers/check_pr).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Weighting prompts
|
||||
|
||||
Text-guided diffusion models generate images based on a given text prompt. The text prompt
|
||||
can include multiple concepts that the model should generate and it's often desirable to weight
|
||||
certain parts of the prompt more or less.
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusion models work by conditioning the cross attention layers of the diffusion model with contextualized text embeddings (see the [Stable Diffusion Guide for more information](../stable-diffusion)).
|
||||
Thus a simple way to emphasize (or de-emphasize) certain parts of the prompt is by increasing or reducing the scale of the text embedding vector that corresponds to the relevant part of the prompt.
|
||||
This is called "prompt-weighting" and has been a highly demanded feature by the community (see issue [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/2431)).
|
||||
|
||||
## How to do prompt-weighting in Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
We believe the role of `diffusers` is to be a toolbox that provides essential features that enable other projects, such as [InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI) or [diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers), to build powerful UIs. In order to support arbitrary methods to manipulate prompts, `diffusers` exposes a [`prompt_embeds`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.14.0/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img#diffusers.StableDiffusionPipeline.__call__.prompt_embeds) function argument to many pipelines such as [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], allowing to directly pass the "prompt-weighted"/scaled text embeddings to the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
The [compel library](https://github.com/damian0815/compel) provides an easy way to emphasize or de-emphasize portions of the prompt for you. We strongly recommend it instead of preparing the embeddings yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's look at a simple example. Imagine you want to generate an image of `"a red cat playing with a ball"` as
|
||||
follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, UniPCMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4")
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = UniPCMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a red cat playing with a ball"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(33)
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, generator=generator, num_inference_steps=20).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This gives you:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, there is no "ball" in the image. Let's emphasize this part!
|
||||
|
||||
For this we should install the `compel` library:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install compel
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and then create a `Compel` object:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from compel import Compel
|
||||
|
||||
compel_proc = Compel(tokenizer=pipe.tokenizer, text_encoder=pipe.text_encoder)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we emphasize the part "ball" with the `"++"` syntax:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "a red cat playing with a ball++"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and instead of passing this to the pipeline directly, we have to process it using `compel_proc`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt_embeds = compel_proc(prompt)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can pass `prompt_embeds` directly to the pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(33)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds, generator=generator, num_inference_steps=20).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We now get the following image which has a "ball"!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, we de-emphasize parts of the sentence by using the `--` suffix for words, feel free to give it
|
||||
a try!
|
||||
|
||||
If your favorite pipeline does not have a `prompt_embeds` input, please make sure to open an issue, the
|
||||
diffusers team tries to be as responsive as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, please check out the documentation of the [compel](https://github.com/damian0815/compel) library for
|
||||
more information.
|
||||
@@ -1,290 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Understanding pipelines, models and schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers is designed to be a user-friendly and flexible toolbox for building diffusion systems tailored to your use-case. At the core of the toolbox are models and schedulers. While the [`DiffusionPipeline`] bundles these components together for convenience, you can also unbundle the pipeline and use the models and schedulers separately to create new diffusion systems.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to use models and schedulers to assemble a diffusion system for inference, starting with a basic pipeline and then progressing to the Stable Diffusion pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
## Deconstruct a basic pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
A pipeline is a quick and easy way to run a model for inference, requiring no more than four lines of code to generate an image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DDPMPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> ddpm = DDPMPipeline.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cat-256").to("cuda")
|
||||
>>> image = ddpm(num_inference_steps=25).images[0]
|
||||
>>> image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/ddpm-cat.png" alt="Image of cat created from DDPMPipeline"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
That was super easy, but how did the pipeline do that? Let's breakdown the pipeline and take a look at what's happening under the hood.
|
||||
|
||||
In the example above, the pipeline contains a UNet model and a DDPM scheduler. The pipeline denoises an image by taking random noise the size of the desired output and passing it through the model several times. At each timestep, the model predicts the *noise residual* and the scheduler uses it to predict a less noisy image. The pipeline repeats this process until it reaches the end of the specified number of inference steps.
|
||||
|
||||
To recreate the pipeline with the model and scheduler separately, let's write our own denoising process.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Load the model and scheduler:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cat-256")
|
||||
>>> model = UNet2DModel.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cat-256").to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Set the number of timesteps to run the denoising process for:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> scheduler.set_timesteps(50)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Setting the scheduler timesteps creates a tensor with evenly spaced elements in it, 50 in this example. Each element corresponds to a timestep at which the model denoises an image. When you create the denoising loop later, you'll iterate over this tensor to denoise an image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> scheduler.timesteps
|
||||
tensor([980, 960, 940, 920, 900, 880, 860, 840, 820, 800, 780, 760, 740, 720,
|
||||
700, 680, 660, 640, 620, 600, 580, 560, 540, 520, 500, 480, 460, 440,
|
||||
420, 400, 380, 360, 340, 320, 300, 280, 260, 240, 220, 200, 180, 160,
|
||||
140, 120, 100, 80, 60, 40, 20, 0])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Create some random noise with the same shape as the desired output:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> sample_size = model.config.sample_size
|
||||
>>> noise = torch.randn((1, 3, sample_size, sample_size)).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Now write a loop to iterate over the timesteps. At each timestep, the model does a [`UNet2DModel.forward`] pass and returns the noisy residual. The scheduler's [`~DDPMScheduler.step`] method takes the noisy residual, timestep, and input and it predicts the image at the previous timestep. This output becomes the next input to the model in the denoising loop, and it'll repeat until it reaches the end of the `timesteps` array.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> input = noise
|
||||
|
||||
>>> for t in scheduler.timesteps:
|
||||
... with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... noisy_residual = model(input, t).sample
|
||||
>>> previous_noisy_sample = scheduler.step(noisy_residual, t, input).prev_sample
|
||||
>>> input = previous_noisy_sample
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is the entire denoising process, and you can use this same pattern to write any diffusion system.
|
||||
|
||||
5. The last step is to convert the denoised output into an image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from PIL import Image
|
||||
>>> import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image = (input / 2 + 0.5).clamp(0, 1)
|
||||
>>> image = image.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1).numpy()[0]
|
||||
>>> image = Image.fromarray((image * 255)).round().astype("uint8")
|
||||
>>> image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the next section, you'll put your skills to the test and breakdown the more complex Stable Diffusion pipeline. The steps are more or less the same. You'll initialize the necessary components, and set the number of timesteps to create a `timestep` array. The `timestep` array is used in the denoising loop, and for each element in this array, the model predicts a less noisy image. The denoising loop iterates over the `timestep`'s, and at each timestep, it outputs a noisy residual and the scheduler uses it to predict a less noisy image at the previous timestep. This process is repeated until you reach the end of the `timestep` array.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's try it out!
|
||||
|
||||
## Deconstruct the Stable Diffusion pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion is a text-to-image *latent diffusion* model. It is called a latent diffusion model because it works with a lower-dimensional representation of the image instead of the actual pixel space, which makes it more memory efficient. The encoder compresses the image into a smaller representation, and a decoder to convert the compressed representation back into an image. For text-to-image models, you'll need a tokenizer and an encoder to generate text embeddings. From the previous example, you already know you need a UNet model and a scheduler.
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, this is already more complex than the DDPM pipeline which only contains a UNet model. The Stable Diffusion model has three separate pretrained models.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Read the [How does Stable Diffusion work?](https://huggingface.co/blog/stable_diffusion#how-does-stable-diffusion-work) blog for more details about how the VAE, UNet, and text encoder models.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you know what you need for the Stable Diffusion pipeline, load all these components with the [`~ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] method. You can find them in the pretrained [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) checkpoint, and each component is stored in a separate subfolder:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from PIL import Image
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from transformers import CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import AutoencoderKL, UNet2DConditionModel, PNDMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", subfolder="vae")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", subfolder="tokenizer")
|
||||
>>> text_encoder = CLIPTextModel.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", subfolder="text_encoder")
|
||||
>>> unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", subfolder="unet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of the default [`PNDMScheduler`], exchange it for the [`UniPCMultistepScheduler`] to see how easy it is to plug a different scheduler in:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import UniPCMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> scheduler = UniPCMultistepScheduler.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To speed up inference, move the models to a GPU since, unlike the scheduler, they have trainable weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> torch_device = "cuda"
|
||||
>>> vae.to(torch_device)
|
||||
>>> text_encoder.to(torch_device)
|
||||
>>> unet.to(torch_device)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Create text embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to tokenize the text to generate embeddings. The text is used to condition the UNet model and steer the diffusion process towards something that resembles the input prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 The `guidance_scale` parameter determines how much weight should be given to the prompt when generating an image.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to choose any prompt you like if you want to generate something else!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> prompt = ["a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse"]
|
||||
>>> height = 512 # default height of Stable Diffusion
|
||||
>>> width = 512 # default width of Stable Diffusion
|
||||
>>> num_inference_steps = 25 # Number of denoising steps
|
||||
>>> guidance_scale = 7.5 # Scale for classifier-free guidance
|
||||
>>> generator = torch.manual_seed(0) # Seed generator to create the inital latent noise
|
||||
>>> batch_size = len(prompt)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Tokenize the text and generate the embeddings from the prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> text_input = tokenizer(
|
||||
... prompt, padding="max_length", max_length=tokenizer.model_max_length, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
|
||||
>>> with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... text_embeddings = text_encoder(text_input.input_ids.to(torch_device))[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You'll also need to generate the *unconditional text embeddings* which are the embeddings for the padding token. These need to have the same shape (`batch_size` and `seq_length`) as the conditional `text_embeddings`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> max_length = text_input.input_ids.shape[-1]
|
||||
>>> uncond_input = tokenizer([""] * batch_size, padding="max_length", max_length=max_length, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> uncond_embeddings = text_encoder(uncond_input.input_ids.to(torch_device))[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's concatenate the conditional and unconditional embeddings into a batch to avoid doing two forward passes:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> text_embeddings = torch.cat([uncond_embeddings, text_embeddings])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Create random noise
|
||||
|
||||
Next, generate some initial random noise as a starting point for the diffusion process. This is the latent representation of the image, and it'll be gradually denoised. At this point, the `latent` image is smaller than the final image size but that's okay though because the model will transform it into the final 512x512 image dimensions later.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 The height and width are divided by 8 because the `vae` model has 3 down-sampling layers. You can check by running the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
2 ** (len(vae.config.block_out_channels) - 1) == 8
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> latents = torch.randn(
|
||||
... (batch_size, unet.in_channels, height // 8, width // 8),
|
||||
... generator=generator,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> latents = latents.to(torch_device)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Denoise the image
|
||||
|
||||
Start by scaling the input with the initial noise distribution, *sigma*, the noise scale value, which is required for improved schedulers like [`UniPCMultistepScheduler`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> latents = latents * scheduler.init_noise_sigma
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The last step is to create the denoising loop that'll progressively transform the pure noise in `latents` to an image described by your prompt. Remember, the denoising loop needs to do three things:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Set the scheduler's timesteps to use during denoising.
