mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
synced 2026-02-25 04:10:34 +08:00
Compare commits
83 Commits
debug-add-
...
v0.22.1-pa
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
a1d33fc9a5 | ||
|
|
1a4db89def | ||
|
|
df60b35e47 | ||
|
|
aec3de8bdb | ||
|
|
d61889fc17 | ||
|
|
2b23ec82e8 | ||
|
|
080081bded | ||
|
|
dd9a5caf61 | ||
|
|
a35e72b032 | ||
|
|
beb8f216ed | ||
|
|
7ad70cee74 | ||
|
|
60c5eb5877 | ||
|
|
d122206466 | ||
|
|
c84982a804 | ||
|
|
84e7bb875d | ||
|
|
072e00897a | ||
|
|
b91d5ddd1a | ||
|
|
2a8cf8e39f | ||
|
|
9ced7844da | ||
|
|
9723f8a557 | ||
|
|
b81f709fb6 | ||
|
|
75ea54a151 | ||
|
|
c0f0582651 | ||
|
|
b81c69e489 | ||
|
|
02ba50c610 | ||
|
|
4f2bf67355 | ||
|
|
29cf163b95 | ||
|
|
839c2a5ece | ||
|
|
5712c3d2ef | ||
|
|
151998e1c2 | ||
|
|
d1eb14bc35 | ||
|
|
5c75a5fbc4 | ||
|
|
442017ccc8 | ||
|
|
f1d052c5b8 | ||
|
|
ce9484b139 | ||
|
|
ed00ead345 | ||
|
|
f0b2f6ce05 | ||
|
|
32fea1cc9b | ||
|
|
bb46be2f18 | ||
|
|
ac7b1716b7 | ||
|
|
3fc10ded00 | ||
|
|
5b087e82d1 | ||
|
|
8f3100db9f | ||
|
|
3ec828d6dd | ||
|
|
9135e54e76 | ||
|
|
e140c0562e | ||
|
|
595ba6f786 | ||
|
|
798591346d | ||
|
|
f912f39b50 | ||
|
|
0d4b459be6 | ||
|
|
cee1cd6e9c | ||
|
|
5b448a5e5d | ||
|
|
a69ebe5527 | ||
|
|
ce7f334472 | ||
|
|
8959c5b9de | ||
|
|
bc8a08f67c | ||
|
|
dbce14da56 | ||
|
|
71ad02607d | ||
|
|
dd981256ad | ||
|
|
0c9f174d59 | ||
|
|
d420d71398 | ||
|
|
a1fad8286f | ||
|
|
dc943eb99d | ||
|
|
0fc25715a1 | ||
|
|
de71fa59f5 | ||
|
|
dcbfe662ef | ||
|
|
958e17dada | ||
|
|
7c3a75a1ce | ||
|
|
b8896a154a | ||
|
|
c7617e482a | ||
|
|
77241c48af | ||
|
|
096f84b05f | ||
|
|
9e1edfc1ad | ||
|
|
6b06c30a65 | ||
|
|
188d864fa3 | ||
|
|
6e608d8a35 | ||
|
|
33293ed504 | ||
|
|
48ce118d1c | ||
|
|
1ade42f729 | ||
|
|
677df5ac12 | ||
|
|
16851efa0f | ||
|
|
0eac9cd04e | ||
|
|
bc7a4d4917 |
2
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
install_libgl1: true
|
||||
package: diffusers
|
||||
notebook_folder: diffusers_doc
|
||||
languages: en ko zh
|
||||
languages: en ko zh ja pt
|
||||
|
||||
secrets:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.HUGGINGFACE_PUSH }}
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
@@ -15,4 +15,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
pr_number: ${{ github.event.number }}
|
||||
install_libgl1: true
|
||||
package: diffusers
|
||||
languages: en ko zh
|
||||
languages: en ko zh ja pt
|
||||
|
||||
50
.github/workflows/push_tests.yml
vendored
50
.github/workflows/push_tests.yml
vendored
@@ -156,6 +156,56 @@ jobs:
|
||||
name: torch_cuda_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
peft_cuda_tests:
|
||||
name: PEFT CUDA Tests
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m pip install -e .[quality,test]
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run slow PEFT CUDA tests
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_peft_cuda \
|
||||
tests/lora/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_peft_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_peft_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: torch_peft_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
flax_tpu_tests:
|
||||
name: Flax TPU Tests
|
||||
runs-on: docker-tpu
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Pipelines should be used **only** for inference.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be very readable, self-explanatory, and easy to tweak.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be designed to build on top of each other and be easy to integrate into higher-level APIs.
|
||||
- Pipelines are **not** intended to be feature-complete user interfaces. For future complete user interfaces one should rather have a look at [InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI), [Diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers), and [lama-cleaner](https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner)
|
||||
- Pipelines are **not** intended to be feature-complete user interfaces. For future complete user interfaces one should rather have a look at [InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI), [Diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers), and [lama-cleaner](https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner).
|
||||
- Every pipeline should have one and only one way to run it via a `__call__` method. The naming of the `__call__` arguments should be shared across all pipelines.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be named after the task they are intended to solve.
|
||||
- In almost all cases, novel diffusion pipelines shall be implemented in a new pipeline folder/file.
|
||||
@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Schedulers all inherit from `SchedulerMixin` and `ConfigMixin`.
|
||||
- Schedulers can be easily swapped out with the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/configuration#diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config) method as explained in detail [here](./using-diffusers/schedulers.md).
|
||||
- Every scheduler has to have a `set_num_inference_steps`, and a `step` function. `set_num_inference_steps(...)` has to be called before every denoising process, *i.e.* before `step(...)` is called.
|
||||
- Every scheduler exposes the timesteps to be "looped over" via a `timesteps` attribute, which is an array of timesteps the model will be called upon
|
||||
- Every scheduler exposes the timesteps to be "looped over" via a `timesteps` attribute, which is an array of timesteps the model will be called upon.
|
||||
- The `step(...)` function takes a predicted model output and the "current" sample (x_t) and returns the "previous", slightly more denoised sample (x_t-1).
|
||||
- Given the complexity of diffusion schedulers, the `step` function does not expose all the complexity and can be a bit of a "black box".
|
||||
- In almost all cases, novel schedulers shall be implemented in a new scheduling file.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -40,6 +40,7 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip && \
|
||||
scipy \
|
||||
tensorboard \
|
||||
transformers \
|
||||
omegaconf
|
||||
omegaconf \
|
||||
pytorch-lightning
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:11.7.1-cudnn8-runtime-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-runtime-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,8 +25,8 @@ ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
torch==2.0.1 \
|
||||
torchvision==0.15.2 \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
invisible_watermark && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ The `preview` command only works with existing doc files. When you add a complet
|
||||
Accepted files are Markdown (.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Create a file with its extension and put it in the source directory. You can then link it to the toc-tree by putting
|
||||
the filename without the extension in the [`_toctree.yml`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/docs/source/_toctree.yml) file.
|
||||
the filename without the extension in the [`_toctree.yml`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/docs/source/en/_toctree.yml) file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Renaming section headers and moving sections
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -81,14 +81,14 @@ Therefore, we simply keep a little map of moved sections at the end of the docum
|
||||
|
||||
So if you renamed a section from: "Section A" to "Section B", then you can add at the end of the file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```md
|
||||
Sections that were moved:
|
||||
|
||||
[ <a href="#section-b">Section A</a><a id="section-a"></a> ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
and of course, if you moved it to another file, then:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```md
|
||||
Sections that were moved:
|
||||
|
||||
[ <a href="../new-file#section-b">Section A</a><a id="section-a"></a> ]
|
||||
@@ -109,8 +109,8 @@ although we can write them directly in Markdown.
|
||||
|
||||
Adding a new tutorial or section is done in two steps:
|
||||
|
||||
- Add a new file under `docs/source`. This file can either be ReStructuredText (.rst) or Markdown (.md).
|
||||
- Link that file in `docs/source/_toctree.yml` on the correct toc-tree.
|
||||
- Add a new Markdown (.md) file under `docs/source/<languageCode>`.
|
||||
- Link that file in `docs/source/<languageCode>/_toctree.yml` on the correct toc-tree.
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to put your new file under the proper section. It's unlikely to go in the first section (*Get Started*), so
|
||||
depending on the intended targets (beginners, more advanced users, or researchers) it should go in sections two, three, or four.
|
||||
@@ -119,7 +119,7 @@ depending on the intended targets (beginners, more advanced users, or researcher
|
||||
|
||||
When adding a new pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
- create a file `xxx.md` under `docs/source/api/pipelines` (don't hesitate to copy an existing file as template).
|
||||
- Create a file `xxx.md` under `docs/source/<languageCode>/api/pipelines` (don't hesitate to copy an existing file as template).
|
||||
- Link that file in (*Diffusers Summary*) section in `docs/source/api/pipelines/overview.md`, along with the link to the paper, and a colab notebook (if available).
|
||||
- Write a short overview of the diffusion model:
|
||||
- Overview with paper & authors
|
||||
@@ -128,9 +128,7 @@ When adding a new pipeline:
|
||||
- Possible an end-to-end example of how to use it
|
||||
- Add all the pipeline classes that should be linked in the diffusion model. These classes should be added using our Markdown syntax. By default as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
## XXXPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[[autodoc]] XXXPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -138,7 +136,7 @@ When adding a new pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
This will include every public method of the pipeline that is documented, as well as the `__call__` method that is not documented by default. If you just want to add additional methods that are not documented, you can put the list of all methods to add in a list that contains `all`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```
|
||||
[[autodoc]] XXXPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -148,7 +146,7 @@ This will include every public method of the pipeline that is documented, as wel
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can follow the same process to create a new scheduler under the `docs/source/api/schedulers` folder
|
||||
You can follow the same process to create a new scheduler under the `docs/source/<languageCode>/api/schedulers` folder.
|
||||
|
||||
### Writing source documentation
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -164,7 +162,7 @@ provide its path. For instance: \[\`pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput\`\]. This will
|
||||
`pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput` in the description. To get rid of the path and only keep the name of the object you are
|
||||
linking to in the description, add a ~: \[\`~pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput\`\] will generate a link with `ImagePipelineOutput` in the description.
|
||||
|
||||
The same works for methods so you can either use \[\`XXXClass.method\`\] or \[~\`XXXClass.method\`\].
|
||||
The same works for methods so you can either use \[\`XXXClass.method\`\] or \[\`~XXXClass.method\`\].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Defining arguments in a method
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -172,7 +170,7 @@ Arguments should be defined with the `Args:` (or `Arguments:` or `Parameters:`)
|
||||
an indentation. The argument should be followed by its type, with its shape if it is a tensor, a colon, and its
|
||||
description:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
n_layers (`int`): The number of layers of the model.
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -182,7 +180,7 @@ after the argument.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example showcasing everything so far:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
input_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`):
|
||||
Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.
|
||||
@@ -197,16 +195,16 @@ For optional arguments or arguments with defaults we follow the following syntax
|
||||
following signature:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def my_function(x: str = None, a: float = 1):
|
||||
def my_function(x: str=None, a: float=3.14):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
then its documentation should look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
x (`str`, *optional*):
|
||||
This argument controls ...
|
||||
a (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
|
||||
a (`float`, *optional*, defaults to `3.14`):
|
||||
This argument is used to ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -235,14 +233,14 @@ building the return.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of a single value return:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`List[int]`: A list of integers in the range [0, 1] --- 1 for a special token, 0 for a sequence token.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of a tuple return, comprising several objects:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` comprising various elements depending on the configuration ([`BertConfig`]) and inputs:
|
||||
- ** loss** (*optional*, returned when `masked_lm_labels` is provided) `torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(1,)` --
|
||||
@@ -268,4 +266,3 @@ We have an automatic script running with the `make style` command that will make
|
||||
This script may have some weird failures if you made a syntax mistake or if you uncover a bug. Therefore, it's
|
||||
recommended to commit your changes before running `make style`, so you can revert the changes done by that script
|
||||
easily.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
- local: tutorials/tutorial_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/write_own_pipeline
|
||||
title: Understanding models and schedulers
|
||||
title: Understanding pipelines, models and schedulers
|
||||
- local: tutorials/autopipeline
|
||||
title: AutoPipeline
|
||||
- local: tutorials/basic_training
|
||||
@@ -29,15 +29,19 @@
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/schedulers
|
||||
title: Load and compare different schedulers
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Load community pipelines
|
||||
title: Load community pipelines and components
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/using_safetensors
|
||||
title: Load safetensors
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/other-formats
|
||||
title: Load different Stable Diffusion formats
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/loading_adapters
|
||||
title: Load adapters
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/push_to_hub
|
||||
title: Push files to the Hub
|
||||
title: Loading & Hub
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/unconditional_image_generation
|
||||
title: Unconditional image generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation
|
||||
@@ -68,8 +72,12 @@
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/sdxl
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/kandinsky
|
||||
title: Kandinsky
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/controlnet
|
||||
title: ControlNet
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/callback
|
||||
title: Callback
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/shap-e
|
||||
title: Shap-E
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/diffedit
|
||||
@@ -81,8 +89,8 @@
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_examples
|
||||
title: Community pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/contribute_pipeline
|
||||
title: How to contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
title: Pipelines for Inference
|
||||
title: Contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
title: Specific pipeline examples
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
@@ -162,22 +170,14 @@
|
||||
title: Conceptual Guides
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/attnprocessor
|
||||
title: Attention Processor
|
||||
- local: api/diffusion_pipeline
|
||||
title: Diffusion Pipeline
|
||||
- local: api/logging
|
||||
title: Logging
|
||||
- local: api/configuration
|
||||
title: Configuration
|
||||
- local: api/outputs
|
||||
title: Outputs
|
||||
- local: api/loaders
|
||||
title: Loaders
|
||||
- local: api/utilities
|
||||
title: Utilities
|
||||
- local: api/image_processor
|
||||
title: VAE Image Processor
|
||||
- local: api/logging
|
||||
title: Logging
|
||||
- local: api/outputs
|
||||
title: Outputs
|
||||
title: Main Classes
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/models/overview
|
||||
@@ -190,6 +190,8 @@
|
||||
title: UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/unet3d-cond
|
||||
title: UNet3DConditionModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/unet-motion
|
||||
title: UNetMotionModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/vq
|
||||
title: VQModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/autoencoderkl
|
||||
@@ -212,6 +214,8 @@
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/alt_diffusion
|
||||
title: AltDiffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/animatediff
|
||||
title: AnimateDiff
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/attend_and_excite
|
||||
title: Attend-and-Excite
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/audio_diffusion
|
||||
@@ -247,9 +251,11 @@
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pix2pix
|
||||
title: InstructPix2Pix
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/kandinsky
|
||||
title: Kandinsky
|
||||
title: Kandinsky 2.1
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/kandinsky_v22
|
||||
title: Kandinsky 2.2
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/latent_consistency_models
|
||||
title: Latent Consistency Models
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/latent_diffusion
|
||||
title: Latent Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/panorama
|
||||
@@ -257,11 +263,13 @@
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/musicldm
|
||||
title: MusicLDM
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/paint_by_example
|
||||
title: PaintByExample
|
||||
title: Paint By Example
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/paradigms
|
||||
title: Parallel Sampling of Diffusion Models
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pix2pix_zero
|
||||
title: Pix2Pix Zero
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pixart
|
||||
title: PixArt
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pndm
|
||||
title: PNDM
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/repaint
|
||||
@@ -302,7 +310,7 @@
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/ldm3d_diffusion
|
||||
title: LDM3D Text-to-(RGB, Depth)
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/adapter
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion T2I-adapter
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion T2I-Adapter
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/gligen
|
||||
title: GLIGEN (Grounded Language-to-Image Generation)
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion
|
||||
@@ -317,7 +325,7 @@
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/text_to_video_zero
|
||||
title: Text2Video-Zero
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/unclip
|
||||
title: UnCLIP
|
||||
title: unCLIP
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond
|
||||
title: Unconditional Latent Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/unidiffuser
|
||||
@@ -366,6 +374,8 @@
|
||||
title: KDPM2AncestralDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/dpm_discrete
|
||||
title: KDPM2DiscreteScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/lcm
|
||||
title: LCMScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/lms_discrete
|
||||
title: LMSDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/pndm
|
||||
@@ -381,4 +391,18 @@
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/vq_diffusion
|
||||
title: VQDiffusionScheduler
|
||||
title: Schedulers
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/internal_classes_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: api/attnprocessor
|
||||
title: Attention Processor
|
||||
- local: api/activations
|
||||
title: Custom activation functions
|
||||
- local: api/normalization
|
||||
title: Custom normalization layers
|
||||
- local: api/utilities
|
||||
title: Utilities
|
||||
- local: api/image_processor
|
||||
title: VAE Image Processor
|
||||
title: Internal classes
|
||||
title: API
|
||||
|
||||
15
docs/source/en/api/activations.md
Normal file
15
docs/source/en/api/activations.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
# Activation functions
|
||||
|
||||
Customized activation functions for supporting various models in 🤗 Diffusers.
|
||||
|
||||
## GELU
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.activations.GELU
|
||||
|
||||
## GEGLU
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.activations.GEGLU
|
||||
|
||||
## ApproximateGELU
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.activations.ApproximateGELU
|
||||
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] is the quickest way to load any pretrained diffusion pipeline from the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers) for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You shouldn't use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] class for training or finetuning a diffusion model. Individual
|
||||
components (for example, [`UNet2DModel`] and [`UNet2DConditionModel`]) of diffusion pipelines are usually trained individually, so we suggest directly working with them instead.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The pipeline type (for example [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]) of any diffusion pipeline loaded with [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] is automatically
|
||||
detected and pipeline components are loaded and passed to the `__init__` function of the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
Any pipeline object can be saved locally with [`~DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`].
|
||||
|
||||
## DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- device
|
||||
- to
|
||||
- components
|
||||
3
docs/source/en/api/internal_classes_overview.md
Normal file
3
docs/source/en/api/internal_classes_overview.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The APIs in this section are more experimental and prone to breaking changes. Most of them are used internally for development, but they may also be useful to you if you're interested in building a diffusion model with some custom parts or if you're interested in some of our helper utilities for working with 🤗 Diffusers.
|
||||
@@ -12,13 +12,13 @@ By default the [`ControlNetModel`] should be loaded with [`~ModelMixin.from_pret
|
||||
from the original format using [`FromOriginalControlnetMixin.from_single_file`] as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlnetPipeline, ControlNetModel
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline, ControlNetModel
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/ControlNet-v1-1/blob/main/control_v11p_sd15_canny.pth" # can also be a local path
|
||||
controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_single_file(url)
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/blob/main/v1-5-pruned.safetensors" # can also be a local path
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionControlnetPipeline.from_single_file(url, controlnet=controlnet)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline.from_single_file(url, controlnet=controlnet)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ControlNetModel
|
||||
|
||||
13
docs/source/en/api/models/unet-motion.md
Normal file
13
docs/source/en/api/models/unet-motion.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
# UNetMotionModel
|
||||
|
||||
The [UNet](https://huggingface.co/papers/1505.04597) model was originally introduced by Ronneberger et al for biomedical image segmentation, but it is also commonly used in 🤗 Diffusers because it outputs images that are the same size as the input. It is one of the most important components of a diffusion system because it facilitates the actual diffusion process. There are several variants of the UNet model in 🤗 Diffusers, depending on it's number of dimensions and whether it is a conditional model or not. This is a 2D UNet model.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*There is large consent that successful training of deep networks requires many thousand annotated training samples. In this paper, we present a network and training strategy that relies on the strong use of data augmentation to use the available annotated samples more efficiently. The architecture consists of a contracting path to capture context and a symmetric expanding path that enables precise localization. We show that such a network can be trained end-to-end from very few images and outperforms the prior best method (a sliding-window convolutional network) on the ISBI challenge for segmentation of neuronal structures in electron microscopic stacks. Using the same network trained on transmitted light microscopy images (phase contrast and DIC) we won the ISBI cell tracking challenge 2015 in these categories by a large margin. Moreover, the network is fast. Segmentation of a 512x512 image takes less than a second on a recent GPU. The full implementation (based on Caffe) and the trained networks are available at http://lmb.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/people/ronneber/u-net.*
|
||||
|
||||
## UNetMotionModel
|
||||
[[autodoc]] UNetMotionModel
|
||||
|
||||
## UNet3DConditionOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.unet_3d_condition.UNet3DConditionOutput
|
||||
15
docs/source/en/api/normalization.md
Normal file
15
docs/source/en/api/normalization.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
# Normalization layers
|
||||
|
||||
Customized normalization layers for supporting various models in 🤗 Diffusers.
|
||||
|
||||
## AdaLayerNorm
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.normalization.AdaLayerNorm
|
||||
|
||||
## AdaLayerNormZero
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.normalization.AdaLayerNormZero
|
||||
|
||||
## AdaGroupNorm
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.normalization.AdaGroupNorm
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
230
docs/source/en/api/pipelines/animatediff.md
Normal file
230
docs/source/en/api/pipelines/animatediff.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,230 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Text-to-Video Generation with AnimateDiff
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[AnimateDiff: Animate Your Personalized Text-to-Image Diffusion Models without Specific Tuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.04725) by Yuwei Guo, Ceyuan Yang*, Anyi Rao, Yaohui Wang, Yu Qiao, Dahua Lin, Bo Dai
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
With the advance of text-to-image models (e.g., Stable Diffusion) and corresponding personalization techniques such as DreamBooth and LoRA, everyone can manifest their imagination into high-quality images at an affordable cost. Subsequently, there is a great demand for image animation techniques to further combine generated static images with motion dynamics. In this report, we propose a practical framework to animate most of the existing personalized text-to-image models once and for all, saving efforts in model-specific tuning. At the core of the proposed framework is to insert a newly initialized motion modeling module into the frozen text-to-image model and train it on video clips to distill reasonable motion priors. Once trained, by simply injecting this motion modeling module, all personalized versions derived from the same base T2I readily become text-driven models that produce diverse and personalized animated images. We conduct our evaluation on several public representative personalized text-to-image models across anime pictures and realistic photographs, and demonstrate that our proposed framework helps these models generate temporally smooth animation clips while preserving the domain and diversity of their outputs. Code and pre-trained weights will be publicly available at this https URL .
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Demo
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [AnimateDiffPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/animatediff/pipeline_animatediff.py) | *Text-to-Video Generation with AnimateDiff* |
|
||||
|
||||
## Available checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
Motion Adapter checkpoints can be found under [guoyww](https://huggingface.co/guoyww/). These checkpoints are meant to work with any model based on Stable Diffusion 1.4/1.5
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
AnimateDiff works with a MotionAdapter checkpoint and a Stable Diffusion model checkpoint. The MotionAdapter is a collection of Motion Modules that are responsible for adding coherent motion across image frames. These modules are applied after the Resnet and Attention blocks in Stable Diffusion UNet.
|
||||
|
||||
The following example demonstrates how to use a *MotionAdapter* checkpoint with Diffusers for inference based on StableDiffusion-1.4/1.5.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import MotionAdapter, AnimateDiffPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_gif
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the motion adapter
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5-2")
|
||||
# load SD 1.5 based finetuned model
|
||||
model_id = "SG161222/Realistic_Vision_V5.1_noVAE"
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, motion_adapter=adapter)
|
||||
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id, subfolder="scheduler", clip_sample=False, timestep_spacing="linspace", steps_offset=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
# enable memory savings
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=(
|
||||
"masterpiece, bestquality, highlydetailed, ultradetailed, sunset, "
|
||||
"orange sky, warm lighting, fishing boats, ocean waves seagulls, "
|
||||
"rippling water, wharf, silhouette, serene atmosphere, dusk, evening glow, "
|
||||
"golden hour, coastal landscape, seaside scenery"
|
||||
),
|
||||
negative_prompt="bad quality, worse quality",
|
||||
num_frames=16,
|
||||
guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
generator=torch.Generator("cpu").manual_seed(42),
|
||||
)
|
||||
frames = output.frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_gif(frames, "animation.gif")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><center>
|
||||
masterpiece, bestquality, sunset.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/animatediff-realistic-doc.gif"
|
||||
alt="masterpiece, bestquality, sunset"
|
||||
style="width: 300px;" />
|
||||
</center></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
AnimateDiff tends to work better with finetuned Stable Diffusion models. If you plan on using a scheduler that can clip samples, make sure to disable it by setting `clip_sample=False` in the scheduler as this can also have an adverse effect on generated samples.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Motion LoRAs
|
||||
|
||||
Motion LoRAs are a collection of LoRAs that work with the `guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5-2` checkpoint. These LoRAs are responsible for adding specific types of motion to the animations.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import MotionAdapter, AnimateDiffPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_gif
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the motion adapter
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5-2")
|
||||
# load SD 1.5 based finetuned model
|
||||
model_id = "SG161222/Realistic_Vision_V5.1_noVAE"
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, motion_adapter=adapter)
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("guoyww/animatediff-motion-lora-zoom-out", adapter_name="zoom-out")
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id, subfolder="scheduler", clip_sample=False, timestep_spacing="linspace", steps_offset=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
# enable memory savings
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=(
|
||||
"masterpiece, bestquality, highlydetailed, ultradetailed, sunset, "
|
||||
"orange sky, warm lighting, fishing boats, ocean waves seagulls, "
|
||||
"rippling water, wharf, silhouette, serene atmosphere, dusk, evening glow, "
|
||||
"golden hour, coastal landscape, seaside scenery"
|
||||
),
|
||||
negative_prompt="bad quality, worse quality",
|
||||
num_frames=16,
|
||||
guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
generator=torch.Generator("cpu").manual_seed(42),
|
||||
)
|
||||
frames = output.frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_gif(frames, "animation.gif")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><center>
|
||||
masterpiece, bestquality, sunset.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/animatediff-zoom-out-lora.gif"
|
||||
alt="masterpiece, bestquality, sunset"
|
||||
style="width: 300px;" />
|
||||
</center></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Motion LoRAs with PEFT
|
||||
|
||||
You can also leverage the [PEFT](https://github.com/huggingface/peft) backend to combine Motion LoRA's and create more complex animations.
|
||||
|
||||
First install PEFT with
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install peft
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can use the following code to combine Motion LoRAs.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import MotionAdapter, AnimateDiffPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_gif
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the motion adapter
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5-2")
|
||||
# load SD 1.5 based finetuned model
|
||||
model_id = "SG161222/Realistic_Vision_V5.1_noVAE"
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, motion_adapter=adapter)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("diffusers/animatediff-motion-lora-zoom-out", adapter_name="zoom-out")
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("diffusers/animatediff-motion-lora-pan-left", adapter_name="pan-left")
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters(["zoom-out", "pan-left"], adapter_weights=[1.0, 1.0])
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id, subfolder="scheduler", clip_sample=False, timestep_spacing="linspace", steps_offset=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
# enable memory savings
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=(
|
||||
"masterpiece, bestquality, highlydetailed, ultradetailed, sunset, "
|
||||
"orange sky, warm lighting, fishing boats, ocean waves seagulls, "
|
||||
"rippling water, wharf, silhouette, serene atmosphere, dusk, evening glow, "
|
||||
"golden hour, coastal landscape, seaside scenery"
|
||||
),
|
||||
negative_prompt="bad quality, worse quality",
|
||||
num_frames=16,
|
||||
guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
generator=torch.Generator("cpu").manual_seed(42),
|
||||
)
|
||||
frames = output.frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_gif(frames, "animation.gif")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><center>
|
||||
masterpiece, bestquality, sunset.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/animatediff-zoom-out-pan-left-lora.gif"
|
||||
alt="masterpiece, bestquality, sunset"
|
||||
style="width: 300px;" />
|
||||
</center></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## AnimateDiffPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AnimateDiffPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_freeu
|
||||
- disable_freeu
|
||||
- enable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_vae_tiling
|
||||
- disable_vae_tiling
|
||||
|
||||
## AnimateDiffPipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.animatediff.AnimateDiffPipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ You can find additional information about Attend-and-Excite on the [project page
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ The original codebase, training scripts and example notebooks can be found at [t
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ During inference:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -70,9 +70,7 @@ The following example demonstrates how to construct good music generation using
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between
|
||||
scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines)
|
||||
section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [salesforce/LAVIS](https://github.com/sale
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [lllyasviel/ControlNet](https://github.com
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ If you don't see a checkpoint you're interested in, you can train your own SDXL
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,6 +41,15 @@ Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to le
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionXLControlNetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StableDiffusionXLControlNetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionXLControlNetInpaintPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StableDiffusionXLControlNetInpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
## StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The original codebase of this implementation can be found at [Harmonai-org](http
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [hohonathanho/diffusion](https://github.co
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [facebookresearch/dit](https://github.com/
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,462 +7,60 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Kandinsky
|
||||
# Kandinsky 2.1
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
Kandinsky 2.1 is created by [Arseniy Shakhmatov](https://github.com/cene555), [Anton Razzhigaev](https://github.com/razzant), [Aleksandr Nikolich](https://github.com/AlexWortega), [Igor Pavlov](https://github.com/boomb0om), [Andrey Kuznetsov](https://github.com/kuznetsoffandrey) and [Denis Dimitrov](https://github.com/denndimitrov).
|
||||
|
||||
Kandinsky inherits best practices from [DALL-E 2](https://huggingface.co/papers/2204.06125) and [Latent Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/latent_diffusion), while introducing some new ideas.
|
||||
The description from it's GitHub page is:
|
||||
|
||||
It uses [CLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip) for encoding images and text, and a diffusion image prior (mapping) between latent spaces of CLIP modalities. This approach enhances the visual performance of the model and unveils new horizons in blending images and text-guided image manipulation.
|
||||
*Kandinsky 2.1 inherits best practicies from Dall-E 2 and Latent diffusion, while introducing some new ideas. As text and image encoder it uses CLIP model and diffusion image prior (mapping) between latent spaces of CLIP modalities. This approach increases the visual performance of the model and unveils new horizons in blending images and text-guided image manipulation.*
|
||||
|
||||
The Kandinsky model is created by [Arseniy Shakhmatov](https://github.com/cene555), [Anton Razzhigaev](https://github.com/razzant), [Aleksandr Nikolich](https://github.com/AlexWortega), [Igor Pavlov](https://github.com/boomb0om), [Andrey Kuznetsov](https://github.com/kuznetsoffandrey) and [Denis Dimitrov](https://github.com/denndimitrov). The original codebase can be found [here](https://github.com/ai-forever/Kandinsky-2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we will walk you through some examples of how to use the Kandinsky pipelines to create some visually aesthetic artwork.
