mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
synced 2025-12-07 04:54:47 +08:00
Compare commits
2 Commits
typo-in-wo
...
tests-memo
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
795f2c90fd | ||
|
|
84e2337807 |
3
.github/workflows/benchmark.yml
vendored
3
.github/workflows/benchmark.yml
vendored
@@ -31,6 +31,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install pandas peft
|
||||
@@ -39,7 +40,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
- name: Diffusers Benchmarking
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.DIFFUSERS_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.DIFFUSERS_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
BASE_PATH: benchmark_outputs
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
export TOTAL_GPU_MEMORY=$(python -c "import torch; print(torch.cuda.get_device_properties(0).total_memory / (1024**3))")
|
||||
|
||||
40
.github/workflows/build_docker_images.yml
vendored
40
.github/workflows/build_docker_images.yml
vendored
@@ -20,22 +20,22 @@ env:
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
test-build-docker-images:
|
||||
runs-on: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'pull_request'
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Find Changed Dockerfiles
|
||||
id: file_changes
|
||||
uses: jitterbit/get-changed-files@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
format: 'space-delimited'
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build Changed Docker Images
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CHANGED_FILES="${{ steps.file_changes.outputs.all }}"
|
||||
@@ -50,9 +50,9 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: steps.file_changes.outputs.all != ''
|
||||
|
||||
build-and-push-docker-images:
|
||||
runs-on: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: github.event_name != 'pull_request'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: read
|
||||
packages: write
|
||||
@@ -69,18 +69,17 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- diffusers-flax-tpu
|
||||
- diffusers-onnxruntime-cpu
|
||||
- diffusers-onnxruntime-cuda
|
||||
- diffusers-doc-builder
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout repository
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Login to Docker Hub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ env.REGISTRY }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
@@ -91,11 +90,24 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to a Slack channel
|
||||
id: slack
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@6c661ce58804a1a20f6dc5fbee7f0381b469e001
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# Slack channel id, channel name, or user id to post message.
|
||||
# See also: https://api.slack.com/methods/chat.postMessage#channels
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
title: "🤗 Results of the ${{ matrix.image-name }} Docker Image build"
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
channel-id: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
# For posting a rich message using Block Kit
|
||||
payload: |
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": "${{ matrix.image-name }} Docker Image build result: ${{ job.status }}\n${{ github.event.head_commit.url }}",
|
||||
"blocks": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "mrkdwn",
|
||||
"text": "${{ matrix.image-name }} Docker Image build result: ${{ job.status }}\n${{ github.event.head_commit.url }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
package: diffusers
|
||||
notebook_folder: diffusers_doc
|
||||
languages: en ko zh ja pt
|
||||
custom_container: diffusers/diffusers-doc-builder
|
||||
|
||||
secrets:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.HUGGINGFACE_PUSH }}
|
||||
hf_token: ${{ secrets.HF_DOC_BUILD_PUSH }}
|
||||
|
||||
1
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
1
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
@@ -20,4 +20,3 @@ jobs:
|
||||
install_libgl1: true
|
||||
package: diffusers
|
||||
languages: en ko zh ja pt
|
||||
custom_container: diffusers/diffusers-doc-builder
|
||||
|
||||
85
.github/workflows/mirror_community_pipeline.yml
vendored
85
.github/workflows/mirror_community_pipeline.yml
vendored
@@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Mirror Community Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
# Push changes on the main branch
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- 'examples/community/**.py'
|
||||
|
||||
# And on tag creation (e.g. `v0.28.1`)
|
||||
tags:
|
||||
- '*'
|
||||
|
||||
# Manual trigger with ref input
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
ref:
|
||||
description: "Either 'main' or a tag ref"
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
default: 'main'
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
mirror_community_pipeline:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# Checkout to correct ref
|
||||
# If workflow dispatch
|
||||
# If ref is 'main', set:
|
||||
# CHECKOUT_REF=refs/heads/main
|
||||
# PATH_IN_REPO=main
|
||||
# Else it must be a tag. Set:
|
||||
# CHECKOUT_REF=refs/tags/{tag}
|
||||
# PATH_IN_REPO={tag}
|
||||
# If not workflow dispatch
|
||||
# If ref is 'refs/heads/main' => set 'main'
|
||||
# Else it must be a tag => set {tag}
|
||||
- name: Set checkout_ref and path_in_repo
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ "${{ github.event_name }}" == "workflow_dispatch" ]; then
|
||||
if [ -z "${{ github.event.inputs.ref }}" ]; then
|
||||
echo "Error: Missing ref input"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
elif [ "${{ github.event.inputs.ref }}" == "main" ]; then
|
||||
echo "CHECKOUT_REF=refs/heads/main" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
echo "PATH_IN_REPO=main" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "CHECKOUT_REF=refs/tags/${{ github.event.inputs.ref }}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
echo "PATH_IN_REPO=${{ github.event.inputs.ref }}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
elif [ "${{ github.ref }}" == "refs/heads/main" ]; then
|
||||
echo "CHECKOUT_REF=${{ github.ref }}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
echo "PATH_IN_REPO=main" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
# e.g. refs/tags/v0.28.1 -> v0.28.1
|
||||
echo "CHECKOUT_REF=${{ github.ref }}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
echo "PATH_IN_REPO=${${{ github.ref }}#refs/tags/}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
ref: ${{ env.CHECKOUT_REF }}
|
||||
|
||||
# Setup + install dependencies
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.10"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install uv
|
||||
uv pip install --upgrade huggingface_hub
|
||||
|
||||
# Check secret is set
|