|
||||
2. Iterate over the timesteps.
|
||||
3. At each timestep, call the UNet model to predict the noise residual and pass it to the scheduler to compute the previous noisy sample.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from tqdm.auto import tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
>>> scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> for t in tqdm(scheduler.timesteps):
|
||||
... # expand the latents if we are doing classifier-free guidance to avoid doing two forward passes.
|
||||
... latent_model_input = torch.cat([latents] * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
... latent_model_input = scheduler.scale_model_input(latent_model_input, timestep=t)
|
||||
|
||||
... # predict the noise residual
|
||||
... with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... noise_pred = unet(latent_model_input, t, encoder_hidden_states=text_embeddings).sample
|
||||
|
||||
... # perform guidance
|
||||
... noise_pred_uncond, noise_pred_text = noise_pred.chunk(2)
|
||||
... noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond)
|
||||
|
||||
... # compute the previous noisy sample x_t -> x_t-1
|
||||
... latents = scheduler.step(noise_pred, t, latents).prev_sample
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Decode the image
|
||||
|
||||
The final step is to use the `vae` to decode the latent representation into an image and get the decoded output with `sample`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# scale and decode the image latents with vae
|
||||
latents = 1 / 0.18215 * latents
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
image = vae.decode(latents).sample
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, convert the image to a `PIL.Image` to see your generated image!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> image = (image / 2 + 0.5).clamp(0, 1)
|
||||
>>> image = image.detach().cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1).numpy()
|
||||
>>> images = (image * 255).round().astype("uint8")
|
||||
>>> pil_images = [Image.fromarray(image) for image in images]
|
||||
>>> pil_images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/blog/assets/98_stable_diffusion/stable_diffusion_k_lms.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
From basic to complex pipelines, you've seen that all you really need to write your own diffusion system is a denoising loop. The loop should set the scheduler's timesteps, iterate over them, and alternate between calling the UNet model to predict the noise residual and passing it to the scheduler to compute the previous noisy sample.
|
||||
|
||||
This is really what 🧨 Diffusers is designed for: to make it intuitive and easy to write your own diffusion system using models and schedulers.
|
||||
|
||||
For your next steps, feel free to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Learn how to [build and contribute a pipeline](using-diffusers/#contribute_pipeline) to 🧨 Diffusers. We can't wait and see what you'll come up with!
|
||||
* Explore [existing pipelines](./api/pipelines/overview) in the library, and see if you can deconstruct and build a pipeline from scratch using the models and schedulers separately.
|
||||
@@ -1,238 +0,0 @@
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: index
|
||||
title: 🧨 Diffusers
|
||||
- local: quicktour
|
||||
title: 快速入门
|
||||
- local: stable_diffusion
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion
|
||||
- local: installation
|
||||
title: 安装
|
||||
title: 开始
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: tutorials/basic_training
|
||||
title: Train a diffusion model
|
||||
title: Tutorials
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/loading
|
||||
title: Loading Pipelines, Models, and Schedulers
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/schedulers
|
||||
title: Using different Schedulers
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/configuration
|
||||
title: Configuring Pipelines, Models, and Schedulers
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Loading and Adding Custom Pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/kerascv
|
||||
title: Using KerasCV Stable Diffusion Checkpoints in Diffusers
|
||||
title: Loading & Hub
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/unconditional_image_generation
|
||||
title: Unconditional Image Generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation
|
||||
title: Text-to-Image Generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/img2img
|
||||
title: Text-Guided Image-to-Image
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/inpaint
|
||||
title: Text-Guided Image-Inpainting
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/depth2img
|
||||
title: Text-Guided Depth-to-Image
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/controlling_generation
|
||||
title: Controlling generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/reusing_seeds
|
||||
title: Reusing seeds for deterministic generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/reproducibility
|
||||
title: Reproducibility
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_examples
|
||||
title: Community Pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/contribute_pipeline
|
||||
title: How to contribute a Pipeline
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/using_safetensors
|
||||
title: Using safetensors
|
||||
title: Pipelines for Inference
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/rl
|
||||
title: Reinforcement Learning
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/audio
|
||||
title: Audio
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/other-modalities
|
||||
title: Other Modalities
|
||||
title: Taking Diffusers Beyond Images
|
||||
title: Using Diffusers
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: optimization/fp16
|
||||
title: Memory and Speed
|
||||
- local: optimization/torch2.0
|
||||
title: Torch2.0 support
|
||||
- local: optimization/xformers
|
||||
title: xFormers
|
||||
- local: optimization/onnx
|
||||
title: ONNX
|
||||
- local: optimization/open_vino
|
||||
title: OpenVINO
|
||||
- local: optimization/mps
|
||||
title: MPS
|
||||
- local: optimization/habana
|
||||
title: Habana Gaudi
|
||||
title: Optimization/Special Hardware
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: training/unconditional_training
|
||||
title: Unconditional Image Generation
|
||||
- local: training/text_inversion
|
||||
title: Textual Inversion
|
||||
- local: training/dreambooth
|
||||
title: DreamBooth
|
||||
- local: training/text2image
|
||||
title: Text-to-image
|
||||
- local: training/lora
|
||||
title: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models (LoRA)
|
||||
title: Training
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: conceptual/philosophy
|
||||
title: Philosophy
|
||||
- local: conceptual/contribution
|
||||
title: How to contribute?
|
||||
- local: conceptual/ethical_guidelines
|
||||
title: Diffusers' Ethical Guidelines
|
||||
title: Conceptual Guides
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/models
|
||||
title: Models
|
||||
- local: api/diffusion_pipeline
|
||||
title: Diffusion Pipeline
|
||||
- local: api/logging
|
||||
title: Logging
|
||||
- local: api/configuration
|
||||
title: Configuration
|
||||
- local: api/outputs
|
||||
title: Outputs
|
||||
- local: api/loaders
|
||||
title: Loaders
|
||||
title: Main Classes
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/alt_diffusion
|
||||
title: AltDiffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/audio_diffusion
|
||||
title: Audio Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/cycle_diffusion
|
||||
title: Cycle Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/dance_diffusion
|
||||
title: Dance Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/ddim
|
||||
title: DDIM
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/ddpm
|
||||
title: DDPM
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/dit
|
||||
title: DiT
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/latent_diffusion
|
||||
title: Latent Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/paint_by_example
|
||||
title: PaintByExample
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pndm
|
||||
title: PNDM
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/repaint
|
||||
title: RePaint
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe
|
||||
title: Safe Stable Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/score_sde_ve
|
||||
title: Score SDE VE
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion
|
||||
title: Semantic Guidance
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img
|
||||
title: Text-to-Image
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img
|
||||
title: Image-to-Image
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/inpaint
|
||||
title: Inpaint
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/depth2img
|
||||
title: Depth-to-Image
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/image_variation
|
||||
title: Image-Variation
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/upscale
|
||||
title: Super-Resolution
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/latent_upscale
|
||||
title: Stable-Diffusion-Latent-Upscaler
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix
|
||||
title: InstructPix2Pix
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/attend_and_excite
|
||||
title: Attend and Excite
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero
|
||||
title: Pix2Pix Zero
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/self_attention_guidance
|
||||
title: Self-Attention Guidance
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/panorama
|
||||
title: MultiDiffusion Panorama
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/controlnet
|
||||
title: Text-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion 2
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_unclip
|
||||
title: Stable unCLIP
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stochastic_karras_ve
|
||||
title: Stochastic Karras VE
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/unclip
|
||||
title: UnCLIP
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond
|
||||
title: Unconditional Latent Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion
|
||||
title: Versatile Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/vq_diffusion
|
||||
title: VQ Diffusion
|
||||
title: Pipelines
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/ddim
|
||||
title: DDIM
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/ddim_inverse
|
||||
title: DDIMInverse
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/ddpm
|
||||
title: DDPM
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/deis
|
||||
title: DEIS
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/dpm_discrete
|
||||
title: DPM Discrete Scheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/dpm_discrete_ancestral
|
||||
title: DPM Discrete Scheduler with ancestral sampling
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/euler_ancestral
|
||||
title: Euler Ancestral Scheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/euler
|
||||
title: Euler scheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/heun
|
||||
title: Heun Scheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/ipndm
|
||||
title: IPNDM
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/lms_discrete
|
||||
title: Linear Multistep
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/multistep_dpm_solver
|
||||
title: Multistep DPM-Solver
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/pndm
|
||||
title: PNDM
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/repaint
|
||||
title: RePaint Scheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/singlestep_dpm_solver
|
||||
title: Singlestep DPM-Solver
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/stochastic_karras_ve
|
||||
title: Stochastic Kerras VE
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/unipc
|
||||
title: UniPCMultistepScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/score_sde_ve
|
||||
title: VE-SDE
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/score_sde_vp
|
||||
title: VP-SDE
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/vq_diffusion
|
||||
title: VQDiffusionScheduler
|
||||
title: Schedulers
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/experimental/rl
|
||||
title: RL Planning
|
||||
title: Experimental Features
|
||||
title: API
|
||||
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/huggingface/diffusers/77aadfee6a891ab9fcfb780f87c693f7a5beeb8e/docs/source/imgs/diffusers_library.jpg" width="400"/>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
# 🧨 Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
🤗Diffusers提供了预训练好的视觉和音频扩散模型,并可以作为推理和训练的模块化工具箱。
|
||||
|
||||
更准确地说,🤗Diffusers提供了:
|
||||
|
||||
- 最先进的扩散管道,可以在推理中仅用几行代码运行(详情看[**Using Diffusers**](./using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation))或看[**管道**](#pipelines) 以获取所有支持的管道及其对应的论文的概述。
|
||||
- 可以在推理中交替使用的各种噪声调度程序,以便在推理过程中权衡如何选择速度和质量。有关更多信息,可以看[**Schedulers**](./api/schedulers/overview)。
|
||||
- 多种类型的模型,如U-Net,可用作端到端扩散系统中的构建模块。有关更多详细信息,可以看 [**Models**](./api/models) 。
|
||||
- 训练示例,展示如何训练最流行的扩散模型任务。更多相关信息,可以看[**Training**](./training/overview)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 🧨 Diffusers pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
下表总结了所有官方支持的pipelines及其对应的论文,部分提供了colab,可以直接尝试一下。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| 管道 | 论文 | 任务 | Colab
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|:---:|
|
||||
| [alt_diffusion](./api/pipelines/alt_diffusion) | [**AltDiffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [audio_diffusion](./api/pipelines/audio_diffusion) | [**Audio Diffusion**](https://github.com/teticio/audio-diffusion.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/teticio/audio-diffusion/blob/master/notebooks/audio_diffusion_pipeline.ipynb)
|
||||
| [controlnet](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/controlnet) | [**ControlNet with Stable Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/controlnet.ipynb)
|
||||
| [cycle_diffusion](./api/pipelines/cycle_diffusion) | [**Cycle Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.05559) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [dance_diffusion](./api/pipelines/dance_diffusion) | [**Dance Diffusion**](https://github.com/williamberman/diffusers.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [ddpm](./api/pipelines/ddpm) | [**Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [ddim](./api/pipelines/ddim) | [**Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [**High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [**High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion_uncond](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond) | [**High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [paint_by_example](./api/pipelines/paint_by_example) | [**Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13227) | Image-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [pndm](./api/pipelines/pndm) | [**Pseudo Numerical Methods for Diffusion Models on Manifolds**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09778) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_ve](./api/pipelines/score_sde_ve) | [**Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations**](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_vp](./api/pipelines/score_sde_vp) | [**Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations**](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [semantic_stable_diffusion](./api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion) | [**Semantic Guidance**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12247) | Text-Guided Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ml-research/semantic-image-editing/blob/main/examples/SemanticGuidance.ipynb)
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_text2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img) | [**Stable Diffusion**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-to-Image Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/training_example.ipynb)
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_img2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) | [**Stable Diffusion**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/image_2_image_using_diffusers.ipynb)
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_inpaint](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/inpaint) | [**Stable Diffusion**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/in_painting_with_stable_diffusion_using_diffusers.ipynb)
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_panorama](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/panorama) | [**MultiDiffusion**](https://multidiffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Panorama Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix) | [**InstructPix2Pix**](https://github.com/timothybrooks/instruct-pix2pix) | Text-Guided Image Editing|
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix_zero](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero) | [**Zero-shot Image-to-Image Translation**](https://pix2pixzero.github.io/) | Text-Guided Image Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_attend_and_excite](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/attend_and_excite) | [**Attend and Excite for Stable Diffusion**](https://attendandexcite.github.io/Attend-and-Excite/) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_self_attention_guidance](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/self_attention_guidance) | [**Self-Attention Guidance**](https://ku-cvlab.github.io/Self-Attention-Guidance) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_image_variation](./stable_diffusion/image_variation) | [**Stable Diffusion Image Variations**](https://github.com/LambdaLabsML/lambda-diffusers#stable-diffusion-image-variations) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_latent_upscale](./stable_diffusion/latent_upscale) | [**Stable Diffusion Latent Upscaler**](https://twitter.com/StabilityAI/status/1590531958815064065) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Stable Diffusion 2**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Stable Diffusion 2**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Depth-Conditional Stable Diffusion**](https://github.com/Stability-AI/stablediffusion#depth-conditional-stable-diffusion) | Depth-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [**Stable Diffusion 2**](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_safe](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe) | [**Safe Stable Diffusion**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105) | Text-Guided Generation | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ml-research/safe-latent-diffusion/blob/main/examples/Safe%20Latent%20Diffusion.ipynb)
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | **Stable unCLIP** | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | **Stable unCLIP** | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stochastic_karras_ve](./api/pipelines/stochastic_karras_ve) | [**Elucidating the Design Space of Diffusion-Based Generative Models**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00364) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [unclip](./api/pipelines/unclip) | [Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06125) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Image Variations Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Dual Image and Text Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [vq_diffusion](./api/pipelines/vq_diffusion) | [Vector Quantized Diffusion Model for Text-to-Image Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.14822) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 管道是如何使用相应论文中提出的扩散模型的简单示例。
|
||||
@@ -1,147 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 安装
|
||||
|
||||
安装🤗 Diffusers 到你正在使用的任何深度学习框架中。
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers已在Python 3.7+、PyTorch 1.7.0+和Flax上进行了测试。按照下面的安装说明,针对你正在使用的深度学习框架进行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
- [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) installation instructions.