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-to-Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
For text-to-image generation, we need to use both [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`] and [`KandinskyPipeline`].
|
||||
The first step is to encode text prompts with CLIP and then diffuse the CLIP text embeddings to CLIP image embeddings,
|
||||
as first proposed in [DALL-E 2](https://cdn.openai.com/papers/dall-e-2.pdf).
|
||||
Let's throw a fun prompt at Kandinsky to see what it comes up with.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's instantiate the prior pipeline and the text-to-image pipeline. Both
|
||||
pipelines are diffusion models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the text-to-image pipeline use [`DDIMScheduler`], you can change the scheduler to [`DDPMScheduler`]
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", subfolder="ddpm_scheduler")
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", scheduler=scheduler, torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Now we pass the prompt through the prior to generate image embeddings. The prior
|
||||
returns both the image embeddings corresponding to the prompt and negative/unconditional image
|
||||
embeddings corresponding to an empty string.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, guidance_scale=1.0).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The text-to-image pipeline expects both `image_embeds`, `negative_image_embeds` and the original
|
||||
`prompt` as the text-to-image pipeline uses another text encoder to better guide the second diffusion
|
||||
process of `t2i_pipe`.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the prior returns unconditioned negative image embeddings corresponding to the negative prompt of `""`.
|
||||
For better results, you can also pass a `negative_prompt` to the prior. This will increase the effective batch size
|
||||
of the prior by a factor of 2.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, negative_prompt, guidance_scale=1.0).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we can pass the embeddings as well as the prompt to the text-to-image pipeline. Remember that
|
||||
in case you are using a customized negative prompt, that you should pass this one also to the text-to-image pipelines
|
||||
with `negative_prompt=negative_prompt`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = t2i_pipe(
|
||||
prompt, image_embeds=image_embeds, negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds, height=768, width=768
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image.save("cheeseburger_monster.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
One cheeseburger monster coming up! Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
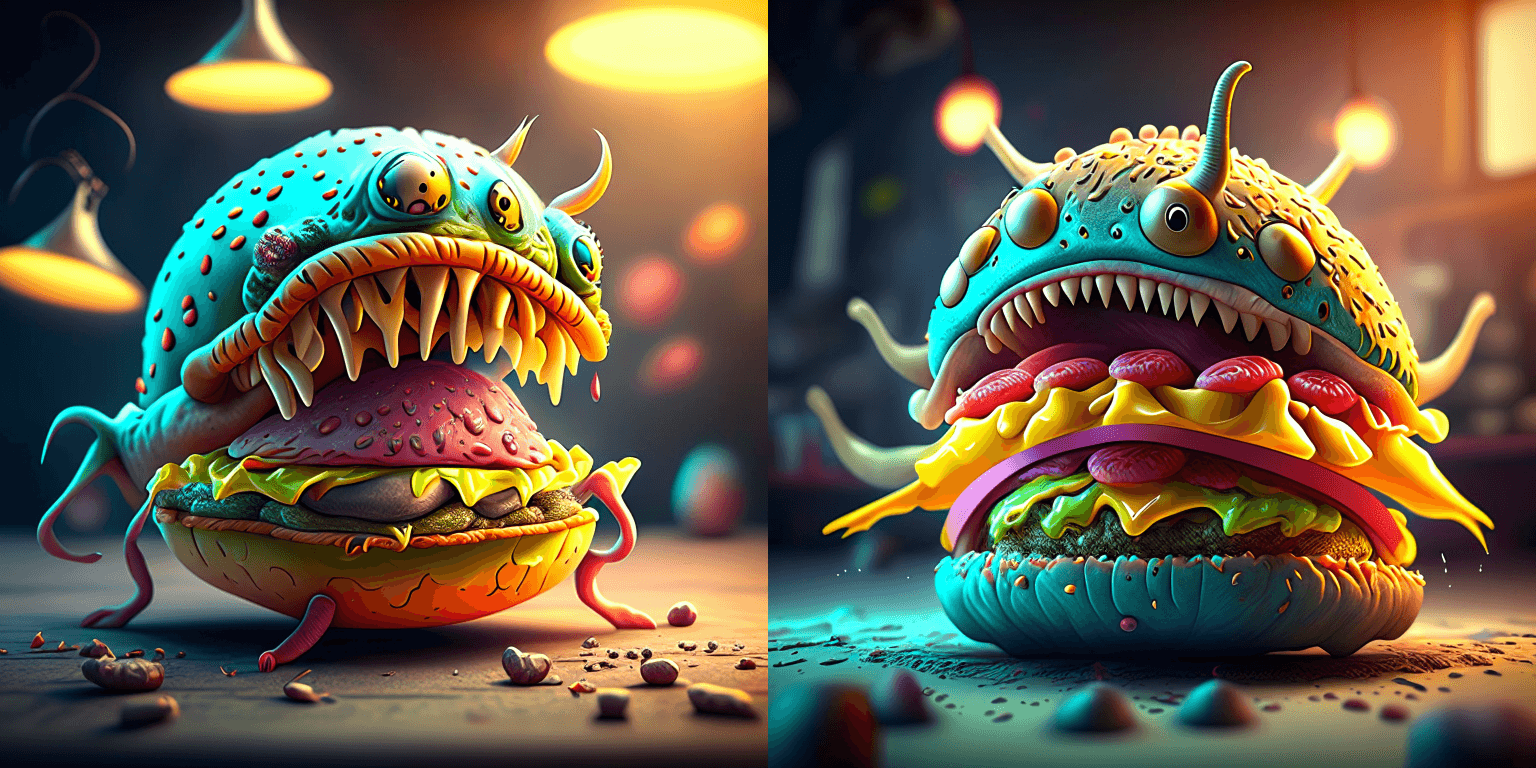

|
||||
The original codebase can be found at [ai-forever/Kandinsky-2](https://github.com/ai-forever/Kandinsky-2).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
We also provide an end-to-end Kandinsky pipeline [`KandinskyCombinedPipeline`], which combines both the prior pipeline and text-to-image pipeline, and lets you perform inference in a single step. You can create the combined pipeline with the [`~AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained`] method
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Under the hood, it will automatically load both [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`] and [`KandinskyPipeline`]. To generate images, you no longer need to call both pipelines and pass the outputs from one to another. You only need to call the combined pipeline once. You can set different `guidance_scale` and `num_inference_steps` for the prior pipeline with the `prior_guidance_scale` and `prior_num_inference_steps` arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, prior_guidance_scale =1.0, guidance_scacle = 4.0, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The Kandinsky model works extremely well with creative prompts. Here is some of the amazing art that can be created using the exact same process but with different prompts.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "bird eye view shot of a full body woman with cyan light orange magenta makeup, digital art, long braided hair her face separated by makeup in the style of yin Yang surrealism, symmetrical face, real image, contrasting tone, pastel gradient background"
|
||||
```
|
||||
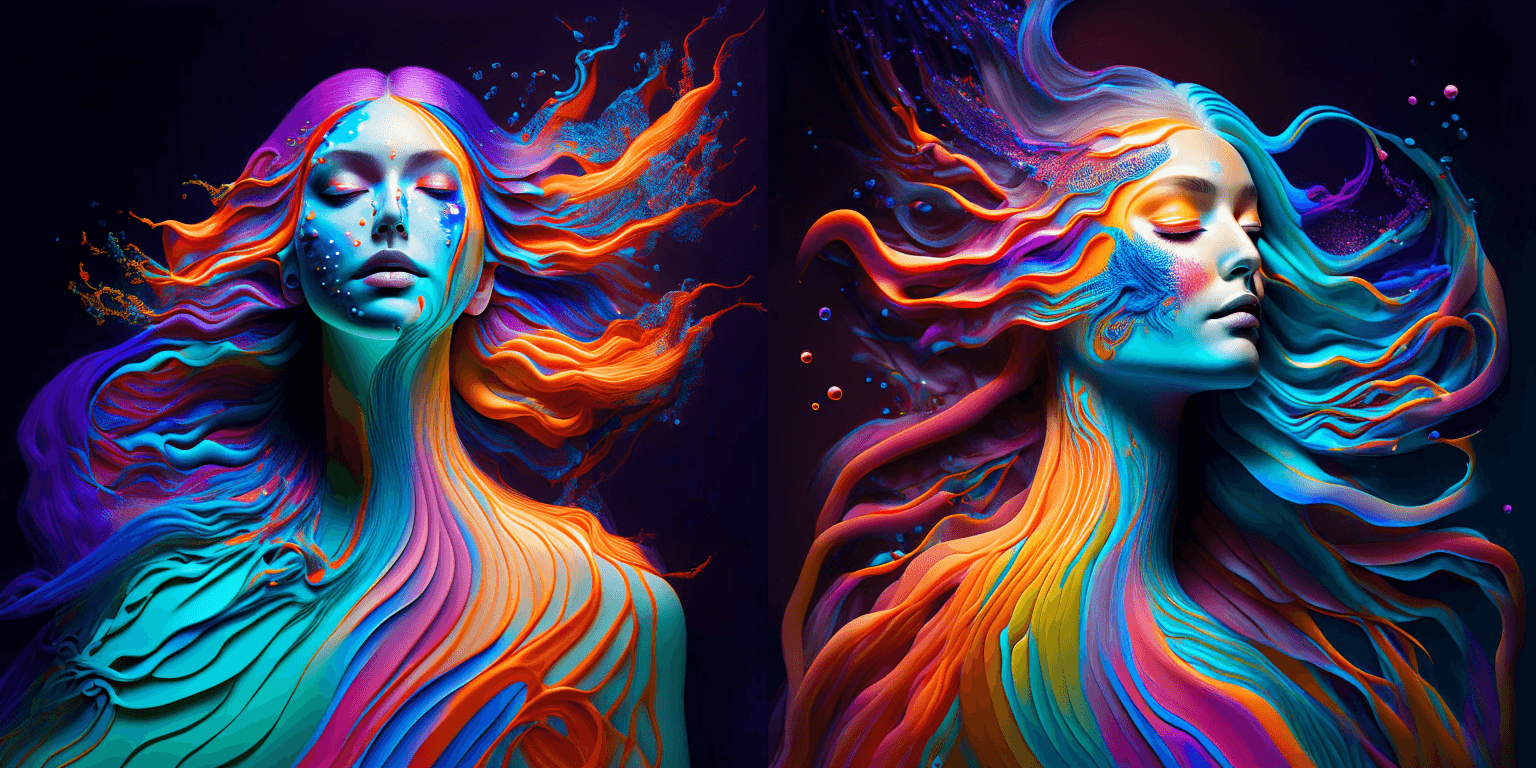

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "A car exploding into colorful dust"
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "editorial photography of an organic, almost liquid smoke style armchair"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "birds eye view of a quilted paper style alien planet landscape, vibrant colours, Cinematic lighting"
|
||||
```
|
||||
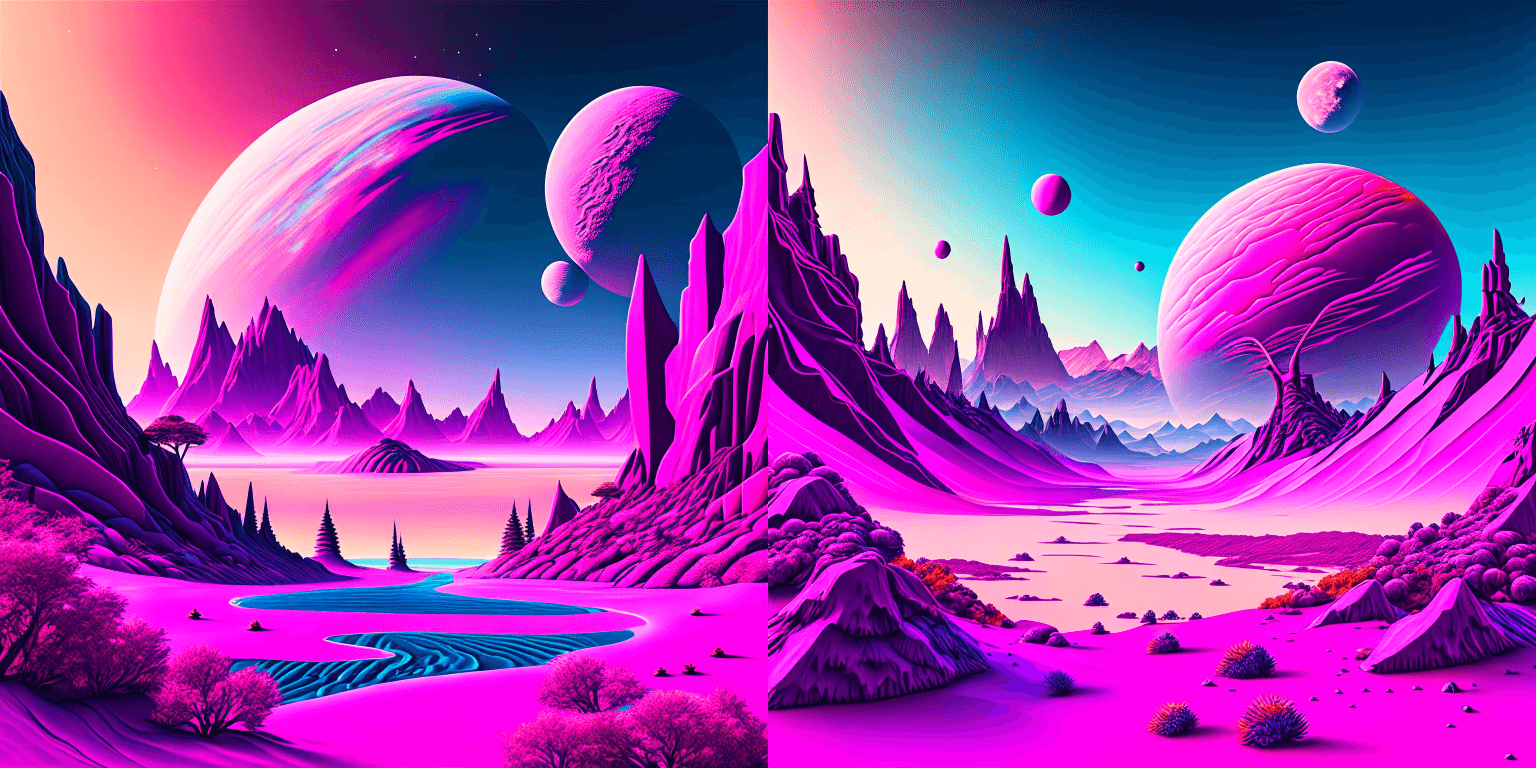

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Text Guided Image-to-Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
The same Kandinsky model weights can be used for text-guided image-to-image translation. In this case, just make sure to load the weights using the [`KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline`] pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: You can also directly move the weights of the text-to-image pipelines to the image-to-image pipelines
|
||||
without loading them twice by making use of the [`~DiffusionPipeline.components`] function as explained [here](#converting-between-different-pipelines).
|
||||
|
||||
Let's download an image.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
# download image
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
original_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
original_image = original_image.resize((768, 512))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline, KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
# create prior
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# create img2img pipeline
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, Cinematic lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, negative_prompt).to_tuple()
|
||||
|
||||
out = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=original_image,
|
||||
image_embeds=image_embeds,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
strength=0.3,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
out.images[0].save("fantasy_land.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the [`KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline`] for end-to-end image-to-image generation with Kandinsky 2.1
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, Cinematic lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
original_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
original_image.thumbnail((768, 768))
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=original_image, strength=0.3).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Text Guided Inpainting Generation
|
||||
|
||||
You can use [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`] to edit images. In this example, we will add a hat to the portrait of a cat.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyInpaintPipeline, KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a hat"
|
||||
prior_output = pipe_prior(prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-inpaint", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinsky/cat.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
mask = np.zeros((768, 768), dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
# Let's mask out an area above the cat's head
|
||||
mask[:250, 250:-250] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
out = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=init_image,
|
||||
mask_image=mask,
|
||||
**prior_output,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=150,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
image = out.images[0]
|
||||
image.save("cat_with_hat.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To use the [`KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline`] to perform end-to-end image inpainting generation, you can run below code instead
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForInpainting
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-inpaint", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=original_image, mask_image=mask).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
🚨🚨🚨 __Breaking change for Kandinsky Mask Inpainting__ 🚨🚨🚨
|
||||
|
||||
We introduced a breaking change for Kandinsky inpainting pipeline in the following pull request: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/4207. Previously we accepted a mask format where black pixels represent the masked-out area. This is inconsistent with all other pipelines in diffusers. We have changed the mask format in Knaindsky and now using white pixels instead.
|
||||
Please upgrade your inpainting code to follow the above. If you are using Kandinsky Inpaint in production. You now need to change the mask to:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# For PIL input
|
||||
import PIL.ImageOps
|
||||
mask = PIL.ImageOps.invert(mask)
|
||||
|
||||
# For PyTorch and Numpy input
|
||||
mask = 1 - mask
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Interpolate
|
||||
|
||||
The [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`] also comes with a cool utility function that will allow you to interpolate the latent space of different images and texts super easily. Here is an example of how you can create an Impressionist-style portrait for your pet based on "The Starry Night".
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you can interpolate between texts and images - in the below example, we passed a text prompt "a cat" and two images to the `interplate` function, along with a `weights` variable containing the corresponding weights for each condition we interplate.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyPriorPipeline, KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
img1 = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinsky/cat.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
img2 = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinsky/starry_night.jpeg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# add all the conditions we want to interpolate, can be either text or image
|
||||
images_texts = ["a cat", img1, img2]
|
||||
|
||||
# specify the weights for each condition in images_texts
|
||||
weights = [0.3, 0.3, 0.4]
|
||||
|
||||
# We can leave the prompt empty
|
||||
prompt = ""
|
||||
prior_out = pipe_prior.interpolate(images_texts, weights)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, **prior_out, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
image.save("starry_cat.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
Running Kandinsky in inference requires running both a first prior pipeline: [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`]
|
||||
and a second image decoding pipeline which is one of [`KandinskyPipeline`], [`KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline`], or [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
The bulk of the computation time will always be the second image decoding pipeline, so when looking
|
||||
into optimizing the model, one should look into the second image decoding pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
When running with PyTorch < 2.0, we strongly recommend making use of [`xformers`](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers)
|
||||
to speed-up the optimization. This can be done by simply running:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When running on PyTorch >= 2.0, PyTorch's SDPA attention will automatically be used. For more information on
|
||||
PyTorch's SDPA, feel free to have a look at [this blog post](https://pytorch.org/blog/accelerated-diffusers-pt-20/).
|
||||
|
||||
To have explicit control , you can also manually set the pipeline to use PyTorch's 2.0 efficient attention:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The slowest and most memory intense attention processor is the default `AttnAddedKVProcessor` processor.
|
||||
We do **not** recommend using it except for testing purposes or cases where very high determistic behaviour is desired.
|
||||
You can set it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With PyTorch >= 2.0, you can also use Kandinsky with `torch.compile` which depending
|
||||
on your hardware can significantly speed-up your inference time once the model is compiled.
|
||||
To use Kandinsksy with `torch.compile`, you can do:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet = torch.compile(t2i_pipe.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After compilation you should see a very fast inference time. For more information,
|
||||
feel free to have a look at [Our PyTorch 2.0 benchmark](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/optimization/torch2.0).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To generate images directly from a single pipeline, you can use [`KandinskyCombinedPipeline`], [`KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline`], [`KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline`].
|
||||
These combined pipelines wrap the [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`] and [`KandinskyPipeline`], [`KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline`], [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`] respectively into a single
|
||||
pipeline for a simpler user experience
|
||||
Check out the [Kandinsky Community](https://huggingface.co/kandinsky-community) organization on the Hub for the official model checkpoints for tasks like text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky_combined.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky_combined.py) | *End-to-end Text-to-Image, image-to-image, Inpainting Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky_inpaint.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky_inpaint.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky_img2img.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky_img2img.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
## KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- interpolate
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
## KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyCombinedPipeline
|
||||
## KandinskyCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
## KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
## KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,348 +9,77 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Kandinsky 2.2
|
||||
|
||||
The Kandinsky 2.2 release includes robust new text-to-image models that support text-to-image generation, image-to-image generation, image interpolation, and text-guided image inpainting. The general workflow to perform these tasks using Kandinsky 2.2 is the same as in Kandinsky 2.1. First, you will need to use a prior pipeline to generate image embeddings based on your text prompt, and then use one of the image decoding pipelines to generate the output image. The only difference is that in Kandinsky 2.2, all of the decoding pipelines no longer accept the `prompt` input, and the image generation process is conditioned with only `image_embeds` and `negative_image_embeds`.
|
||||
Kandinsky 2.1 is created by [Arseniy Shakhmatov](https://github.com/cene555), [Anton Razzhigaev](https://github.com/razzant), [Aleksandr Nikolich](https://github.com/AlexWortega), [Igor Pavlov](https://github.com/boomb0om), [Andrey Kuznetsov](https://github.com/kuznetsoffandrey) and [Denis Dimitrov](https://github.com/denndimitrov).
|
||||
|
||||
Same as with Kandinsky 2.1, the easiest way to perform text-to-image generation is to use the combined Kandinsky pipeline. This process is exactly the same as Kandinsky 2.1. All you need to do is to replace the Kandinsky 2.1 checkpoint with 2.2.
|
||||
The description from it's GitHub page is:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
*Kandinsky 2.2 brings substantial improvements upon its predecessor, Kandinsky 2.1, by introducing a new, more powerful image encoder - CLIP-ViT-G and the ControlNet support. The switch to CLIP-ViT-G as the image encoder significantly increases the model's capability to generate more aesthetic pictures and better understand text, thus enhancing the model's overall performance. The addition of the ControlNet mechanism allows the model to effectively control the process of generating images. This leads to more accurate and visually appealing outputs and opens new possibilities for text-guided image manipulation.*
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, prior_guidance_scale =1.0, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's look at an example where we take separate steps to run the prior pipeline and text-to-image pipeline. This way, we can understand what's happening under the hood and how Kandinsky 2.2 differs from Kandinsky 2.1.
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's create the prior pipeline and text-to-image pipeline with Kandinsky 2.2 checkpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can then use `pipe_prior` to generate image embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "portrait of a women, blue eyes, cinematic"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, guidance_scale=1.0).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can pass these embeddings to the text-to-image pipeline. When using Kandinsky 2.2 you don't need to pass the `prompt` (but you do with the previous version, Kandinsky 2.1).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
image = t2i_pipe(image_embeds=image_embeds, negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds, height=768, width=768).images[
|
||||
0
|
||||
]
|
||||
image.save("portrait.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We used the text-to-image pipeline as an example, but the same process applies to all decoding pipelines in Kandinsky 2.2. For more information, please refer to our API section for each pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we give a simple example of how to use [`KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline`] to add control to the text-to-image generation with a depth image.
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's take an image and extract its depth map.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
img = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinskyv22/cat.png"
|
||||
).resize((768, 768))
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We can use the `depth-estimation` pipeline from transformers to process the image and retrieve its depth map.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def make_hint(image, depth_estimator):
|
||||
image = depth_estimator(image)["depth"]
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
detected_map = torch.from_numpy(image).float() / 255.0
|
||||
hint = detected_map.permute(2, 0, 1)
|
||||
return hint
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
depth_estimator = pipeline("depth-estimation")
|
||||
hint = make_hint(img, depth_estimator).unsqueeze(0).half().to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
Now, we load the prior pipeline and the text-to-image controlnet pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyV22PriorPipeline, KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyV22PriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior = pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-controlnet-depth", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We pass the prompt and negative prompt through the prior to generate image embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "A robot, 4k photo"
|
||||
|
||||
negative_prior_prompt = "lowres, text, error, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, ugly, duplicate, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, extra fingers, mutated hands, poorly drawn hands, poorly drawn face, mutation, deformed, blurry, dehydrated, bad anatomy, bad proportions, extra limbs, cloned face, disfigured, gross proportions, malformed limbs, missing arms, missing legs, extra arms, extra legs, fused fingers, too many fingers, long neck, username, watermark, signature"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(43)
|
||||
image_emb, zero_image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prior_prompt, generator=generator
|
||||
).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can pass the image embeddings and the depth image we extracted to the controlnet pipeline. With Kandinsky 2.2, only prior pipelines accept `prompt` input. You do not need to pass the prompt to the controlnet pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
images = pipe(
|
||||
image_embeds=image_emb,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds=zero_image_emb,
|
||||
hint=hint,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
).images
|
||||
|
||||
images[0].save("robot_cat.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The output image looks as follow:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Image-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning
|
||||
|
||||
Kandinsky 2.2 also includes a [`KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline`] that will allow you to add control to the image generation process with both the image and its depth map. This pipeline works really well with [`KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline`], which generates image embeddings based on both a text prompt and an image.
|
||||
|
||||
For our robot cat example, we will pass the prompt and cat image together to the prior pipeline to generate an image embedding. We will then use that image embedding and the depth map of the cat to further control the image generation process.
|
||||
|
||||
We can use the same cat image and its depth map from the last example.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline, KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
img = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinskyv22/cat.png"
|
||||
).resize((768, 768))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def make_hint(image, depth_estimator):
|
||||
image = depth_estimator(image)["depth"]
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
detected_map = torch.from_numpy(image).float() / 255.0
|
||||
hint = detected_map.permute(2, 0, 1)
|
||||
return hint
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
depth_estimator = pipeline("depth-estimation")
|
||||
hint = make_hint(img, depth_estimator).unsqueeze(0).half().to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior = pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-controlnet-depth", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A robot, 4k photo"
|
||||
negative_prior_prompt = "lowres, text, error, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, ugly, duplicate, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, extra fingers, mutated hands, poorly drawn hands, poorly drawn face, mutation, deformed, blurry, dehydrated, bad anatomy, bad proportions, extra limbs, cloned face, disfigured, gross proportions, malformed limbs, missing arms, missing legs, extra arms, extra legs, fused fingers, too many fingers, long neck, username, watermark, signature"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(43)
|
||||
|
||||
# run prior pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
img_emb = pipe_prior(prompt=prompt, image=img, strength=0.85, generator=generator)
|
||||
negative_emb = pipe_prior(prompt=negative_prior_prompt, image=img, strength=1, generator=generator)
|
||||
|
||||
# run controlnet img2img pipeline
|
||||
images = pipe(
|
||||
image=img,
|
||||
strength=0.5,
|
||||
image_embeds=img_emb.image_embeds,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds=negative_emb.image_embeds,
|
||||
hint=hint,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
).images
|
||||
|
||||
images[0].save("robot_cat.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the output. Compared with the output from our text-to-image controlnet example, it kept a lot more cat facial details from the original image and worked into the robot style we asked for.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
Running Kandinsky in inference requires running both a first prior pipeline: [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`]
|
||||
and a second image decoding pipeline which is one of [`KandinskyPipeline`], [`KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline`], or [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
The bulk of the computation time will always be the second image decoding pipeline, so when looking
|
||||
into optimizing the model, one should look into the second image decoding pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
When running with PyTorch < 2.0, we strongly recommend making use of [`xformers`](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers)
|
||||
to speed-up the optimization. This can be done by simply running:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When running on PyTorch >= 2.0, PyTorch's SDPA attention will automatically be used. For more information on
|
||||
PyTorch's SDPA, feel free to have a look at [this blog post](https://pytorch.org/blog/accelerated-diffusers-pt-20/).
|
||||
|
||||
To have explicit control , you can also manually set the pipeline to use PyTorch's 2.0 efficient attention:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The slowest and most memory intense attention processor is the default `AttnAddedKVProcessor` processor.
|
||||
We do **not** recommend using it except for testing purposes or cases where very high determistic behaviour is desired.
|
||||
You can set it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With PyTorch >= 2.0, you can also use Kandinsky with `torch.compile` which depending
|
||||
on your hardware can significantly speed-up your inference time once the model is compiled.
|
||||
To use Kandinsksy with `torch.compile`, you can do:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet = torch.compile(t2i_pipe.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After compilation you should see a very fast inference time. For more information,
|
||||
feel free to have a look at [Our PyTorch 2.0 benchmark](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/optimization/torch2.0).
|
||||
The original codebase can be found at [ai-forever/Kandinsky-2](https://github.com/ai-forever/Kandinsky-2).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To generate images directly from a single pipeline, you can use [`KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline`], [`KandinskyV22Img2ImgCombinedPipeline`], [`KandinskyV22InpaintCombinedPipeline`].
|
||||
These combined pipelines wrap the [`KandinskyV22PriorPipeline`] and [`KandinskyV22Pipeline`], [`KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline`], [`KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline`] respectively into a single
|
||||
pipeline for a simpler user experience
|
||||
Check out the [Kandinsky Community](https://huggingface.co/kandinsky-community) organization on the Hub for the official model checkpoints for tasks like text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2_combined.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2_combined.py) | *End-to-end Text-to-Image, image-to-image, Inpainting Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2_inpaint.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2_inpaint.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2_img2img.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2_img2img.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2_controlnet.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2_controlnet.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2_controlnet_img2img.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2_controlnet_img2img.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22Pipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22PriorPipeline
|
||||
## KandinskyV22PriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22PriorPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- interpolate
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline
|
||||
## KandinskyV22Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22Pipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- interpolate
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline
|
||||
## KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22Img2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
## KandinskyV22Img2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22Img2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22InpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
## KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22InpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22InpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
40
docs/source/en/api/pipelines/latent_consistency_models.md
Normal file
40
docs/source/en/api/pipelines/latent_consistency_models.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
# Latent Consistency Models
|
||||
|
||||
Latent Consistency Models (LCMs) were proposed in [Latent Consistency Models: Synthesizing High-Resolution Images with Few-Step Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.04378) by Simian Luo, Yiqin Tan, Longbo Huang, Jian Li, and Hang Zhao.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the [paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.04378.pdf) is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
*Latent Diffusion models (LDMs) have achieved remarkable results in synthesizing high-resolution images. However, the iterative sampling process is computationally intensive and leads to slow generation. Inspired by Consistency Models (song et al.), we propose Latent Consistency Models (LCMs), enabling swift inference with minimal steps on any pre-trained LDMs, including Stable Diffusion (rombach et al). Viewing the guided reverse diffusion process as solving an augmented probability flow ODE (PF-ODE), LCMs are designed to directly predict the solution of such ODE in latent space, mitigating the need for numerous iterations and allowing rapid, high-fidelity sampling. Efficiently distilled from pre-trained classifier-free guided diffusion models, a high-quality 768 x 768 2~4-step LCM takes only 32 A100 GPU hours for training. Furthermore, we introduce Latent Consistency Fine-tuning (LCF), a novel method that is tailored for fine-tuning LCMs on customized image datasets. Evaluation on the LAION-5B-Aesthetics dataset demonstrates that LCMs achieve state-of-the-art text-to-image generation performance with few-step inference.*
|
||||
|
||||
A demo for the [SimianLuo/LCM_Dreamshaper_v7](https://huggingface.co/SimianLuo/LCM_Dreamshaper_v7) checkpoint can be found [here](https://huggingface.co/spaces/SimianLuo/Latent_Consistency_Model).
|
||||
|
||||
The pipelines were contributed by [luosiallen](https://luosiallen.github.io/), [nagolinc](https://github.com/nagolinc), and [dg845](https://github.com/dg845).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## LatentConsistencyModelPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LatentConsistencyModelPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_freeu
|
||||
- disable_freeu
|
||||
- enable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_vae_tiling
|
||||
- disable_vae_tiling
|
||||
|
||||
## LatentConsistencyModelImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LatentConsistencyModelImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_freeu
|
||||
- disable_freeu
|
||||
- enable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_vae_tiling
|
||||
- disable_vae_tiling
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [Compvis/latent-diffusion](https://github.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [CompVis/latent-diffusion](https://github.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ You can find additional information about model editing on the [project page](ht
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -45,9 +45,7 @@ During inference:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between
|
||||
scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines)
|
||||
section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,16 +12,74 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines provide a simple way to run state-of-the-art diffusion models in inference by bundling all of the necessary components (multiple independently-trained models, schedulers, and processors) into a single end-to-end class. Pipelines are flexible and they can be adapted to use different scheduler or even model components.
|
||||
Pipelines provide a simple way to run state-of-the-art diffusion models in inference by bundling all of the necessary components (multiple independently-trained models, schedulers, and processors) into a single end-to-end class. Pipelines are flexible and they can be adapted to use different schedulers or even model components.
|
||||
|
||||
All pipelines are built from the base [`DiffusionPipeline`] class which provides basic functionality for loading, downloading, and saving all the components.
|
||||
All pipelines are built from the base [`DiffusionPipeline`] class which provides basic functionality for loading, downloading, and saving all the components. Specific pipeline types (for example [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]) loaded with [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] are automatically detected and the pipeline components are loaded and passed to the `__init__` function of the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines do not offer any training functionality. You'll notice PyTorch's autograd is disabled by decorating the [`~DiffusionPipeline.__call__`] method with a [`torch.no_grad`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.no_grad.html) decorator because pipelines should not be used for training. If you're interested in training, please take a look at the [Training](../traininig/overview) guides instead!
|
||||
You shouldn't use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] class for training. Individual components (for example, [`UNet2DModel`] and [`UNet2DConditionModel`]) of diffusion pipelines are usually trained individually, so we suggest directly working with them instead.
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines do not offer any training functionality. You'll notice PyTorch's autograd is disabled by decorating the [`~DiffusionPipeline.__call__`] method with a [`torch.no_grad`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.no_grad.html) decorator because pipelines should not be used for training. If you're interested in training, please take a look at the [Training](../../training/overview) guides instead!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The table below lists all the pipelines currently available in 🤗 Diffusers and the tasks they support. Click on a pipeline to view its abstract and published paper.