||||
- name: whoami
|
||||
run: huggingface-cli whoami
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN_MIRROR_COMMUNITY_PIPELINES }}
|
||||
|
||||
# Push to HF! (under subfolder based on checkout ref)
|
||||
# https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/community-pipelines-mirror
|
||||
- name: Mirror community pipeline to HF
|
||||
run: huggingface-cli upload diffusers/community-pipelines-mirror ./examples/community ${PATH_IN_REPO} --repo-type dataset
|
||||
env:
|
||||
PATH_IN_REPO: ${{ env.PATH_IN_REPO }}
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN_MIRROR_COMMUNITY_PIPELINES }}
|
||||
370
.github/workflows/nightly_tests.yml
vendored
370
.github/workflows/nightly_tests.yml
vendored
@@ -1,7 +1,6 @@
|
||||
name: Nightly and release tests on main/release branch
|
||||
name: Nightly tests on main
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 0 * * *" # every day at midnight
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,348 +12,121 @@ env:
|
||||
PYTEST_TIMEOUT: 600
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
RUN_NIGHTLY: yes
|
||||
PIPELINE_USAGE_CUTOFF: 5000
|
||||
SLACK_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
setup_torch_cuda_pipeline_matrix:
|
||||
name: Setup Torch Pipelines Matrix
|
||||
runs-on: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
pipeline_test_matrix: ${{ steps.fetch_pipeline_matrix.outputs.pipeline_test_matrix }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.8"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
- name: Fetch Pipeline Matrix
|
||||
id: fetch_pipeline_matrix
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
matrix=$(python utils/fetch_torch_cuda_pipeline_test_matrix.py)
|
||||
echo $matrix
|
||||
echo "pipeline_test_matrix=$matrix" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Pipeline Tests Artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: test-pipelines.json
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_nightly_tests_for_torch_pipelines:
|
||||
name: Torch Pipelines CUDA Nightly Tests
|
||||
needs: setup_torch_cuda_pipeline_matrix
|
||||
run_nightly_tests:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
module: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup_torch_cuda_pipeline_matrix.outputs.pipeline_test_matrix) }}
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- name: Nightly PyTorch CUDA tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
runner: docker-gpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
report: torch_cuda
|
||||
- name: Nightly Flax TPU tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: flax
|
||||
runner: docker-tpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-flax-tpu
|
||||
report: flax_tpu
|
||||
- name: Nightly ONNXRuntime CUDA tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: onnxruntime
|
||||
runner: docker-gpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-onnxruntime-cuda
|
||||
report: onnx_cuda
|
||||
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.config.name }}
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.config.runner }}
|
||||
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface/diffusers:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
image: ${{ matrix.config.image }}
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ ${{ matrix.config.runner == 'docker-tpu' && '--privileged' || '--gpus 0'}}
|
||||
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: nvidia-smi
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.runner == 'docker-gpu' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -U transformers@git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate
|
||||
python -m uv pip install pytest-reportlog
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Nightly PyTorch CUDA checkpoint (pipelines) tests
|
||||
- name: Run nightly PyTorch CUDA tests
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'pytorch' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda \
|
||||
--report-log=tests_pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda.log \
|
||||
tests/pipelines/${{ matrix.module }}
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
--report-log=${{ matrix.config.report }}.log \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run nightly Flax TPU tests
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'flax' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 0 \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Flax" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
--report-log=${{ matrix.config.report }}.log \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run nightly ONNXRuntime CUDA tests
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'onnxruntime' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
--report-log=${{ matrix.config.report }}.log \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_${{ matrix.config.report }}_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_test_reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.config.report }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report and Notify Channel
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
python scripts/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_nightly_tests_for_other_torch_modules:
|
||||
name: Torch Non-Pipelines CUDA Nightly Tests
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
module: [models, schedulers, others, examples]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
python -m uv pip install pytest-reportlog
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run nightly PyTorch CUDA tests for non-pipeline modules
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.module != 'examples'}}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_torch_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda \
|
||||
--report-log=tests_torch_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda.log \
|
||||
tests/${{ matrix.module }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run nightly example tests with Torch
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.module == 'examples' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m uv pip install peft@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v --make-reports=examples_torch_cuda \
|
||||
--report-log=examples_torch_cuda.log \
|
||||
examples/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_torch_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_torch_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: torch_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report and Notify Channel
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
python scripts/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_lora_nightly_tests:
|
||||
name: Nightly LoRA Tests with PEFT and TORCH