|
||||
- [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) installation instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用pip安装
|
||||
|
||||
你需要在[虚拟环境](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html)中安装🤗 Diffusers 。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你对 Python 虚拟环境不熟悉,可以看看这个[教程](https://packaging.python.org/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/).
|
||||
|
||||
使用虚拟环境你可以轻松管理不同的项目,避免了依赖项之间的兼容性问题。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,在你的项目目录下创建一个虚拟环境:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
激活虚拟环境:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在你就可以安装 🤗 Diffusers了!使用下边这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
**PyTorch**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install diffusers["torch"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Flax**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install diffusers["flax"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 从源代码安装
|
||||
|
||||
在从源代码安装 `diffusers` 之前,你先确定你已经安装了 `torch` 和 `accelerate`。
|
||||
|
||||
`torch`的安装教程可以看 `torch` [文档](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally).
|
||||
|
||||
安装 `accelerate`
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install accelerate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
从源码安装 🤗 Diffusers 使用以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令安装的是最新的 `main`版本,而不是最近的`stable`版。
|
||||
`main`是一直和最新进展保持一致的。比如,上次正式版发布了,有bug,新的正式版还没推出,但是`main`中可以看到这个bug被修复了。
|
||||
但是这也意味着 `main`版本并不总是稳定的。
|
||||
|
||||
我们努力保持`main`版本正常运行,大多数问题都能在几个小时或一天之内解决
|
||||
|
||||
如果你遇到了问题,可以提 [Issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues),这样我们就能更快修复问题了。
|
||||
|
||||
## 可修改安装
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想做以下两件事,那你可能需要一个可修改代码的安装方式:
|
||||
|
||||
* 使用 `main`版本的源代码。
|
||||
* 为 🤗 Diffusers 贡献,需要测试代码中的变化。
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令克隆并安装 🤗 Diffusers:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
cd diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**PyTorch**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install -e ".[torch]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Flax**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install -e ".[flax]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这些命令将连接你克隆的版本库和你的 Python 库路径。
|
||||
现在,除了正常的库路径外,Python 还会在你克隆的文件夹内寻找。
|
||||
例如,如果你的 Python 包通常安装在 `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.7/Site-packages/`,Python 也会搜索你克隆到的文件夹。`~/diffusers/`。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想继续使用这个库,你必须保留 `diffusers` 文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以用下面的命令轻松地将你克隆的🤗Diffusers仓库更新到最新版本。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ~/diffusers/
|
||||
git pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你的Python环境将在下次运行时找到`main`版本的🤗 Diffusers。
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意遥测日志
|
||||
|
||||
我们的库会在使用`from_pretrained()`请求期间收集信息。这些数据包括Diffusers和PyTorch/Flax的版本,请求的模型或管道,以及预训练检查点的路径(如果它被托管在Hub上)。
|
||||
|
||||
这些使用数据有助于我们调试问题并优先考虑新功能。
|
||||
当从HuggingFace Hub加载模型和管道时才会发送遥测数据,并且在本地使用时不会收集数据。
|
||||
|
||||
我们知道并不是每个人都想分享这些的信息,我们尊重您的隐私,
|
||||
因此您可以通过在终端中设置“DISABLE_TELEMETRY”环境变量来禁用遥测数据的收集:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux/MacOS中:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export DISABLE_TELEMETRY=YES
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在Windows中:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
set DISABLE_TELEMETRY=YES
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,331 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
# 快速上手
|
||||
|
||||
训练扩散模型,是为了对随机高斯噪声进行逐步去噪,以生成令人感兴趣的样本,比如图像或者语音。
|
||||
|
||||
扩散模型的发展引起了人们对生成式人工智能的极大兴趣,你可能已经在网上见过扩散生成的图像了。🧨 Diffusers库的目的是让大家更易上手扩散模型。
|
||||
|
||||
无论你是开发人员还是普通用户,本文将向你介绍🧨 Diffusers 并帮助你快速开始生成内容!
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers 库的三个主要组件:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
无论你是开发者还是普通用户,这个快速指南将向你介绍🧨 Diffusers,并帮助你快速使用和生成!该库三个主要部分如下:
|
||||
|
||||
* [`DiffusionPipeline`]是一个高级的端到端类,旨在通过预训练的扩散模型快速生成样本进行推理。
|
||||
* 作为创建扩散系统做组件的流行的预训练[模型](./api/models)框架和模块。
|
||||
* 许多不同的[调度器](./api/schedulers/overview):控制如何在训练过程中添加噪声的算法,以及如何在推理过程中生成去噪图像的算法。
|
||||
|
||||
快速入门将告诉你如何使用[`DiffusionPipeline`]进行推理,然后指导你如何结合模型和调度器以复现[`DiffusionPipeline`]内部发生的事情。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
快速入门是🧨[Diffusers入门](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/diffusers_intro.ipynb)的简化版,可以帮助你快速上手。如果你想了解更多关于🧨 Diffusers的目标、设计理念以及关于它的核心API的更多细节,可以点击🧨[Diffusers入门](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/diffusers_intro.ipynb)查看。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
在开始之前,确认一下你已经安装好了所需要的库:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade diffusers accelerate transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- [🤗 Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index) 在推理和训练过程中加速模型加载。
|
||||
- [🤗 Transformers](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index) 是运行最流行的扩散模型所必须的库,比如[Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
## 扩散模型管道
|
||||
|
||||
[`DiffusionPipeline`]是用预训练的扩散系统进行推理的最简单方法。它是一个包含模型和调度器的端到端系统。你可以直接使用[`DiffusionPipeline`]完成许多任务。请查看下面的表格以了解一些支持的任务,要获取完整的支持任务列表,请查看[🧨 Diffusers 总结](./api/pipelines/overview#diffusers-summary) 。
|
||||
|
||||
| **任务** | **描述** | **管道**
|
||||
|------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------|
|
||||
| Unconditional Image Generation | 从高斯噪声中生成图片 | [unconditional_image_generation](./using-diffusers/unconditional_image_generation) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Image Generation | 给定文本提示生成图像 | [conditional_image_generation](./using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Image-to-Image Translation | 在文本提示的指导下调整图像 | [img2img](./using-diffusers/img2img) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Image-Inpainting | 给出图像、遮罩和文本提示,填充图像的遮罩部分 | [inpaint](./using-diffusers/inpaint) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Depth-to-Image Translation | 在文本提示的指导下调整图像的部分内容,同时通过深度估计保留其结构 | [depth2img](./using-diffusers/depth2img) |
|
||||
|
||||
首先创建一个[`DiffusionPipeline`]的实例,并指定要下载的pipeline检查点。
|
||||
你可以使用存储在Hugging Face Hub上的任何[`DiffusionPipeline`][检查点](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads)。
|
||||
在教程中,你将加载[`stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)检查点,用于文本到图像的生成。
|
||||
|
||||
首先创建一个[DiffusionPipeline]实例,并指定要下载的管道检查点。
|
||||
您可以在Hugging Face Hub上使用[DiffusionPipeline]的任何检查点。
|
||||
在本快速入门中,您将加载stable-diffusion-v1-5检查点,用于文本到图像生成。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>。
|
||||
|
||||
对于[Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion)模型,在运行该模型之前,请先仔细阅读[许可证](https://huggingface.co/spaces/CompVis/stable-diffusion-license)。🧨 Diffusers实现了一个[`safety_checker`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py),以防止有攻击性的或有害的内容,但Stable Diffusion模型改进图像的生成能力仍有可能产生潜在的有害内容。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
用[`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`]方法加载模型。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
[`DiffusionPipeline`]会下载并缓存所有的建模、标记化和调度组件。你可以看到Stable Diffusion的pipeline是由[`UNet2DConditionModel`]和[`PNDMScheduler`]等组件组成的:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pipeline
|
||||
StableDiffusionPipeline {
|
||||
"_class_name": "StableDiffusionPipeline",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.13.1",
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"scheduler": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"PNDMScheduler"
|
||||
],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"unet": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"UNet2DConditionModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"vae": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"AutoencoderKL"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们强烈建议你在GPU上运行这个pipeline,因为该模型由大约14亿个参数组成。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以像在Pytorch里那样把生成器对象移到GPU上:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以向`pipeline`传递一个文本提示来生成图像,然后获得去噪的图像。默认情况下,图像输出被放在一个[`PIL.Image`](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/Image.html?highlight=image#the-image-class)对象中。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> image = pipeline("An image of a squirrel in Picasso style").images[0]
|
||||
>>> image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/image_of_squirrel_painting.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
调用`save`保存图像:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> image.save("image_of_squirrel_painting.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 本地管道
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以在本地使用管道。唯一的区别是你需提前下载权重:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git lfs install
|
||||
git clone https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将下载好的权重加载到管道中:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以像上一节中那样运行管道了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 更换调度器
|
||||
|
||||
不同的调度器对去噪速度和质量的权衡是不同的。要想知道哪种调度器最适合你,最好的办法就是试用一下。🧨 Diffusers的主要特点之一是允许你轻松切换不同的调度器。例如,要用[`EulerDiscreteScheduler`]替换默认的[`PNDMScheduler`],用[`~diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config`]方法加载即可:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import EulerDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
>>> pipeline.scheduler = EulerDiscreteScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
试着用新的调度器生成一个图像,看看你能否发现不同之处。
|
||||
|
||||
在下一节中,你将仔细观察组成[`DiffusionPipeline`]的组件——模型和调度器,并学习如何使用这些组件来生成猫咪的图像。
|
||||
|
||||
## 模型
|
||||
|
||||
大多数模型取一个噪声样本,在每个时间点预测*噪声残差*(其他模型则直接学习预测前一个样本或速度或[`v-prediction`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/5e5ce13e2f89ac45a0066cb3f369462a3cf1d9ef/src/diffusers/schedulers/scheduling_ddim.py#L110)),即噪声较小的图像与输入图像的差异。你可以混搭模型创建其他扩散系统。
|
||||
|
||||
模型是用[`~ModelMixin.from_pretrained`]方法启动的,该方法还在本地缓存了模型权重,所以下次加载模型时更快。对于快速入门,你默认加载的是[`UNet2DModel`],这是一个基础的无条件图像生成模型,该模型有一个在猫咪图像上训练的检查点:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import UNet2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> repo_id = "google/ddpm-cat-256"