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| [AltDiffusion](alt_diffusion) | image2image |
|
||||
| [Attend-and-Excite](attend_and_excite) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Audio Diffusion](audio_diffusion) | image2audio |
|
||||
| [AudioLDM](audioldm) | text2audio |
|
||||
| [AudioLDM2](audioldm2) | text2audio |
|
||||
| [BLIP Diffusion](blip_diffusion) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Consistency Models](consistency_models) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [ControlNet](controlnet) | text2image, image2image, inpainting |
|
||||
| [ControlNet with Stable Diffusion XL](controlnet_sdxl) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Cycle Diffusion](cycle_diffusion) | image2image |
|
||||
| [Dance Diffusion](dance_diffusion) | unconditional audio generation |
|
||||
| [DDIM](ddim) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [DDPM](ddpm) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [DeepFloyd IF](deepfloyd_if) | text2image, image2image, inpainting, super-resolution |
|
||||
| [DiffEdit](diffedit) | inpainting |
|
||||
| [DiT](dit) | text2image |
|
||||
| [GLIGEN](gligen) | text2image |
|
||||
| [InstructPix2Pix](pix2pix) | image editing |
|
||||
| [Kandinsky](kandinsky) | text2image, image2image, inpainting, interpolation |
|
||||
| [Kandinsky 2.2](kandinsky_v22) | text2image, image2image, inpainting |
|
||||
| [Latent Diffusion](latent_diffusion) | text2image, super-resolution |
|
||||
| [LDM3D](ldm3d_diffusion) | text2image, text-to-3D |
|
||||
| [MultiDiffusion](panorama) | text2image |
|
||||
| [MusicLDM](musicldm) | text2audio |
|
||||
| [PaintByExample](paint_by_example) | inpainting |
|
||||
| [ParaDiGMS](paradigms) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Pix2Pix Zero](pix2pix_zero) | image editing |
|
||||
| [PNDM](pndm) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [RePaint](repaint) | inpainting |
|
||||
| [ScoreSdeVe](score_sde_ve) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [Self-Attention Guidance](self_attention_guidance) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Semantic Guidance](semantic_stable_diffusion) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Shap-E](shap_e) | text-to-3D, image-to-3D |
|
||||
| [Spectrogram Diffusion](spectrogram_diffusion) | |
|
||||
| [Stable Diffusion](stable_diffusion/overview) | text2image, image2image, depth2image, inpainting, image variation, latent upscaler, super-resolution |
|
||||
| [Stable Diffusion Model Editing](model_editing) | model editing |
|
||||
| [Stable Diffusion XL](stable_diffusion_xl) | text2image, image2image, inpainting |
|
||||
| [Stable unCLIP](stable_unclip) | text2image, image variation |
|
||||
| [KarrasVe](karras_ve) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [T2I Adapter](adapter) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Text2Video](text_to_video) | text2video, video2video |
|
||||
| [Text2Video Zero](text_to_video_zero) | text2video |
|
||||
| [UnCLIP](unclip) | text2image, image variation |
|
||||
| [Unconditional Latent Diffusion](latent_diffusion_uncond) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [UniDiffuser](unidiffuser) | text2image, image2text, image variation, text variation, unconditional image generation, unconditional audio generation |
|
||||
| [Value-guided planning](value_guided_sampling) | value guided sampling |
|
||||
| [Versatile Diffusion](versatile_diffusion) | text2image, image variation |
|
||||
| [VQ Diffusion](vq_diffusion) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Wuerstchen](wuerstchen) | text2image |
|
||||
|
||||
## DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PaintByExample
|
||||
# Paint By Example
|
||||
|
||||
[Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models](https://huggingface.co/papers/2211.13227) is by Binxin Yang, Shuyang Gu, Bo Zhang, Ting Zhang, Xuejin Chen, Xiaoyan Sun, Dong Chen, Fang Wen.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ PaintByExample is supported by the official [Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example](ht
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ But with circular padding, the right and the left parts are matching (`circular_
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ in parallel on multiple GPUs. But [`StableDiffusionParadigmsPipeline`] is design
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ You can find additional information about InstructPix2Pix on the [project page](
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
36
docs/source/en/api/pipelines/pixart.md
Normal file
36
docs/source/en/api/pipelines/pixart.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PixArt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[PixArt-α: Fast Training of Diffusion Transformer for Photorealistic Text-to-Image Synthesis](https://huggingface.co/papers/2310.00426) is Junsong Chen, Jincheng Yu, Chongjian Ge, Lewei Yao, Enze Xie, Yue Wu, Zhongdao Wang, James Kwok, Ping Luo, Huchuan Lu, and Zhenguo Li.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*The most advanced text-to-image (T2I) models require significant training costs (e.g., millions of GPU hours), seriously hindering the fundamental innovation for the AIGC community while increasing CO2 emissions. This paper introduces PIXART-α, a Transformer-based T2I diffusion model whose image generation quality is competitive with state-of-the-art image generators (e.g., Imagen, SDXL, and even Midjourney), reaching near-commercial application standards. Additionally, it supports high-resolution image synthesis up to 1024px resolution with low training cost, as shown in Figure 1 and 2. To achieve this goal, three core designs are proposed: (1) Training strategy decomposition: We devise three distinct training steps that separately optimize pixel dependency, text-image alignment, and image aesthetic quality; (2) Efficient T2I Transformer: We incorporate cross-attention modules into Diffusion Transformer (DiT) to inject text conditions and streamline the computation-intensive class-condition branch; (3) High-informative data: We emphasize the significance of concept density in text-image pairs and leverage a large Vision-Language model to auto-label dense pseudo-captions to assist text-image alignment learning. As a result, PIXART-α's training speed markedly surpasses existing large-scale T2I models, e.g., PIXART-α only takes 10.8% of Stable Diffusion v1.5's training time (675 vs. 6,250 A100 GPU days), saving nearly $300,000 ($26,000 vs. $320,000) and reducing 90% CO2 emissions. Moreover, compared with a larger SOTA model, RAPHAEL, our training cost is merely 1%. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PIXART-α excels in image quality, artistry, and semantic control. We hope PIXART-α will provide new insights to the AIGC community and startups to accelerate building their own high-quality yet low-cost generative models from scratch.*
|
||||
|
||||
You can find the original codebase at [PixArt-alpha/PixArt-alpha](https://github.com/PixArt-alpha/PixArt-alpha) and all the available checkpoints at [PixArt-alpha](https://huggingface.co/PixArt-alpha).
|
||||
|
||||
Some notes about this pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
* It uses a Transformer backbone (instead of a UNet) for denoising. As such it has a similar architecture as [DiT](./dit.md).
|
||||
* It was trained using text conditions computed from T5. This aspect makes the pipeline better at following complex text prompts with intricate details.
|
||||
* It is good at producing high-resolution images at different aspect ratios. To get the best results, the authors recommend some size brackets which can be found [here](https://github.com/PixArt-alpha/PixArt-alpha/blob/08fbbd281ec96866109bdd2cdb75f2f58fb17610/diffusion/data/datasets/utils.py).
|
||||
* It rivals the quality of state-of-the-art text-to-image generation systems (as of this writing) such as Stable Diffusion XL, Imagen, and DALL-E 2, while being more efficient than them.
|
||||
|
||||
## PixArtAlphaPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PixArtAlphaPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [luping-liu/PNDM](https://github.com/lupin
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [andreas128/RePaint](https://github.com/an
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [yang-song/score_sde_pytorch](https://gith
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ You can find additional information about Self-Attention Guidance on the [projec
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [openai/shap-e](https://github.com/openai/
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
See the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
See the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ As depicted above the model takes as input a MIDI file and tokenizes it into a s
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Text-to-(RGB, depth)
|
||||
|
||||
LDM3D was proposed in [LDM3D: Latent Diffusion Model for 3D](https://huggingface.co/papers/2305.10853) by Gabriela Ben Melech Stan, Diana Wofk, Scottie Fox, Alex Redden, Will Saxton, Jean Yu, Estelle Aflalo, Shao-Yen Tseng, Fabio Nonato, Matthias Muller, and Vasudev Lal. LDM3D generates an image and a depth map from a given text prompt unlike the existing text-to-image diffusion models such as [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion/overview) which only generates an image. With almost the same number of parameters, LDM3D achieves to create a latent space that can compress both the RGB images and the depth maps.
|
||||
LDM3D was proposed in [LDM3D: Latent Diffusion Model for 3D](https://huggingface.co/papers/2305.10853) by Gabriela Ben Melech Stan, Diana Wofk, Scottie Fox, Alex Redden, Will Saxton, Jean Yu, Estelle Aflalo, Shao-Yen Tseng, Fabio Nonato, Matthias Muller, and Vasudev Lal. LDM3D generates an image and a depth map from a given text prompt unlike the existing text-to-image diffusion models such as [Stable Diffusion](./overview) which only generates an image. With almost the same number of parameters, LDM3D achieves to create a latent space that can compress both the RGB images and the depth maps.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,10 +36,8 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<th class="px-4 py-2 font-medium text-gray-900 text-left">
|
||||
Space
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
|
||||
<tbody class="divide-y divide-gray-200">
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
@@ -49,7 +47,6 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/stabilityai/stable-diffusion"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./img2img">StableDiffusionImg2Img</a>
|
||||
@@ -58,7 +55,6 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface/diffuse-the-rest"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./inpaint">StableDiffusionInpaint</a>
|
||||
@@ -67,7 +63,6 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./depth2img">StableDiffusionDepth2Img</a>
|
||||
@@ -76,7 +71,6 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/radames/stable-diffusion-depth2img"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./image_variation">StableDiffusionImageVariation</a>
|
||||
@@ -85,7 +79,6 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/lambdalabs/stable-diffusion-image-variations"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./stable_diffusion_safe">StableDiffusionPipelineSafe</a>
|
||||
@@ -94,7 +87,6 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/AIML-TUDA/unsafe-vs-safe-stable-diffusion"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./stable_diffusion_2">StableDiffusion2</a>
|
||||
@@ -103,7 +95,6 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/stabilityai/stable-diffusion"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./stable_diffusion_xl">StableDiffusionXL</a>
|
||||
@@ -112,7 +103,6 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/RamAnanth1/stable-diffusion-xl"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./latent_upscale">StableDiffusionLatentUpscale</a>
|
||||
@@ -121,14 +111,12 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-projects/stable-diffusion-latent-upscaler"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./upscale">StableDiffusionUpscale</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">super-resolution</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./ldm3d_diffusion">StableDiffusionLDM3D</a>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,6 +20,9 @@ The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips
|
||||
|
||||
- Using SDXL with a DPM++ scheduler for less than 50 steps is known to produce [visual artifacts](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/5433) because the solver becomes numerically unstable. To fix this issue, take a look at this [PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/5541) which recommends for ODE/SDE solvers:
|
||||
- set `use_karras_sigmas=True` or `lu_lambdas=True` to improve image quality
|
||||
- set `euler_at_final=True` if you're using a solver with uniform step sizes (DPM++2M or DPM++2M SDE)
|
||||
- Most SDXL checkpoints work best with an image size of 1024x1024. Image sizes of 768x768 and 512x512 are also supported, but the results aren't as good. Anything below 512x512 is not recommended and likely won't for for default checkpoints like [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0).
|
||||
- SDXL can pass a different prompt for each of the text encoders it was trained on. We can even pass different parts of the same prompt to the text encoders.
|
||||
- SDXL output images can be improved by making use of a refiner model in an image-to-image setting.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The abstract from the paper:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,9 +7,9 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# UnCLIP
|
||||
# unCLIP
|
||||
|
||||
[Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://huggingface.co/papers/2204.06125) is by Aditya Ramesh, Prafulla Dhariwal, Alex Nichol, Casey Chu, Mark Chen. The UnCLIP model in 🤗 Diffusers comes from kakaobrain's [karlo]((https://github.com/kakaobrain/karlo)).
|
||||
[Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://huggingface.co/papers/2204.06125) is by Aditya Ramesh, Prafulla Dhariwal, Alex Nichol, Casey Chu, Mark Chen. The unCLIP model in 🤗 Diffusers comes from kakaobrain's [karlo]((https://github.com/kakaobrain/karlo)).
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is following:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ You can find lucidrains DALL-E 2 recreation at [lucidrains/DALLE2-pytorch](https
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -34,4 +34,4 @@ Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to le
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## ImagePipelineOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ You can load the more memory intensive "all-in-one" [`VersatileDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [microsoft/VQ-Diffusion](https://github.co
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
9
docs/source/en/api/schedulers/lcm.md
Normal file
9
docs/source/en/api/schedulers/lcm.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
# Latent Consistency Model Multistep Scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Multistep and onestep scheduler (Algorithm 3) introduced alongside latent consistency models in the paper [Latent Consistency Models: Synthesizing High-Resolution Images with Few-Step Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.04378) by Simian Luo, Yiqin Tan, Longbo Huang, Jian Li, and Hang Zhao.
|
||||
This scheduler should be able to generate good samples from [`LatentConsistencyModelPipeline`] in 1-8 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
## LCMScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LCMScheduler
|
||||
@@ -28,11 +28,11 @@ the core library.
|
||||
In the following, we give an overview of different ways to contribute, ranked by difficulty in ascending order. All of them are valuable to the community.
|
||||
|
||||
* 1. Asking and answering questions on [the Diffusers discussion forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers) or on [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR).
|
||||
* 2. Opening new issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose)
|
||||
* 3. Answering issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues)
|
||||
* 2. Opening new issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose).
|
||||
* 3. Answering issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues).
|
||||
* 4. Fix a simple issue, marked by the "Good first issue" label, see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22).
|
||||
* 5. Contribute to the [documentation](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source).
|
||||
* 6. Contribute a [Community Pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3Acommunity-examples)
|
||||
* 6. Contribute a [Community Pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3Acommunity-examples).
|
||||
* 7. Contribute to the [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples).
|
||||
* 8. Fix a more difficult issue, marked by the "Good second issue" label, see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22).
|
||||
* 9. Add a new pipeline, model, or scheduler, see ["New Pipeline/Model"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22) and ["New scheduler"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22) issues. For this contribution, please have a look at [Design Philosophy](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/PHILOSOPHY.md).
|
||||
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ In the following, we give an overview of different ways to contribute, ranked by
|
||||
As said before, **all contributions are valuable to the community**.
|
||||
In the following, we will explain each contribution a bit more in detail.
|
||||
|
||||
For all contributions 4.-9. you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in [Opening a pull request](#how-to-open-a-pr)
|
||||
For all contributions 4 - 9, you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in [Opening a pull request](#how-to-open-a-pr).
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Asking and answering questions on the Diffusers discussion forum or on the Diffusers Discord
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ Any question or comment related to the Diffusers library can be asked on the [di
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
|
||||
Every question that is asked on the forum or on Discord actively encourages the community to publicly
|
||||
share knowledge and might very well help a beginner in the future that has the same question you're
|
||||
share knowledge and might very well help a beginner in the future who has the same question you're
|
||||
having. Please do pose any questions you might have.
|
||||
In the same spirit, you are of immense help to the community by answering such questions because this way you are publicly documenting knowledge for everybody to learn from.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -91,12 +91,12 @@ open a new issue nevertheless and link to the related issue.
|
||||
|
||||
New issues usually include the following.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.1. Reproducible, minimal bug reports.
|
||||
#### 2.1. Reproducible, minimal bug reports
|
||||
|
||||
A bug report should always have a reproducible code snippet and be as minimal and concise as possible.
|
||||
This means in more detail:
|
||||
- Narrow the bug down as much as you can, **do not just dump your whole code file**
|
||||
- Format your code
|
||||
- Narrow the bug down as much as you can, **do not just dump your whole code file**.
|
||||
- Format your code.
|
||||
- Do not include any external libraries except for Diffusers depending on them.
|
||||
- **Always** provide all necessary information about your environment; for this, you can run: `diffusers-cli env` in your shell and copy-paste the displayed information to the issue.
|
||||
- Explain the issue. If the reader doesn't know what the issue is and why it is an issue, she cannot solve it.
|
||||
@@ -105,9 +105,9 @@ This means in more detail:
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, please have a look through the [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue) section.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a bug report [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose).
|
||||
You can open a bug report [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&projects=&template=bug-report.yml).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.2. Feature requests.
|
||||
#### 2.2. Feature requests
|
||||
|
||||
A world-class feature request addresses the following points:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -125,26 +125,26 @@ Awesome! Tell us what problem it solved for you.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a feature request [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feature_request.md&title=).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.3 Feedback.
|
||||
#### 2.3 Feedback
|
||||
|
||||
Feedback about the library design and why it is good or not good helps the core maintainers immensely to build a user-friendly library. To understand the philosophy behind the current design philosophy, please have a look [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy). If you feel like a certain design choice does not fit with the current design philosophy, please explain why and how it should be changed. If a certain design choice follows the design philosophy too much, hence restricting use cases, explain why and how it should be changed.
|
||||
If a certain design choice is very useful for you, please also leave a note as this is great feedback for future design decisions.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open an issue about feedback [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.4 Technical questions.
|
||||
#### 2.4 Technical questions
|
||||
|
||||
Technical questions are mainly about why certain code of the library was written in a certain way, or what a certain part of the code does. Please make sure to link to the code in question and please provide detail on
|
||||
Technical questions are mainly about why certain code of the library was written in a certain way, or what a certain part of the code does. Please make sure to link to the code in question and please provide details on
|
||||
why this part of the code is difficult to understand.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open an issue about a technical question [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&template=bug-report.yml).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.5 Proposal to add a new model, scheduler, or pipeline.
|
||||
#### 2.5 Proposal to add a new model, scheduler, or pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
If the diffusion model community released a new model, pipeline, or scheduler that you would like to see in the Diffusers library, please provide the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
* Short description of the diffusion pipeline, model, or scheduler and link to the paper or public release.
|
||||
* Link to any of its open-source implementation.
|
||||
* Link to any of its open-source implementation(s).
|
||||
* Link to the model weights if they are available.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are willing to contribute to the model yourself, let us know so we can best guide you. Also, don't forget
|
||||
@@ -156,21 +156,21 @@ You can open a request for a model/pipeline/scheduler [here](https://github.com/
|
||||
|
||||
Answering issues on GitHub might require some technical knowledge of Diffusers, but we encourage everybody to give it a try even if you are not 100% certain that your answer is correct.
|
||||
Some tips to give a high-quality answer to an issue:
|
||||
- Be as concise and minimal as possible
|
||||
- Be as concise and minimal as possible.
|
||||
- Stay on topic. An answer to the issue should concern the issue and only the issue.
|
||||
- Provide links to code, papers, or other sources that prove or encourage your point.
|
||||
- Answer in code. If a simple code snippet is the answer to the issue or shows how the issue can be solved, please provide a fully reproducible code snippet.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, many issues tend to be simply off-topic, duplicates of other issues, or irrelevant. It is of great
|
||||
help to the maintainers if you can answer such issues, encouraging the author of the issue to be
|
||||
more precise, provide the link to a duplicated issue or redirect them to [the forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) or [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)
|
||||
more precise, provide the link to a duplicated issue or redirect them to [the forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) or [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR).
|
||||
|
||||
If you have verified that the issued bug report is correct and requires a correction in the source code,
|
||||
please have a look at the next sections.
|
||||
|
||||
For all of the following contributions, you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in the [Opening a pull request](#how-to-open-a-pr) section.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Fixing a `Good first issue`
|
||||
### 4. Fixing a "Good first issue"
|
||||
|
||||
*Good first issues* are marked by the [Good first issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22) label. Usually, the issue already
|
||||
explains how a potential solution should look so that it is easier to fix.
|
||||
@@ -188,7 +188,7 @@ valuable contribution**.
|
||||
Contributing to the library can have many forms:
|
||||
|
||||
- Correcting spelling or grammatical errors.
|
||||
- Correct incorrect formatting of the docstring. If you see that the official documentation is weirdly displayed or a link is broken, we are very happy if you take some time to correct it.
|
||||
- Correct incorrect formatting of the docstring. If you see that the official documentation is weirdly displayed or a link is broken, we would be very happy if you take some time to correct it.
|
||||
- Correct the shape or dimensions of a docstring input or output tensor.
|
||||
- Clarify documentation that is hard to understand or incorrect.
|
||||
- Update outdated code examples.
|
||||
@@ -202,7 +202,7 @@ Please have a look at [this page](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/
|
||||
### 6. Contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[Pipelines](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/overview) are usually the first point of contact between the Diffusers library and the user.
|
||||
Pipelines are examples of how to use Diffusers [models](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models) and [schedulers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/schedulers/overview).
|
||||
Pipelines are examples of how to use Diffusers [models](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models/overview) and [schedulers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/schedulers/overview).
|
||||
We support two types of pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
- Official Pipelines
|
||||
@@ -242,46 +242,46 @@ We support two types of training examples:
|
||||
|
||||
Research training examples are located in [examples/research_projects](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects) whereas official training examples include all folders under [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples) except the `research_projects` and `community` folders.
|
||||
The official training examples are maintained by the Diffusers' core maintainers whereas the research training examples are maintained by the community.
|
||||
This is because of the same reasons put forward in [6. Contribute a community pipeline](#contribute-a-community-pipeline) for official pipelines vs. community pipelines: It is not feasible for the core maintainers to maintain all possible training methods for diffusion models.
|
||||
This is because of the same reasons put forward in [6. Contribute a community pipeline](#6-contribute-a-community-pipeline) for official pipelines vs. community pipelines: It is not feasible for the core maintainers to maintain all possible training methods for diffusion models.
|
||||
If the Diffusers core maintainers and the community consider a certain training paradigm to be too experimental or not popular enough, the corresponding training code should be put in the `research_projects` folder and maintained by the author.
|
||||
|
||||
Both official training and research examples consist of a directory that contains one or more training scripts, a requirements.txt file, and a README.md file. In order for the user to make use of the
|
||||
training examples, it is required to clone the repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
as well as to install all additional dependencies required for training:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -r /examples/<your-example-folder>/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore when adding an example, the `requirements.txt` file shall define all pip dependencies required for your training example so that once all those are installed, the user can run the example's training script. See, for example, the [DreamBooth `requirements.txt` file](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/requirements.txt).
|
||||
|
||||
Training examples of the Diffusers library should adhere to the following philosophy:
|
||||
- All the code necessary to run the examples should be found in a single Python file
|
||||
- One should be able to run the example from the command line with `python <your-example>.py --args`
|
||||
- All the code necessary to run the examples should be found in a single Python file.
|
||||
- One should be able to run the example from the command line with `python <your-example>.py --args`.
|
||||
- Examples should be kept simple and serve as **an example** on how to use Diffusers for training. The purpose of example scripts is **not** to create state-of-the-art diffusion models, but rather to reproduce known training schemes without adding too much custom logic. As a byproduct of this point, our examples also strive to serve as good educational materials.
|
||||
|
||||
To contribute an example, it is highly recommended to look at already existing examples such as [dreambooth](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py) to get an idea of how they should look like.
|
||||
We strongly advise contributors to make use of the [Accelerate library](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate) as it's tightly integrated
|
||||
with Diffusers.
|
||||
Once an example script works, please make sure to add a comprehensive `README.md` that states how to use the example exactly. This README should include:
|
||||
- An example command on how to run the example script as shown [here e.g.](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#running-locally-with-pytorch).
|
||||
- A link to some training results (logs, models, ...) that show what the user can expect as shown [here e.g.](https://api.wandb.ai/report/patrickvonplaten/xm6cd5q5).
|
||||
- An example command on how to run the example script as shown [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#running-locally-with-pytorch).
|
||||
- A link to some training results (logs, models, etc.) that show what the user can expect as shown [here](https://api.wandb.ai/report/patrickvonplaten/xm6cd5q5).
|
||||
- If you are adding a non-official/research training example, **please don't forget** to add a sentence that you are maintaining this training example which includes your git handle as shown [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/intel_opts#diffusers-examples-with-intel-optimizations).
|
||||
|
||||
If you are contributing to the official training examples, please also make sure to add a test to [examples/test_examples.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/test_examples.py). This is not necessary for non-official training examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Fixing a `Good second issue`
|
||||
### 8. Fixing a "Good second issue"
|
||||
|
||||
*Good second issues* are marked by the [Good second issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22) label. Good second issues are
|
||||
usually more complicated to solve than [Good first issues](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22).
|
||||
The issue description usually gives less guidance on how to fix the issue and requires
|
||||
a decent understanding of the library by the interested contributor.
|
||||
If you are interested in tackling a second good issue, feel free to open a PR to fix it and link the PR to the issue. If you see that a PR has already been opened for this issue but did not get merged, have a look to understand why it wasn't merged and try to open an improved PR.
|
||||
If you are interested in tackling a good second issue, feel free to open a PR to fix it and link the PR to the issue. If you see that a PR has already been opened for this issue but did not get merged, have a look to understand why it wasn't merged and try to open an improved PR.
|
||||
Good second issues are usually more difficult to get merged compared to good first issues, so don't hesitate to ask for help from the core maintainers. If your PR is almost finished the core maintainers can also jump into your PR and commit to it in order to get it merged.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Adding pipelines, models, schedulers
|
||||
@@ -297,7 +297,7 @@ if you don't know yet what specific component you would like to add:
|
||||
- [Model or pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22)
|
||||
- [Scheduler](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22)
|
||||
|
||||
Before adding any of the three components, it is strongly recommended that you give the [Philosophy guide](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22) a read to better understand the design of any of the three components. Please be aware that
|
||||
Before adding any of the three components, it is strongly recommended that you give the [Philosophy guide](philosophy) a read to better understand the design of any of the three components. Please be aware that
|
||||
we cannot merge model, scheduler, or pipeline additions that strongly diverge from our design philosophy
|
||||
as it will lead to API inconsistencies. If you fundamentally disagree with a design choice, please
|
||||
open a [Feedback issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=) instead so that it can be discussed whether a certain design
|
||||
@@ -337,8 +337,8 @@ to be merged;
|
||||
9. Add high-coverage tests. No quality testing = no merge.
|
||||
- If you are adding new `@slow` tests, make sure they pass using
|
||||
`RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest tests/test_my_new_model.py`.
|
||||
CircleCI does not run the slow tests, but GitHub actions does every night!
|
||||
10. All public methods must have informative docstrings that work nicely with markdown. See `[pipeline_latent_diffusion.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/latent_diffusion/pipeline_latent_diffusion.py)` for an example.
|
||||
CircleCI does not run the slow tests, but GitHub Actions does every night!
|
||||
10. All public methods must have informative docstrings that work nicely with markdown. See [`pipeline_latent_diffusion.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/latent_diffusion/pipeline_latent_diffusion.py) for an example.
|
||||
11. Due to the rapidly growing repository, it is important to make sure that no files that would significantly weigh down the repository are added. This includes images, videos, and other non-text files. We prefer to leverage a hf.co hosted `dataset` like
|
||||
[`hf-internal-testing`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing) or [huggingface/documentation-images](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images) to place these files.
|
||||
If an external contribution, feel free to add the images to your PR and ask a Hugging Face member to migrate your images
|
||||
@@ -364,7 +364,7 @@ under your GitHub user account.
|
||||
2. Clone your fork to your local disk, and add the base repository as a remote:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git clone git@github.com:<your Github handle>/diffusers.git
|
||||
$ git clone git@github.com:<your GitHub handle>/diffusers.git
|
||||
$ cd diffusers
|
||||
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -395,7 +395,14 @@ passes. You should run the tests impacted by your changes like this:
|
||||
$ pytest tests/<TEST_TO_RUN>.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also run the full suite with the following command, but it takes
|
||||
Before you run the tests, please make sure you install the dependencies required for testing. You can do so
|
||||
with this command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pip install -e ".[test]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also run the full test suite with the following command, but it takes
|
||||
a beefy machine to produce a result in a decent amount of time now that
|
||||
Diffusers has grown a lot. Here is the command for it:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -423,7 +430,7 @@ make a commit with `git commit` to record your changes locally:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git add modified_file.py
|
||||
$ git commit
|
||||
$ git commit -m "A descriptive message about your changes."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is a good idea to sync your copy of the code with the original
|
||||
@@ -443,7 +450,7 @@ Push the changes to your account using:
|
||||
webpage of your fork on GitHub. Click on 'Pull request' to send your changes
|
||||
to the project maintainers for review.
|
||||
|
||||
7. It's ok if maintainers ask you for changes. It happens to core contributors
|
||||
7. It's OK if maintainers ask you for changes. It happens to core contributors
|
||||
too! So everyone can see the changes in the Pull request, work in your local
|
||||
branch and push the changes to your fork. They will automatically appear in
|
||||
the pull request.
|
||||
@@ -486,7 +493,7 @@ To avoid pinging the upstream repository which adds reference notes to each upst
|
||||
when syncing the main branch of a forked repository, please, follow these steps:
|
||||
1. When possible, avoid syncing with the upstream using a branch and PR on the forked repository. Instead, merge directly into the forked main.
|
||||
2. If a PR is absolutely necessary, use the following steps after checking out your branch:
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git checkout -b your-branch-for-syncing
|
||||
$ git pull --squash --no-commit upstream main
|
||||
$ git commit -m '<your message without GitHub references>'
|
||||
@@ -495,4 +502,4 @@ $ git push --set-upstream origin your-branch-for-syncing
|
||||
|
||||
### Style guide
|
||||
|
||||
For documentation strings, 🧨 Diffusers follows the [google style](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html).
|
||||
For documentation strings, 🧨 Diffusers follows the [Google style](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 🧨 Diffusers’ Ethical Guidelines
|
||||
|
||||
## Preamble
|
||||
@@ -42,7 +54,7 @@ The team works daily to make the technical and non-technical tools available to
|
||||
|
||||
- **Encouraging safety in deployment**
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Safe Stable Diffusion**](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe): It mitigates the well-known issue that models, like Stable Diffusion, that are trained on unfiltered, web-crawled datasets tend to suffer from inappropriate degeneration. Related paper: [Safe Latent Diffusion: Mitigating Inappropriate Degeneration in Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105).
|
||||
- [**Safe Stable Diffusion**](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/stable_diffusion_safe): It mitigates the well-known issue that models, like Stable Diffusion, that are trained on unfiltered, web-crawled datasets tend to suffer from inappropriate degeneration. Related paper: [Safe Latent Diffusion: Mitigating Inappropriate Degeneration in Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105).
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Safety Checker**](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py): It checks and compares the class probability of a set of hard-coded harmful concepts in the embedding space against an image after it has been generated. The harmful concepts are intentionally hidden to prevent reverse engineering of the checker.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ The methods shown in this document can also be used to evaluate different [noise
|
||||
We cover Diffusion models with the following pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
- Text-guided image generation (such as the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img)).
|
||||
- Text-guided image generation, additionally conditioned on an input image (such as the [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img), and [`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix)).
|
||||
- Text-guided image generation, additionally conditioned on an input image (such as the [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) and [`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/pix2pix)).
|
||||
- Class-conditioned image generation models (such as the [`DiTPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/dit)).
|
||||
|
||||
## Qualitative Evaluation
|
||||
@@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ import torch
|
||||
seed = 0
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(sample_prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(sample_prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -141,7 +141,7 @@ prompts = [
|
||||
"A small cabin on top of a snowy mountain in the style of Disney, artstation",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, output_type="np").images
|
||||
|
||||
print(images.shape)
|
||||
# (6, 512, 512, 3)
|
||||
@@ -155,13 +155,11 @@ from functools import partial
|
||||
|
||||
clip_score_fn = partial(clip_score, model_name_or_path="openai/clip-vit-base-patch16")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def calculate_clip_score(images, prompts):
|
||||
images_int = (images * 255).astype("uint8")
|
||||
clip_score = clip_score_fn(torch.from_numpy(images_int).permute(0, 3, 1, 2), prompts).detach()
|
||||
return round(float(clip_score), 4)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sd_clip_score = calculate_clip_score(images, prompts)
|
||||
print(f"CLIP score: {sd_clip_score}")
|
||||
# CLIP score: 35.7038
|
||||
@@ -176,7 +174,7 @@ fixed seed with the [v1-4 Stable Diffusion checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/Co
|
||||
seed = 0
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="np").images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we load the [v1-5 checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) to generate images:
|
||||
@@ -185,7 +183,7 @@ Then we load the [v1-5 checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffus
|
||||
model_ckpt_1_5 = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
sd_pipeline_1_5 = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_ckpt_1_5, torch_dtype=weight_dtype).to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
images_1_5 = sd_pipeline_1_5(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
images_1_5 = sd_pipeline_1_5(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="np").images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And finally, we compare their CLIP scores:
|
||||
@@ -295,12 +293,11 @@ def edit_image(input_image, instruction):
|
||||
image = instruct_pix2pix_pipeline(
|
||||
instruction,
|
||||
image=input_image,
|
||||
output_type="numpy",
|
||||
output_type="np",
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
input_images = []
|
||||
original_captions = []
|
||||
modified_captions = []
|
||||
@@ -417,7 +414,7 @@ It should be noted that the `StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline` exposes t
|
||||
|
||||
We can extend the idea of this metric to measure how similar the original image and edited version are. To do that, we can just do `F.cosine_similarity(img_feat_two, img_feat_one)`. For these kinds of edits, we would still want the primary semantics of the images to be preserved as much as possible, i.e., a high similarity score.
|
||||
|
||||
We can use these metrics for similar pipelines such as the [`StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero#diffusers.StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline).
|
||||
We can use these metrics for similar pipelines such as the [`StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/pix2pix_zero#diffusers.StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -427,7 +424,7 @@ Both CLIP score and CLIP direction similarity rely on the CLIP model, which can
|
||||
|
||||
***Extending metrics like IS, FID (discussed later), or KID can be difficult*** when the model under evaluation was pre-trained on a large image-captioning dataset (such as the [LAION-5B dataset](https://laion.ai/blog/laion-5b/)). This is because underlying these metrics is an InceptionNet (pre-trained on the ImageNet-1k dataset) used for extracting intermediate image features. The pre-training dataset of Stable Diffusion may have limited overlap with the pre-training dataset of InceptionNet, so it is not a good candidate here for feature extraction.
|
||||
|
||||
***Using the above metrics helps evaluate models that are class-conditioned. For example, [DiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview). It was pre-trained being conditioned on the ImageNet-1k classes.***
|
||||
***Using the above metrics helps evaluate models that are class-conditioned. For example, [DiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/dit). It was pre-trained being conditioned on the ImageNet-1k classes.***
|
||||
|
||||
### Class-conditioned image generation
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -452,7 +449,6 @@ def download(url, local_filepath):
|
||||
f.write(r.content)
|
||||
return local_filepath
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dummy_dataset_url = "https://hf.co/datasets/sayakpaul/sample-datasets/resolve/main/sample-imagenet-images.zip"
|
||||
local_filepath = download(dummy_dataset_url, dummy_dataset_url.split("/")[-1])
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -470,7 +466,7 @@ image_paths = sorted([os.path.join(dataset_path, x) for x in os.listdir(dataset_
|
||||
real_images = [np.array(Image.open(path).convert("RGB")) for path in image_paths]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These are 10 images from the following Imagenet-1k classes: "cassette_player", "chain_saw" (x2), "church", "gas_pump" (x3), "parachute" (x2), and "tench".
|
||||
These are 10 images from the following ImageNet-1k classes: "cassette_player", "chain_saw" (x2), "church", "gas_pump" (x3), "parachute" (x2), and "tench".