|
||||
>>> model = UNet2DModel.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
想知道模型的参数,调用 `model.config`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model.config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
模型配置是一个🧊冻结的🧊字典,意思是这些参数在模型创建后就不变了。这是特意设置的,确保在开始时用于定义模型架构的参数保持不变,其他参数仍然可以在推理过程中进行调整。
|
||||
|
||||
一些最重要的参数:
|
||||
|
||||
* `sample_size`:输入样本的高度和宽度尺寸。
|
||||
* `in_channels`:输入样本的输入通道数。
|
||||
* `down_block_types`和`up_block_types`:用于创建U-Net架构的下采样和上采样块的类型。
|
||||
* `block_out_channels`:下采样块的输出通道数;也以相反的顺序用于上采样块的输入通道数。
|
||||
* `layers_per_block`:每个U-Net块中存在的ResNet块的数量。
|
||||
|
||||
为了使用该模型进行推理,用随机高斯噪声生成图像形状。它应该有一个`batch`轴,因为模型可以接收多个随机噪声,一个`channel`轴,对应于输入通道的数量,以及一个`sample_size`轴,对应图像的高度和宽度。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> noisy_sample = torch.randn(1, model.config.in_channels, model.config.sample_size, model.config.sample_size)
|
||||
>>> noisy_sample.shape
|
||||
torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对于推理,将噪声图像和一个`timestep`传递给模型。`timestep` 表示输入图像的噪声程度,开始时噪声更多,结束时噪声更少。这有助于模型确定其在扩散过程中的位置,是更接近开始还是结束。使用 `sample` 获得模型输出:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... noisy_residual = model(sample=noisy_sample, timestep=2).sample
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
想生成实际的样本,你需要一个调度器指导去噪过程。在下一节中,你将学习如何把模型与调度器结合起来。
|
||||
|
||||
## 调度器
|
||||
|
||||
调度器管理一个噪声样本到一个噪声较小的样本的处理过程,给出模型输出 —— 在这种情况下,它是`noisy_residual`。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers是一个用于构建扩散系统的工具箱。预定义好的扩散系统[`DiffusionPipeline`]能方便你快速试用,你也可以单独选择自己的模型和调度器组件来建立一个自定义的扩散系统。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
在快速入门教程中,你将用它的[`~diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config`]方法实例化[`DDPMScheduler`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DDPMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_config(repo_id)
|
||||
>>> scheduler
|
||||
DDPMScheduler {
|
||||
"_class_name": "DDPMScheduler",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.13.1",
|
||||
"beta_end": 0.02,
|
||||
"beta_schedule": "linear",
|
||||
"beta_start": 0.0001,
|
||||
"clip_sample": true,
|
||||
"clip_sample_range": 1.0,
|
||||
"num_train_timesteps": 1000,
|
||||
"prediction_type": "epsilon",
|
||||
"trained_betas": null,
|
||||
"variance_type": "fixed_small"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
💡 注意调度器是如何从配置中实例化的。与模型不同,调度器没有可训练的权重,而且是无参数的。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
* `num_train_timesteps`:去噪过程的长度,或者换句话说,将随机高斯噪声处理成数据样本所需的时间步数。
|
||||
* `beta_schedule`:用于推理和训练的噪声表。
|
||||
* `beta_start`和`beta_end`:噪声表的开始和结束噪声值。
|
||||
|
||||
要预测一个噪音稍小的图像,请将 模型输出、`timestep`和当前`sample` 传递给调度器的[`~diffusers.DDPMScheduler.step`]方法:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> less_noisy_sample = scheduler.step(model_output=noisy_residual, timestep=2, sample=noisy_sample).prev_sample
|
||||
>>> less_noisy_sample.shape
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这个 `less_noisy_sample` 去噪样本 可以被传递到下一个`timestep` ,处理后会将变得噪声更小。现在让我们把所有步骤合起来,可视化整个去噪过程。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,创建一个函数,对去噪后的图像进行后处理并显示为`PIL.Image`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import PIL.Image
|
||||
>>> import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def display_sample(sample, i):
|
||||
... image_processed = sample.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
|
||||
... image_processed = (image_processed + 1.0) * 127.5
|
||||
... image_processed = image_processed.numpy().astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
... image_pil = PIL.Image.fromarray(image_processed[0])
|
||||
... display(f"Image at step {i}")
|
||||
... display(image_pil)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将输入和模型移到GPU上加速去噪过程:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model.to("cuda")
|
||||
>>> noisy_sample = noisy_sample.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在创建一个去噪循环,该循环预测噪声较少样本的残差,并使用调度程序计算噪声较少的样本:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
>>> sample = noisy_sample
|
||||
|
||||
>>> for i, t in enumerate(tqdm.tqdm(scheduler.timesteps)):
|
||||
... # 1. predict noise residual
|
||||
... with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... residual = model(sample, t).sample
|
||||
|
||||
... # 2. compute less noisy image and set x_t -> x_t-1
|
||||
... sample = scheduler.step(residual, t, sample).prev_sample
|
||||
|
||||
... # 3. optionally look at image
|
||||
... if (i + 1) % 50 == 0:
|
||||
... display_sample(sample, i + 1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
看!这样就从噪声中生成出一只猫了!😻
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/diffusion-quicktour.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## 下一步
|
||||
|
||||
希望你在这次快速入门教程中用🧨Diffuser 生成了一些很酷的图像! 下一步你可以:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在[训练](./tutorials/basic_training)教程中训练或微调一个模型来生成你自己的图像。
|
||||
* 查看官方和社区的[训练或微调脚本](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples#-diffusers-examples)的例子,了解更多使用情况。
|
||||
* 在[使用不同的调度器](./using-diffusers/schedulers)指南中了解更多关于加载、访问、更改和比较调度器的信息。
|
||||
* 在[Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion)教程中探索提示工程、速度和内存优化,以及生成更高质量图像的技巧。
|
||||
* 通过[在GPU上优化PyTorch](./optimization/fp16)指南,以及运行[Apple (M1/M2)上的Stable Diffusion](./optimization/mps)和[ONNX Runtime](./optimization/onnx)的教程,更深入地了解如何加速🧨Diffuser。
|
||||
@@ -42,8 +42,6 @@ Training examples show how to pretrain or fine-tune diffusion models for a varie
|
||||
| [**Text-to-Image fine-tuning**](./text_to_image) | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [**Textual Inversion**](./textual_inversion) | ✅ | - | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/sd_textual_inversion_training.ipynb)
|
||||
| [**Dreambooth**](./dreambooth) | ✅ | - | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/sd_dreambooth_training.ipynb)
|
||||
| [**ControlNet**](./controlnet) | ✅ | ✅ | -
|
||||
| [**InstructPix2Pix**](./instruct_pix2pix) | ✅ | ✅ | -
|
||||
| [**Reinforcement Learning for Control**](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/rl/run_diffusers_locomotion.py) | - | - | coming soon.
|
||||
|
||||
## Community
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,9 +28,7 @@ Stable Diffusion v1.1-1.4 Comparison | Run all 4 model checkpoints for Stable Di
|
||||
MagicMix | Diffusion Pipeline for semantic mixing of an image and a text prompt | [MagicMix](#magic-mix) | - | [Partho Das](https://github.com/daspartho) |
|
||||
| Stable UnCLIP | Diffusion Pipeline for combining prior model (generate clip image embedding from text, UnCLIPPipeline `"kakaobrain/karlo-v1-alpha"`) and decoder pipeline (decode clip image embedding to image, StableDiffusionImageVariationPipeline `"lambdalabs/sd-image-variations-diffusers"` ). | [Stable UnCLIP](#stable-unclip) | - |[Ray Wang](https://wrong.wang) |
|
||||
| UnCLIP Text Interpolation Pipeline | Diffusion Pipeline that allows passing two prompts and produces images while interpolating between the text-embeddings of the two prompts | [UnCLIP Text Interpolation Pipeline](#unclip-text-interpolation-pipeline) | - | [Naga Sai Abhinay Devarinti](https://github.com/Abhinay1997/) |
|
||||
| UnCLIP Image Interpolation Pipeline | Diffusion Pipeline that allows passing two images/image_embeddings and produces images while interpolating between their image-embeddings | [UnCLIP Image Interpolation Pipeline](#unclip-image-interpolation-pipeline) | - | [Naga Sai Abhinay Devarinti](https://github.com/Abhinay1997/) |
|
||||
| DDIM Noise Comparative Analysis Pipeline | Investigating how the diffusion models learn visual concepts from each noise level (which is a contribution of [P2 weighting (CVPR 2022)](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.00227)) | [DDIM Noise Comparative Analysis Pipeline](#ddim-noise-comparative-analysis-pipeline) | - |[Aengus (Duc-Anh)](https://github.com/aengusng8) |
|
||||
| CLIP Guided Img2Img Stable Diffusion Pipeline | Doing CLIP guidance for image to image generation with Stable Diffusion | [CLIP Guided Img2Img Stable Diffusion](#clip-guided-img2img-stable-diffusion) | - | [Nipun Jindal](https://github.com/nipunjindal/) |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -50,11 +48,11 @@ The following code requires roughly 12GB of GPU RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPImageProcessor, CLIPModel
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor, CLIPModel
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPImageProcessor.from_pretrained("laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K")
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained("laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K")
|
||||
clip_model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -991,142 +989,3 @@ The resulting images in order:-
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### UnCLIP Image Interpolation Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
This Diffusion Pipeline takes two images or an image_embeddings tensor of size 2 and interpolates between their embeddings using spherical interpolation ( slerp ). The input images/image_embeddings are converted to image embeddings by the pipeline's image_encoder and the interpolation is done on the resulting image_embeddings over the number of steps specified. Defaults to 5 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
device = torch.device("cpu" if not torch.cuda.is_available() else "cuda")
|
||||
dtype = torch.float16 if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.bfloat16
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kakaobrain/karlo-v1-alpha-image-variations",
|
||||
torch_dtype=dtype,
|
||||
custom_pipeline="unclip_image_interpolation"
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
images = [Image.open('./starry_night.jpg'), Image.open('./flowers.jpg')]
|
||||
#For best results keep the prompts close in length to each other. Of course, feel free to try out with differing lengths.
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device=device).manual_seed(42)
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipe(image = images ,steps = 6, generator = generator)
|
||||
|
||||
for i,image in enumerate(output.images):
|
||||
image.save('starry_to_flowers_%s.jpg' % i)
|
||||
```
|
||||
The original images:-
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The resulting images in order:-
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||

|
||||

|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### DDIM Noise Comparative Analysis Pipeline
|
||||
#### **Research question: What visual concepts do the diffusion models learn from each noise level during training?**
|
||||
The [P2 weighting (CVPR 2022)](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.00227) paper proposed an approach to answer the above question, which is their second contribution.
|
||||
The approach consists of the following steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. The input is an image x0.
|
||||
2. Perturb it to xt using a diffusion process q(xt|x0).
|
||||
- `strength` is a value between 0.0 and 1.0, that controls the amount of noise that is added to the input image. Values that approach 1.0 allow for lots of variations but will also produce images that are not semantically consistent with the input.
|
||||
3. Reconstruct the image with the learned denoising process pθ(ˆx0|xt).
|
||||
4. Compare x0 and ˆx0 among various t to show how each step contributes to the sample.
|
||||
The authors used [openai/guided-diffusion](https://github.com/openai/guided-diffusion) model to denoise images in FFHQ dataset. This pipeline extends their second contribution by investigating DDIM on any input image.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
image_path = "path/to/your/image" # images from CelebA-HQ might be better
|
||||
image_pil = Image.open(image_path)
|
||||
image_name = image_path.split("/")[-1].split(".")[0]
|
||||
|
||||
device = torch.device("cpu" if not torch.cuda.is_available() else "cuda")
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"google/ddpm-ema-celebahq-256",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="ddim_noise_comparative_analysis",
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
for strength in np.linspace(0.1, 1, 25):
|
||||
denoised_image, latent_timestep = pipe(
|
||||
image_pil, strength=strength, return_dict=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
denoised_image = denoised_image[0]
|
||||
denoised_image.save(
|
||||
f"noise_comparative_analysis_{image_name}_{latent_timestep}.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the result of this pipeline (which is DDIM) on CelebA-HQ dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
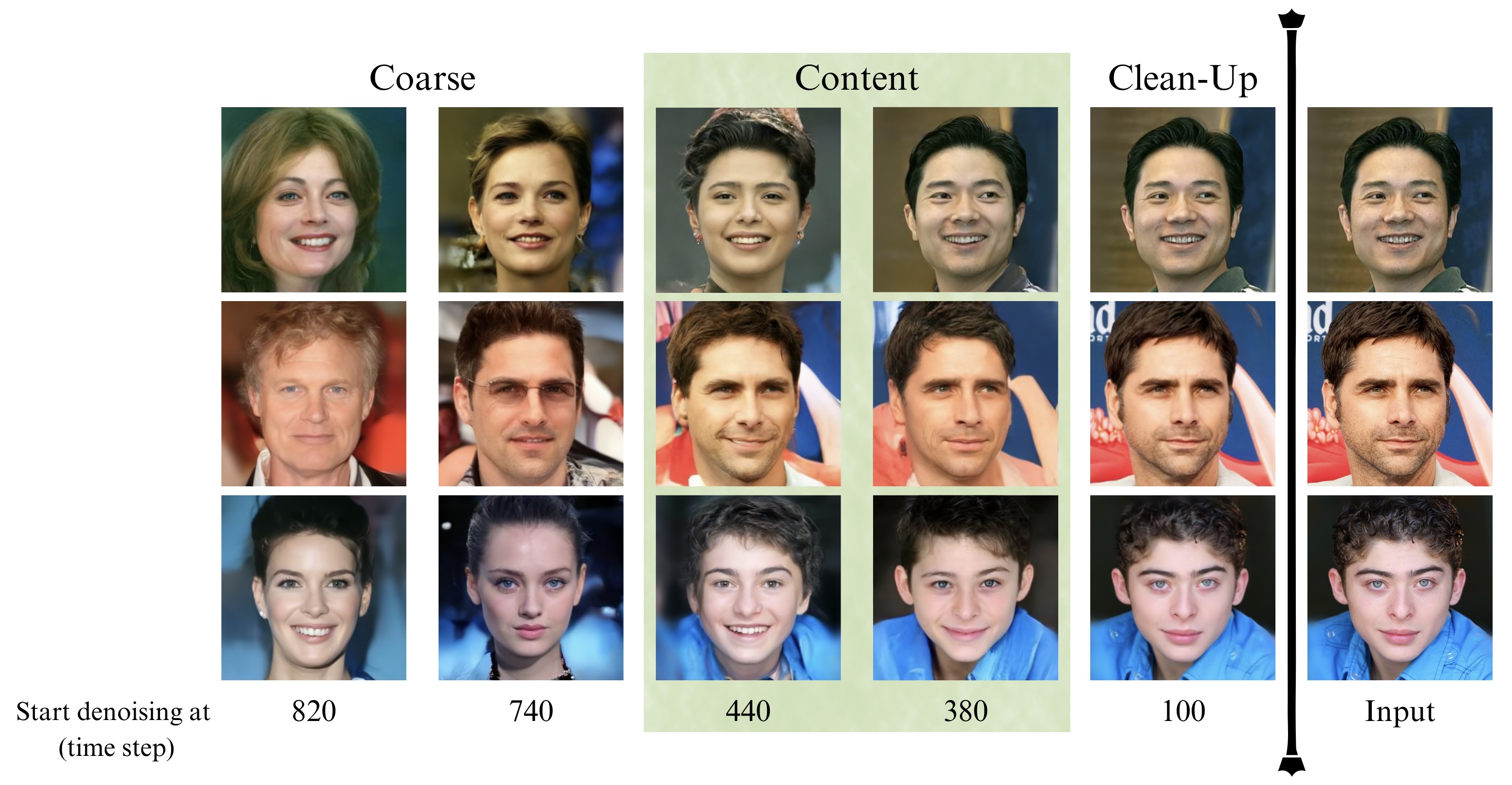
|
||||
|
||||
### CLIP Guided Img2Img Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
CLIP guided Img2Img stable diffusion can help to generate more realistic images with an initial image
|
||||
by guiding stable diffusion at every denoising step with an additional CLIP model.
|
||||
|
||||
The following code requires roughly 12GB of GPU RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor, CLIPModel
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K"
|
||||
)
|
||||
clip_model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
guided_pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
# custom_pipeline="clip_guided_stable_diffusion",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="/home/njindal/diffusers/examples/community/clip_guided_stable_diffusion.py",
|
||||
clip_model=clip_model,
|
||||
feature_extractor=feature_extractor,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
guided_pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
guided_pipeline = guided_pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
prompt = "fantasy book cover, full moon, fantasy forest landscape, golden vector elements, fantasy magic, dark light night, intricate, elegant, sharp focus, illustration, highly detailed, digital painting, concept art, matte, art by WLOP and Artgerm and Albert Bierstadt, masterpiece"
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
init_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
image = guided_pipeline(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=30,
|
||||
image=init_image,
|
||||
strength=0.75,
|
||||
guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
clip_guidance_scale=100,
|
||||
num_cutouts=4,
|
||||
use_cutouts=False,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
display(image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Init Image
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Output Image
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@@ -238,7 +238,7 @@ class BitDiffusion(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> Union[Tuple, ImagePipelineOutput]:
|
||||
latents = torch.randn(
|
||||
(batch_size, self.unet.config.in_channels, height, width),
|
||||
(batch_size, self.unet.in_channels, height, width),
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
)
|
||||
latents = decimal_to_bits(latents) * self.bit_scale
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -199,20 +199,24 @@ class CheckpointMergerPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
if not attr.startswith("_"):
|
||||
checkpoint_path_1 = os.path.join(cached_folders[1], attr)
|
||||
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_path_1):
|
||||
files = [
|
||||
*glob.glob(os.path.join(checkpoint_path_1, "*.safetensors")),
|
||||
*glob.glob(os.path.join(checkpoint_path_1, "*.bin")),
|
||||
]
|
||||
files = list(
|
||||
(
|
||||
*glob.glob(os.path.join(checkpoint_path_1, "*.safetensors")),
|
||||
*glob.glob(os.path.join(checkpoint_path_1, "*.bin")),
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
checkpoint_path_1 = files[0] if len(files) > 0 else None
|
||||
if len(cached_folders) < 3:
|
||||
checkpoint_path_2 = None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
checkpoint_path_2 = os.path.join(cached_folders[2], attr)
|
||||
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_path_2):
|
||||
files = [
|
||||
*glob.glob(os.path.join(checkpoint_path_2, "*.safetensors")),
|
||||
*glob.glob(os.path.join(checkpoint_path_2, "*.bin")),
|
||||
]