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/evaluation_diffusion_models/real-images.png" alt="real-images"><br>
|
||||
@@ -488,7 +484,6 @@ def preprocess_image(image):
|
||||
image = image.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) / 255.0
|
||||
return F.center_crop(image, (256, 256))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
real_images = torch.cat([preprocess_image(image) for image in real_images])
|
||||
print(real_images.shape)
|
||||
# torch.Size([10, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
@@ -517,7 +512,7 @@ words = [
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
class_ids = dit_pipeline.get_label_ids(words)
|
||||
output = dit_pipeline(class_labels=class_ids, generator=generator, output_type="numpy")
|
||||
output = dit_pipeline(class_labels=class_ids, generator=generator, output_type="np")
|
||||
|
||||
fake_images = output.images
|
||||
fake_images = torch.tensor(fake_images)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ In a nutshell, Diffusers is built to be a natural extension of PyTorch. Therefor
|
||||
## Usability over Performance
|
||||
|
||||
- While Diffusers has many built-in performance-enhancing features (see [Memory and Speed](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/optimization/fp16)), models are always loaded with the highest precision and lowest optimization. Therefore, by default diffusion pipelines are always instantiated on CPU with float32 precision if not otherwise defined by the user. This ensures usability across different platforms and accelerators and means that no complex installations are required to run the library.
|
||||
- Diffusers aim at being a **light-weight** package and therefore has very few required dependencies, but many soft dependencies that can improve performance (such as `accelerate`, `safetensors`, `onnx`, etc...). We strive to keep the library as lightweight as possible so that it can be added without much concern as a dependency on other packages.
|
||||
- Diffusers aims to be a **light-weight** package and therefore has very few required dependencies, but many soft dependencies that can improve performance (such as `accelerate`, `safetensors`, `onnx`, etc...). We strive to keep the library as lightweight as possible so that it can be added without much concern as a dependency on other packages.
|
||||
- Diffusers prefers simple, self-explainable code over condensed, magic code. This means that short-hand code syntaxes such as lambda functions, and advanced PyTorch operators are often not desired.
|
||||
|
||||
## Simple over easy
|
||||
@@ -31,13 +31,13 @@ As PyTorch states, **explicit is better than implicit** and **simple is better t
|
||||
- We follow PyTorch's API with methods like [`DiffusionPipeline.to`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/diffusion_pipeline#diffusers.DiffusionPipeline.to) to let the user handle device management.
|
||||
- Raising concise error messages is preferred to silently correct erroneous input. Diffusers aims at teaching the user, rather than making the library as easy to use as possible.
|
||||
- Complex model vs. scheduler logic is exposed instead of magically handled inside. Schedulers/Samplers are separated from diffusion models with minimal dependencies on each other. This forces the user to write the unrolled denoising loop. However, the separation allows for easier debugging and gives the user more control over adapting the denoising process or switching out diffusion models or schedulers.
|
||||
- Separately trained components of the diffusion pipeline, *e.g.* the text encoder, the unet, and the variational autoencoder, each have their own model class. This forces the user to handle the interaction between the different model components, and the serialization format separates the model components into different files. However, this allows for easier debugging and customization. Dreambooth or textual inversion training
|
||||
is very simple thanks to diffusers' ability to separate single components of the diffusion pipeline.
|
||||
- Separately trained components of the diffusion pipeline, *e.g.* the text encoder, the unet, and the variational autoencoder, each have their own model class. This forces the user to handle the interaction between the different model components, and the serialization format separates the model components into different files. However, this allows for easier debugging and customization. DreamBooth or Textual Inversion training
|
||||
is very simple thanks to Diffusers' ability to separate single components of the diffusion pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tweakable, contributor-friendly over abstraction
|
||||
|
||||
For large parts of the library, Diffusers adopts an important design principle of the [Transformers library](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers), which is to prefer copy-pasted code over hasty abstractions. This design principle is very opinionated and stands in stark contrast to popular design principles such as [Don't repeat yourself (DRY)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Don%27t_repeat_yourself).
|
||||
In short, just like Transformers does for modeling files, diffusers prefers to keep an extremely low level of abstraction and very self-contained code for pipelines and schedulers.
|
||||
In short, just like Transformers does for modeling files, Diffusers prefers to keep an extremely low level of abstraction and very self-contained code for pipelines and schedulers.
|
||||
Functions, long code blocks, and even classes can be copied across multiple files which at first can look like a bad, sloppy design choice that makes the library unmaintainable.
|
||||
**However**, this design has proven to be extremely successful for Transformers and makes a lot of sense for community-driven, open-source machine learning libraries because:
|
||||
- Machine Learning is an extremely fast-moving field in which paradigms, model architectures, and algorithms are changing rapidly, which therefore makes it very difficult to define long-lasting code abstractions.
|
||||
@@ -47,15 +47,15 @@ Functions, long code blocks, and even classes can be copied across multiple file
|
||||
At Hugging Face, we call this design the **single-file policy** which means that almost all of the code of a certain class should be written in a single, self-contained file. To read more about the philosophy, you can have a look
|
||||
at [this blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/transformers-design-philosophy).
|
||||
|
||||
In diffusers, we follow this philosophy for both pipelines and schedulers, but only partly for diffusion models. The reason we don't follow this design fully for diffusion models is because almost all diffusion pipelines, such
|
||||
as [DDPM](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.12.0/en/api/pipelines/ddpm), [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.12.0/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview#stable-diffusion-pipelines), [UnCLIP (Dalle-2)](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.12.0/en/api/pipelines/unclip#overview) and [Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/) all rely on the same diffusion model, the [UNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models#diffusers.UNet2DConditionModel).
|
||||
In Diffusers, we follow this philosophy for both pipelines and schedulers, but only partly for diffusion models. The reason we don't follow this design fully for diffusion models is because almost all diffusion pipelines, such
|
||||
as [DDPM](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/ddpm), [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview#stable-diffusion-pipelines), [unCLIP (DALL·E 2)](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/unclip) and [Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/) all rely on the same diffusion model, the [UNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models/unet2d-cond).
|
||||
|
||||
Great, now you should have generally understood why 🧨 Diffusers is designed the way it is 🤗.
|
||||
We try to apply these design principles consistently across the library. Nevertheless, there are some minor exceptions to the philosophy or some unlucky design choices. If you have feedback regarding the design, we would ❤️ to hear it [directly on GitHub](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=).
|
||||
|
||||
## Design Philosophy in Details
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's look a bit into the nitty-gritty details of the design philosophy. Diffusers essentially consist of three major classes, [pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines), [models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models), and [schedulers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers).
|
||||
Now, let's look a bit into the nitty-gritty details of the design philosophy. Diffusers essentially consists of three major classes: [pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines), [models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models), and [schedulers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers).
|
||||
Let's walk through more in-detail design decisions for each class.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pipelines
|
||||
@@ -83,14 +83,14 @@ The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Models correspond to **a type of model architecture**. *E.g.* the [`UNet2DConditionModel`] class is used for all UNet variations that expect 2D image inputs and are conditioned on some context.
|
||||
- All models can be found in [`src/diffusers/models`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models) and every model architecture shall be defined in its file, e.g. [`unet_2d_condition.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unet_2d_condition.py), [`transformer_2d.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/transformer_2d.py), etc...
|
||||
- Models **do not** follow the single-file policy and should make use of smaller model building blocks, such as [`attention.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/attention.py), [`resnet.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/resnet.py), [`embeddings.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/embeddings.py), etc... **Note**: This is in stark contrast to Transformers' modeling files and shows that models do not really follow the single-file policy.
|
||||
- Models intend to expose complexity, just like PyTorch's module does, and give clear error messages.
|
||||
- Models intend to expose complexity, just like PyTorch's `Module` class, and give clear error messages.
|
||||
- Models all inherit from `ModelMixin` and `ConfigMixin`.
|
||||
- Models can be optimized for performance when it doesn’t demand major code changes, keeps backward compatibility, and gives significant memory or compute gain.
|
||||
- Models should by default have the highest precision and lowest performance setting.
|
||||
- To integrate new model checkpoints whose general architecture can be classified as an architecture that already exists in Diffusers, the existing model architecture shall be adapted to make it work with the new checkpoint. One should only create a new file if the model architecture is fundamentally different.
|
||||
- Models should be designed to be easily extendable to future changes. This can be achieved by limiting public function arguments, configuration arguments, and "foreseeing" future changes, *e.g.* it is usually better to add `string` "...type" arguments that can easily be extended to new future types instead of boolean `is_..._type` arguments. Only the minimum amount of changes shall be made to existing architectures to make a new model checkpoint work.
|
||||
- The model design is a difficult trade-off between keeping code readable and concise and supporting many model checkpoints. For most parts of the modeling code, classes shall be adapted for new model checkpoints, while there are some exceptions where it is preferred to add new classes to make sure the code is kept concise and
|
||||
readable longterm, such as [UNet blocks](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unet_2d_blocks.py) and [Attention processors](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/attention_processor.py).
|
||||
readable long-term, such as [UNet blocks](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unet_2d_blocks.py) and [Attention processors](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/attention_processor.py).
|
||||
|
||||
### Schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -99,10 +99,10 @@ Schedulers are responsible to guide the denoising process for inference as well
|
||||
The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- All schedulers are found in [`src/diffusers/schedulers`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers).
|
||||
- Schedulers are **not** allowed to import from large utils files and shall be kept very self-contained.
|
||||
- One scheduler python file corresponds to one scheduler algorithm (as might be defined in a paper).
|
||||
- One scheduler Python file corresponds to one scheduler algorithm (as might be defined in a paper).
|
||||
- If schedulers share similar functionalities, we can make use of the `#Copied from` mechanism.
|
||||
- Schedulers all inherit from `SchedulerMixin` and `ConfigMixin`.
|
||||
- Schedulers can be easily swapped out with the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/configuration#diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config) method as explained in detail [here](./using-diffusers/schedulers.md).
|
||||
- Schedulers can be easily swapped out with the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/configuration#diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config) method as explained in detail [here](../using-diffusers/schedulers.md).
|
||||
- Every scheduler has to have a `set_num_inference_steps`, and a `step` function. `set_num_inference_steps(...)` has to be called before every denoising process, *i.e.* before `step(...)` is called.
|
||||
- Every scheduler exposes the timesteps to be "looped over" via a `timesteps` attribute, which is an array of timesteps the model will be called upon.
|
||||
- The `step(...)` function takes a predicted model output and the "current" sample (x_t) and returns the "previous", slightly more denoised sample (x_t-1).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
The library has three main components:
|
||||
|
||||
- State-of-the-art [diffusion pipelines](api/pipelines/overview) for inference with just a few lines of code.
|
||||
- State-of-the-art diffusion pipelines for inference with just a few lines of code. There are many pipelines in 🤗 Diffusers, check out the table in the pipeline [overview](api/pipelines/overview) for a complete list of available pipelines and the task they solve.
|
||||
- Interchangeable [noise schedulers](api/schedulers/overview) for balancing trade-offs between generation speed and quality.
|
||||
- Pretrained [models](api/models) that can be used as building blocks, and combined with schedulers, for creating your own end-to-end diffusion systems.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -46,53 +46,3 @@ The library has three main components:
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Paper/Repository | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [alt_diffusion](./api/pipelines/alt_diffusion) | [AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [audio_diffusion](./api/pipelines/audio_diffusion) | [Audio Diffusion](https://github.com/teticio/audio-diffusion.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [controlnet](./api/pipelines/controlnet) | [Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [cycle_diffusion](./api/pipelines/cycle_diffusion) | [Unifying Diffusion Models' Latent Space, with Applications to CycleDiffusion and Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.05559) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [dance_diffusion](./api/pipelines/dance_diffusion) | [Dance Diffusion](https://github.com/williamberman/diffusers.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [ddpm](./api/pipelines/ddpm) | [Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [ddim](./api/pipelines/ddim) | [Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [if](./if) | [**IF**](./api/pipelines/if) | Image Generation |
|
||||
| [if_img2img](./if) | [**IF**](./api/pipelines/if) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [if_inpainting](./if) | [**IF**](./api/pipelines/if) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion_uncond](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [paint_by_example](./api/pipelines/paint_by_example) | [Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13227) | Image-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [pndm](./api/pipelines/pndm) | [Pseudo Numerical Methods for Diffusion Models on Manifolds](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09778) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_ve](./api/pipelines/score_sde_ve) | [Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_vp](./api/pipelines/score_sde_vp) | [Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [semantic_stable_diffusion](./api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion) | [Semantic Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12247) | Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_adapter](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/adapter) | [**T2I-Adapter**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.08453) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation | -
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_text2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_img2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_inpaint](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/inpaint) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_panorama](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/panorama) | [MultiDiffusion](https://multidiffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Panorama Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix) | [InstructPix2Pix: Learning to Follow Image Editing Instructions](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09800) | Text-Guided Image Editing|
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix_zero](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero) | [Zero-shot Image-to-Image Translation](https://pix2pixzero.github.io/) | Text-Guided Image Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_attend_and_excite](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/attend_and_excite) | [Attend-and-Excite: Attention-Based Semantic Guidance for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13826) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_self_attention_guidance](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/self_attention_guidance) | [Improving Sample Quality of Diffusion Models Using Self-Attention Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.00939) | Text-to-Image Generation Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_image_variation](./stable_diffusion/image_variation) | [Stable Diffusion Image Variations](https://github.com/LambdaLabsML/lambda-diffusers#stable-diffusion-image-variations) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_latent_upscale](./stable_diffusion/latent_upscale) | [Stable Diffusion Latent Upscaler](https://twitter.com/StabilityAI/status/1590531958815064065) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_model_editing](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/model_editing) | [Editing Implicit Assumptions in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://time-diffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Image Model Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Depth-Conditional Stable Diffusion](https://github.com/Stability-AI/stablediffusion#depth-conditional-stable-diffusion) | Depth-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_safe](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe) | [Safe Stable Diffusion](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105) | Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | Stable unCLIP | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | Stable unCLIP | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stochastic_karras_ve](./api/pipelines/stochastic_karras_ve) | [Elucidating the Design Space of Diffusion-Based Generative Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00364) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [text_to_video_sd](./api/pipelines/text_to_video) | [Modelscope's Text-to-video-synthesis Model in Open Domain](https://modelscope.cn/models/damo/text-to-video-synthesis/summary) | Text-to-Video Generation |
|
||||
| [unclip](./api/pipelines/unclip) | [Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06125)(implementation by [kakaobrain](https://github.com/kakaobrain/karlo)) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Image Variations Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Dual Image and Text Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [vq_diffusion](./api/pipelines/vq_diffusion) | [Vector Quantized Diffusion Model for Text-to-Image Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.14822) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_ldm3d](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/ldm3d_diffusion) | [LDM3D: Latent Diffusion Model for 3D](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.10853) | Text to Image and Depth Generation |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,12 +12,10 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Install 🤗 Diffusers for whichever deep learning library you're working with.
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is tested on Python 3.8+, PyTorch 1.7.0+, and Flax. Follow the installation instructions below for the deep learning library you are using:
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is tested on Python 3.8+, PyTorch 1.7.0+ and Flax. Follow the installation instructions below for the deep learning library you are using:
|
||||
|
||||
- [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) installation instructions.
|
||||
- [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) installation instructions.
|
||||
- [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) installation instructions
|
||||
- [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) installation instructions
|
||||
|
||||
## Install with pip
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +35,7 @@ Activate the virtual environment:
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers also relies on the 🤗 Transformers library, and you can install both with the following command:
|
||||
You should also install 🤗 Transformers because 🤗 Diffusers relies on its models:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
@@ -52,11 +50,17 @@ pip install diffusers["flax"] transformers
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Install with conda
|
||||
|
||||
After activating your virtual environment, with `conda` (maintained by the community):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
conda install -c conda-forge diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Install from source
|
||||
|
||||
Before installing 🤗 Diffusers from source, make sure you have `torch` and 🤗 Accelerate installed.
|
||||
|
||||
For `torch` installation, refer to the `torch` [installation](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally) guide.
|
||||
Before installing 🤗 Diffusers from source, make sure you have PyTorch and 🤗 Accelerate installed.
|
||||
|
||||
To install 🤗 Accelerate:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +68,7 @@ To install 🤗 Accelerate:
|
||||
pip install accelerate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Install 🤗 Diffusers from source with the following command:
|
||||
Then install 🤗 Diffusers from source:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
@@ -75,7 +79,7 @@ The `main` version is useful for staying up-to-date with the latest developments
|
||||
For instance, if a bug has been fixed since the last official release but a new release hasn't been rolled out yet.
|
||||
However, this means the `main` version may not always be stable.
|
||||
We strive to keep the `main` version operational, and most issues are usually resolved within a few hours or a day.
|
||||
If you run into a problem, please open an [Issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose), so we can fix it even sooner!
|
||||
If you run into a problem, please open an [Issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose) so we can fix it even sooner!
|
||||
|
||||
## Editable install
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -123,17 +127,29 @@ git pull
|
||||
|
||||
Your Python environment will find the `main` version of 🤗 Diffusers on the next run.
|
||||
|
||||
## Notice on telemetry logging
|
||||
## Cache
|
||||
|
||||
Our library gathers telemetry information during `from_pretrained()` requests.
|
||||
This data includes the version of Diffusers and PyTorch/Flax, the requested model or pipeline class,
|
||||
and the path to a pre-trained checkpoint if it is hosted on the Hub.
|
||||
Model weights and files are downloaded from the Hub to a cache which is usually your home directory. You can change the cache location by specifying the `HF_HOME` or `HUGGINFACE_HUB_CACHE` environment variables or configuring the `cache_dir` parameter in methods like [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`].
|
||||
|
||||
Cached files allow you to run 🤗 Diffusers offline. To prevent 🤗 Diffusers from connecting to the internet, set the `HF_HUB_OFFLINE` environment variable to `True` and 🤗 Diffusers will only load previously downloaded files in the cache.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
export HF_HUB_OFFLINE=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about managing and cleaning the cache, take a look at the [caching](https://huggingface.co/docs/huggingface_hub/guides/manage-cache) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
## Telemetry logging
|
||||
|
||||
Our library gathers telemetry information during [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] requests.
|
||||
The data gathered includes the version of 🤗 Diffusers and PyTorch/Flax, the requested model or pipeline class,
|
||||
and the path to a pretrained checkpoint if it is hosted on the Hugging Face Hub.
|
||||
This usage data helps us debug issues and prioritize new features.
|
||||
Telemetry is only sent when loading models and pipelines from the HuggingFace Hub,
|
||||
and is not collected during local usage.
|
||||
Telemetry is only sent when loading models and pipelines from the Hub,
|
||||
and it is not collected if you're loading local files.
|
||||
|
||||
We understand that not everyone wants to share additional information, and we respect your privacy,
|
||||
so you can disable telemetry collection by setting the `DISABLE_TELEMETRY` environment variable from your terminal:
|
||||
We understand that not everyone wants to share additional information,and we respect your privacy.
|
||||
You can disable telemetry collection by setting the `DISABLE_TELEMETRY` environment variable from your terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
On Linux/MacOS:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,6 +12,6 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Generating high-quality outputs is computationally intensive, especially during each iterative step where you go from a noisy output to a less noisy output. One of 🤗 Diffuser's goal is to make this technology widely accessible to everyone, which includes enabling fast inference on consumer and specialized hardware.
|
||||
Generating high-quality outputs is computationally intensive, especially during each iterative step where you go from a noisy output to a less noisy output. One of 🤗 Diffuser's goals is to make this technology widely accessible to everyone, which includes enabling fast inference on consumer and specialized hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
This section will cover tips and tricks - like half-precision weights and sliced attention - for optimizing inference speed and reducing memory-consumption. You'll also learn how to speed up your PyTorch code with [`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html) or [ONNX Runtime](https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/), and enable memory-efficient attention with [xFormers](https://facebookresearch.github.io/xformers/). There are also guides for running inference on specific hardware like Apple Silicon, and Intel or Habana processors.
|
||||
This section will cover tips and tricks - like half-precision weights and sliced attention - for optimizing inference speed and reducing memory-consumption. You'll also learn how to speed up your PyTorch code with [`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html) or [ONNX Runtime](https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/), and enable memory-efficient attention with [xFormers](https://facebookresearch.github.io/xformers/). There are also guides for running inference on specific hardware like Apple Silicon, and Intel or Habana processors.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ The quicktour will show you how to use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] for inference,
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The quicktour is a simplified version of the introductory 🧨 Diffusers [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/diffusers_intro.ipynb) to help you get started quickly. If you want to learn more about 🧨 Diffusers goal, design philosophy, and additional details about it's core API, check out the notebook!
|
||||
The quicktour is a simplified version of the introductory 🧨 Diffusers [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/diffusers_intro.ipynb) to help you get started quickly. If you want to learn more about 🧨 Diffusers' goal, design philosophy, and additional details about its core API, check out the notebook!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ The [`DiffusionPipeline`] downloads and caches all modeling, tokenization, and s
|
||||
>>> pipeline
|
||||
StableDiffusionPipeline {
|
||||
"_class_name": "StableDiffusionPipeline",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.13.1",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.21.4",
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"scheduler": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
@@ -133,7 +133,7 @@ Then load the saved weights into the pipeline:
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can run the pipeline as you would in the section above.
|
||||
Now, you can run the pipeline as you would in the section above.
|
||||
|
||||
### Swapping schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -191,7 +191,7 @@ To use the model for inference, create the image shape with random Gaussian nois
|
||||
torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For inference, pass the noisy image to the model and a `timestep`. The `timestep` indicates how noisy the input image is, with more noise at the beginning and less at the end. This helps the model determine its position in the diffusion process, whether it is closer to the start or the end. Use the `sample` method to get the model output:
|
||||
For inference, pass the noisy image and a `timestep` to the model. The `timestep` indicates how noisy the input image is, with more noise at the beginning and less at the end. This helps the model determine its position in the diffusion process, whether it is closer to the start or the end. Use the `sample` method to get the model output:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
@@ -210,23 +210,28 @@ Schedulers manage going from a noisy sample to a less noisy sample given the mod
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For the quicktour, you'll instantiate the [`DDPMScheduler`] with it's [`~diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config`] method:
|
||||
For the quicktour, you'll instantiate the [`DDPMScheduler`] with its [`~diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config`] method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DDPMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_config(repo_id)
|
||||
>>> scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
>>> scheduler
|
||||
DDPMScheduler {
|
||||
"_class_name": "DDPMScheduler",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.13.1",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.21.4",
|
||||
"beta_end": 0.02,
|
||||
"beta_schedule": "linear",
|
||||
"beta_start": 0.0001,
|
||||
"clip_sample": true,
|
||||
"clip_sample_range": 1.0,
|
||||
"dynamic_thresholding_ratio": 0.995,
|
||||
"num_train_timesteps": 1000,
|
||||
"prediction_type": "epsilon",
|
||||
"sample_max_value": 1.0,
|
||||
"steps_offset": 0,
|
||||
"thresholding": false,
|
||||
"timestep_spacing": "leading",
|
||||
"trained_betas": null,
|
||||
"variance_type": "fixed_small"
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -234,13 +239,13 @@ DDPMScheduler {
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Notice how the scheduler is instantiated from a configuration. Unlike a model, a scheduler does not have trainable weights and is parameter-free!
|
||||
💡 Unlike a model, a scheduler does not have trainable weights and is parameter-free!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the most important parameters are:
|
||||
|
||||
* `num_train_timesteps`: the length of the denoising process or in other words, the number of timesteps required to process random Gaussian noise into a data sample.
|
||||
* `num_train_timesteps`: the length of the denoising process or, in other words, the number of timesteps required to process random Gaussian noise into a data sample.
|
||||
* `beta_schedule`: the type of noise schedule to use for inference and training.
|
||||
* `beta_start` and `beta_end`: the start and end noise values for the noise schedule.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -249,9 +254,10 @@ To predict a slightly less noisy image, pass the following to the scheduler's [`
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> less_noisy_sample = scheduler.step(model_output=noisy_residual, timestep=2, sample=noisy_sample).prev_sample
|
||||
>>> less_noisy_sample.shape
|
||||
torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `less_noisy_sample` can be passed to the next `timestep` where it'll get even less noisier! Let's bring it all together now and visualize the entire denoising process.
|
||||
The `less_noisy_sample` can be passed to the next `timestep` where it'll get even less noisy! Let's bring it all together now and visualize the entire denoising process.
|
||||
|
||||
First, create a function that postprocesses and displays the denoised image as a `PIL.Image`:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -305,10 +311,10 @@ Sit back and watch as a cat is generated from nothing but noise! 😻
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
Hopefully you generated some cool images with 🧨 Diffusers in this quicktour! For your next steps, you can:
|
||||
Hopefully, you generated some cool images with 🧨 Diffusers in this quicktour! For your next steps, you can:
|
||||
|
||||
* Train or finetune a model to generate your own images in the [training](./tutorials/basic_training) tutorial.
|
||||
* See example official and community [training or finetuning scripts](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples#-diffusers-examples) for a variety of use cases.
|
||||
* Learn more about loading, accessing, changing and comparing schedulers in the [Using different Schedulers](./using-diffusers/schedulers) guide.
|
||||
* Explore prompt engineering, speed and memory optimizations, and tips and tricks for generating higher quality images with the [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion) guide.
|
||||
* Learn more about loading, accessing, changing, and comparing schedulers in the [Using different Schedulers](./using-diffusers/schedulers) guide.
|
||||
* Explore prompt engineering, speed and memory optimizations, and tips and tricks for generating higher-quality images with the [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion) guide.
|
||||
* Dive deeper into speeding up 🧨 Diffusers with guides on [optimized PyTorch on a GPU](./optimization/fp16), and inference guides for running [Stable Diffusion on Apple Silicon (M1/M2)](./optimization/mps) and [ONNX Runtime](./optimization/onnx).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
Getting the [`DiffusionPipeline`] to generate images in a certain style or include what you want can be tricky. Often times, you have to run the [`DiffusionPipeline`] several times before you end up with an image you're happy with. But generating something out of nothing is a computationally intensive process, especially if you're running inference over and over again.
|
||||
|
||||
This is why it's important to get the most *computational* (speed) and *memory* (GPU RAM) efficiency from the pipeline to reduce the time between inference cycles so you can iterate faster.
|
||||
This is why it's important to get the most *computational* (speed) and *memory* (GPU vRAM) efficiency from the pipeline to reduce the time between inference cycles so you can iterate faster.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial walks you through how to generate faster and better with the [`DiffusionPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -108,6 +108,7 @@ pipeline.scheduler.compatibles
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddpm.DDPMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_singlestep.DPMSolverSinglestepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_k_dpm_2_ancestral_discrete.KDPM2AncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.utils.dummy_torch_and_torchsde_objects.DPMSolverSDEScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_heun_discrete.HeunDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_pndm.PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_ancestral_discrete.EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
@@ -115,7 +116,7 @@ pipeline.scheduler.compatibles
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The Stable Diffusion model uses the [`PNDMScheduler`] by default which usually requires ~50 inference steps, but more performant schedulers like [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`], require only ~20 or 25 inference steps. Use the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`] method to load a new scheduler:
|
||||
The Stable Diffusion model uses the [`PNDMScheduler`] by default which usually requires ~50 inference steps, but more performant schedulers like [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`], require only ~20 or 25 inference steps. Use the [`~ConfigMixin.from_config`] method to load a new scheduler:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
@@ -155,13 +156,13 @@ def get_inputs(batch_size=1):
|
||||
Start with `batch_size=4` and see how much memory you've consumed:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(**get_inputs(batch_size=4)).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, 2, 2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Unless you have a GPU with more RAM, the code above probably returned an `OOM` error! Most of the memory is taken up by the cross-attention layers. Instead of running this operation in a batch, you can run it sequentially to save a significant amount of memory. All you have to do is configure the pipeline to use the [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_attention_slicing`] function:
|
||||
Unless you have a GPU with more vRAM, the code above probably returned an `OOM` error! Most of the memory is taken up by the cross-attention layers. Instead of running this operation in a batch, you can run it sequentially to save a significant amount of memory. All you have to do is configure the pipeline to use the [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_attention_slicing`] function:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
@@ -192,7 +193,7 @@ As the field grows, there are more and more high-quality checkpoints finetuned t
|
||||
|
||||
### Better pipeline components
|
||||
|
||||
You can also try replacing the current pipeline components with a newer version. Let's try loading the latest [autodecoder](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1/tree/main/vae) from Stability AI into the pipeline, and generate some images:
|
||||
You can also try replacing the current pipeline components with a newer version. Let's try loading the latest [autoencoder](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1/tree/main/vae) from Stability AI into the pipeline, and generate some images:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoencoderKL
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Distributed inference with multiple GPUs
|
||||
|
||||
On distributed setups, you can run inference across multiple GPUs with 🤗 [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index) or [PyTorch Distributed](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/dist_overview.html), which is useful for generating with multiple prompts in parallel.
|
||||
@@ -13,6 +25,7 @@ To begin, create a Python file and initialize an [`accelerate.PartialState`] to
|
||||
Now use the [`~accelerate.PartialState.split_between_processes`] utility as a context manager to automatically distribute the prompts between the number of processes.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate import PartialState
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -92,4 +105,4 @@ Once you've completed the inference script, use the `--nproc_per_node` argument
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
torchrun run_distributed.py --nproc_per_node=2
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# AutoPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is able to complete many different tasks, and you can often reuse the same pretrained weights for multiple tasks such as text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting. If you're new to the library and diffusion models though, it may be difficult to know which pipeline to use for a task. For example, if you're using the [runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) checkpoint for text-to-image, you might not know that you could also use it for image-to-image and inpainting by loading the checkpoint with the [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`] and [`StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline`] classes respectively.