|
||||
files = list(
|
||||
(
|
||||
*glob.glob(os.path.join(checkpoint_path_2, "*.safetensors")),
|
||||
*glob.glob(os.path.join(checkpoint_path_2, "*.bin")),
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
checkpoint_path_2 = files[0] if len(files) > 0 else None
|
||||
# For an attr if both checkpoint_path_1 and 2 are None, ignore.
|
||||
# If atleast one is present, deal with it according to interp method, of course only if the state_dict keys match.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,13 +5,12 @@ import torch
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
from torch.nn import functional as F
|
||||
from torchvision import transforms
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPImageProcessor, CLIPModel, CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor, CLIPModel, CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import (
|
||||
AutoencoderKL,
|
||||
DDIMScheduler,
|
||||
DiffusionPipeline,
|
||||
DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
LMSDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
UNet2DConditionModel,
|
||||
@@ -64,8 +63,8 @@ class CLIPGuidedStableDiffusion(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
clip_model: CLIPModel,
|
||||
tokenizer: CLIPTokenizer,
|
||||
unet: UNet2DConditionModel,
|
||||
scheduler: Union[PNDMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler, DDIMScheduler, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler],
|
||||
feature_extractor: CLIPImageProcessor,
|
||||
scheduler: Union[PNDMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler, DDIMScheduler],
|
||||
feature_extractor: CLIPFeatureExtractor,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.register_modules(
|
||||
@@ -126,12 +125,17 @@ class CLIPGuidedStableDiffusion(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
):
|
||||
latents = latents.detach().requires_grad_()
|
||||
|
||||
latent_model_input = self.scheduler.scale_model_input(latents, timestep)
|
||||
if isinstance(self.scheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler):
|
||||
sigma = self.scheduler.sigmas[index]
|
||||
# the model input needs to be scaled to match the continuous ODE formulation in K-LMS
|
||||
latent_model_input = latents / ((sigma**2 + 1) ** 0.5)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
latent_model_input = latents
|
||||
|
||||
# predict the noise residual
|
||||
noise_pred = self.unet(latent_model_input, timestep, encoder_hidden_states=text_embeddings).sample
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(self.scheduler, (PNDMScheduler, DDIMScheduler, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler)):
|
||||
if isinstance(self.scheduler, (PNDMScheduler, DDIMScheduler)):
|
||||
alpha_prod_t = self.scheduler.alphas_cumprod[timestep]
|
||||
beta_prod_t = 1 - alpha_prod_t
|
||||
# compute predicted original sample from predicted noise also called
|
||||
@@ -254,7 +258,7 @@ class CLIPGuidedStableDiffusion(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
# Unlike in other pipelines, latents need to be generated in the target device
|
||||
# for 1-to-1 results reproducibility with the CompVis implementation.
|
||||
# However this currently doesn't work in `mps`.
|
||||
latents_shape = (batch_size * num_images_per_prompt, self.unet.config.in_channels, height // 8, width // 8)
|
||||
latents_shape = (batch_size * num_images_per_prompt, self.unet.in_channels, height // 8, width // 8)
|
||||
latents_dtype = text_embeddings.dtype
|
||||
if latents is None:
|
||||
if self.device.type == "mps":
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,496 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
from torch.nn import functional as F
|
||||
from torchvision import transforms
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor, CLIPModel, CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import (
|
||||
AutoencoderKL,
|
||||
DDIMScheduler,
|
||||
DiffusionPipeline,
|
||||
DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
LMSDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
UNet2DConditionModel,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.pipeline_stable_diffusion import StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import (
|
||||
PIL_INTERPOLATION,
|
||||
deprecate,
|
||||
randn_tensor,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
EXAMPLE_DOC_STRING = """
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
```
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor, CLIPModel
|
||||
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K"
|
||||
)
|
||||
clip_model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
guided_pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
# custom_pipeline="clip_guided_stable_diffusion",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="/home/njindal/diffusers/examples/community/clip_guided_stable_diffusion.py",
|
||||
clip_model=clip_model,
|
||||
feature_extractor=feature_extractor,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
guided_pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
guided_pipeline = guided_pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "fantasy book cover, full moon, fantasy forest landscape, golden vector elements, fantasy magic, dark light night, intricate, elegant, sharp focus, illustration, highly detailed, digital painting, concept art, matte, art by WLOP and Artgerm and Albert Bierstadt, masterpiece"
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
init_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
|
||||
image = guided_pipeline(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=30,
|
||||
image=init_image,
|
||||
strength=0.75,
|
||||
guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
clip_guidance_scale=100,
|
||||
num_cutouts=4,
|
||||
use_cutouts=False,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
display(image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess(image, w, h):
|
||||
if isinstance(image, torch.Tensor):
|
||||
return image
|
||||
elif isinstance(image, PIL.Image.Image):
|
||||
image = [image]
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(image[0], PIL.Image.Image):
|
||||
image = [np.array(i.resize((w, h), resample=PIL_INTERPOLATION["lanczos"]))[None, :] for i in image]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate(image, axis=0)
|
||||
image = np.array(image).astype(np.float32) / 255.0
|
||||
image = image.transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
image = 2.0 * image - 1.0
|
||||
image = torch.from_numpy(image)
|
||||
elif isinstance(image[0], torch.Tensor):
|
||||
image = torch.cat(image, dim=0)
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MakeCutouts(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, cut_size, cut_power=1.0):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
|
||||
self.cut_size = cut_size
|
||||
self.cut_power = cut_power
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, pixel_values, num_cutouts):
|
||||
sideY, sideX = pixel_values.shape[2:4]
|
||||
max_size = min(sideX, sideY)
|
||||
min_size = min(sideX, sideY, self.cut_size)
|
||||
cutouts = []
|
||||
for _ in range(num_cutouts):
|
||||
size = int(torch.rand([]) ** self.cut_power * (max_size - min_size) + min_size)
|
||||
offsetx = torch.randint(0, sideX - size + 1, ())
|
||||
offsety = torch.randint(0, sideY - size + 1, ())
|
||||
cutout = pixel_values[:, :, offsety : offsety + size, offsetx : offsetx + size]
|
||||
cutouts.append(F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(cutout, self.cut_size))
|
||||
return torch.cat(cutouts)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def spherical_dist_loss(x, y):
|
||||
x = F.normalize(x, dim=-1)
|
||||
y = F.normalize(y, dim=-1)
|
||||
return (x - y).norm(dim=-1).div(2).arcsin().pow(2).mul(2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def set_requires_grad(model, value):
|
||||
for param in model.parameters():
|
||||
param.requires_grad = value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CLIPGuidedStableDiffusion(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
"""CLIP guided stable diffusion based on the amazing repo by @crowsonkb and @Jack000
|
||||
- https://github.com/Jack000/glid-3-xl
|
||||
- https://github.dev/crowsonkb/k-diffusion
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
vae: AutoencoderKL,
|
||||
text_encoder: CLIPTextModel,
|
||||
clip_model: CLIPModel,
|
||||
tokenizer: CLIPTokenizer,
|
||||
unet: UNet2DConditionModel,
|
||||
scheduler: Union[PNDMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler, DDIMScheduler, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler],
|
||||
feature_extractor: CLIPFeatureExtractor,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.register_modules(
|
||||
vae=vae,
|
||||
text_encoder=text_encoder,
|
||||
clip_model=clip_model,
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
unet=unet,
|
||||
scheduler=scheduler,
|
||||
feature_extractor=feature_extractor,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=feature_extractor.image_mean, std=feature_extractor.image_std)
|
||||
self.cut_out_size = (
|
||||
feature_extractor.size
|
||||
if isinstance(feature_extractor.size, int)
|
||||
else feature_extractor.size["shortest_edge"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.make_cutouts = MakeCutouts(self.cut_out_size)
|
||||
|
||||
set_requires_grad(self.text_encoder, False)
|
||||
set_requires_grad(self.clip_model, False)
|
||||
|
||||
def enable_attention_slicing(self, slice_size: Optional[Union[str, int]] = "auto"):
|
||||
if slice_size == "auto":
|
||||
# half the attention head size is usually a good trade-off between
|
||||
# speed and memory
|
||||
slice_size = self.unet.config.attention_head_dim // 2
|
||||
self.unet.set_attention_slice(slice_size)
|
||||
|
||||
def disable_attention_slicing(self):
|
||||
self.enable_attention_slicing(None)
|
||||
|
||||
def freeze_vae(self):
|
||||
set_requires_grad(self.vae, False)
|
||||
|
||||
def unfreeze_vae(self):
|
||||
set_requires_grad(self.vae, True)
|
||||
|
||||
def freeze_unet(self):
|
||||
set_requires_grad(self.unet, False)
|
||||
|
||||
def unfreeze_unet(self):
|
||||
set_requires_grad(self.unet, True)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_timesteps(self, num_inference_steps, strength, device):
|
||||
# get the original timestep using init_timestep
|
||||
init_timestep = min(int(num_inference_steps * strength), num_inference_steps)
|
||||
|
||||
t_start = max(num_inference_steps - init_timestep, 0)
|
||||
timesteps = self.scheduler.timesteps[t_start:]
|
||||
|
||||
return timesteps, num_inference_steps - t_start
|
||||
|
||||
def prepare_latents(self, image, timestep, batch_size, num_images_per_prompt, dtype, device, generator=None):
|
||||
if not isinstance(image, (torch.Tensor, PIL.Image.Image, list)):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"`image` has to be of type `torch.Tensor`, `PIL.Image.Image` or list but is {type(image)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
image = image.to(device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
batch_size = batch_size * num_images_per_prompt
|
||||
if isinstance(generator, list) and len(generator) != batch_size:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"You have passed a list of generators of length {len(generator)}, but requested an effective batch"
|
||||
f" size of {batch_size}. Make sure the batch size matches the length of the generators."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(generator, list):
|
||||
init_latents = [
|
||||
self.vae.encode(image[i : i + 1]).latent_dist.sample(generator[i]) for i in range(batch_size)
|
||||
]
|
||||
init_latents = torch.cat(init_latents, dim=0)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
init_latents = self.vae.encode(image).latent_dist.sample(generator)
|
||||
|
||||
init_latents = self.vae.config.scaling_factor * init_latents
|
||||
|
||||
if batch_size > init_latents.shape[0] and batch_size % init_latents.shape[0] == 0:
|
||||
# expand init_latents for batch_size
|
||||
deprecation_message = (
|
||||
f"You have passed {batch_size} text prompts (`prompt`), but only {init_latents.shape[0]} initial"
|
||||
" images (`image`). Initial images are now duplicating to match the number of text prompts. Note"
|
||||
" that this behavior is deprecated and will be removed in a version 1.0.0. Please make sure to update"
|
||||
" your script to pass as many initial images as text prompts to suppress this warning."
|
||||
)
|
||||
deprecate("len(prompt) != len(image)", "1.0.0", deprecation_message, standard_warn=False)
|
||||
additional_image_per_prompt = batch_size // init_latents.shape[0]
|
||||
init_latents = torch.cat([init_latents] * additional_image_per_prompt, dim=0)
|
||||
elif batch_size > init_latents.shape[0] and batch_size % init_latents.shape[0] != 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Cannot duplicate `image` of batch size {init_latents.shape[0]} to {batch_size} text prompts."
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
init_latents = torch.cat([init_latents], dim=0)
|
||||
|
||||
shape = init_latents.shape
|
||||
noise = randn_tensor(shape, generator=generator, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
# get latents
|
||||
init_latents = self.scheduler.add_noise(init_latents, noise, timestep)
|
||||
latents = init_latents
|
||||
|
||||
return latents
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.enable_grad()
|
||||
def cond_fn(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
latents,
|
||||
timestep,
|
||||
index,
|
||||
text_embeddings,
|
||||
noise_pred_original,
|
||||
text_embeddings_clip,
|
||||
clip_guidance_scale,
|
||||
num_cutouts,
|
||||
use_cutouts=True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
latents = latents.detach().requires_grad_()
|
||||
|
||||
latent_model_input = self.scheduler.scale_model_input(latents, timestep)
|
||||
|
||||
# predict the noise residual
|
||||
noise_pred = self.unet(latent_model_input, timestep, encoder_hidden_states=text_embeddings).sample
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(self.scheduler, (PNDMScheduler, DDIMScheduler, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler)):
|
||||
alpha_prod_t = self.scheduler.alphas_cumprod[timestep]
|
||||
beta_prod_t = 1 - alpha_prod_t
|
||||
# compute predicted original sample from predicted noise also called
|
||||
# "predicted x_0" of formula (12) from https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.02502.pdf
|
||||
pred_original_sample = (latents - beta_prod_t ** (0.5) * noise_pred) / alpha_prod_t ** (0.5)
|
||||
|
||||
fac = torch.sqrt(beta_prod_t)
|
||||
sample = pred_original_sample * (fac) + latents * (1 - fac)
|
||||
elif isinstance(self.scheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler):
|
||||
sigma = self.scheduler.sigmas[index]
|
||||
sample = latents - sigma * noise_pred
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"scheduler type {type(self.scheduler)} not supported")
|
||||
|
||||
sample = 1 / self.vae.config.scaling_factor * sample
|
||||
image = self.vae.decode(sample).sample
|
||||
image = (image / 2 + 0.5).clamp(0, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
if use_cutouts:
|
||||
image = self.make_cutouts(image, num_cutouts)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image = transforms.Resize(self.cut_out_size)(image)
|
||||
image = self.normalize(image).to(latents.dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
image_embeddings_clip = self.clip_model.get_image_features(image)
|
||||
image_embeddings_clip = image_embeddings_clip / image_embeddings_clip.norm(p=2, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
|
||||
|
||||
if use_cutouts:
|
||||
dists = spherical_dist_loss(image_embeddings_clip, text_embeddings_clip)
|
||||
dists = dists.view([num_cutouts, sample.shape[0], -1])
|
||||
loss = dists.sum(2).mean(0).sum() * clip_guidance_scale
|
||||
else:
|
||||
loss = spherical_dist_loss(image_embeddings_clip, text_embeddings_clip).mean() * clip_guidance_scale
|
||||
|
||||
grads = -torch.autograd.grad(loss, latents)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(self.scheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler):
|
||||
latents = latents.detach() + grads * (sigma**2)
|
||||
noise_pred = noise_pred_original
|
||||
else:
|
||||
noise_pred = noise_pred_original - torch.sqrt(beta_prod_t) * grads
|
||||
return noise_pred, latents
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def __call__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
prompt: Union[str, List[str]],
|
||||
height: Optional[int] = 512,
|
||||
width: Optional[int] = 512,
|
||||
image: Union[torch.FloatTensor, PIL.Image.Image] = None,
|
||||
strength: float = 0.8,
|
||||
num_inference_steps: Optional[int] = 50,
|
||||
guidance_scale: Optional[float] = 7.5,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt: Optional[int] = 1,
|
||||
eta: float = 0.0,
|
||||
clip_guidance_scale: Optional[float] = 100,
|
||||
clip_prompt: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
num_cutouts: Optional[int] = 4,
|
||||
use_cutouts: Optional[bool] = True,
|
||||
generator: Optional[torch.Generator] = None,
|
||||
latents: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
|
||||
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
|
||||
return_dict: bool = True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
if isinstance(prompt, str):
|
||||
batch_size = 1
|
||||
elif isinstance(prompt, list):
|
||||
batch_size = len(prompt)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`prompt` has to be of type `str` or `list` but is {type(prompt)}")
|
||||
|
||||
if height % 8 != 0 or width % 8 != 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`height` and `width` have to be divisible by 8 but are {height} and {width}.")
|
||||
|
||||
# get prompt text embeddings
|
||||
text_input = self.tokenizer(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
padding="max_length",
|
||||
max_length=self.tokenizer.model_max_length,
|
||||
truncation=True,
|
||||
return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
)
|
||||
text_embeddings = self.text_encoder(text_input.input_ids.to(self.device))[0]
|
||||
# duplicate text embeddings for each generation per prompt
|
||||
text_embeddings = text_embeddings.repeat_interleave(num_images_per_prompt, dim=0)
|
||||
|
||||
# set timesteps
|
||||
accepts_offset = "offset" in set(inspect.signature(self.scheduler.set_timesteps).parameters.keys())
|
||||
extra_set_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if accepts_offset:
|
||||
extra_set_kwargs["offset"] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
self.scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps, **extra_set_kwargs)
|
||||
# Some schedulers like PNDM have timesteps as arrays
|
||||
# It's more optimized to move all timesteps to correct device beforehand
|
||||
self.scheduler.timesteps.to(self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
timesteps, num_inference_steps = self.get_timesteps(num_inference_steps, strength, self.device)
|
||||
latent_timestep = timesteps[:1].repeat(batch_size * num_images_per_prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
# Preprocess image
|
||||
image = preprocess(image, width, height)
|
||||
latents = self.prepare_latents(
|
||||
image, latent_timestep, batch_size, num_images_per_prompt, text_embeddings.dtype, self.device, generator
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if clip_guidance_scale > 0:
|
||||
if clip_prompt is not None:
|
||||
clip_text_input = self.tokenizer(
|
||||
clip_prompt,
|
||||
padding="max_length",
|
||||
max_length=self.tokenizer.model_max_length,
|
||||
truncation=True,
|
||||
return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
).input_ids.to(self.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
clip_text_input = text_input.input_ids.to(self.device)
|
||||
text_embeddings_clip = self.clip_model.get_text_features(clip_text_input)
|
||||
text_embeddings_clip = text_embeddings_clip / text_embeddings_clip.norm(p=2, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
|
||||
# duplicate text embeddings clip for each generation per prompt
|
||||
text_embeddings_clip = text_embeddings_clip.repeat_interleave(num_images_per_prompt, dim=0)
|
||||
|
||||
# here `guidance_scale` is defined analog to the guidance weight `w` of equation (2)
|
||||
# of the Imagen paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.11487.pdf . `guidance_scale = 1`
|
||||
# corresponds to doing no classifier free guidance.
|
||||
do_classifier_free_guidance = guidance_scale > 1.0
|
||||
# get unconditional embeddings for classifier free guidance
|
||||
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
|
||||
max_length = text_input.input_ids.shape[-1]
|
||||
uncond_input = self.tokenizer([""], padding="max_length", max_length=max_length, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
uncond_embeddings = self.text_encoder(uncond_input.input_ids.to(self.device))[0]
|
||||
# duplicate unconditional embeddings for each generation per prompt
|
||||
uncond_embeddings = uncond_embeddings.repeat_interleave(num_images_per_prompt, dim=0)
|
||||
|
||||
# For classifier free guidance, we need to do two forward passes.
|
||||
# Here we concatenate the unconditional and text embeddings into a single batch
|
||||
# to avoid doing two forward passes
|
||||
text_embeddings = torch.cat([uncond_embeddings, text_embeddings])
|
||||
|
||||
# get the initial random noise unless the user supplied it
|
||||
|
||||
# Unlike in other pipelines, latents need to be generated in the target device
|
||||
# for 1-to-1 results reproducibility with the CompVis implementation.
|
||||
# However this currently doesn't work in `mps`.
|
||||
latents_shape = (batch_size * num_images_per_prompt, self.unet.config.in_channels, height // 8, width // 8)
|
||||
latents_dtype = text_embeddings.dtype
|
||||
if latents is None:
|
||||
if self.device.type == "mps":
|
||||
# randn does not work reproducibly on mps
|
||||
latents = torch.randn(latents_shape, generator=generator, device="cpu", dtype=latents_dtype).to(
|
||||
self.device
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
latents = torch.randn(latents_shape, generator=generator, device=self.device, dtype=latents_dtype)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if latents.shape != latents_shape:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unexpected latents shape, got {latents.shape}, expected {latents_shape}")
|
||||
latents = latents.to(self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
# scale the initial noise by the standard deviation required by the scheduler
|
||||
latents = latents * self.scheduler.init_noise_sigma
|
||||
|
||||
# prepare extra kwargs for the scheduler step, since not all schedulers have the same signature
|
||||
# eta (η) is only used with the DDIMScheduler, it will be ignored for other schedulers.
|
||||
# eta corresponds to η in DDIM paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502
|
||||
# and should be between [0, 1]
|
||||
accepts_eta = "eta" in set(inspect.signature(self.scheduler.step).parameters.keys())
|
||||
extra_step_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if accepts_eta:
|
||||
extra_step_kwargs["eta"] = eta
|
||||
|
||||
# check if the scheduler accepts generator
|
||||
accepts_generator = "generator" in set(inspect.signature(self.scheduler.step).parameters.keys())
|
||||
if accepts_generator:
|
||||
extra_step_kwargs["generator"] = generator
|
||||
|
||||
with self.progress_bar(total=num_inference_steps):
|
||||
for i, t in enumerate(timesteps):
|
||||
# expand the latents if we are doing classifier free guidance
|
||||
latent_model_input = torch.cat([latents] * 2) if do_classifier_free_guidance else latents
|
||||
latent_model_input = self.scheduler.scale_model_input(latent_model_input, t)
|
||||
|
||||
# predict the noise residual
|
||||
noise_pred = self.unet(latent_model_input, t, encoder_hidden_states=text_embeddings).sample
|
||||
|
||||
# perform classifier free guidance
|
||||
if do_classifier_free_guidance:
|
||||
noise_pred_uncond, noise_pred_text = noise_pred.chunk(2)
|
||||
noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond)
|
||||
|
||||
# perform clip guidance
|
||||
if clip_guidance_scale > 0:
|
||||
text_embeddings_for_guidance = (
|
||||
text_embeddings.chunk(2)[1] if do_classifier_free_guidance else text_embeddings
|
||||
)
|
||||
noise_pred, latents = self.cond_fn(
|
||||
latents,
|
||||
t,
|
||||
i,
|
||||
text_embeddings_for_guidance,
|
||||
noise_pred,
|
||||
text_embeddings_clip,
|
||||
clip_guidance_scale,
|
||||
num_cutouts,
|
||||
use_cutouts,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# compute the previous noisy sample x_t -> x_t-1
|
||||
latents = self.scheduler.step(noise_pred, t, latents, **extra_step_kwargs).prev_sample
|
||||
|
||||
# scale and decode the image latents with vae
|
||||
latents = 1 / self.vae.config.scaling_factor * latents
|
||||
image = self.vae.decode(latents).sample
|
||||
|
||||
image = (image / 2 + 0.5).clamp(0, 1)
|
||||
image = image.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1).numpy()
|
||||
|
||||
if output_type == "pil":
|
||||
image = self.numpy_to_pil(image)
|
||||
|
||||
if not return_dict:
|
||||
return (image, None)
|
||||
|
||||
return StableDiffusionPipelineOutput(images=image, nsfw_content_detected=None)
|
||||
@@ -17,13 +17,11 @@ from typing import Callable, List, Optional, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from packaging import version
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPImageProcessor, CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor, CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.configuration_utils import FrozenDict
|
||||
from diffusers.models import AutoencoderKL, UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
from diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.pipeline_stable_diffusion import StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
from diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.safety_checker import StableDiffusionSafetyChecker
|
||||
from diffusers.schedulers import (
|
||||
DDIMScheduler,
|
||||
DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +30,11 @@ from diffusers.schedulers import (
|
||||
LMSDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import deprecate, is_accelerate_available, logging
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import is_accelerate_available
|
||||
|
||||
from ...utils import deprecate, logging
|
||||
from . import StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
from .safety_checker import StableDiffusionSafetyChecker
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__) # pylint: disable=invalid-name
|
||||
@@ -62,7 +64,7 @@ class ComposableStableDiffusionPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
safety_checker ([`StableDiffusionSafetyChecker`]):
|
||||
Classification module that estimates whether generated images could be considered offensive or harmful.