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +18,7 @@ The `AutoPipeline` class is designed to simplify the variety of pipelines in
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the [AutoPipeline](./pipelines/auto_pipeline) reference to see which tasks are supported. Currently, it supports text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting.
|
||||
Take a look at the [AutoPipeline](../api/pipelines/auto_pipeline) reference to see which tasks are supported. Currently, it supports text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,6 +38,7 @@ pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
prompt = "peasant and dragon combat, wood cutting style, viking era, bevel with rune"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=25).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
@@ -35,12 +48,16 @@ image = pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=25).images[0]
|
||||
Under the hood, [`AutoPipelineForText2Image`]:
|
||||
|
||||
1. automatically detects a `"stable-diffusion"` class from the [`model_index.json`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/blob/main/model_index.json) file
|
||||
2. loads the corresponding text-to-image [`StableDiffusionPipline`] based on the `"stable-diffusion"` class name
|
||||
2. loads the corresponding text-to-image [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] based on the `"stable-diffusion"` class name
|
||||
|
||||
Likewise, for image-to-image, [`AutoPipelineForImage2Image`] detects a `"stable-diffusion"` checkpoint from the `model_index.json` file and it'll load the corresponding [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`] behind the scenes. You can also pass any additional arguments specific to the pipeline class such as `strength`, which determines the amount of noise or variation added to an input image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
@@ -56,6 +73,7 @@ image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
image.thumbnail((768, 768))
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, image, num_inference_steps=200, strength=0.75, guidance_scale=10.5).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
@@ -67,6 +85,7 @@ And if you want to do inpainting, then [`AutoPipelineForInpainting`] loads the u
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForInpainting
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
@@ -80,6 +99,7 @@ mask_image = load_image(mask_url).convert("RGB")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A majestic tiger sitting on a bench"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image, num_inference_steps=50, strength=0.80).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
@@ -106,6 +126,7 @@ The [`~AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pipe`] method detects the original pipeli
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image, AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline_text2img = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
@@ -126,6 +147,7 @@ If you passed an optional argument - like disabling the safety checker - to the
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image, AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline_text2img = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
@@ -135,7 +157,7 @@ pipeline_text2img = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline_img2img = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pipe(pipeline_text2img)
|
||||
print(pipe.config.requires_safety_checker)
|
||||
print(pipeline_img2img.config.requires_safety_checker)
|
||||
"False"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -143,4 +165,6 @@ You can overwrite any of the arguments and even configuration from the original
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline_img2img = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pipe(pipeline_text2img, requires_safety_checker=True, strength=0.3)
|
||||
print(pipeline_img2img.config.requires_safety_checker)
|
||||
"True"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ Before you begin, make sure you have 🤗 Datasets installed to load and preproc
|
||||
#!pip install diffusers[training]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We encourage you to share your model with the community, and in order to do that, you'll need to login to your Hugging Face account (create one [here](https://hf.co/join) if you don't already have one!). You can login from a notebook and enter your token when prompted:
|
||||
We encourage you to share your model with the community, and in order to do that, you'll need to login to your Hugging Face account (create one [here](https://hf.co/join) if you don't already have one!). You can login from a notebook and enter your token when prompted. Make sure your token has the write role.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
@@ -59,7 +59,6 @@ For convenience, create a `TrainingConfig` class containing the training hyperpa
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> @dataclass
|
||||
... class TrainingConfig:
|
||||
... image_size = 128 # the generated image resolution
|
||||
@@ -75,6 +74,7 @@ For convenience, create a `TrainingConfig` class containing the training hyperpa
|
||||
... output_dir = "ddpm-butterflies-128" # the model name locally and on the HF Hub
|
||||
|
||||
... push_to_hub = True # whether to upload the saved model to the HF Hub
|
||||
... hub_model_id = "<your-username>/<my-awesome-model>" # the name of the repository to create on the HF Hub
|
||||
... hub_private_repo = False
|
||||
... overwrite_output_dir = True # overwrite the old model when re-running the notebook
|
||||
... seed = 0
|
||||
@@ -253,10 +253,8 @@ Then, you'll need a way to evaluate the model. For evaluation, you can use the [
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DDPMPipeline
|
||||
>>> from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
>>> import math
|
||||
>>> import os
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def evaluate(config, epoch, pipeline):
|
||||
... # Sample some images from random noise (this is the backward diffusion process).
|
||||
... # The default pipeline output type is `List[PIL.Image]`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,4 +20,4 @@ After completing the tutorials, you'll have gained the necessary skills to start
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to join our community on [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/JfAtkvEtRb) or the [forums](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) to connect and collaborate with other users and developers!
|
||||
|
||||
Let's start diffusing! 🧨
|
||||
Let's start diffusing! 🧨
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,11 +10,11 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
# Inference with PEFT
|
||||
|
||||
There are many adapters trained in different styles to achieve different effects. You can even combine multiple adapters to create new and unique images. With the 🤗 [PEFT](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/index) integration in 🤗 Diffusers, it is really easy to load and manage adapters for inference. In this guide, you'll learn how to use different adapters with [Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL)](./pipelines/stable_diffusion/stable_diffusion_xl) for inference.
|
||||
There are many adapters trained in different styles to achieve different effects. You can even combine multiple adapters to create new and unique images. With the 🤗 [PEFT](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/index) integration in 🤗 Diffusers, it is really easy to load and manage adapters for inference. In this guide, you'll learn how to use different adapters with [Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL)](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/stable_diffusion_xl) for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
Throughout this guide, you'll use LoRA as the main adapter technique, so we'll use the terms LoRA and adapter interchangeably. You should have some familiarity with LoRA, and if you don't, we welcome you to check out the [LoRA guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/conceptual_guides/lora).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ image
|
||||
|
||||
With the `adapter_name` parameter, it is really easy to use another adapter for inference! Load the [nerijs/pixel-art-xl](https://huggingface.co/nerijs/pixel-art-xl) adapter that has been fine-tuned to generate pixel art images, and let's call it `"pixel"`.
|
||||
|
||||
The pipeline automatically sets the first loaded adapter (`"toy"`) as the active adapter. But you can activate the `"pixel"` adapter with the [`~diffusers.loaders.set_adapters`] method as shown below:
|
||||
The pipeline automatically sets the first loaded adapter (`"toy"`) as the active adapter. But you can activate the `"pixel"` adapter with the [`~diffusers.loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.set_adapters`] method as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("nerijs/pixel-art-xl", weight_name="pixel-art-xl.safetensors", adapter_name="pixel")
|
||||
@@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ image
|
||||
|
||||
You can also perform multi-adapter inference where you combine different adapter checkpoints for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
Once again, use the [`~diffusers.loaders.set_adapters`] method to activate two LoRA checkpoints and specify the weight for how the checkpoints should be combined.
|
||||
Once again, use the [`~diffusers.loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.set_adapters`] method to activate two LoRA checkpoints and specify the weight for how the checkpoints should be combined.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters(["pixel", "toy"], adapter_weights=[0.5, 1.0])
|
||||
@@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ image
|
||||
|
||||
Impressive! As you can see, the model was able to generate an image that mixes the characteristics of both adapters.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to go back to using only one adapter, use the [`~diffusers.loaders.set_adapters`] method to activate the `"toy"` adapter:
|
||||
If you want to go back to using only one adapter, use the [`~diffusers.loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.set_adapters`] method to activate the `"toy"` adapter:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# First, set the adapter.
|
||||
@@ -134,7 +134,7 @@ image
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to switch to only the base model, disable all LoRAs with the [`~diffusers.loaders.disable_lora`] method.
|
||||
If you want to switch to only the base model, disable all LoRAs with the [`~diffusers.loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.disable_lora`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@@ -150,16 +150,18 @@ image
|
||||
|
||||
## Monitoring active adapters
|
||||
|
||||
You have attached multiple adapters in this tutorial, and if you're feeling a bit lost on what adapters have been attached to the pipeline's components, you can easily check the list of active adapters using the [`~diffusers.loaders.get_active_adapters`] method:
|
||||
You have attached multiple adapters in this tutorial, and if you're feeling a bit lost on what adapters have been attached to the pipeline's components, you can easily check the list of active adapters using the [`~diffusers.loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.get_active_adapters`] method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```py
|
||||
active_adapters = pipe.get_active_adapters()
|
||||
>>> ["toy", "pixel"]
|
||||
active_adapters
|
||||
["toy", "pixel"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also get the active adapters of each pipeline component with [`~diffusers.loaders.get_list_adapters`]:
|
||||
You can also get the active adapters of each pipeline component with [`~diffusers.loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.get_list_adapters`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```py
|
||||
list_adapters_component_wise = pipe.get_list_adapters()
|
||||
>>> {"text_encoder": ["toy", "pixel"], "unet": ["toy", "pixel"], "text_encoder_2": ["toy", "pixel"]}
|
||||
list_adapters_component_wise
|
||||
{"text_encoder": ["toy", "pixel"], "unet": ["toy", "pixel"], "text_encoder_2": ["toy", "pixel"]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
60
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/callback.md
Normal file
60
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/callback.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Using callback
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Most 🤗 Diffusers pipeline now accept a `callback_on_step_end` argument that allows you to change the default behavior of denoising loop with custom defined functions. Here is an example of a callback function we can write to disable classifier free guidance after 40% of inference steps to save compute with minimum tradeoff in performance.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def callback_dynamic_cfg(pipe, step_index, timestep, callback_kwargs):
|
||||
# adjust the batch_size of prompt_embeds according to guidance_scale
|
||||
if step_index == int(pipe.num_timestep * 0.4):
|
||||
prompt_embeds = callback_kwargs["prompt_embeds"]
|
||||
prompt_embeds =prompt_embeds.chunk(2)[-1]
|
||||
|
||||
# update guidance_scale and prompt_embeds
|
||||
pipe._guidance_scale = 0.0
|
||||
callback_kwargs["prompt_embeds"] = prompt_embeds
|
||||
return callback_kwargs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Your callback function has below arguments:
|
||||
* `pipe` is the pipeline instance, which provides access to useful properties such as `num_timestep` and `guidance_scale`. You can modify these properties by updating the underlying attributes. In this example, we disable CFG by setting `pipe._guidance_scale` to be `0`.
|
||||
* `step_index` and `timestep` tell you where you are in the denoising loop. In our example, we use `step_index` to decide when to turn off CFG.
|
||||
* `callback_kwargs` is a dict that contains tensor variables you can modify during the denoising loop. It only includes variables specified in the `callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs` argument passed to the pipeline's `__call__` method. Different pipelines may use different sets of variables so please check the pipeline class's `_callback_tensor_inputs` attribute for the list of variables that you can modify. Common variables include `latents` and `prompt_embeds`. In our example, we need to adjust the batch size of `prompt_embeds` after setting `guidance_scale` to be `0` in order for it to work properly.
|
||||
|
||||
You can pass the callback function as `callback_on_step_end` argument to the pipeline along with `callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(1)
|
||||
out= pipe(prompt, generator=generator, callback_on_step_end = callback_custom_cfg, callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs=['prompt_embeds'])
|
||||
|
||||
out.images[0].save("out_custom_cfg.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Your callback function will be executed at the end of each denoising step and modify pipeline attributes and tensor variables for the next denoising step. We successfully added the "dynamic CFG" feature to the stable diffusion pipeline without having to modify the code at all.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Currently we only support `callback_on_step_end`. If you have a solid use case and require a callback function with a different execution point, please open an [feature request](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose) so we can add it!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# How to contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
# Contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Control image brightness
|
||||
|
||||
The Stable Diffusion pipeline is mediocre at generating images that are either very bright or dark as explained in the [Common Diffusion Noise Schedules and Sample Steps are Flawed](https://huggingface.co/papers/2305.08891) paper. The solutions proposed in the paper are currently implemented in the [`DDIMScheduler`] which you can use to improve the lighting in your images.
|
||||
@@ -22,15 +34,15 @@ Next, configure the following parameters in the [`DDIMScheduler`]:
|
||||
2. `timestep_spacing="trailing"`, starts sampling from the last timestep
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("ptx0/pseudo-journey-v2", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("ptx0/pseudo-journey-v2", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
# switch the scheduler in the pipeline to use the DDIMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipeline.scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_config(
|
||||
... pipeline.scheduler.config, rescale_betas_zero_snr=True, timestep_spacing="trailing"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_config(
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler.config, rescale_betas_zero_snr=True, timestep_spacing="trailing"
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, in your call to the pipeline, set `guidance_rescale` to prevent overexposure:
|
||||
@@ -38,6 +50,7 @@ Finally, in your call to the pipeline, set `guidance_rescale` to prevent overexp
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A lion in galaxies, spirals, nebulae, stars, smoke, iridescent, intricate detail, octane render, 8k"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, guidance_rescale=0.7).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ Most examples of preserving semantics reduce to being able to accurately map a c
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, there are qualities of generated images that we would like to influence beyond semantic preservation. I.e. in general, we would like our outputs to be of good quality, adhere to a particular style, or be realistic.
|
||||
|
||||
We will document some of the techniques `diffusers` supports to control generation of diffusion models. Much is cutting edge research and can be quite nuanced. If something needs clarifying or you have a suggestion, don't hesitate to open a discussion on the [forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/) or a [GitHub issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues).
|
||||
We will document some of the techniques `diffusers` supports to control generation of diffusion models. Much is cutting edge research and can be quite nuanced. If something needs clarifying or you have a suggestion, don't hesitate to open a discussion on the [forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) or a [GitHub issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a high level explanation of how the generation can be controlled as well as a snippet of the technicals. For more in depth explanations on the technicals, the original papers which are linked from the pipelines are always the best resources.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,11 +26,11 @@ Depending on the use case, one should choose a technique accordingly. In many ca
|
||||
|
||||
Unless otherwise mentioned, these are techniques that work with existing models and don't require their own weights.
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Instruct Pix2Pix](#instruct-pix2pix)
|
||||
2. [Pix2Pix Zero](#pix2pixzero)
|
||||
1. [InstructPix2Pix](#instruct-pix2pix)
|
||||
2. [Pix2Pix Zero](#pix2pix-zero)
|
||||
3. [Attend and Excite](#attend-and-excite)
|
||||
4. [Semantic Guidance](#semantic-guidance)
|
||||
5. [Self-attention Guidance](#self-attention-guidance)
|
||||
4. [Semantic Guidance](#semantic-guidance-sega)
|
||||
5. [Self-attention Guidance](#self-attention-guidance-sag)
|
||||
6. [Depth2Image](#depth2image)
|
||||
7. [MultiDiffusion Panorama](#multidiffusion-panorama)
|
||||
8. [DreamBooth](#dreambooth)
|
||||
@@ -47,11 +47,11 @@ For convenience, we provide a table to denote which methods are inference-only a
|
||||
|
||||
| **Method** | **Inference only** | **Requires training /<br> fine-tuning** | **Comments** |
|
||||
| :-------------------------------------------------: | :----------------: | :-------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
|
||||
| [Instruct Pix2Pix](#instruct-pix2pix) | ✅ | ❌ | Can additionally be<br>fine-tuned for better <br>performance on specific <br>edit instructions. |
|
||||
| [Pix2Pix Zero](#pix2pixzero) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [InstructPix2Pix](#instruct-pix2pix) | ✅ | ❌ | Can additionally be<br>fine-tuned for better <br>performance on specific <br>edit instructions. |
|
||||
| [Pix2Pix Zero](#pix2pix-zero) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [Attend and Excite](#attend-and-excite) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [Semantic Guidance](#semantic-guidance) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [Self-attention Guidance](#self-attention-guidance) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [Semantic Guidance](#semantic-guidance-sega) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [Self-attention Guidance](#self-attention-guidance-sag) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [Depth2Image](#depth2image) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [MultiDiffusion Panorama](#multidiffusion-panorama) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [DreamBooth](#dreambooth) | ❌ | ✅ | |
|
||||
@@ -63,14 +63,12 @@ For convenience, we provide a table to denote which methods are inference-only a
|
||||
| [DiffEdit](#diffedit) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [T2I-Adapter](#t2i-adapter) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
| [Fabric](#fabric) | ✅ | ❌ | |
|
||||
## Instruct Pix2Pix
|
||||
## InstructPix2Pix
|
||||
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09800)
|
||||
|
||||
[Instruct Pix2Pix](../api/pipelines/pix2pix) is fine-tuned from stable diffusion to support editing input images. It takes as inputs an image and a prompt describing an edit, and it outputs the edited image.
|
||||
Instruct Pix2Pix has been explicitly trained to work well with [InstructGPT](https://openai.com/blog/instruction-following/)-like prompts.
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../api/pipelines/pix2pix) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
[InstructPix2Pix](../api/pipelines/pix2pix) is fine-tuned from Stable Diffusion to support editing input images. It takes as inputs an image and a prompt describing an edit, and it outputs the edited image.
|
||||
InstructPix2Pix has been explicitly trained to work well with [InstructGPT](https://openai.com/blog/instruction-following/)-like prompts.
|
||||
|
||||
## Pix2Pix Zero
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -84,7 +82,7 @@ Pix2Pix Zero can be used both to edit synthetic images as well as real images.
|
||||
|
||||
- To edit synthetic images, one first generates an image given a caption.
|
||||
Next, we generate image captions for the concept that shall be edited and for the new target concept. We can use a model like [Flan-T5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/flan-t5) for this purpose. Then, "mean" prompt embeddings for both the source and target concepts are created via the text encoder. Finally, the pix2pix-zero algorithm is used to edit the synthetic image.
|
||||
- To edit a real image, one first generates an image caption using a model like [BLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/blip). Then one applies ddim inversion on the prompt and image to generate "inverse" latents. Similar to before, "mean" prompt embeddings for both source and target concepts are created and finally the pix2pix-zero algorithm in combination with the "inverse" latents is used to edit the image.
|
||||
- To edit a real image, one first generates an image caption using a model like [BLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/blip). Then one applies DDIM inversion on the prompt and image to generate "inverse" latents. Similar to before, "mean" prompt embeddings for both source and target concepts are created and finally the pix2pix-zero algorithm in combination with the "inverse" latents is used to edit the image.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -96,7 +94,13 @@ can edit an image in less than a minute on a consumer GPU as shown [here](../api
|
||||
As mentioned above, Pix2Pix Zero includes optimizing the latents (and not any of the UNet, VAE, or the text encoder) to steer the generation toward a specific concept. This means that the overall
|
||||
pipeline might require more memory than a standard [StableDiffusionPipeline](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img).
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../api/pipelines/pix2pix_zero) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
An important distinction between methods like InstructPix2Pix and Pix2Pix Zero is that the former
|
||||
involves fine-tuning the pre-trained weights while the latter does not. This means that you can
|
||||
apply Pix2Pix Zero to any of the available Stable Diffusion models.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Attend and Excite
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -108,20 +112,16 @@ A set of token indices are given as input, corresponding to the subjects in the
|
||||
|
||||
Like Pix2Pix Zero, Attend and Excite also involves a mini optimization loop (leaving the pre-trained weights untouched) in its pipeline and can require more memory than the usual [StableDiffusionPipeline](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img).
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../api/pipelines/attend_and_excite) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Semantic Guidance (SEGA)
|
||||
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12247)
|
||||
|
||||
SEGA allows applying or removing one or more concepts from an image. The strength of the concept can also be controlled. I.e. the smile concept can be used to incrementally increase or decrease the smile of a portrait.
|
||||
[SEGA](../api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion) allows applying or removing one or more concepts from an image. The strength of the concept can also be controlled. I.e. the smile concept can be used to incrementally increase or decrease the smile of a portrait.
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to how classifier free guidance provides guidance via empty prompt inputs, SEGA provides guidance on conceptual prompts. Multiple of these conceptual prompts can be applied simultaneously. Each conceptual prompt can either add or remove their concept depending on if the guidance is applied positively or negatively.
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike Pix2Pix Zero or Attend and Excite, SEGA directly interacts with the diffusion process instead of performing any explicit gradient-based optimization.
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Self-attention Guidance (SAG)
|
||||
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.00939)
|
||||
@@ -130,34 +130,20 @@ See [here](../api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion) for more information on h
|
||||
|
||||
SAG provides guidance from predictions not conditioned on high-frequency details to fully conditioned images. The high frequency details are extracted out of the UNet self-attention maps.
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../api/pipelines/self_attention_guidance) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Depth2Image
|
||||
|
||||
[Project](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-depth)
|
||||
|
||||
[Depth2Image](../pipelines/stable_diffusion_2#depthtoimage) is fine-tuned from Stable Diffusion to better preserve semantics for text guided image variation.
|
||||
[Depth2Image](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/depth2img) is fine-tuned from Stable Diffusion to better preserve semantics for text guided image variation.
|
||||
|
||||
It conditions on a monocular depth estimate of the original image.
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2#depthtoimage) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
An important distinction between methods like InstructPix2Pix and Pix2Pix Zero is that the former
|
||||
involves fine-tuning the pre-trained weights while the latter does not. This means that you can
|
||||
apply Pix2Pix Zero to any of the available Stable Diffusion models.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## MultiDiffusion Panorama
|
||||
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.08113)
|
||||
|
||||
MultiDiffusion defines a new generation process over a pre-trained diffusion model. This process binds together multiple diffusion generation methods that can be readily applied to generate high quality and diverse images. Results adhere to user-provided controls, such as desired aspect ratio (e.g., panorama), and spatial guiding signals, ranging from tight segmentation masks to bounding boxes.
|
||||
[MultiDiffusion Panorama](../api/pipelines/panorama) allows to generate high-quality images at arbitrary aspect ratios (e.g., panoramas).
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../api/pipelines/panorama) for more information on how to use it to generate panoramic images.
|
||||
[MultiDiffusion Panorama](../api/pipelines/panorama) defines a new generation process over a pre-trained diffusion model. This process binds together multiple diffusion generation methods that can be readily applied to generate high quality and diverse images. Results adhere to user-provided controls, such as desired aspect ratio (e.g., panorama), and spatial guiding signals, ranging from tight segmentation masks to bounding boxes.
|
||||
MultiDiffusion Panorama allows to generate high-quality images at arbitrary aspect ratios (e.g., panoramas).
|
||||
|
||||
## Fine-tuning your own models
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -165,44 +151,39 @@ In addition to pre-trained models, Diffusers has training scripts for fine-tunin
|
||||
|
||||
## DreamBooth
|
||||
|
||||
[DreamBooth](../training/dreambooth) fine-tunes a model to teach it about a new subject. I.e. a few pictures of a person can be used to generate images of that person in different styles.
|
||||
[Project](https://dreambooth.github.io/)
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../training/dreambooth) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
[DreamBooth](../training/dreambooth) fine-tunes a model to teach it about a new subject. I.e. a few pictures of a person can be used to generate images of that person in different styles.
|
||||
|
||||
## Textual Inversion
|
||||
|
||||
[Textual Inversion](../training/text_inversion) fine-tunes a model to teach it about a new concept. I.e. a few pictures of a style of artwork can be used to generate images in that style.
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.01618)
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../training/text_inversion) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
[Textual Inversion](../training/text_inversion) fine-tunes a model to teach it about a new concept. I.e. a few pictures of a style of artwork can be used to generate images in that style.
|
||||
|
||||
## ControlNet
|
||||
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543)
|
||||
|
||||
[ControlNet](../api/pipelines/controlnet) is an auxiliary network which adds an extra condition.
|
||||
[ControlNet](../api/pipelines/controlnet) is an auxiliary network which adds an extra condition.
|
||||
There are 8 canonical pre-trained ControlNets trained on different conditionings such as edge detection, scribbles,
|
||||
depth maps, and semantic segmentations.
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../api/pipelines/controlnet) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prompt Weighting
|
||||
|
||||
Prompt weighting is a simple technique that puts more attention weight on certain parts of the text
|
||||
[Prompt weighting](../using-diffusers/weighted_prompts) is a simple technique that puts more attention weight on certain parts of the text
|
||||
input.
|
||||
|
||||
For a more in-detail explanation and examples, see [here](../using-diffusers/weighted_prompts).
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.04488)
|
||||
|
||||
[Custom Diffusion](../training/custom_diffusion) only fine-tunes the cross-attention maps of a pre-trained
|
||||
text-to-image diffusion model. It also allows for additionally performing textual inversion. It supports
|
||||
text-to-image diffusion model. It also allows for additionally performing Textual Inversion. It supports
|
||||
multi-concept training by design. Like DreamBooth and Textual Inversion, Custom Diffusion is also used to
|
||||
teach a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model about new concepts to generate outputs involving the
|
||||
concept(s) of interest.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, check out our [official doc](../training/custom_diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
## Model Editing
|
||||
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.08084)
|
||||
@@ -211,8 +192,6 @@ The [text-to-image model editing pipeline](../api/pipelines/model_editing) helps
|
||||
diffusion model might make about the subjects present in the input prompt. For example, if you prompt Stable Diffusion to generate images for "A pack of roses", the roses in the generated images
|
||||
are more likely to be red. This pipeline helps you change that assumption.
|
||||
|
||||
To know more details, check out the [official doc](../api/pipelines/model_editing).
|
||||
|
||||
## DiffEdit
|
||||
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.11427)
|
||||
@@ -220,8 +199,6 @@ To know more details, check out the [official doc](../api/pipelines/model_editin
|
||||
[DiffEdit](../api/pipelines/diffedit) allows for semantic editing of input images along with
|
||||
input prompts while preserving the original input images as much as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
To know more details, check out the [official doc](../api/pipelines/diffedit).
|
||||
|
||||
## T2I-Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.08453)
|
||||
@@ -230,15 +207,11 @@ To know more details, check out the [official doc](../api/pipelines/diffedit).
|
||||
There are 8 canonical pre-trained adapters trained on different conditionings such as edge detection, sketch,
|
||||
depth maps, and semantic segmentations.
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/adapter) for more information on how to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Fabric
|
||||
|
||||
[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.10159)
|
||||
|
||||
[Fabric](../api/pipelines/fabric) is a training-free
|
||||
[Fabric](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/442017ccc877279bcf24fbe92f92d3d0def191b6/examples/community#stable-diffusion-fabric-pipeline) is a training-free
|
||||
approach applicable to a wide range of popular diffusion models, which exploits
|
||||
the self-attention layer present in the most widely used architectures to condition
|
||||
the diffusion process on a set of feedback images.
|
||||
|
||||
To know more details, check out the [official doc](../api/pipelines/fabric).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# ControlNet
|
||||
|
||||
ControlNet is a type of model for controlling image diffusion models by conditioning the model with an additional input image. There are many types of conditioning inputs (canny edge, user sketching, human pose, depth, and more) you can use to control a diffusion model. This is hugely useful because it affords you greater control over image generation, making it easier to generate specific images without experimenting with different text prompts or denoising values as much.
|
||||
@@ -351,9 +363,9 @@ prompt = "aerial view, a futuristic research complex in a bright foggy jungle, h
|
||||
negative_prompt = 'low quality, bad quality, sketches'
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
|
||||
image=image,
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
|
||||
image=canny_image,
|
||||
controlnet_conditioning_scale=0.5,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
images
|
||||
@@ -421,7 +433,7 @@ Prepare the canny image conditioning:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
|
||||
canny_image = load_image(
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,273 +14,106 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
> **For more information about community pipelines, please have a look at [this issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841).**
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
**Community** examples consist of both inference and training examples that have been added by the community.
|
||||
Please have a look at the following table to get an overview of all community examples. Click on the **Code Example** to get a copy-and-paste ready code example that you can try out.
|
||||
If a community doesn't work as expected, please open an issue and ping the author on it.
|
||||
For more context about the design choices behind community pipelines, please have a look at [this issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841).
|
||||
|
||||
| Example | Description | Code Example | Colab | Author |
|
||||
|:---------------------------------------|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:------------------------------------------------------------------|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------:|
|
||||
| CLIP Guided Stable Diffusion | Doing CLIP guidance for text to image generation with Stable Diffusion | [CLIP Guided Stable Diffusion](#clip-guided-stable-diffusion) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/CLIP_Guided_Stable_diffusion_with_diffusers.ipynb) | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj/) |
|
||||
| One Step U-Net (Dummy) | Example showcasing of how to use Community Pipelines (see https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841) | [One Step U-Net](#one-step-unet) | - | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/) |
|
||||
| Stable Diffusion Interpolation | Interpolate the latent space of Stable Diffusion between different prompts/seeds | [Stable Diffusion Interpolation](#stable-diffusion-interpolation) | - | [Nate Raw](https://github.com/nateraw/) |
|
||||
| Stable Diffusion Mega | **One** Stable Diffusion Pipeline with all functionalities of [Text2Image](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion.py), [Image2Image](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_img2img.py) and [Inpainting](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_inpaint.py) | [Stable Diffusion Mega](#stable-diffusion-mega) | - | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/) |
|
||||
| Long Prompt Weighting Stable Diffusion | **One** Stable Diffusion Pipeline without tokens length limit, and support parsing weighting in prompt. | [Long Prompt Weighting Stable Diffusion](#long-prompt-weighting-stable-diffusion) | - | [SkyTNT](https://github.com/SkyTNT) |
|
||||
| Speech to Image | Using automatic-speech-recognition to transcribe text and Stable Diffusion to generate images | [Speech to Image](#speech-to-image) | - | [Mikail Duzenli](https://github.com/MikailINTech)
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipelines allow you to get creative and build your own unique pipelines to share with the community. You can find all community pipelines in the [diffusers/examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) folder along with inference and training examples for how to use them. This guide showcases some of the community pipelines and hopefully it'll inspire you to create your own (feel free to open a PR with your own pipeline and we will merge it!).
|
||||
|
||||
To load a community pipeline, use the `custom_pipeline` argument in [`DiffusionPipeline`] to specify one of the files in [diffusers/examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community):
|
||||
|
||||
To load a custom pipeline you just need to pass the `custom_pipeline` argument to `DiffusionPipeline`, as one of the files in `diffusers/examples/community`. Feel free to send a PR with your own pipelines, we will merge them quickly.
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", custom_pipeline="filename_in_the_community_folder", use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usages
|
||||
If a community pipeline doesn't work as expected, please open a GitHub issue and mention the author.
|
||||
|
||||
### CLIP Guided Stable Diffusion
|
||||
You can learn more about community pipelines in the how to [load community pipelines](custom_pipeline_overview) and how to [contribute a community pipeline](contribute_pipeline) guides.
|
||||
|
||||
CLIP guided stable diffusion can help to generate more realistic images
|
||||
by guiding stable diffusion at every denoising step with an additional CLIP model.
|
||||
## Multilingual Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
The following code requires roughly 12GB of GPU RAM.
|
||||
The multilingual Stable Diffusion pipeline uses a pretrained [XLM-RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/papluca/xlm-roberta-base-language-detection) to identify a language and the [mBART-large-50](https://huggingface.co/facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-one-mmt) model to handle the translation. This allows you to generate images from text in 20 languages.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPImageProcessor, CLIPModel
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPImageProcessor.from_pretrained("laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K")
|
||||
clip_model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
guided_pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="clip_guided_stable_diffusion",
|
||||
clip_model=clip_model,
|
||||
feature_extractor=feature_extractor,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
guided_pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
guided_pipeline = guided_pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "fantasy book cover, full moon, fantasy forest landscape, golden vector elements, fantasy magic, dark light night, intricate, elegant, sharp focus, illustration, highly detailed, digital painting, concept art, matte, art by WLOP and Artgerm and Albert Bierstadt, masterpiece"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
images = []
|
||||
for i in range(4):
|
||||
image = guided_pipeline(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
clip_guidance_scale=100,
|
||||
num_cutouts=4,
|
||||
use_cutouts=False,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
images.append(image)
|
||||
|
||||
# save images locally
|
||||
for i, img in enumerate(images):
|
||||
img.save(f"./clip_guided_sd/image_{i}.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `images` list contains a list of PIL images that can be saved locally or displayed directly in a google colab.
|
||||
Generated images tend to be of higher qualtiy than natively using stable diffusion. E.g. the above script generates the following images:
|
||||
|
||||
.
|
||||
|
||||
### One Step Unet
|
||||
|
||||
The dummy "one-step-unet" can be run as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cifar10-32", custom_pipeline="one_step_unet")
|
||||
pipe()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: This community pipeline is not useful as a feature, but rather just serves as an example of how community pipelines can be added (see https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841).
|
||||
|
||||
### Stable Diffusion Interpolation
|
||||
|
||||
The following code can be run on a GPU of at least 8GB VRAM and should take approximately 5 minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
safety_checker=None, # Very important for videos...lots of false positives while interpolating
|
||||
custom_pipeline="interpolate_stable_diffusion",
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
|
||||
frame_filepaths = pipe.walk(
|
||||
prompts=["a dog", "a cat", "a horse"],
|
||||
seeds=[42, 1337, 1234],
|
||||
num_interpolation_steps=16,
|
||||
output_dir="./dreams",
|
||||
batch_size=4,
|
||||
height=512,
|
||||
width=512,
|
||||
guidance_scale=8.5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The output of the `walk(...)` function returns a list of images saved under the folder as defined in `output_dir`. You can use these images to create videos of stable diffusion.
|
||||
|
||||
> **Please have a look at https://github.com/nateraw/stable-diffusion-videos for more in-detail information on how to create videos using stable diffusion as well as more feature-complete functionality.**
|
||||
|
||||
### Stable Diffusion Mega
|
||||
|
||||
The Stable Diffusion Mega Pipeline lets you use the main use cases of the stable diffusion pipeline in a single class.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python3
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def download_image(url):
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
return PIL.Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="stable_diffusion_mega",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-to-Image
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe.text2img("An astronaut riding a horse").images
|
||||
|
||||
### Image-to-Image
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = download_image(
|
||||
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, trending on artstation"
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipe.img2img(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, strength=0.75, guidance_scale=7.5).images
|
||||
|
||||
### Inpainting
|
||||
|
||||
img_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo.png"
|
||||
mask_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo_mask.png"
|
||||
init_image = download_image(img_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
mask_image = download_image(mask_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a cat sitting on a bench"
|
||||
images = pipe.inpaint(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image, strength=0.75).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As shown above this one pipeline can run all both "text-to-image", "image-to-image", and "inpainting" in one pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
### Long Prompt Weighting Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
The Pipeline lets you input prompt without 77 token length limit. And you can increase words weighting by using "()" or decrease words weighting by using "[]"
|
||||
The Pipeline also lets you use the main use cases of the stable diffusion pipeline in a single class.
|
||||
|
||||
#### pytorch
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"hakurei/waifu-diffusion", custom_pipeline="lpw_stable_diffusion", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "best_quality (1girl:1.3) bow bride brown_hair closed_mouth frilled_bow frilled_hair_tubes frills (full_body:1.3) fox_ear hair_bow hair_tubes happy hood japanese_clothes kimono long_sleeves red_bow smile solo tabi uchikake white_kimono wide_sleeves cherry_blossoms"
|
||||
neg_prompt = "lowres, bad_anatomy, error_body, error_hair, error_arm, error_hands, bad_hands, error_fingers, bad_fingers, missing_fingers, error_legs, bad_legs, multiple_legs, missing_legs, error_lighting, error_shadow, error_reflection, text, error, extra_digit, fewer_digits, cropped, worst_quality, low_quality, normal_quality, jpeg_artifacts, signature, watermark, username, blurry"
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.text2img(prompt, negative_prompt=neg_prompt, width=512, height=512, max_embeddings_multiples=3).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### onnxruntime
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="lpw_stable_diffusion_onnx",
|
||||
revision="onnx",
|
||||
provider="CUDAExecutionProvider",
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars, best quality"
|
||||
neg_prompt = "lowres, bad anatomy, error body, error hair, error arm, error hands, bad hands, error fingers, bad fingers, missing fingers, error legs, bad legs, multiple legs, missing legs, error lighting, error shadow, error reflection, text, error, extra digit, fewer digits, cropped, worst quality, low quality, normal quality, jpeg artifacts, signature, watermark, username, blurry"
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.text2img(prompt, negative_prompt=neg_prompt, width=512, height=512, max_embeddings_multiples=3).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
if you see `Token indices sequence length is longer than the specified maximum sequence length for this model ( *** > 77 ) . Running this sequence through the model will result in indexing errors`. Do not worry, it is normal.