|
||||
Please, refer to the [model card](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) for details.
|
||||
feature_extractor ([`CLIPImageProcessor`]):
|
||||
feature_extractor ([`CLIPFeatureExtractor`]):
|
||||
Model that extracts features from generated images to be used as inputs for the `safety_checker`.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_optional_components = ["safety_checker", "feature_extractor"]
|
||||
@@ -82,7 +84,7 @@ class ComposableStableDiffusionPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
],
|
||||
safety_checker: StableDiffusionSafetyChecker,
|
||||
feature_extractor: CLIPImageProcessor,
|
||||
feature_extractor: CLIPFeatureExtractor,
|
||||
requires_safety_checker: bool = True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
@@ -511,7 +513,7 @@ class ComposableStableDiffusionPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
timesteps = self.scheduler.timesteps
|
||||
|
||||
# 5. Prepare latent variables
|
||||
num_channels_latents = self.unet.config.in_channels
|
||||
num_channels_latents = self.unet.in_channels
|
||||
latents = self.prepare_latents(
|
||||
batch_size * num_images_per_prompt,
|
||||
num_channels_latents,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,190 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torchvision import transforms
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers.pipeline_utils import DiffusionPipeline, ImagePipelineOutput
|
||||
from diffusers.schedulers import DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import randn_tensor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
trans = transforms.Compose(
|
||||
[
|
||||
transforms.Resize((256, 256)),
|
||||
transforms.ToTensor(),
|
||||
transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5]),
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess(image):
|
||||
if isinstance(image, torch.Tensor):
|
||||
return image
|
||||
elif isinstance(image, PIL.Image.Image):
|
||||
image = [image]
|
||||
|
||||
image = [trans(img.convert("RGB")) for img in image]
|
||||
image = torch.stack(image)
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DDIMNoiseComparativeAnalysisPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
This model inherits from [`DiffusionPipeline`]. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the
|
||||
library implements for all the pipelines (such as downloading or saving, running on a particular device, etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters:
|
||||
unet ([`UNet2DModel`]): U-Net architecture to denoise the encoded image.
|
||||
scheduler ([`SchedulerMixin`]):
|
||||
A scheduler to be used in combination with `unet` to denoise the encoded image. Can be one of
|
||||
[`DDPMScheduler`], or [`DDIMScheduler`].
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure scheduler can always be converted to DDIM
|
||||
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_config(scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
|
||||
|
||||
def check_inputs(self, strength):
|
||||
if strength < 0 or strength > 1:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"The value of strength should in [0.0, 1.0] but is {strength}")
|
||||
|
||||
def get_timesteps(self, num_inference_steps, strength, device):
|
||||
# get the original timestep using init_timestep
|
||||
init_timestep = min(int(num_inference_steps * strength), num_inference_steps)
|
||||
|
||||
t_start = max(num_inference_steps - init_timestep, 0)
|
||||
timesteps = self.scheduler.timesteps[t_start:]
|
||||
|
||||
return timesteps, num_inference_steps - t_start
|
||||
|
||||
def prepare_latents(self, image, timestep, batch_size, dtype, device, generator=None):
|
||||
if not isinstance(image, (torch.Tensor, PIL.Image.Image, list)):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"`image` has to be of type `torch.Tensor`, `PIL.Image.Image` or list but is {type(image)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
init_latents = image.to(device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(generator, list) and len(generator) != batch_size:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"You have passed a list of generators of length {len(generator)}, but requested an effective batch"
|
||||
f" size of {batch_size}. Make sure the batch size matches the length of the generators."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
shape = init_latents.shape
|
||||
noise = randn_tensor(shape, generator=generator, device=device, dtype=dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
# get latents
|
||||
print("add noise to latents at timestep", timestep)
|
||||
init_latents = self.scheduler.add_noise(init_latents, noise, timestep)
|
||||
latents = init_latents
|
||||
|
||||
return latents
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def __call__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
image: Union[torch.FloatTensor, PIL.Image.Image] = None,
|
||||
strength: float = 0.8,
|
||||
batch_size: int = 1,
|
||||
generator: Optional[Union[torch.Generator, List[torch.Generator]]] = None,
|
||||
eta: float = 0.0,
|
||||
num_inference_steps: int = 50,
|
||||
use_clipped_model_output: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
output_type: Optional[str] = "pil",
|
||||
return_dict: bool = True,
|
||||
) -> Union[ImagePipelineOutput, Tuple]:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
image (`torch.FloatTensor` or `PIL.Image.Image`):
|
||||
`Image`, or tensor representing an image batch, that will be used as the starting point for the
|
||||
process.
|
||||
strength (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 0.8):
|
||||
Conceptually, indicates how much to transform the reference `image`. Must be between 0 and 1. `image`
|
||||
will be used as a starting point, adding more noise to it the larger the `strength`. The number of
|
||||
denoising steps depends on the amount of noise initially added. When `strength` is 1, added noise will
|
||||
be maximum and the denoising process will run for the full number of iterations specified in
|
||||
`num_inference_steps`. A value of 1, therefore, essentially ignores `image`.
|
||||
batch_size (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
|
||||
The number of images to generate.
|
||||
generator (`torch.Generator`, *optional*):
|
||||
One or a list of [torch generator(s)](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html)
|
||||
to make generation deterministic.
|
||||
eta (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 0.0):
|
||||
The eta parameter which controls the scale of the variance (0 is DDIM and 1 is one type of DDPM).
|
||||
num_inference_steps (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 50):
|
||||
The number of denoising steps. More denoising steps usually lead to a higher quality image at the
|
||||
expense of slower inference.
|
||||
use_clipped_model_output (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `None`):
|
||||
if `True` or `False`, see documentation for `DDIMScheduler.step`. If `None`, nothing is passed
|
||||
downstream to the scheduler. So use `None` for schedulers which don't support this argument.
|
||||
output_type (`str`, *optional*, defaults to `"pil"`):
|
||||
The output format of the generate image. Choose between
|
||||
[PIL](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/): `PIL.Image.Image` or `np.array`.
|
||||
return_dict (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether or not to return a [`~pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput`] instead of a plain tuple.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
[`~pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput`] or `tuple`: [`~pipelines.utils.ImagePipelineOutput`] if `return_dict` is
|
||||
True, otherwise a `tuple. When returning a tuple, the first element is a list with the generated images.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# 1. Check inputs. Raise error if not correct
|
||||
self.check_inputs(strength)
|
||||
|
||||
# 2. Preprocess image
|
||||
image = preprocess(image)
|
||||
|
||||
# 3. set timesteps
|
||||
self.scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps, device=self.device)
|
||||
timesteps, num_inference_steps = self.get_timesteps(num_inference_steps, strength, self.device)
|
||||
latent_timestep = timesteps[:1].repeat(batch_size)
|
||||
|
||||
# 4. Prepare latent variables
|
||||
latents = self.prepare_latents(image, latent_timestep, batch_size, self.unet.dtype, self.device, generator)
|
||||
image = latents
|
||||
|
||||
# 5. Denoising loop
|
||||
for t in self.progress_bar(timesteps):
|
||||
# 1. predict noise model_output
|
||||
model_output = self.unet(image, t).sample
|
||||
|
||||
# 2. predict previous mean of image x_t-1 and add variance depending on eta
|
||||
# eta corresponds to η in paper and should be between [0, 1]
|
||||
# do x_t -> x_t-1
|
||||
image = self.scheduler.step(
|
||||
model_output,
|
||||
t,
|
||||
image,
|
||||
eta=eta,
|
||||
use_clipped_model_output=use_clipped_model_output,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).prev_sample
|
||||
|
||||
image = (image / 2 + 0.5).clamp(0, 1)
|
||||
image = image.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1).numpy()
|
||||
if output_type == "pil":
|
||||
image = self.numpy_to_pil(image)
|
||||
|
||||
if not return_dict:
|
||||
return (image, latent_timestep.item())
|
||||
|
||||
return ImagePipelineOutput(images=image)
|
||||
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
# TODO: remove and import from diffusers.utils when the new version of diffusers is released
|
||||
from packaging import version
|
||||
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPImageProcessor, CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor, CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.models import AutoencoderKL, UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ logger = logging.get_logger(__name__) # pylint: disable=invalid-name
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess(image):
|
||||
w, h = image.size
|
||||
w, h = (x - x % 32 for x in (w, h)) # resize to integer multiple of 32
|
||||
w, h = map(lambda x: x - x % 32, (w, h)) # resize to integer multiple of 32
|
||||
image = image.resize((w, h), resample=PIL_INTERPOLATION["lanczos"])
|
||||
image = np.array(image).astype(np.float32) / 255.0
|
||||
image = image[None].transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ class ImagicStableDiffusionPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
safety_checker ([`StableDiffusionSafetyChecker`]):
|
||||
Classification module that estimates whether generated images could be considered offsensive or harmful.
|
||||
Please, refer to the [model card](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) for details.
|
||||
feature_extractor ([`CLIPImageProcessor`]):
|
||||
feature_extractor ([`CLIPFeatureExtractor`]):
|
||||
Model that extracts features from generated images to be used as inputs for the `safety_checker`.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -92,7 +92,7 @@ class ImagicStableDiffusionPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
unet: UNet2DConditionModel,
|
||||
scheduler: Union[DDIMScheduler, PNDMScheduler, LMSDiscreteScheduler],
|
||||
safety_checker: StableDiffusionSafetyChecker,
|
||||
feature_extractor: CLIPImageProcessor,
|
||||
feature_extractor: CLIPFeatureExtractor,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.register_modules(
|
||||
@@ -424,7 +424,7 @@ class ImagicStableDiffusionPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
# Unlike in other pipelines, latents need to be generated in the target device
|
||||
# for 1-to-1 results reproducibility with the CompVis implementation.
|
||||
# However this currently doesn't work in `mps`.
|
||||
latents_shape = (1, self.unet.config.in_channels, height // 8, width // 8)
|
||||
latents_shape = (1, self.unet.in_channels, height // 8, width // 8)
|
||||
latents_dtype = text_embeddings.dtype
|
||||
if self.device.type == "mps":
|
||||
# randn does not exist on mps
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user