|
||||
|
||||
### Speech to Image
|
||||
|
||||
The following code can generate an image from an audio sample using pre-trained OpenAI whisper-small and Stable Diffusion.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
WhisperForConditionalGeneration,
|
||||
WhisperProcessor,
|
||||
pipeline,
|
||||
MBart50TokenizerFast,
|
||||
MBartForConditionalGeneration,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
device_dict = {"cuda": 0, "cpu": -1}
|
||||
|
||||
ds = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/librispeech_asr_dummy", "clean", split="validation")
|
||||
# add language detection pipeline
|
||||
language_detection_model_ckpt = "papluca/xlm-roberta-base-language-detection"
|
||||
language_detection_pipeline = pipeline("text-classification",
|
||||
model=language_detection_model_ckpt,
|
||||
device=device_dict[device])
|
||||
|
||||
audio_sample = ds[3]
|
||||
|
||||
text = audio_sample["text"].lower()
|
||||
speech_data = audio_sample["audio"]["array"]
|
||||
|
||||
model = WhisperForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("openai/whisper-small").to(device)
|
||||
processor = WhisperProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/whisper-small")
|
||||
# add model for language translation
|
||||
trans_tokenizer = MBart50TokenizerFast.from_pretrained("facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-one-mmt")
|
||||
trans_model = MBartForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-one-mmt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
diffuser_pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="speech_to_image_diffusion",
|
||||
speech_model=model,
|
||||
speech_processor=processor,
|
||||
custom_pipeline="multilingual_stable_diffusion",
|
||||
detection_pipeline=language_detection_pipeline,
|
||||
translation_model=trans_model,
|
||||
translation_tokenizer=trans_tokenizer,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
diffuser_pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
diffuser_pipeline = diffuser_pipeline.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
output = diffuser_pipeline(speech_data)
|
||||
plt.imshow(output.images[0])
|
||||
```
|
||||
This example produces the following image:
|
||||
prompt = ["a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse",
|
||||
"Una casa en la playa",
|
||||
"Ein Hund, der Orange isst",
|
||||
"Un restaurant parisien"]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
images = diffuser_pipeline(prompt).images
|
||||
grid = make_image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=2)
|
||||
grid
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4313860/198328706-295824a4-9856-4ce5-8e66-278ceb42fd29.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## MagicMix
|
||||
|
||||
[MagicMix](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.16056) is a pipeline that can mix an image and text prompt to generate a new image that preserves the image structure. The `mix_factor` determines how much influence the prompt has on the layout generation, `kmin` controls the number of steps during the content generation process, and `kmax` determines how much information is kept in the layout of the original image.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="magic_mix",
|
||||
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", subfolder="scheduler"),
|
||||
).to('cuda')
|
||||
|
||||
img = load_image("https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/59410571/209578593-141467c7-d831-4792-8b9a-b17dc5e47816.jpg")
|
||||
mix_img = pipeline(img, prompt="bed", kmin = 0.3, kmax = 0.5, mix_factor = 0.5)
|
||||
mix_img
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/59410571/209578593-141467c7-d831-4792-8b9a-b17dc5e47816.jpg" />
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">image prompt</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/59410571/209578602-70f323fa-05b7-4dd6-b055-e40683e37914.jpg" />
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">image and text prompt mix</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
@@ -10,10 +10,12 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Load community pipelines
|
||||
# Load community pipelines and components
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
## Community pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipelines are any [`DiffusionPipeline`] class that are different from the original implementation as specified in their paper (for example, the [`StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline`] corresponds to the [Text-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) paper). They provide additional functionality or extend the original implementation of a pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
There are many cool community pipelines like [Speech to Image](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community#speech-to-image) or [Composable Stable Diffusion](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community#composable-stable-diffusion), and you can find all the official community pipelines [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community).
|
||||
@@ -54,4 +56,111 @@ pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about community pipelines, take a look at the [Community pipelines](custom_pipeline_examples) guide for how to use them and if you're interested in adding a community pipeline check out the [How to contribute a community pipeline](contribute_pipeline) guide!
|
||||
For more information about community pipelines, take a look at the [Community pipelines](custom_pipeline_examples) guide for how to use them and if you're interested in adding a community pipeline check out the [How to contribute a community pipeline](contribute_pipeline) guide!
|
||||
|
||||
## Community components
|
||||
|
||||
If your pipeline has custom components that Diffusers doesn't support already, you need to accompany the Python modules that implement them. These customized components could be VAE, UNet, scheduler, etc. For the text encoder, we rely on `transformers` anyway. So, that should be handled separately (more info here). The pipeline code itself can be customized as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Community components allow users to build pipelines that may have customized components that are not part of Diffusers. This section shows how users should use community components to build a community pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
You'll use the [showlab/show-1-base](https://huggingface.co/showlab/show-1-base) pipeline checkpoint as an example here. Here, you have a custom UNet and a customized pipeline (`TextToVideoIFPipeline`). For convenience, let's call the UNet `ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel`.
|
||||
|
||||
"showlab/show-1-base" already provides the checkpoints in the Diffusers format, which is a great starting point. So, let's start loading up the components which are already well-supported:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Text encoder**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import T5Tokenizer, T5EncoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_id = "showlab/show-1-base"
|
||||
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained(pipe_id, subfolder="tokenizer")
|
||||
text_encoder = T5EncoderModel.from_pretrained(pipe_id, subfolder="text_encoder")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Scheduler**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_pretrained(pipe_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Image processor**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(pipe_id, subfolder="feature_extractor")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you need to implement the custom UNet. The implementation is available [here](https://github.com/showlab/Show-1/blob/main/showone/models/unet_3d_condition.py). So, let's create a Python script called `showone_unet_3d_condition.py` and copy over the implementation, changing the `UNet3DConditionModel` classname to `ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel` to avoid any conflicts with Diffusers. This is because Diffusers already has one `UNet3DConditionModel`. We put all the components needed to implement the class in `showone_unet_3d_condition.py` only. You can find the entire file [here](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/unet/showone_unet_3d_condition.py).
|
||||
|
||||
Once this is done, we can initialize the UNet:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from showone_unet_3d_condition import ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel
|
||||
|
||||
unet = ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel.from_pretrained(pipe_id, subfolder="unet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then implement the custom `TextToVideoIFPipeline` in another Python script: `pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py`. This is already available [here](https://github.com/showlab/Show-1/blob/main/showone/pipelines/pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py).
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have all the components, initialize the `TextToVideoIFPipeline`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from pipeline_t2v_base_pixel import TextToVideoIFPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = TextToVideoIFPipeline(
|
||||
unet=unet,
|
||||
text_encoder=text_encoder,
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
scheduler=scheduler,
|
||||
feature_extractor=feature_extractor
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline.to(device="cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.torch_dtype = torch.float16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Push to the pipeline to the Hub to share with the community:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.push_to_hub("custom-t2v-pipeline")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After the pipeline is successfully pushed, you need a couple of changes:
|
||||
|
||||
1. In `model_index.json` file, change the `_class_name` attribute. It should be like [so](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/model_index.json#L2).
|
||||
2. Upload `showone_unet_3d_condition.py` to the `unet` directory ([example](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/unet/showone_unet_3d_condition.py)).
|
||||
3. Upload `pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py` to the pipeline base directory ([example](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/unet/showone_unet_3d_condition.py)).
|
||||
|
||||
To run inference, just do:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"<change-username>/<change-id>", trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "hello"
|
||||
|
||||
# Text embeds
|
||||
prompt_embeds, negative_embeds = pipeline.encode_prompt(prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
# Keyframes generation (8x64x40, 2fps)
|
||||
video_frames = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds,
|
||||
negative_prompt_embeds=negative_embeds,
|
||||
num_frames=8,
|
||||
height=40,
|
||||
width=64,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=2,
|
||||
guidance_scale=9.0,
|
||||
output_type="pt"
|
||||
).frames
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, notice the use of the `trust_remote_code` argument while initializing the pipeline. It is responsible for handling all the "magic" behind the scenes.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# DiffEdit
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Distilled Stable Diffusion inference
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Improve generation quality with FreeU
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +23,7 @@ However, the skip connection can sometimes introduce unnatural image details. [F
|
||||
|
||||
FreeU is applied during inference and it does not require any additional training. The technique works for different tasks such as text-to-image, image-to-image, and text-to-video.
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, you will apply FreeU to the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], [`StableDiffusionXLPipeline`], and [`TextToVideoSDPipeline`].
|
||||
In this guide, you will apply FreeU to the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], [`StableDiffusionXLPipeline`], and [`TextToVideoSDPipeline`]. You need to install Diffusers from source to run the examples below.
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -46,6 +58,7 @@ And then run inference:
|
||||
prompt = "A squirrel eating a burger"
|
||||
seed = 2023
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=torch.manual_seed(seed)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The figure below compares non-FreeU and FreeU results respectively for the same hyperparameters used above (`prompt` and `seed`):
|
||||
@@ -68,9 +81,9 @@ seed = 2023
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline.enable_freeu(s1=0.9, s2=0.2, b1=1.1, b2=1.2)
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=torch.manual_seed(seed)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
@@ -88,13 +101,13 @@ pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
prompt = "A squirrel eating a burger"
|
||||
seed = 2023
|
||||
|
||||
# Comes from
|
||||
# Comes from
|
||||
# https://wandb.ai/nasirk24/UNET-FreeU-SDXL/reports/FreeU-SDXL-Optimal-Parameters--Vmlldzo1NDg4NTUw
|
||||
pipeline.enable_freeu(s1=0.6, s2=0.4, b1=1.1, b2=1.2)
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=torch.manual_seed(seed)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Text-to-video generation
|
||||
@@ -107,8 +120,7 @@ from diffusers.utils import export_to_video
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "cerspense/zeroscope_v2_576w"
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("cerspense/zeroscope_v2_576w", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
seed = 2023
|
||||
@@ -120,4 +132,4 @@ video_frames = pipe(prompt, height=320, width=576, num_frames=30, generator=torc
|
||||
export_to_video(video_frames, "astronaut_rides_horse.mp4")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks to [kadirnar](https://github.com/kadirnar/) for helping to integrate the feature, and to [justindujardin](https://github.com/justindujardin) for the helpful discussions.
|
||||
Thanks to [kadirnar](https://github.com/kadirnar/) for helping to integrate the feature, and to [justindujardin](https://github.com/justindujardin) for the helpful discussions.
|
||||
|
||||
692
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/kandinsky.md
Normal file
692
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/kandinsky.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,692 @@
|
||||
# Kandinsky
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
The Kandinsky models are a series of multilingual text-to-image generation models. The Kandinsky 2.0 model uses two multilingual text encoders and concatenates those results for the UNet.
|
||||
|
||||
[Kandinsky 2.1](../api/pipelines/kandinsky) changes the architecture to include an image prior model ([`CLIP`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip)) to generate a mapping between text and image embeddings. The mapping provides better text-image alignment and it is used with the text embeddings during training, leading to higher quality results. Finally, Kandinsky 2.1 uses a [Modulating Quantized Vectors (MoVQ)](https://huggingface.co/papers/2209.09002) decoder - which adds a spatial conditional normalization layer to increase photorealism - to decode the latents into images.
|
||||
|
||||
[Kandinsky 2.2](../api/pipelines/kandinsky_v22) improves on the previous model by replacing the image encoder of the image prior model with a larger CLIP-ViT-G model to improve quality. The image prior model was also retrained on images with different resolutions and aspect ratios to generate higher-resolution images and different image sizes.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to use the Kandinsky models for text-to-image, image-to-image, inpainting, interpolation, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, make sure you have the following libraries installed:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# uncomment to install the necessary libraries in Colab
|
||||
#!pip install transformers accelerate safetensors
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Kandinsky 2.1 and 2.2 usage is very similar! The only difference is Kandinsky 2.2 doesn't accept `prompt` as an input when decoding the latents. Instead, Kandinsky 2.2 only accepts `image_embeds` during decoding.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Text-to-image
|
||||
|
||||
To use the Kandinsky models for any task, you always start by setting up the prior pipeline to encode the prompt and generate the image embeddings. The prior pipeline also generates `negative_image_embeds` that correspond to the negative prompt `""`. For better results, you can pass an actual `negative_prompt` to the prior pipeline, but this'll increase the effective batch size of the prior pipeline by 2x.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="text-to-image">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyPriorPipeline, KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
prior_pipeline = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline = KandinskyPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality" # optional to include a negative prompt, but results are usually better
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = prior_pipeline(prompt, negative_prompt, guidance_scale=1.0).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now pass all the prompts and embeddings to the [`KandinskyPipeline`] to generate an image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, image_embeds=image_embeds, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/kandinsky-docs/cheeseburger.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.2">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyV22PriorPipeline, KandinskyV22Pipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
prior_pipeline = KandinskyV22PriorPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline = KandinskyV22Pipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality" # optional to include a negative prompt, but results are usually better
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = prior_pipeline(prompt, guidance_scale=1.0).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pass the `image_embeds` and `negative_image_embeds` to the [`KandinskyV22Pipeline`] to generate an image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = pipeline(image_embeds=image_embeds, negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/kandinsky-text-to-image.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers also provides an end-to-end API with the [`KandinskyCombinedPipeline`] and [`KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline`], meaning you don't have to separately load the prior and text-to-image pipeline. The combined pipeline automatically loads both the prior model and the decoder. You can still set different values for the prior pipeline with the `prior_guidance_scale` and `prior_num_inference_steps` parameters if you want.
|
||||
|
||||
Use the [`AutoPipelineForText2Image`] to automatically call the combined pipelines under the hood:
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="text-to-image">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, prior_guidance_scale=1.0, guidance_scale = 4.0, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.2">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, prior_guidance_scale=1.0, guidance_scale = 4.0, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## Image-to-image
|
||||
|
||||
For image-to-image, pass the initial image and text prompt to condition the image with to the pipeline. Start by loading the prior pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="image-to-image">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline, KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
prior_pipeline = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline = KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.2">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline, KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
prior_pipeline = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline = KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
Download an image to condition on:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
# download image
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
original_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
original_image = original_image.resize((768, 512))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Generate the `image_embeds` and `negative_image_embeds` with the prior pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, Cinematic lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = prior_pipeline(prompt, negative_prompt).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now pass the original image, and all the prompts and embeddings to the pipeline to generate an image:
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="image-to-image">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, image=original_image, image_embeds=image_emebds, negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds, height=768, width=768, strength=0.3).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/kandinsky-docs/img2img_fantasyland.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.2">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = pipeline(image=original_image, image_embeds=image_emebds, negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds, height=768, width=768, strength=0.3).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/kandinsky-image-to-image.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers also provides an end-to-end API with the [`KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline`] and [`KandinskyV22Img2ImgCombinedPipeline`], meaning you don't have to separately load the prior and image-to-image pipeline. The combined pipeline automatically loads both the prior model and the decoder. You can still set different values for the prior pipeline with the `prior_guidance_scale` and `prior_num_inference_steps` parameters if you want.
|
||||
|
||||
Use the [`AutoPipelineForImage2Image`] to automatically call the combined pipelines under the hood:
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="image-to-image">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, Cinematic lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
original_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
original_image.thumbnail((768, 768))
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt=prompt, image=original_image, strength=0.3).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.2">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, Cinematic lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
original_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
original_image.thumbnail((768, 768))
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt=prompt, image=original_image, strength=0.3).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## Inpainting
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ The Kandinsky models uses ⬜️ **white pixels** to represent the masked area now instead of black pixels. If you are using [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`] in production, you need to change the mask to use white pixels:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# For PIL input
|
||||
import PIL.ImageOps
|
||||
mask = PIL.ImageOps.invert(mask)
|
||||
|
||||
# For PyTorch and NumPy input
|
||||
mask = 1 - mask
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For inpainting, you'll need the original image, a mask of the area to replace in the original image, and a text prompt of what to inpaint. Load the prior pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="inpaint">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyInpaintPipeline, KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
prior_pipeline = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline = KandinskyInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-inpaint", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.2">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline, KandinskyV22PriorPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
prior_pipeline = KandinskyV22PriorPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline = KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder-inpaint", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
Load an initial image and create a mask:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
init_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinsky/cat.png")
|
||||
mask = np.zeros((768, 768), dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
# mask area above cat's head
|
||||
mask[:250, 250:-250] = 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generate the embeddings with the prior pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "a hat"
|
||||
prior_output = prior_pipeline(prompt)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now pass the initial image, mask, and prompt and embeddings to the pipeline to generate an image:
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="inpaint">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, image=init_image, mask_image=mask, **prior_output, height=768, width=768, num_inference_steps=150).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/kandinsky-docs/inpaint_cat_hat.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.2">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = pipeline(image=init_image, mask_image=mask, **prior_output, height=768, width=768, num_inference_steps=150).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/kandinskyv22-inpaint.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the end-to-end [`KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline`] and [`KandinskyV22InpaintCombinedPipeline`] to call the prior and decoder pipelines together under the hood. Use the [`AutoPipelineForInpainting`] for this:
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="inpaint">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForInpainting
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-inpaint", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a hat"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=original_image, mask_image=mask).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.2">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForInpainting
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder-inpaint", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a hat"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=original_image, mask_image=mask).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## Interpolation
|
||||
|
||||
Interpolation allows you to explore the latent space between the image and text embeddings which is a cool way to see some of the prior model's intermediate outputs. Load the prior pipeline and two images you'd like to interpolate:
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="interpolate">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyPriorPipeline, KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
prior_pipeline = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
img_1 = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinsky/cat.png")
|
||||
img_2 = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinsky/starry_night.jpeg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.2">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyV22PriorPipeline, KandinskyV22Pipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
prior_pipeline = KandinskyV22PriorPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
img_1 = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinsky/cat.png")
|
||||
img_2 = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinsky/starry_night.jpeg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinsky/cat.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">a cat</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinsky/starry_night.jpeg"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">Van Gogh's Starry Night painting</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Specify the text or images to interpolate, and set the weights for each text or image. Experiment with the weights to see how they affect the interpolation!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
images_texts = ["a cat", img1, img2]
|
||||
weights = [0.3, 0.3, 0.4]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Call the `interpolate` function to generate the embeddings, and then pass them to the pipeline to generate the image:
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="interpolate">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# prompt can be left empty
|
||||
prompt = ""
|
||||
prior_out = prior_pipeline.interpolate(images_texts, weights)
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = KandinskyPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, **prior_out, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/kandinsky-docs/starry_cat.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Kandinsky 2.2">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# prompt can be left empty
|
||||
prompt = ""
|
||||
prior_out = prior_pipeline.interpolate(images_texts, weights)
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = KandinskyV22Pipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, **prior_out, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/kandinskyv22-interpolate.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## ControlNet
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ ControlNet is only supported for Kandinsky 2.2!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
ControlNet enables conditioning large pretrained diffusion models with additional inputs such as a depth map or edge detection. For example, you can condition Kandinsky 2.2 with a depth map so the model understands and preserves the structure of the depth image.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's load an image and extract it's depth map:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
img = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinskyv22/cat.png"
|
||||
).resize((768, 768))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinskyv22/cat.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can use the `depth-estimation` [`~transformers.Pipeline`] from 🤗 Transformers to process the image and retrieve the depth map:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def make_hint(image, depth_estimator):
|
||||
image = depth_estimator(image)["depth"]
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
detected_map = torch.from_numpy(image).float() / 255.0
|
||||
hint = detected_map.permute(2, 0, 1)
|
||||
return hint
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
depth_estimator = pipeline("depth-estimation")
|
||||
hint = make_hint(img, depth_estimator).unsqueeze(0).half().to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-to-image [[controlnet-text-to-image]]
|
||||
|
||||
Load the prior pipeline and the [`KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyV22PriorPipeline, KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
prior_pipeline = KandinskyV22PriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-controlnet-depth", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generate the image embeddings from a prompt and negative prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A robot, 4k photo"
|
||||
|
||||
negative_prior_prompt = "lowres, text, error, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, ugly, duplicate, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, extra fingers, mutated hands, poorly drawn hands, poorly drawn face, mutation, deformed, blurry, dehydrated, bad anatomy, bad proportions, extra limbs, cloned face, disfigured, gross proportions, malformed limbs, missing arms, missing legs, extra arms, extra legs, fused fingers, too many fingers, long neck, username, watermark, signature"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(43)
|
||||
image_emb, zero_image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prior_prompt, generator=generator
|
||||
).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, pass the image embeddings and the depth image to the [`KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline`] to generate an image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = pipeline(image_embeds=image_emb, negative_image_embeds=zero_image_emb, hint=hint, num_inference_steps=50, generator=generator, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinskyv22/robot_cat_text2img.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### Image-to-image [[controlnet-image-to-image]]
|
||||
|
||||
For image-to-image with ControlNet, you'll need to use the:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline`] to generate the image embeddings from a text prompt and an image
|
||||
- [`KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline`] to generate an image from the initial image and the image embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
Process and extract a depth map of an initial image of a cat with the `depth-estimation` [`~transformers.Pipeline`] from 🤗 Transformers:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline, KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
img = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinskyv22/cat.png"
|
||||
).resize((768, 768))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def make_hint(image, depth_estimator):
|
||||
image = depth_estimator(image)["depth"]
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
detected_map = torch.from_numpy(image).float() / 255.0
|
||||
hint = detected_map.permute(2, 0, 1)
|
||||
return hint
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
depth_estimator = pipeline("depth-estimation")
|
||||
hint = make_hint(img, depth_estimator).unsqueeze(0).half().to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Load the prior pipeline and the [`KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prior_pipeline = KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-controlnet-depth", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pass a text prompt and the initial image to the prior pipeline to generate the image embeddings:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A robot, 4k photo"
|
||||
negative_prior_prompt = "lowres, text, error, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, ugly, duplicate, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, extra fingers, mutated hands, poorly drawn hands, poorly drawn face, mutation, deformed, blurry, dehydrated, bad anatomy, bad proportions, extra limbs, cloned face, disfigured, gross proportions, malformed limbs, missing arms, missing legs, extra arms, extra legs, fused fingers, too many fingers, long neck, username, watermark, signature"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(43)
|
||||
|
||||
img_emb = pipe_prior(prompt=prompt, image=img, strength=0.85, generator=generator)
|
||||
negative_emb = pipe_prior(prompt=negative_prior_prompt, image=img, strength=1, generator=generator)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can run the [`KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline`] to generate an image from the initial image and the image embeddings:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = pipeline(image=img, strength=0.5, image_embeds=img_emb.image_embeds, negative_image_embeds=negative_emb.image_embeds, hint=hint, num_inference_steps=50, generator=generator, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinskyv22/robot_cat.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Optimizations
|
||||
|
||||
Kandinsky is unique because it requires a prior pipeline to generate the mappings, and a second pipeline to decode the latents into an image. Optimization efforts should be focused on the second pipeline because that is where the bulk of the computation is done. Here are some tips to improve Kandinsky during inference.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Enable [xFormers](https://moon-ci-docs.huggingface.co/optimization/xformers) if you're using PyTorch < 2.0:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
+ pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Enable `torch.compile` if you're using PyTorch 2.0 to automatically use scaled dot-product attention (SDPA):
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
+ pipe.unet = torch.compile(pipe.unet, mode="reduced-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
+ pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is the same as explicitly setting the attention processor to use [`~models.attention_processor.AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Offload the model to the CPU with [`~KandinskyPriorPipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload`] to avoid out-of-memory errors:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
+ pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. By default, the text-to-image pipeline uses the [`DDIMScheduler`] but you can replace it with another scheduler like [`DDPMScheduler`] to see how that affects the tradeoff between inference speed and image quality:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DDPMSCheduler
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", subfolder="ddpm_scheduler")
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", scheduler=scheduler, torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -29,11 +29,11 @@ This guide will show you how to load:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Skip to the [DiffusionPipeline explained](#diffusionpipeline-explained) section if you interested in learning in more detail about how the [`DiffusionPipeline`] class works.
|
||||
💡 Skip to the [DiffusionPipeline explained](#diffusionpipeline-explained) section if you are interested in learning in more detail about how the [`DiffusionPipeline`] class works.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] class is the simplest and most generic way to load any diffusion model from the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers). The [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method automatically detects the correct pipeline class from the checkpoint, downloads and caches all the required configuration and weight files, and returns a pipeline instance ready for inference.
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] class is the simplest and most generic way to load the latest trending diffusion model from the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=trending). The [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method automatically detects the correct pipeline class from the checkpoint, downloads, and caches all the required configuration and weight files, and returns a pipeline instance ready for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also load a checkpoint with it's specific pipeline class. The example above loaded a Stable Diffusion model; to get the same result, use the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] class:
|
||||
You can also load a checkpoint with its specific pipeline class. The example above loaded a Stable Diffusion model; to get the same result, use the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] class:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A checkpoint (such as [`CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4`](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) or [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)) may also be used for more than one task, like text-to-image or image-to-image. To differentiate what task you want to use the checkpoint for, you have to load it directly with it's corresponding task-specific pipeline class:
|
||||
A checkpoint (such as [`CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4`](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) or [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)) may also be used for more than one task, like text-to-image or image-to-image. To differentiate what task you want to use the checkpoint for, you have to load it directly with its corresponding task-specific pipeline class:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
@@ -103,12 +103,10 @@ Let's use the [`SchedulerMixin.from_pretrained`] method to replace the default [
|
||||
Then you can pass the new [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`] instance to the `scheduler` argument in [`DiffusionPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, EulerDiscreteScheduler, DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, EulerDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = EulerDiscreteScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, scheduler=scheduler, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -121,6 +119,9 @@ from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, safety_checker=None, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
You have disabled the safety checker for <class 'diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.pipeline_stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipeline'> by passing `safety_checker=None`. Ensure that you abide by the conditions of the Stable Diffusion license and do not expose unfiltered results in services or applications open to the public. Both the diffusers team and Hugging Face strongly recommend keeping the safety filter enabled in all public-facing circumstances, disabling it only for use cases that involve analyzing network behavior or auditing its results. For more information, please have a look at https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/254 .
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Reuse components across pipelines
|
||||
@@ -163,10 +164,10 @@ stable_diffusion_img2img = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline(
|
||||
|
||||
## Checkpoint variants
|
||||
|
||||
A checkpoint variant is usually a checkpoint where it's weights are:
|
||||
A checkpoint variant is usually a checkpoint whose weights are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Stored in a different floating point type for lower precision and lower storage, such as [`torch.float16`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html#data-types), because it only requires half the bandwidth and storage to download. You can't use this variant if you're continuing training or using a CPU.
|
||||
- Non-exponential mean averaged (EMA) weights which shouldn't be used for inference. You should use these to continue finetuning a model.
|
||||
- Non-exponential mean averaged (EMA) weights, which shouldn't be used for inference. You should use these to continue fine-tuning a model.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -174,7 +175,7 @@ A checkpoint variant is usually a checkpoint where it's weights are:
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Otherwise, a variant is **identical** to the original checkpoint. They have exactly the same serialization format (like [Safetensors](./using_safetensors)), model structure, and weights have identical tensor shapes.
|
||||
Otherwise, a variant is **identical** to the original checkpoint. They have exactly the same serialization format (like [Safetensors](./using_safetensors)), model structure, and weights that have identical tensor shapes.
|
||||
|
||||
| **checkpoint type** | **weight name** | **argument for loading weights** |
|
||||
|---------------------|-------------------------------------|----------------------------------|
|
||||
@@ -202,7 +203,7 @@ stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To save a checkpoint stored in a different floating point type or as a non-EMA variant, use the [`DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`] method and specify the `variant` argument. You should try and save a variant to the same folder as the original checkpoint, so you can load both from the same folder:
|
||||
To save a checkpoint stored in a different floating-point type or as a non-EMA variant, use the [`DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`] method and specify the `variant` argument. You should try and save a variant to the same folder as the original checkpoint, so you can load both from the same folder:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -247,7 +248,7 @@ The above example is therefore deprecated and won't be supported anymore for `di
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
If you load diffusers pipelines or models with `revision="fp16"` or `revision="non_ema"`,
|
||||
please make sure to update to code and use `variant="fp16"` or `variation="non_ema"` respectively
|
||||
please make sure to update the code and use `variant="fp16"` or `variation="non_ema"` respectively
|
||||
instead.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
@@ -255,7 +256,7 @@ instead.
|
||||
|
||||
## Models
|
||||
|
||||
Models are loaded from the [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] method, which downloads and caches the latest version of the model weights and configurations. If the latest files are available in the local cache, [`~ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] reuses files in the cache instead of redownloading them.
|
||||
Models are loaded from the [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] method, which downloads and caches the latest version of the model weights and configurations. If the latest files are available in the local cache, [`~ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] reuses files in the cache instead of re-downloading them.
|
||||
|
||||
Models can be loaded from a subfolder with the `subfolder` argument. For example, the model weights for `runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5` are stored in the [`unet`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main/unet) subfolder:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -281,9 +282,9 @@ You can also load and save model variants by specifying the `variant` argument i
|
||||
from diffusers import UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
|
||||
model = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", subfolder="unet", variant="non-ema", use_safetensors=True
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", subfolder="unet", variant="non_ema", use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.save_pretrained("./local-unet", variant="non-ema")
|
||||
model.save_pretrained("./local-unet", variant="non_ema")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Schedulers
|
||||
@@ -291,7 +292,7 @@ model.save_pretrained("./local-unet", variant="non-ema")
|
||||
Schedulers are loaded from the [`SchedulerMixin.from_pretrained`] method, and unlike models, schedulers are **not parameterized** or **trained**; they are defined by a configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
Loading schedulers does not consume any significant amount of memory and the same configuration file can be used for a variety of different schedulers.
|
||||
For example, the following schedulers are compatible with [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] which means you can load the same scheduler configuration file in any of these classes:
|
||||
For example, the following schedulers are compatible with [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], which means you can load the same scheduler configuration file in any of these classes:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -300,8 +301,8 @@ from diffusers import (
|
||||
DDIMScheduler,
|
||||
PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
LMSDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
EulerDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
EulerDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -324,9 +325,9 @@ pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, scheduler=dpm, use_s
|
||||
As a class method, [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] is responsible for two things:
|
||||
|
||||
- Download the latest version of the folder structure required for inference and cache it. If the latest folder structure is available in the local cache, [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] reuses the cache and won't redownload the files.
|
||||
- Load the cached weights into the correct pipeline [class](./api/pipelines/overview#diffusers-summary) - retrieved from the `model_index.json` file - and return an instance of it.
|
||||
- Load the cached weights into the correct pipeline [class](../api/pipelines/overview#diffusers-summary) - retrieved from the `model_index.json` file - and return an instance of it.
|
||||
|
||||
The pipelines underlying folder structure corresponds directly with their class instances. For example, the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] corresponds to the folder structure in [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5).
|
||||
The pipelines' underlying folder structure corresponds directly with their class instances. For example, the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] corresponds to the folder structure in [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -338,13 +339,13 @@ print(pipeline)
|
||||
|
||||
You'll see pipeline is an instance of [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], which consists of seven components:
|
||||
|
||||
- `"feature_extractor"`: a [`~transformers.CLIPFeatureExtractor`] from 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- `"feature_extractor"`: a [`~transformers.CLIPImageProcessor`] from 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- `"safety_checker"`: a [component](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/e55687e1e15407f60f32242027b7bb8170e58266/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py#L32) for screening against harmful content.
|
||||
- `"scheduler"`: an instance of [`PNDMScheduler`].
|
||||
- `"text_encoder"`: a [`~transformers.CLIPTextModel`] from 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- `"tokenizer"`: a [`~transformers.CLIPTokenizer`] from 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- `"unet"`: an instance of [`UNet2DConditionModel`].
|
||||
- `"vae"` an instance of [`AutoencoderKL`].
|
||||
- `"vae"`: an instance of [`AutoencoderKL`].
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
StableDiffusionPipeline {
|
||||
@@ -379,7 +380,7 @@ StableDiffusionPipeline {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Compare the components of the pipeline instance to the [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) folder structure, and you'll see there is a separate folder for each of the components in the repository:
|
||||
Compare the components of the pipeline instance to the [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main) folder structure, and you'll see there is a separate folder for each of the components in the repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
@@ -388,12 +389,18 @@ Compare the components of the pipeline instance to the [`runwayml/stable-diffusi
|
||||
├── model_index.json
|
||||
├── safety_checker
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ └── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
| ├── model.fp16.safetensors
|
||||
│ ├── model.safetensors
|
||||
│ ├── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
| └── pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
├── scheduler
|
||||
│ └── scheduler_config.json
|
||||
├── text_encoder
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ └── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
| ├── model.fp16.safetensors
|
||||
│ ├── model.safetensors
|
||||
│ |── pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
| └── pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
├── tokenizer
|
||||
│ ├── merges.txt
|
||||
│ ├── special_tokens_map.json
|
||||
@@ -402,9 +409,17 @@ Compare the components of the pipeline instance to the [`runwayml/stable-diffusi
|
||||
├── unet
|
||||
│ ├── config.json
|
||||
│ ├── diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
└── vae
|
||||
├── config.json
|
||||
├── diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
| |── diffusion_pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
│ |── diffusion_pytorch_model.f16.safetensors
|
||||
│ |── diffusion_pytorch_model.non_ema.bin
|
||||
│ |── diffusion_pytorch_model.non_ema.safetensors
|
||||
│ └── diffusion_pytorch_model.safetensors
|
||||
|── vae
|
||||
. ├── config.json
|
||||
. ├── diffusion_pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
├── diffusion_pytorch_model.fp16.bin
|
||||
├── diffusion_pytorch_model.fp16.safetensors
|
||||
└── diffusion_pytorch_model.safetensors
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can access each of the components of the pipeline as an attribute to view its configuration:
|
||||
@@ -424,10 +439,11 @@ CLIPTokenizer(
|
||||
"unk_token": AddedToken("<|endoftext|>", rstrip=False, lstrip=False, single_word=False, normalized=True),
|
||||
"pad_token": "<|endoftext|>",
|
||||
},
|
||||
clean_up_tokenization_spaces=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Every pipeline expects a `model_index.json` file that tells the [`DiffusionPipeline`]:
|
||||
Every pipeline expects a [`model_index.json`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/blob/main/model_index.json) file that tells the [`DiffusionPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
- which pipeline class to load from `_class_name`
|
||||
- which version of 🧨 Diffusers was used to create the model in `_diffusers_version`
|
||||
|
||||
309
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/loading_adapters.md
Normal file
309
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/loading_adapters.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,309 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Load adapters
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
There are several [training](../training/overview) techniques for personalizing diffusion models to generate images of a specific subject or images in certain styles. Each of these training methods produces a different type of adapter. Some of the adapters generate an entirely new model, while other adapters only modify a smaller set of embeddings or weights. This means the loading process for each adapter is also different.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to load DreamBooth, textual inversion, and LoRA weights.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to browse the [Stable Diffusion Conceptualizer](https://huggingface.co/spaces/sd-concepts-library/stable-diffusion-conceptualizer), [LoRA the Explorer](https://huggingface.co/spaces/multimodalart/LoraTheExplorer), and the [Diffusers Models Gallery](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-projects/diffusers-gallery) for checkpoints and embeddings to use.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## DreamBooth
|
||||
|
||||
[DreamBooth](https://dreambooth.github.io/) finetunes an *entire diffusion model* on just several images of a subject to generate images of that subject in new styles and settings. This method works by using a special word in the prompt that the model learns to associate with the subject image. Of all the training methods, DreamBooth produces the largest file size (usually a few GBs) because it is a full checkpoint model.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's load the [herge_style](https://huggingface.co/sd-dreambooth-library/herge-style) checkpoint, which is trained on just 10 images drawn by Hergé, to generate images in that style. For it to work, you need to include the special word `herge_style` in your prompt to trigger the checkpoint:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("sd-dreambooth-library/herge-style", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
prompt = "A cute herge_style brown bear eating a slice of pizza, stunning color scheme, masterpiece, illustration"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/load_dreambooth.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Textual inversion
|
||||
|
||||
[Textual inversion](https://textual-inversion.github.io/) is very similar to DreamBooth and it can also personalize a diffusion model to generate certain concepts (styles, objects) from just a few images. This method works by training and finding new embeddings that represent the images you provide with a special word in the prompt. As a result, the diffusion model weights stay the same and the training process produces a relatively tiny (a few KBs) file.
|
||||
|
||||
Because textual inversion creates embeddings, it cannot be used on its own like DreamBooth and requires another model.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can load the textual inversion embeddings with the [`~loaders.TextualInversionLoaderMixin.load_textual_inversion`] method and generate some images. Let's load the [sd-concepts-library/gta5-artwork](https://huggingface.co/sd-concepts-library/gta5-artwork) embeddings and you'll need to include the special word `<gta5-artwork>` in your prompt to trigger it:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.load_textual_inversion("sd-concepts-library/gta5-artwork")
|
||||
prompt = "A cute brown bear eating a slice of pizza, stunning color scheme, masterpiece, illustration, <gta5-artwork> style"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/load_txt_embed.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Textual inversion can also be trained on undesirable things to create *negative embeddings* to discourage a model from generating images with those undesirable things like blurry images or extra fingers on a hand. This can be an easy way to quickly improve your prompt. You'll also load the embeddings with [`~loaders.TextualInversionLoaderMixin.load_textual_inversion`], but this time, you'll need two more parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
- `weight_name`: specifies the weight file to load if the file was saved in the 🤗 Diffusers format with a specific name or if the file is stored in the A1111 format
|
||||
- `token`: specifies the special word to use in the prompt to trigger the embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
Let's load the [sayakpaul/EasyNegative-test](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/EasyNegative-test) embeddings:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.load_textual_inversion(
|
||||
"sayakpaul/EasyNegative-test", weight_name="EasyNegative.safetensors", token="EasyNegative"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use the `token` to generate an image with the negative embeddings:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A cute brown bear eating a slice of pizza, stunning color scheme, masterpiece, illustration, EasyNegative"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "EasyNegative"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, num_inference_steps=50).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/load_neg_embed.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
[Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA)](https://huggingface.co/papers/2106.09685) is a popular training technique because it is fast and generates smaller file sizes (a couple hundred MBs). Like the other methods in this guide, LoRA can train a model to learn new styles from just a few images. It works by inserting new weights into the diffusion model and then only the new weights are trained instead of the entire model. This makes LoRAs faster to train and easier to store.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
LoRA is a very general training technique that can be used with other training methods. For example, it is common to train a model with DreamBooth and LoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
LoRAs also need to be used with another model:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then use the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method to load the [ostris/super-cereal-sdxl-lora](https://huggingface.co/ostris/super-cereal-sdxl-lora) weights and specify the weights filename from the repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights("ostris/super-cereal-sdxl-lora", weight_name="cereal_box_sdxl_v1.safetensors")
|
||||
prompt = "bears, pizza bites"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/load_lora.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method loads LoRA weights into both the UNet and text encoder. It is the preferred way for loading LoRAs because it can handle cases where:
|
||||
|
||||
- the LoRA weights don't have separate identifiers for the UNet and text encoder
|
||||
- the LoRA weights have separate identifiers for the UNet and text encoder
|
||||
|
||||
But if you only need to load LoRA weights into the UNet, then you can use the [`~loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.load_attn_procs`] method. Let's load the [jbilcke-hf/sdxl-cinematic-1](https://huggingface.co/jbilcke-hf/sdxl-cinematic-1) LoRA:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.unet.load_attn_procs("jbilcke-hf/sdxl-cinematic-1", weight_name="pytorch_lora_weights.safetensors")
|
||||
|
||||
# use cnmt in the prompt to trigger the LoRA
|
||||
prompt = "A cute cnmt eating a slice of pizza, stunning color scheme, masterpiece, illustration"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/load_attn_proc.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For both [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] and [`~loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.load_attn_procs`], you can pass the `cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 0.5}` parameter to adjust how much of the LoRA weights to use. A value of `0` is the same as only using the base model weights, and a value of `1` is equivalent to using the fully finetuned LoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To unload the LoRA weights, use the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.unload_lora_weights`] method to discard the LoRA weights and restore the model to its original weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.unload_lora_weights()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Load multiple LoRAs
|
||||
|
||||
It can be fun to use multiple LoRAs together to create something entirely new and unique. The [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.fuse_lora`] method allows you to fuse the LoRA weights with the original weights of the underlying model.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Fusing the weights can lead to a speedup in inference latency because you don't need to separately load the base model and LoRA! You can save your fused pipeline with [`~DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`] to avoid loading and fusing the weights every time you want to use the model.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Load an initial model:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline, AutoencoderKL
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained("madebyollin/sdxl-vae-fp16-fix", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
vae=vae,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, load the LoRA checkpoint and fuse it with the original weights. The `lora_scale` parameter controls how much to scale the output by with the LoRA weights. It is important to make the `lora_scale` adjustments in the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.fuse_lora`] method because it won't work if you try to pass `scale` to the `cross_attention_kwargs` in the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to reset the original model weights for any reason (use a different `lora_scale`), you should use the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.unfuse_lora`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights("ostris/ikea-instructions-lora-sdxl")
|
||||
pipeline.fuse_lora(lora_scale=0.7)
|
||||
|
||||
# to unfuse the LoRA weights
|
||||
pipeline.unfuse_lora()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then fuse this pipeline with the next set of LoRA weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights("ostris/super-cereal-sdxl-lora")
|
||||
pipeline.fuse_lora(lora_scale=0.7)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
You can't unfuse multiple LoRA checkpoints, so if you need to reset the model to its original weights, you'll need to reload it.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can generate an image that uses the weights from both LoRAs:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A cute brown bear eating a slice of pizza, stunning color scheme, masterpiece, illustration"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 🤗 PEFT
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Read the [Inference with 🤗 PEFT](../tutorials/using_peft_for_inference) tutorial to learn more about its integration with 🤗 Diffusers and how you can easily work with and juggle multiple adapters. You'll need to install 🤗 Diffusers and PEFT from source to run the example in this section.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Another way you can load and use multiple LoRAs is to specify the `adapter_name` parameter in [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`]. This method takes advantage of the 🤗 PEFT integration. For example, load and name both LoRA weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights("ostris/ikea-instructions-lora-sdxl", weight_name="ikea_instructions_xl_v1_5.safetensors", adapter_name="ikea")
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights("ostris/super-cereal-sdxl-lora", weight_name="cereal_box_sdxl_v1.safetensors", adapter_name="cereal")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now use the [`~loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.set_adapters`] to activate both LoRAs, and you can configure how much weight each LoRA should have on the output:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.set_adapters(["ikea", "cereal"], adapter_weights=[0.7, 0.5])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, generate an image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A cute brown bear eating a slice of pizza, stunning color scheme, masterpiece, illustration"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=30, cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 1.0}).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Kohya and TheLastBen
|
||||
|
||||
Other popular LoRA trainers from the community include those by [Kohya](https://github.com/kohya-ss/sd-scripts/) and [TheLastBen](https://github.com/TheLastBen/fast-stable-diffusion). These trainers create different LoRA checkpoints than those trained by 🤗 Diffusers, but they can still be loaded in the same way.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's download the [Blueprintify SD XL 1.0](https://civitai.com/models/150986/blueprintify-sd-xl-10) checkpoint from [Civitai](https://civitai.com/):
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
!wget https://civitai.com/api/download/models/168776 -O blueprintify-sd-xl-10.safetensors
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Load the LoRA checkpoint with the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method, and specify the filename in the `weight_name` parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights("path/to/weights", weight_name="blueprintify-sd-xl-10.safetensors")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generate an image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# use bl3uprint in the prompt to trigger the LoRA
|
||||
prompt = "bl3uprint, a highly detailed blueprint of the eiffel tower, explaining how to build all parts, many txt, blueprint grid backdrop"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Some limitations of using Kohya LoRAs with 🤗 Diffusers include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Images may not look like those generated by UIs - like ComfyUI - for multiple reasons, which are explained [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/4287/#issuecomment-1655110736).
|
||||
- [LyCORIS checkpoints](https://github.com/KohakuBlueleaf/LyCORIS) aren't fully supported. The [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method loads LyCORIS checkpoints with LoRA and LoCon modules, but Hada and LoKR are not supported.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Loading a checkpoint from TheLastBen is very similar. For example, to load the [TheLastBen/William_Eggleston_Style_SDXL](https://huggingface.co/TheLastBen/William_Eggleston_Style_SDXL) checkpoint:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights("TheLastBen/William_Eggleston_Style_SDXL", weight_name="wegg.safetensors")
|
||||
|
||||
# use by william eggleston in the prompt to trigger the LoRA
|
||||
prompt = "a house by william eggleston, sunrays, beautiful, sunlight, sunrays, beautiful"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt=prompt).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -14,4 +14,4 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusers offers many pipelines, models, and schedulers for generative tasks. To make loading these components as simple as possible, we provide a single and unified method - `from_pretrained()` - that loads any of these components from either the Hugging Face [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads) or your local machine. Whenever you load a pipeline or model, the latest files are automatically downloaded and cached so you can quickly reuse them next time without redownloading the files.
|
||||
|
||||
This section will show you everything you need to know about loading pipelines, how to load different components in a pipeline, how to load checkpoint variants, and how to load community pipelines. You'll also learn how to load schedulers and compare the speed and quality trade-offs of using different schedulers. Finally, you'll see how to convert and load KerasCV checkpoints so you can use them in PyTorch with 🧨 Diffusers.
|
||||
This section will show you everything you need to know about loading pipelines, how to load different components in a pipeline, how to load checkpoint variants, and how to load community pipelines. You'll also learn how to load schedulers and compare the speed and quality trade-offs of using different schedulers. Finally, you'll see how to convert and load KerasCV checkpoints so you can use them in PyTorch with 🧨 Diffusers.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion models are available in different formats depending on the framework they're trained and saved with, and where you download them from. Converting these formats for use in 🤗 Diffusers allows you to use all the features supported by the library, such as [using different schedulers](schedulers) for inference, [building your custom pipeline](write_own_pipeline), and a variety of techniques and methods for [optimizing inference speed](./optimization/opt_overview).
|
||||
Stable Diffusion models are available in different formats depending on the framework they're trained and saved with, and where you download them from. Converting these formats for use in 🤗 Diffusers allows you to use all the features supported by the library, such as [using different schedulers](schedulers) for inference, [building your custom pipeline](write_own_pipeline), and a variety of techniques and methods for [optimizing inference speed](../optimization/opt_overview).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ This guide will show you how to convert other Stable Diffusion formats to be com
|
||||
|
||||
The checkpoint - or `.ckpt` - format is commonly used to store and save models. The `.ckpt` file contains the entire model and is typically several GBs in size. While you can load and use a `.ckpt` file directly with the [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.from_single_file`] method, it is generally better to convert the `.ckpt` file to 🤗 Diffusers so both formats are available.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two options for converting a `.ckpt` file; use a Space to convert the checkpoint or convert the `.ckpt` file with a script.
|
||||
There are two options for converting a `.ckpt` file: use a Space to convert the checkpoint or convert the `.ckpt` file with a script.
|
||||
|
||||
### Convert with a Space
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can generate an image like:
|
||||
Then, you can generate an image like:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -136,53 +136,41 @@ image = pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=50).images[0]
|
||||
[Automatic1111](https://github.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui) (A1111) is a popular web UI for Stable Diffusion that supports model sharing platforms like [Civitai](https://civitai.com/). Models trained with the Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) technique are especially popular because they're fast to train and have a much smaller file size than a fully finetuned model. 🤗 Diffusers supports loading A1111 LoRA checkpoints with [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, UniPCMultistepScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"andite/anything-v4.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, safety_checker=None
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"Lykon/dreamshaper-xl-1-0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16"
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler = UniPCMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Download a LoRA checkpoint from Civitai; this example uses the [Howls Moving Castle,Interior/Scenery LoRA (Ghibli Stlye)](https://civitai.com/models/14605?modelVersionId=19998) checkpoint, but feel free to try out any LoRA checkpoint!
|
||||
Download a LoRA checkpoint from Civitai; this example uses the [Blueprintify SD XL 1.0](https://civitai.com/models/150986/blueprintify-sd-xl-10) checkpoint, but feel free to try out any LoRA checkpoint!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# uncomment to download the safetensor weights
|
||||
#!wget https://civitai.com/api/download/models/19998 -O howls_moving_castle.safetensors
|
||||
#!wget https://civitai.com/api/download/models/168776 -O blueprintify.safetensors
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Load the LoRA checkpoint into the pipeline with the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights(".", weight_name="howls_moving_castle.safetensors")
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights(".", weight_name="blueprintify.safetensors")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use the pipeline to generate images:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "masterpiece, illustration, ultra-detailed, cityscape, san francisco, golden gate bridge, california, bay area, in the snow, beautiful detailed starry sky"
|
||||
prompt = "bl3uprint, a highly detailed blueprint of the empire state building, explaining how to build all parts, many txt, blueprint grid backdrop"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "lowres, cropped, worst quality, low quality, normal quality, artifacts, signature, watermark, username, blurry, more than one bridge, bad architecture"
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(
|
||||
image = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
|
||||
width=512,
|
||||
height=512,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt=4,
|
||||
generator=torch.manual_seed(0),
|
||||
).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Display the images:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, 2, 2)
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/a1111-lora-sf.png"/>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/blueprint-lora.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,4 +14,4 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
A pipeline is an end-to-end class that provides a quick and easy way to use a diffusion system for inference by bundling independently trained models and schedulers together. Certain combinations of models and schedulers define specific pipeline types, like [`StableDiffusionXLPipeline`] or [`StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline`], with specific capabilities. All pipeline types inherit from the base [`DiffusionPipeline`] class; pass it any checkpoint, and it'll automatically detect the pipeline type and load the necessary components.
|
||||
|
||||
This section introduces you to some of the more complex pipelines like Stable Diffusion XL, ControlNet, and DiffEdit, which require additional inputs. You'll also learn how to use a distilled version of the Stable Diffusion model to speed up inference, how to control randomness on your hardware when generating images, and how to create a community pipeline for a custom task like generating images from speech.
|
||||
This section demonstrates how to use specific pipelines such as Stable Diffusion XL, ControlNet, and DiffEdit. You'll also learn how to use a distilled version of the Stable Diffusion model to speed up inference, how to create reproducible pipelines, and how to use and contribute community pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Push files to the Hub
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +32,7 @@ notebook_login()
|
||||
|
||||
## Models
|
||||
|
||||
To push a model to the Hub, call [`~diffusers.utils.PushToHubMixin.push_to_hub`] and specfiy the repository id of the model to be stored on the Hub:
|
||||
To push a model to the Hub, call [`~diffusers.utils.PushToHubMixin.push_to_hub`] and specify the repository id of the model to be stored on the Hub:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import ControlNetModel
|
||||
@@ -36,7 +48,7 @@ controlnet = ControlNetModel(
|
||||
controlnet.push_to_hub("my-controlnet-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For model's, you can also specify the [*variant*](loading#checkpoint-variants) of the weights to push to the Hub. For example, to push `fp16` weights:
|
||||
For models, you can also specify the [*variant*](loading#checkpoint-variants) of the weights to push to the Hub. For example, to push `fp16` weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
controlnet.push_to_hub("my-controlnet-model", variant="fp16")
|
||||
@@ -52,7 +64,7 @@ model = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained("your-namespace/my-controlnet-model")
|
||||
|
||||
## Scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
To push a scheduler to the Hub, call [`~diffusers.utils.PushToHubMixin.push_to_hub`] and specfiy the repository id of the scheduler to be stored on the Hub:
|
||||
To push a scheduler to the Hub, call [`~diffusers.utils.PushToHubMixin.push_to_hub`] and specify the repository id of the scheduler to be stored on the Hub:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DDIMScheduler
|
||||
@@ -159,13 +171,13 @@ pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("your-namespace/my-pipeline")
|
||||
Set `private=True` in the [`~diffusers.utils.PushToHubMixin.push_to_hub`] function to keep your model, scheduler, or pipeline files private:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
controlnet.push_to_hub("my-controlnet-model", private=True)
|
||||
controlnet.push_to_hub("my-controlnet-model-private", private=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Private repositories are only visible to you, and other users won't be able to clone the repository and your repository won't appear in search results. Even if a user has the URL to your private repository, they'll receive a `404 - Repo not found error.`
|
||||
Private repositories are only visible to you, and other users won't be able to clone the repository and your repository won't appear in search results. Even if a user has the URL to your private repository, they'll receive a `404 - Sorry, we can't find the page you are looking for.`
|
||||
|
||||
To load a model, scheduler, or pipeline from a private or gated repositories, set `use_auth_token=True`:
|
||||
To load a model, scheduler, or pipeline from private or gated repositories, set `use_auth_token=True`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model = ControlNet.from_pretrained("your-namespace/my-controlnet-model", use_auth_token=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
model = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained("your-namespace/my-controlnet-model-private", use_auth_token=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
A common way to improve the quality of generated images is with *deterministic batch generation*, generate a batch of images and select one image to improve with a more detailed prompt in a second round of inference. The key is to pass a list of [`torch.Generator`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html#generator)'s to the pipeline for batched image generation, and tie each `Generator` to a seed so you can reuse it for an image.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's use [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) for example, and generate several versions of the following prompt:
|
||||
Let's use [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) for example, and generate several versions of the following prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "Labrador in the style of Vermeer"
|
||||
@@ -25,27 +25,27 @@ prompt = "Labrador in the style of Vermeer"
|
||||
Instantiate a pipeline with [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] and place it on a GPU (if available):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, define four different `Generator`'s and assign each `Generator` a seed (`0` to `3`) so you can reuse a `Generator` later for a specific image:
|
||||
Now, define four different `Generator`s and assign each `Generator` a seed (`0` to `3`) so you can reuse a `Generator` later for a specific image:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> generator = [torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(i) for i in range(4)]
|
||||
generator = [torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(i) for i in range(4)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generate the images and have a look:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> images = pipe(prompt, generator=generator, num_images_per_prompt=4).images
|
||||
>>> images
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt, generator=generator, num_images_per_prompt=4).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -60,8 +60,8 @@ generator = [torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(0) for i in range(4)]
|
||||
Create four generators with seed `0`, and generate another batch of images, all of which should look like the first image from the previous round!
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> images = pipe(prompt, generator=generator).images
|
||||
>>> images
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt, generator=generator).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@@ -15,13 +15,13 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusion pipelines are inherently a collection of diffusion models and schedulers that are partly independent from each other. This means that one is able to switch out parts of the pipeline to better customize
|
||||
a pipeline to one's use case. The best example of this is the [Schedulers](../api/schedulers/overview.md).
|
||||
a pipeline to one's use case. The best example of this is the [Schedulers](../api/schedulers/overview).
|
||||
|
||||
Whereas diffusion models usually simply define the forward pass from noise to a less noisy sample,
|
||||
schedulers define the whole denoising process, *i.e.*:
|
||||
- How many denoising steps?
|
||||
- Stochastic or deterministic?
|
||||
- What algorithm to use to find the denoised sample
|
||||
- What algorithm to use to find the denoised sample?
|
||||
|
||||
They can be quite complex and often define a trade-off between **denoising speed** and **denoising quality**.
|
||||
It is extremely difficult to measure quantitatively which scheduler works best for a given diffusion pipeline, so it is often recommended to simply try out which works best.
|
||||
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ pipeline.scheduler
|
||||
```
|
||||
PNDMScheduler {
|
||||
"_class_name": "PNDMScheduler",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.8.0.dev0",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.21.4",
|
||||
"beta_end": 0.012,
|
||||
"beta_schedule": "scaled_linear",
|
||||
"beta_start": 0.00085,
|
||||
@@ -72,6 +72,7 @@ PNDMScheduler {
|
||||
"set_alpha_to_one": false,
|
||||
"skip_prk_steps": true,
|
||||
"steps_offset": 1,
|
||||
"timestep_spacing": "leading",
|
||||
"trained_betas": null
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -101,7 +102,7 @@ image
|
||||
|
||||
## Changing the scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
Now we show how easy it is to change the scheduler of a pipeline. Every scheduler has a property [`SchedulerMixin.compatibles`]
|
||||
Now we show how easy it is to change the scheduler of a pipeline. Every scheduler has a property [`~SchedulerMixin.compatibles`]
|
||||
which defines all compatible schedulers. You can take a look at all available, compatible schedulers for the Stable Diffusion pipeline as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@@ -110,27 +111,40 @@ pipeline.scheduler.compatibles
|
||||
|
||||
**Output**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_lms_discrete.LMSDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddim.DDIMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_multistep.DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
[diffusers.utils.dummy_torch_and_torchsde_objects.DPMSolverSDEScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_discrete.EulerDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_pndm.PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_lms_discrete.LMSDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddim.DDIMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddpm.DDPMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_ancestral_discrete.EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler]
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_heun_discrete.HeunDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_multistep.DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_deis_multistep.DEISMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_pndm.PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_ancestral_discrete.EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_unipc_multistep.UniPCMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_k_dpm_2_discrete.KDPM2DiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_singlestep.DPMSolverSinglestepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_k_dpm_2_ancestral_discrete.KDPM2AncestralDiscreteScheduler]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Cool, lots of schedulers to look at. Feel free to have a look at their respective class definitions:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`LMSDiscreteScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`DDIMScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`PNDMScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`DDPMScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler`].
|
||||
- [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`LMSDiscreteScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`DDIMScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`DDPMScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`HeunDiscreteScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`DEISMultistepScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`PNDMScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`UniPCMultistepScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`KDPM2DiscreteScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`DPMSolverSinglestepScheduler`],
|
||||
- [`KDPM2AncestralDiscreteScheduler`].
|
||||
|
||||
We will now compare the input prompt with all other schedulers. To change the scheduler of the pipeline you can make use of the
|
||||
convenient [`ConfigMixin.config`] property in combination with the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`] function.
|
||||
convenient [`~ConfigMixin.config`] property in combination with the [`~ConfigMixin.from_config`] function.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler.config
|
||||
@@ -139,7 +153,7 @@ pipeline.scheduler.config
|
||||
returns a dictionary of the configuration of the scheduler:
|
||||
|
||||
**Output**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
```py
|
||||
FrozenDict([('num_train_timesteps', 1000),
|
||||
('beta_start', 0.00085),
|
||||
('beta_end', 0.012),
|
||||
@@ -147,9 +161,12 @@ FrozenDict([('num_train_timesteps', 1000),
|
||||
('trained_betas', None),
|
||||
('skip_prk_steps', True),
|
||||
('set_alpha_to_one', False),
|
||||
('prediction_type', 'epsilon'),
|
||||
('timestep_spacing', 'leading'),
|
||||
('steps_offset', 1),
|
||||
('_use_default_values', ['timestep_spacing', 'prediction_type']),
|
||||
('_class_name', 'PNDMScheduler'),
|
||||
('_diffusers_version', '0.8.0.dev0'),
|
||||
('_diffusers_version', '0.21.4'),
|
||||
('clip_sample', False)])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -182,7 +199,7 @@ If you are a JAX/Flax user, please check [this section](#changing-the-scheduler-
|
||||
## Compare schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
So far we have tried running the stable diffusion pipeline with two schedulers: [`PNDMScheduler`] and [`DDIMScheduler`].
|
||||
A number of better schedulers have been released that can be run with much fewer steps, let's compare them here:
|
||||
A number of better schedulers have been released that can be run with much fewer steps; let's compare them here:
|
||||
|
||||
[`LMSDiscreteScheduler`] usually leads to better results:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -241,8 +258,7 @@ image
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
At the time of writing this doc [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`] gives arguably the best speed/quality trade-off and can be run with as little
|
||||
as 20 steps.
|
||||
[`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`] gives a reasonable speed/quality trade-off and can be run with as little as 20 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
@@ -260,12 +276,12 @@ image
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see most images look very similar and are arguably of very similar quality. It often really depends on the specific use case which scheduler to choose. A good approach is always to run multiple different
|
||||
As you can see, most images look very similar and are arguably of very similar quality. It often really depends on the specific use case which scheduler to choose. A good approach is always to run multiple different
|
||||
schedulers to compare results.
|
||||
|
||||
## Changing the Scheduler in Flax
|
||||
|
||||
If you are a JAX/Flax user, you can also change the default pipeline scheduler. This is a complete example of how to run inference using the Flax Stable Diffusion pipeline and the super-fast [DDPM-Solver++ scheduler](../api/schedulers/multistep_dpm_solver):
|
||||
If you are a JAX/Flax user, you can also change the default pipeline scheduler. This is a complete example of how to run inference using the Flax Stable Diffusion pipeline and the super-fast [DPM-Solver++ scheduler](../api/schedulers/multistep_dpm_solver):
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import jax
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Shap-E
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# JAX/Flax
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,31 +1,29 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Textual inversion
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
The [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] supports textual inversion, a technique that enables a model like Stable Diffusion to learn a new concept from just a few sample images. This gives you more control over the generated images and allows you to tailor the model towards specific concepts. You can get started quickly with a collection of community created concepts in the [Stable Diffusion Conceptualizer](https://huggingface.co/spaces/sd-concepts-library/stable-diffusion-conceptualizer).
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to run inference with textual inversion using a pre-learned concept from the Stable Diffusion Conceptualizer. If you're interested in teaching a model new concepts with textual inversion, take a look at the [Textual Inversion](./training/text_inversion) training guide.
|
||||
|
||||
Login to your Hugging Face account:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
notebook_login()
|
||||
```
|
||||
This guide will show you how to run inference with textual inversion using a pre-learned concept from the Stable Diffusion Conceptualizer. If you're interested in teaching a model new concepts with textual inversion, take a look at the [Textual Inversion](../training/text_inversion) training guide.
|
||||
|
||||
Import the necessary libraries:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPFeatureExtractor, CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion 1 and 2
|
||||
@@ -52,7 +50,7 @@ Create a prompt with the pre-learned concept by using the special placeholder to
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "a grafitti in a favela wall with a <cat-toy> on it"
|
||||
|
||||
num_samples = 2
|
||||
num_samples_per_row = 2
|
||||
num_rows = 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -61,10 +59,10 @@ Then run the pipeline (feel free to adjust the parameters like `num_inference_st
|
||||
```py
|
||||
all_images = []
|
||||
for _ in range(num_rows):
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt, num_images_per_prompt=num_samples, num_inference_steps=50, guidance_scale=7.5).images
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt, num_images_per_prompt=num_samples_per_row, num_inference_steps=50, guidance_scale=7.5).images
|
||||
all_images.extend(images)
|
||||
|
||||
grid = make_image_grid(all_images, num_samples, num_rows)
|
||||
grid = make_image_grid(all_images, num_rows, num_samples_per_row)
|
||||
grid
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -72,7 +70,6 @@ grid
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/textual_inversion_inference.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL) can also use textual inversion vectors for inference. In contrast to Stable Diffusion 1 and 2, SDXL has two text encoders so you'll need two textual inversion embeddings - one for each text encoder model.
|
||||
@@ -97,9 +94,9 @@ state_dict
|
||||
[ 0.0475, -0.0508, -0.0145, ..., 0.0070, -0.0089, -0.0163]],
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are two tensors, `"clip-g"` and `"clip-l"`.
|
||||
`"clip-g"` corresponds to the bigger text encoder in SDXL and refers to
|
||||
`pipe.text_encoder_2` and `"clip-l"` refers to `pipe.text_encoder`.
|
||||
There are two tensors, `"clip_g"` and `"clip_l"`.
|
||||
`"clip_g"` corresponds to the bigger text encoder in SDXL and refers to
|
||||
`pipe.text_encoder_2` and `"clip_l"` refers to `pipe.text_encoder`.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can load each tensor separately by passing them along with the correct text encoder and tokenizer
|
||||
to [`~loaders.TextualInversionLoaderMixin.load_textual_inversion`]:
|
||||
@@ -117,4 +114,5 @@ pipe.load_textual_inversion(state_dict["clip_l"], token="unaestheticXLv31", text
|
||||
# the embedding should be used as a negative embedding, so we pass it as a negative prompt
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator().manual_seed(33)
|
||||
image = pipe("a woman standing in front of a mountain", negative_prompt="unaestheticXLv31", generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,15 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Load safetensors
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
@@ -55,11 +67,11 @@ There are several reasons for using safetensors:
|
||||
The time it takes to load the entire pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
"Loaded in safetensors 0:00:02.033658"
|
||||
"Loaded in PyTorch 0:00:02.663379"
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
"Loaded in safetensors 0:00:02.033658"
|
||||
"Loaded in PyTorch 0:00:02.663379"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
But the actual time it takes to load 500MB of the model weights is only:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,6 +41,7 @@ import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = UniPCMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a red cat playing with a ball"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -165,7 +166,9 @@ import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from compel import Compel, DiffusersTextualInversionManager
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True, variant="fp16").to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True, variant="fp16").to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe.load_textual_inversion("sd-concepts-library/midjourney-style")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -173,7 +176,7 @@ Compel provides a `DiffusersTextualInversionManager` class to simplify prompt we
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
textual_inversion_manager = DiffusersTextualInversionManager(pipe)
|
||||
compel = Compel(
|
||||
compel_proc = Compel(
|
||||
tokenizer=pipe.tokenizer,
|
||||
text_encoder=pipe.text_encoder,
|
||||
textual_inversion_manager=textual_inversion_manager)
|
||||
@@ -225,6 +228,8 @@ Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL) has two tokenizers and text encoders so it's usage is
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from compel import Compel, ReturnedEmbeddingsType
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
@@ -251,6 +256,7 @@ conditioning, pooled = compel(prompt)
|
||||
# generate image
|
||||
generator = [torch.Generator().manual_seed(33) for _ in range(len(prompt))]
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt_embeds=conditioning, pooled_prompt_embeds=pooled, generator=generator, num_inference_steps=30).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
@@ -262,4 +268,4 @@ images = pipeline(prompt_embeds=conditioning, pooled_prompt_embeds=pooled, gener
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/compel/sdxl_ball2.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">"a red cat playing with a (ball)0.6"</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -290,5 +290,5 @@ This is really what 🧨 Diffusers is designed for: to make it intuitive and eas
|
||||
|
||||
For your next steps, feel free to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Learn how to [build and contribute a pipeline](contribute_pipeline) to 🧨 Diffusers. We can't wait and see what you'll come up with!
|
||||
* Learn how to [build and contribute a pipeline](../using-diffusers/contribute_pipeline) to 🧨 Diffusers. We can't wait and see what you'll come up with!
|
||||
* Explore [existing pipelines](../api/pipelines/overview) in the library, and see if you can deconstruct and build a pipeline from scratch using the models and schedulers separately.
|
||||
|
||||
10
docs/source/ja/_toctree.yml
Normal file
10
docs/source/ja/_toctree.yml
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: index
|
||||
title: 🧨 Diffusers
|
||||
- local: quicktour
|
||||
title: 簡単な案内
|
||||
- local: stable_diffusion
|
||||
title: 効果的で効率的な拡散モデル
|
||||
- local: installation
|
||||
title: インストール
|
||||
title: はじめに
|
||||
98
docs/source/ja/index.md
Normal file
98
docs/source/ja/index.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/huggingface/diffusers/77aadfee6a891ab9fcfb780f87c693f7a5beeb8e/docs/source/imgs/diffusers_library.jpg" width="400"/>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
# Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers は、画像や音声、さらには分子の3D構造を生成するための、最先端の事前学習済みDiffusion Model(拡散モデル)を提供するライブラリです。シンプルな生成ソリューションをお探しの場合でも、独自の拡散モデルをトレーニングしたい場合でも、🤗 Diffusers はその両方をサポートするモジュール式のツールボックスです。我々のライブラリは、[性能より使いやすさ](conceptual/philosophy#usability-over-performance)、[簡単よりシンプル](conceptual/philosophy#simple-over-easy)、[抽象化よりカスタマイズ性](conceptual/philosophy#tweakable-contributorfriendly-over-abstraction)に重点を置いて設計されています。
|
||||
|
||||
このライブラリには3つの主要コンポーネントがあります:
|
||||
|
||||
- 最先端の[拡散パイプライン](api/pipelines/overview)で数行のコードで生成が可能です。
|
||||
- 交換可能な[ノイズスケジューラ](api/schedulers/overview)で生成速度と品質のトレードオフのバランスをとれます。
|
||||
- 事前に訓練された[モデル](api/models)は、ビルディングブロックとして使用することができ、スケジューラと組み合わせることで、独自のエンドツーエンドの拡散システムを作成することができます。
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="mt-10">
|
||||
<div class="w-full flex flex-col space-y-4 md:space-y-0 md:grid md:grid-cols-2 md:gap-y-4 md:gap-x-5">
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./tutorials/tutorial_overview"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-blue-400 to-blue-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">チュートリアル</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">出力の生成、独自の拡散システムの構築、拡散モデルのトレーニングを開始するために必要な基本的なスキルを学ぶことができます。初めて🤗Diffusersを使用する場合は、ここから始めることをお勧めします!</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./using-diffusers/loading_overview"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-indigo-400 to-indigo-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">ガイド</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">パイプライン、モデル、スケジューラのロードに役立つ実践的なガイドです。また、特定のタスクにパイプラインを使用する方法、出力の生成方法を制御する方法、生成速度を最適化する方法、さまざまなトレーニング手法についても学ぶことができます。</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./conceptual/philosophy"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-pink-400 to-pink-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Conceptual guides</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">ライブラリがなぜこのように設計されたのかを理解し、ライブラリを利用する際の倫理的ガイドラインや安全対策について詳しく学べます。</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./api/models/overview"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-purple-400 to-purple-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Reference</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">🤗 Diffusersのクラスとメソッドがどのように機能するかについての技術的な説明です。</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Paper/Repository | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [alt_diffusion](./api/pipelines/alt_diffusion) | [AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [audio_diffusion](./api/pipelines/audio_diffusion) | [Audio Diffusion](https://github.com/teticio/audio-diffusion.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [controlnet](./api/pipelines/controlnet) | [Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [cycle_diffusion](./api/pipelines/cycle_diffusion) | [Unifying Diffusion Models' Latent Space, with Applications to CycleDiffusion and Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.05559) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [dance_diffusion](./api/pipelines/dance_diffusion) | [Dance Diffusion](https://github.com/williamberman/diffusers.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [ddpm](./api/pipelines/ddpm) | [Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [ddim](./api/pipelines/ddim) | [Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [if](./if) | [**IF**](./api/pipelines/if) | Image Generation |
|
||||
| [if_img2img](./if) | [**IF**](./api/pipelines/if) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [if_inpainting](./if) | [**IF**](./api/pipelines/if) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion_uncond](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [paint_by_example](./api/pipelines/paint_by_example) | [Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13227) | Image-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [pndm](./api/pipelines/pndm) | [Pseudo Numerical Methods for Diffusion Models on Manifolds](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09778) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_ve](./api/pipelines/score_sde_ve) | [Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_vp](./api/pipelines/score_sde_vp) | [Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [semantic_stable_diffusion](./api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion) | [Semantic Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12247) | Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_adapter](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/adapter) | [**T2I-Adapter**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.08453) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation | -
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_text2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_img2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_inpaint](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/inpaint) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_panorama](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/panorama) | [MultiDiffusion](https://multidiffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Panorama Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix) | [InstructPix2Pix: Learning to Follow Image Editing Instructions](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09800) | Text-Guided Image Editing|
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix_zero](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero) | [Zero-shot Image-to-Image Translation](https://pix2pixzero.github.io/) | Text-Guided Image Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_attend_and_excite](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/attend_and_excite) | [Attend-and-Excite: Attention-Based Semantic Guidance for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13826) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_self_attention_guidance](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/self_attention_guidance) | [Improving Sample Quality of Diffusion Models Using Self-Attention Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.00939) | Text-to-Image Generation Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_image_variation](./stable_diffusion/image_variation) | [Stable Diffusion Image Variations](https://github.com/LambdaLabsML/lambda-diffusers#stable-diffusion-image-variations) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_latent_upscale](./stable_diffusion/latent_upscale) | [Stable Diffusion Latent Upscaler](https://twitter.com/StabilityAI/status/1590531958815064065) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_model_editing](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/model_editing) | [Editing Implicit Assumptions in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://time-diffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Image Model Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Depth-Conditional Stable Diffusion](https://github.com/Stability-AI/stablediffusion#depth-conditional-stable-diffusion) | Depth-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_safe](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe) | [Safe Stable Diffusion](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105) | Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | Stable unCLIP | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | Stable unCLIP | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stochastic_karras_ve](./api/pipelines/stochastic_karras_ve) | [Elucidating the Design Space of Diffusion-Based Generative Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00364) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [text_to_video_sd](./api/pipelines/text_to_video) | [Modelscope's Text-to-video-synthesis Model in Open Domain](https://modelscope.cn/models/damo/text-to-video-synthesis/summary) | Text-to-Video Generation |
|
||||
| [unclip](./api/pipelines/unclip) | [Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06125)(implementation by [kakaobrain](https://github.com/kakaobrain/karlo)) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Image Variations Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Dual Image and Text Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [vq_diffusion](./api/pipelines/vq_diffusion) | [Vector Quantized Diffusion Model for Text-to-Image Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.14822) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_ldm3d](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/ldm3d_diffusion) | [LDM3D: Latent Diffusion Model for 3D](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.10853) | Text to Image and Depth Generation |
|
||||
145
docs/source/ja/installation.md
Normal file
145
docs/source/ja/installation.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# インストール
|
||||
|
||||
お使いのディープラーニングライブラリに合わせてDiffusersをインストールできます。
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 DiffusersはPython 3.8+、PyTorch 1.7.0+、Flaxでテストされています。使用するディープラーニングライブラリの以下のインストール手順に従ってください:
|
||||
|
||||
- [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/)のインストール手順。
|
||||
- [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)のインストール手順。
|
||||
|
||||
## pip でインストール
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusersは[仮想環境](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html)の中でインストールすることが推奨されています。
|
||||
Python の仮想環境についてよく知らない場合は、こちらの [ガイド](https://packaging.python.org/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/) を参照してください。
|
||||
仮想環境は異なるプロジェクトの管理を容易にし、依存関係間の互換性の問題を回避します。
|
||||
|
||||
ではさっそく、プロジェクトディレクトリに仮想環境を作ってみます:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
仮想環境をアクティブにします:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers もまた 🤗 Transformers ライブラリに依存しており、以下のコマンドで両方をインストールできます:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install diffusers["torch"] transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install diffusers["flax"] transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## ソースからのインストール
|
||||
|
||||
ソースから🤗 Diffusersをインストールする前に、`torch`と🤗 Accelerateがインストールされていることを確認してください。
|
||||
|
||||
`torch`のインストールについては、`torch` [インストール](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally)ガイドを参照してください。
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Accelerateをインストールするには:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install accelerate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
以下のコマンドでソースから🤗 Diffusersをインストールできます:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
このコマンドは最新の `stable` バージョンではなく、最先端の `main` バージョンをインストールします。
|
||||
`main`バージョンは最新の開発に対応するのに便利です。
|
||||
例えば、前回の公式リリース以降にバグが修正されたが、新しいリリースがまだリリースされていない場合などには都合がいいです。
|
||||
しかし、これは `main` バージョンが常に安定しているとは限らないです。
|
||||
私たちは `main` バージョンを運用し続けるよう努力しており、ほとんどの問題は通常数時間から1日以内に解決されます。
|
||||
もし問題が発生した場合は、[Issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose) を開いてください!
|
||||
|
||||
## 編集可能なインストール
|
||||
|
||||
以下の場合、編集可能なインストールが必要です:
|
||||
|
||||
* ソースコードの `main` バージョンを使用する。
|
||||
* 🤗 Diffusers に貢献し、コードの変更をテストする必要がある場合。
|
||||
|
||||
リポジトリをクローンし、次のコマンドで 🤗 Diffusers をインストールしてください:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
cd diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -e ".[torch]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -e ".[flax]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
これらのコマンドは、リポジトリをクローンしたフォルダと Python のライブラリパスをリンクします。
|
||||
Python は通常のライブラリパスに加えて、クローンしたフォルダの中を探すようになります。
|
||||
例えば、Python パッケージが通常 `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.8/site-packages/` にインストールされている場合、Python はクローンした `~/diffusers/` フォルダも同様に参照します。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
ライブラリを使い続けたい場合は、`diffusers`フォルダを残しておく必要があります。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
これで、以下のコマンドで簡単にクローンを最新版の🤗 Diffusersにアップデートできます:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ~/diffusers/
|
||||
git pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python環境は次の実行時に `main` バージョンの🤗 Diffusersを見つけます。
|
||||
|
||||
## テレメトリー・ロギングに関するお知らせ
|
||||
|
||||
このライブラリは `from_pretrained()` リクエスト中にデータを収集します。
|
||||
このデータには Diffusers と PyTorch/Flax のバージョン、要求されたモデルやパイプラインクラスが含まれます。
|
||||
また、Hubでホストされている場合は、事前に学習されたチェックポイントへのパスが含まれます。
|
||||
この使用データは問題のデバッグや新機能の優先順位付けに役立ちます。
|
||||
テレメトリーはHuggingFace Hubからモデルやパイプラインをロードするときのみ送信されます。ローカルでの使用中は収集されません。
|
||||
|
||||
我々は、すべての人が追加情報を共有したくないことを理解し、あなたのプライバシーを尊重します。
|
||||
そのため、ターミナルから `DISABLE_TELEMETRY` 環境変数を設定することで、データ収集を無効にすることができます:
|
||||
|
||||
Linux/MacOSの場合
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export DISABLE_TELEMETRY=YES
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Windows の場合
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
set DISABLE_TELEMETRY=YES
|
||||
```
|
||||
316
docs/source/ja/quicktour.md
Normal file
316
docs/source/ja/quicktour.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,316 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
# 簡単な案内
|
||||
|
||||
拡散モデル(Diffusion Model)は、ランダムな正規分布から段階的にノイズ除去するように学習され、画像や音声などの目的のものを生成できます。これは生成AIに多大な関心を呼び起こしました。インターネット上で拡散によって生成された画像の例を見たことがあるでしょう。🧨 Diffusersは、誰もが拡散モデルに広くアクセスできるようにすることを目的としたライブラリです。
|
||||
|
||||
この案内では、開発者または日常的なユーザーに関わらず、🧨 Diffusers を紹介し、素早く目的のものを生成できるようにします!このライブラリには3つの主要コンポーネントがあります:
|
||||
|
||||
* [`DiffusionPipeline`]は事前に学習された拡散モデルからサンプルを迅速に生成するために設計された高レベルのエンドツーエンドクラス。
|
||||
* 拡散システムを作成するためのビルディングブロックとして使用できる、人気のある事前学習された[モデル](./api/models)アーキテクチャとモジュール。
|
||||
* 多くの異なる[スケジューラ](./api/schedulers/overview) - ノイズがどのようにトレーニングのために加えられるか、そして生成中にどのようにノイズ除去された画像を生成するかを制御するアルゴリズム。
|
||||
|
||||
この案内では、[`DiffusionPipeline`]を生成に使用する方法を紹介し、モデルとスケジューラを組み合わせて[`DiffusionPipeline`]の内部で起こっていることを再現する方法を説明します。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
この案内は🧨 Diffusers [ノートブック](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/diffusers_intro.ipynb)を簡略化したもので、すぐに使い始めることができます。Diffusers 🧨のゴール、設計哲学、コアAPIの詳細についてもっと知りたい方は、ノートブックをご覧ください!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
始める前に必要なライブラリーがすべてインストールされていることを確認してください:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# uncomment to install the necessary libraries in Colab
|
||||
#!pip install --upgrade diffusers accelerate transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- [🤗 Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index)生成とトレーニングのためのモデルのロードを高速化します
|
||||
- [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview)ような最も一般的な拡散モデルを実行するには、[🤗 Transformers](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index)が必要です。
|
||||
|
||||
## 拡散パイプライン
|
||||
|
||||
[`DiffusionPipeline`]は事前学習された拡散システムを生成に使用する最も簡単な方法です。これはモデルとスケジューラを含むエンドツーエンドのシステムです。[`DiffusionPipeline`]は多くの作業/タスクにすぐに使用することができます。また、サポートされているタスクの完全なリストについては[🧨Diffusersの概要](./api/pipelines/overview#diffusers-summary)の表を参照してください。
|
||||
|
||||
| **タスク** | **説明** | **パイプライン**
|
||||
|------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------|
|
||||
| Unconditional Image Generation | 正規分布から画像生成 | [unconditional_image_generation](./using-diffusers/unconditional_image_generation) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Image Generation | 文章から画像生成 | [conditional_image_generation](./using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Image-to-Image Translation | 画像と文章から新たな画像生成 | [img2img](./using-diffusers/img2img) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Image-Inpainting | 画像、マスク、および文章が指定された場合に、画像のマスクされた部分を文章をもとに修復 | [inpaint](./using-diffusers/inpaint) |
|
||||
| Text-Guided Depth-to-Image Translation | 文章と深度推定によって構造を保持しながら画像生成 | [depth2img](./using-diffusers/depth2img) |
|
||||
|
||||
まず、[`DiffusionPipeline`]のインスタンスを作成し、ダウンロードしたいパイプラインのチェックポイントを指定します。
|
||||
この[`DiffusionPipeline`]はHugging Face Hubに保存されている任意の[チェックポイント](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads)を使用することができます。
|
||||
この案内では、[`stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)チェックポイントでテキストから画像へ生成します。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
[Stable Diffusion]モデルについては、モデルを実行する前にまず[ライセンス](https://huggingface.co/spaces/CompVis/stable-diffusion-license)を注意深くお読みください。🧨 Diffusers は、攻撃的または有害なコンテンツを防ぐために [`safety_checker`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py) を実装していますが、モデルの改良された画像生成機能により、潜在的に有害なコンテンツが生成される可能性があります。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
モデルを[`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`]メソッドでロードします:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
[`DiffusionPipeline`]は全てのモデリング、トークン化、スケジューリングコンポーネントをダウンロードしてキャッシュします。Stable Diffusionパイプラインは[`UNet2DConditionModel`]と[`PNDMScheduler`]などで構成されています:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pipeline
|
||||
StableDiffusionPipeline {
|
||||
"_class_name": "StableDiffusionPipeline",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.13.1",
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"scheduler": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"PNDMScheduler"
|
||||
],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"unet": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"UNet2DConditionModel"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"vae": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
"AutoencoderKL"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
このモデルはおよそ14億個のパラメータで構成されているため、GPU上でパイプラインを実行することを強く推奨します。
|
||||
PyTorchと同じように、ジェネレータオブジェクトをGPUに移すことができます:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
これで、文章を `pipeline` に渡して画像を生成し、ノイズ除去された画像にアクセスできるようになりました。デフォルトでは、画像出力は[`PIL.Image`](https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/Image.html?highlight=image#the-image-class)オブジェクトでラップされます。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> image = pipeline("An image of a squirrel in Picasso style").images[0]
|
||||
>>> image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/image_of_squirrel_painting.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
`save`関数で画像を保存できます:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> image.save("image_of_squirrel_painting.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### ローカルパイプライン
|
||||
|
||||
ローカルでパイプラインを使用することもできます。唯一の違いは、最初にウェイトをダウンロードする必要があることです:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
!git lfs install
|
||||
!git clone https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存したウェイトをパイプラインにロードします:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
これで、上のセクションと同じようにパイプラインを動かすことができます。
|
||||
|
||||
### スケジューラの交換
|
||||
|
||||
スケジューラーによって、ノイズ除去のスピードや品質のトレードオフが異なります。どれが自分に最適かを知る最善の方法は、実際に試してみることです!Diffusers 🧨の主な機能の1つは、スケジューラを簡単に切り替えることができることです。例えば、デフォルトの[`PNDMScheduler`]を[`EulerDiscreteScheduler`]に置き換えるには、[`~diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config`]メソッドでロードできます:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import EulerDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
>>> pipeline.scheduler = EulerDiscreteScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
新しいスケジューラを使って画像を生成し、その違いに気づくかどうか試してみてください!
|
||||
|
||||
次のセクションでは、[`DiffusionPipeline`]を構成するコンポーネント(モデルとスケジューラ)を詳しく見て、これらのコンポーネントを使って猫の画像を生成する方法を学びます。
|
||||
|
||||
## モデル
|
||||
|
||||
ほとんどのモデルはノイズの多いサンプルを取り、各タイムステップで*残りのノイズ*を予測します(他のモデルは前のサンプルを直接予測するか、速度または[`v-prediction`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/5e5ce13e2f89ac45a0066cb3f369462a3cf1d9ef/src/diffusers/schedulers/scheduling_ddim.py#L110)を予測するように学習します)。モデルを混ぜて他の拡散システムを作ることもできます。
|
||||
|
||||
モデルは[`~ModelMixin.from_pretrained`]メソッドで開始されます。このメソッドはモデルをローカルにキャッシュするので、次にモデルをロードするときに高速になります。この案内では、[`UNet2DModel`]をロードします。これは基本的な画像生成モデルであり、猫画像で学習されたチェックポイントを使います:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import UNet2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> repo_id = "google/ddpm-cat-256"
|
||||
>>> model = UNet2DModel.from_pretrained(repo_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
モデルのパラメータにアクセスするには、`model.config` を呼び出せます:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model.config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
モデル構成は🧊凍結🧊されたディクショナリであり、モデル作成後にこれらのパラメー タを変更することはできません。これは意図的なもので、最初にモデル・アーキテクチャを定義するために使用されるパラメータが同じままであることを保証します。他のパラメータは生成中に調整することができます。
|
||||
|
||||
最も重要なパラメータは以下の通りです:
|
||||
|
||||
* sample_size`: 入力サンプルの高さと幅。
|
||||
* `in_channels`: 入力サンプルの入力チャンネル数。
|
||||
* down_block_types` と `up_block_types`: UNet アーキテクチャを作成するために使用されるダウンサンプリングブロックとアップサンプリングブロックのタイプ。
|
||||
* block_out_channels`: ダウンサンプリングブロックの出力チャンネル数。逆順でアップサンプリングブロックの入力チャンネル数にも使用されます。
|
||||
* layer_per_block`: 各 UNet ブロックに含まれる ResNet ブロックの数。
|
||||
|
||||
このモデルを生成に使用するには、ランダムな画像の形の正規分布を作成します。このモデルは複数のランダムな正規分布を受け取ることができるため`batch`軸を入れます。入力チャンネル数に対応する`channel`軸も必要です。画像の高さと幅に対応する`sample_size`軸を持つ必要があります:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> noisy_sample = torch.randn(1, model.config.in_channels, model.config.sample_size, model.config.sample_size)
|
||||
>>> noisy_sample.shape
|
||||
torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
画像生成には、ノイズの多い画像と `timestep` をモデルに渡します。`timestep`は入力画像がどの程度ノイズが多いかを示します。これは、モデルが拡散プロセスにおける自分の位置を決定するのに役立ちます。モデルの出力を得るには `sample` メソッドを使用します:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... noisy_residual = model(sample=noisy_sample, timestep=2).sample
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
しかし、実際の例を生成するには、ノイズ除去プロセスをガイドするスケジューラが必要です。次のセクションでは、モデルをスケジューラと組み合わせる方法を学びます。
|
||||
|
||||
## スケジューラ
|
||||
|
||||
スケジューラは、モデルの出力(この場合は `noisy_residual` )が与えられたときに、ノイズの多いサンプルからノイズの少ないサンプルへの移行を管理します。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
🧨 Diffusersは拡散システムを構築するためのツールボックスです。[`DiffusionPipeline`]は事前に構築された拡散システムを使い始めるのに便利な方法ですが、独自のモデルとスケジューラコンポーネントを個別に選択してカスタム拡散システムを構築することもできます。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
この案内では、[`DDPMScheduler`]を[`~diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config`]メソッドでインスタンス化します:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DDPMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_config(repo_id)
|
||||
>>> scheduler
|
||||
DDPMScheduler {
|
||||
"_class_name": "DDPMScheduler",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.13.1",
|
||||
"beta_end": 0.02,
|
||||
"beta_schedule": "linear",
|
||||
"beta_start": 0.0001,
|
||||
"clip_sample": true,
|
||||
"clip_sample_range": 1.0,
|
||||
"num_train_timesteps": 1000,
|
||||
"prediction_type": "epsilon",
|
||||
"trained_betas": null,
|
||||
"variance_type": "fixed_small"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 スケジューラがどのようにコンフィギュレーションからインスタンス化されるかに注目してください。モデルとは異なり、スケジューラは学習可能な重みを持たず、パラメーターを持ちません!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
最も重要なパラメータは以下の通りです:
|
||||
|
||||
* num_train_timesteps`: ノイズ除去処理の長さ、言い換えれば、ランダムな正規分布をデータサンプルに処理するのに必要なタイムステップ数です。
|
||||
* `beta_schedule`: 生成とトレーニングに使用するノイズスケジュールのタイプ。
|
||||
* `beta_start` と `beta_end`: ノイズスケジュールの開始値と終了値。
|
||||
|
||||
少しノイズの少ない画像を予測するには、スケジューラの [`~diffusers.DDPMScheduler.step`] メソッドに以下を渡します: モデルの出力、`timestep`、現在の `sample`。
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> less_noisy_sample = scheduler.step(model_output=noisy_residual, timestep=2, sample=noisy_sample).prev_sample
|
||||
>>> less_noisy_sample.shape
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`less_noisy_sample`は次の`timestep`に渡すことができ、そこでさらにノイズが少なくなります!
|
||||
|
||||
では、すべてをまとめて、ノイズ除去プロセス全体を視覚化してみましょう。
|
||||
|
||||
まず、ノイズ除去された画像を後処理して `PIL.Image` として表示する関数を作成します:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import PIL.Image
|
||||
>>> import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def display_sample(sample, i):
|
||||
... image_processed = sample.cpu().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
|
||||
... image_processed = (image_processed + 1.0) * 127.5
|
||||
... image_processed = image_processed.numpy().astype(np.uint8)
|
||||
|
||||
... image_pil = PIL.Image.fromarray(image_processed[0])
|
||||
... display(f"Image at step {i}")
|
||||
... display(image_pil)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ノイズ除去処理を高速化するために入力とモデルをGPUに移します:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model.to("cuda")
|
||||
>>> noisy_sample = noisy_sample.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ここで、ノイズが少なくなったサンプルの残りのノイズを予測するノイズ除去ループを作成し、スケジューラを使ってさらにノイズの少ないサンプルを計算します:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
>>> sample = noisy_sample
|
||||
|
||||
>>> for i, t in enumerate(tqdm.tqdm(scheduler.timesteps)):
|
||||
... # 1. predict noise residual
|
||||
... with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... residual = model(sample, t).sample
|
||||
|
||||
... # 2. compute less noisy image and set x_t -> x_t-1
|
||||
... sample = scheduler.step(residual, t, sample).prev_sample
|
||||
|
||||
... # 3. optionally look at image
|
||||
... if (i + 1) % 50 == 0:
|
||||
... display_sample(sample, i + 1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
何もないところから猫が生成されるのを、座って見てください!😻
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/diffusion-quicktour.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## 次のステップ
|
||||
|
||||
このクイックツアーで、🧨ディフューザーを使ったクールな画像をいくつか作成できたと思います!次のステップとして
|
||||
|
||||
* モデルをトレーニングまたは微調整については、[training](./tutorials/basic_training)チュートリアルを参照してください。
|
||||
* 様々な使用例については、公式およびコミュニティの[training or finetuning scripts](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples#-diffusers-examples)の例を参照してください。
|
||||
* スケジューラのロード、アクセス、変更、比較については[Using different Schedulers](./using-diffusers/schedulers)ガイドを参照してください。
|
||||
* プロンプトエンジニアリング、スピードとメモリの最適化、より高品質な画像を生成するためのヒントやトリックについては、[Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion)ガイドを参照してください。
|
||||
* 🧨 Diffusers の高速化については、最適化された [PyTorch on a GPU](./optimization/fp16)のガイド、[Stable Diffusion on Apple Silicon (M1/M2)](./optimization/mps)と[ONNX Runtime](./optimization/onnx)を参照してください。
|
||||
260
docs/source/ja/stable_diffusion.md
Normal file
260
docs/source/ja/stable_diffusion.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,260 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 効果的で効率的な拡散モデル
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
[`DiffusionPipeline`]を使って特定のスタイルで画像を生成したり、希望する画像を生成したりするのは難しいことです。多くの場合、[`DiffusionPipeline`]を何度か実行してからでないと満足のいく画像は得られません。しかし、何もないところから何かを生成するにはたくさんの計算が必要です。生成を何度も何度も実行する場合、特にたくさんの計算量が必要になります。
|
||||
|
||||
そのため、パイプラインから*計算*(速度)と*メモリ*(GPU RAM)の効率を最大限に引き出し、生成サイクル間の時間を短縮することで、より高速な反復処理を行えるようにすることが重要です。
|
||||
|
||||
このチュートリアルでは、[`DiffusionPipeline`]を用いて、より速く、より良い計算を行う方法を説明します。
|
||||
|
||||
まず、[`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)モデルをロードします:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ここで使用するプロンプトの例は年老いた戦士の長の肖像画ですが、ご自由に変更してください:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "portrait photo of a old warrior chief"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Speed
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 GPUを利用できない場合は、[Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/)のようなGPUプロバイダーから無料で利用できます!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
画像生成を高速化する最も簡単な方法の1つは、PyTorchモジュールと同じようにGPU上にパイプラインを配置することです:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
同じイメージを使って改良できるようにするには、[`Generator`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html)を使い、[reproducibility](./using-diffusers/reproducibility)の種を設定します:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
これで画像を生成できます:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_1.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
この処理にはT4 GPUで~30秒かかりました(割り当てられているGPUがT4より優れている場合はもっと速いかもしれません)。デフォルトでは、[`DiffusionPipeline`]は完全な`float32`精度で生成を50ステップ実行します。float16`のような低い精度に変更するか、推論ステップ数を減らすことで高速化することができます。
|
||||
|
||||
まずは `float16` でモデルをロードして画像を生成してみましょう:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_2.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
今回、画像生成にかかった時間はわずか11秒で、以前より3倍近く速くなりました!
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 パイプラインは常に `float16` で実行することを強くお勧めします。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
生成ステップ数を減らすという方法もあります。より効率的なスケジューラを選択することで、出力品質を犠牲にすることなくステップ数を減らすことができます。`compatibles`メソッドを呼び出すことで、[`DiffusionPipeline`]の現在のモデルと互換性のあるスケジューラを見つけることができます:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler.compatibles
|
||||
[
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_lms_discrete.LMSDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_unipc_multistep.UniPCMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_k_dpm_2_discrete.KDPM2DiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_deis_multistep.DEISMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_discrete.EulerDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_multistep.DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddpm.DDPMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_singlestep.DPMSolverSinglestepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_k_dpm_2_ancestral_discrete.KDPM2AncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_heun_discrete.HeunDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_pndm.PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_ancestral_discrete.EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddim.DDIMScheduler,
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusionモデルはデフォルトで[`PNDMScheduler`]を使用します。このスケジューラは通常~50の推論ステップを必要としますが、[`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`]のような高性能なスケジューラでは~20または25の推論ステップで済みます。[`ConfigMixin.from_config`]メソッドを使用すると、新しいスケジューラをロードすることができます:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ここで `num_inference_steps` を20に設定します:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=generator, num_inference_steps=20).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_3.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
推論時間をわずか4秒に短縮することに成功した!⚡️
|
||||
|
||||
## メモリー
|
||||
|
||||
パイプラインのパフォーマンスを向上させるもう1つの鍵は、消費メモリを少なくすることです。一度に生成できる画像の数を確認する最も簡単な方法は、`OutOfMemoryError`(OOM)が発生するまで、さまざまなバッチサイズを試してみることです。
|
||||
|
||||
文章と `Generators` のリストから画像のバッチを生成する関数を作成します。各 `Generator` にシードを割り当てて、良い結果が得られた場合に再利用できるようにします。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def get_inputs(batch_size=1):
|
||||
generator = [torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(i) for i in range(batch_size)]
|
||||
prompts = batch_size * [prompt]
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 20
|
||||
|
||||
return {"prompt": prompts, "generator": generator, "num_inference_steps": num_inference_steps}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`batch_size=4`で開始し、どれだけメモリを消費したかを確認します:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(**get_inputs(batch_size=4)).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, 2, 2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
大容量のRAMを搭載したGPUでない限り、上記のコードはおそらく`OOM`エラーを返したはずです!メモリの大半はクロスアテンションレイヤーが占めています。この処理をバッチで実行する代わりに、逐次実行することでメモリを大幅に節約できます。必要なのは、[`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_attention_slicing`]関数を使用することだけです:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
今度は`batch_size`を8にしてみてください!
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
images = pipeline(**get_inputs(batch_size=8)).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_5.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
以前は4枚の画像のバッチを生成することさえできませんでしたが、今では8枚の画像のバッチを1枚あたり~3.5秒で生成できます!これはおそらく、品質を犠牲にすることなくT4 GPUでできる最速の処理速度です。
|
||||
|
||||
## 品質
|
||||
|
||||
前の2つのセクションでは、`fp16` を使ってパイプラインの速度を最適化する方法、よりパフォーマン スなスケジューラーを使って生成ステップ数を減らす方法、アテンションスライスを有効 にしてメモリ消費量を減らす方法について学びました。今度は、生成される画像の品質を向上させる方法に焦点を当てます。
|
||||
|
||||
### より良いチェックポイント
|
||||
|
||||
最も単純なステップは、より良いチェックポイントを使うことです。Stable Diffusionモデルは良い出発点であり、公式発表以来、いくつかの改良版もリリースされています。しかし、新しいバージョンを使ったからといって、自動的に良い結果が得られるわけではありません。最良の結果を得るためには、自分でさまざまなチェックポイントを試してみたり、ちょっとした研究([ネガティブプロンプト](https://minimaxir.com/2022/11/stable-diffusion-negative-prompt/)の使用など)をしたりする必要があります。
|
||||
|
||||
この分野が成長するにつれて、特定のスタイルを生み出すために微調整された、より質の高いチェックポイントが増えています。[Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads)や[Diffusers Gallery](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-projects/diffusers-gallery)を探索して、興味のあるものを見つけてみてください!
|
||||
|
||||
### より良いパイプラインコンポーネント
|
||||
|
||||
現在のパイプラインコンポーネントを新しいバージョンに置き換えてみることもできます。Stability AIが提供する最新の[autodecoder](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1/tree/main/vae)をパイプラインにロードし、画像を生成してみましょう:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoencoderKL
|
||||
|
||||
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained("stabilityai/sd-vae-ft-mse", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.vae = vae
|
||||
images = pipeline(**get_inputs(batch_size=8)).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_6.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### より良いプロンプト・エンジニアリング
|
||||
|
||||
画像を生成するために使用する文章は、*プロンプトエンジニアリング*と呼ばれる分野を作られるほど、非常に重要です。プロンプト・エンジニアリングで考慮すべき点は以下の通りです:
|
||||
|
||||
- 生成したい画像やその類似画像は、インターネット上にどのように保存されているか?
|
||||
- 私が望むスタイルにモデルを誘導するために、どのような追加詳細を与えるべきか?
|
||||
|
||||
このことを念頭に置いて、プロンプトに色やより質の高いディテールを含めるように改良してみましょう:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt += ", tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes"
|
||||
prompt += " 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
新しいプロンプトで画像のバッチを生成しましょう:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
images = pipeline(**get_inputs(batch_size=8)).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_7.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
かなりいいです!種が`1`の`Generator`に対応する2番目の画像に、被写体の年齢に関するテキストを追加して、もう少し手を加えてみましょう:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompts = [
|
||||
"portrait photo of the oldest warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
"portrait photo of a old warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
"portrait photo of a warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
"portrait photo of a young warrior chief, tribal panther make up, blue on red, side profile, looking away, serious eyes 50mm portrait photography, hard rim lighting photography--beta --ar 2:3 --beta --upbeta",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
generator = [torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(1) for _ in range(len(prompts))]
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt=prompts, generator=generator, num_inference_steps=25).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, 2, 2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_8.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## 次のステップ
|
||||
|
||||
このチュートリアルでは、[`DiffusionPipeline`]を最適化して計算効率とメモリ効率を向上させ、生成される出力の品質を向上させる方法を学びました。パイプラインをさらに高速化することに興味があれば、以下のリソースを参照してください:
|
||||
|
||||
- [PyTorch 2.0](./optimization/torch2.0)と[`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.compile.html)がどのように生成速度を5-300%高速化できるかを学んでください。A100 GPUの場合、画像生成は最大50%速くなります!
|
||||
- PyTorch 2が使えない場合は、[xFormers](./optimization/xformers)をインストールすることをお勧めします。このライブラリのメモリ効率の良いアテンションメカニズムは PyTorch 1.13.1 と相性が良く、高速化とメモリ消費量の削減を同時に実現します。
|
||||
- モデルのオフロードなど、その他の最適化テクニックは [this guide](./optimization/fp16) でカバーされています。
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user