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
python -m uv pip install peft@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
|
||||
python -m uv pip install pytest-reportlog
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run nightly LoRA tests with PEFT and Torch
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_torch_lora_cuda \
|
||||
--report-log=tests_torch_lora_cuda.log \
|
||||
tests/lora
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_torch_lora_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_torch_lora_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: torch_lora_cuda_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report and Notify Channel
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
python scripts/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_flax_tpu_tests:
|
||||
name: Nightly Flax TPU Tests
|
||||
runs-on: docker-tpu
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'schedule'
|
||||
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-flax-tpu
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --privileged
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
python -m uv pip install pytest-reportlog
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run nightly Flax TPU tests
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 0 \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Flax" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_flax_tpu \
|
||||
--report-log=tests_flax_tpu.log \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_flax_tpu_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_flax_tpu_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: flax_tpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report and Notify Channel
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
python scripts/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_nightly_onnx_tests:
|
||||
name: Nightly ONNXRuntime CUDA tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-onnxruntime-cuda
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
python -m uv pip install pytest-reportlog
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run nightly ONNXRuntime CUDA tests
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_onnx_cuda \
|
||||
--report-log=tests_onnx_cuda.log \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_onnx_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_onnx_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.config.report }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report and Notify Channel
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
python scripts/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_nightly_tests_apple_m1:
|
||||
name: Nightly PyTorch MPS tests on MacOS
|
||||
runs-on: [ self-hosted, apple-m1 ]
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'schedule'
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
@@ -390,7 +162,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
shell: arch -arch arm64 bash {0}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /System/Volumes/Data/mnt/cache
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
${CONDA_RUN} python -m pytest -n 1 -s -v --make-reports=tests_torch_mps \
|
||||
--report-log=tests_torch_mps.log \
|
||||
|
||||
9
.github/workflows/pr_test_fetcher.yml
vendored
9
.github/workflows/pr_test_fetcher.yml
vendored
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ concurrency:
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
setup_pr_tests:
|
||||
name: Setup PR Tests
|
||||
runs-on: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runs-on: docker-cpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@@ -32,6 +32,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 0
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
@@ -73,7 +74,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
max-parallel: 2
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
modules: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup_pr_tests.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
runs-on: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runs-on: docker-cpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@@ -88,6 +89,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m pip install accelerate
|
||||
@@ -123,7 +125,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- name: Hub tests for models, schedulers, and pipelines
|
||||
framework: hub_tests_pytorch
|
||||
runner: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_hub
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -145,6 +147,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
37
.github/workflows/pr_test_peft_backend.yml
vendored
37
.github/workflows/pr_test_peft_backend.yml
vendored
@@ -32,11 +32,9 @@ jobs:
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install .[quality]
|
||||
- name: Check quality
|
||||
run: make quality
|
||||
- name: Check if failure
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "Quality check failed. Please ensure the right dependency versions are installed with 'pip install -e .[quality]' and run 'make style && make quality'" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
ruff check examples tests src utils scripts
|
||||
ruff format examples tests src utils scripts --check
|
||||
|
||||
check_repository_consistency:
|
||||
needs: check_code_quality
|
||||
@@ -51,15 +49,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install .[quality]
|
||||
- name: Check repo consistency
|
||||
- name: Check quality
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/check_copies.py
|
||||
python utils/check_dummies.py
|
||||
make deps_table_check_updated
|
||||
- name: Check if failure
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "Repo consistency check failed. Please ensure the right dependency versions are installed with 'pip install -e .[quality]' and run 'make fix-copies'" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_fast_tests:
|
||||
needs: [check_code_quality, check_repository_consistency]
|
||||
@@ -71,7 +65,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
name: LoRA - ${{ matrix.lib-versions }}
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runs-on: docker-cpu
|
||||
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
@@ -89,10 +83,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.lib-versions }}" == "main" ]; then
|
||||
python -m pip install -U peft@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -U peft@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -U transformers@git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -U accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
else
|
||||
@@ -107,25 +102,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Run fast PyTorch LoRA CPU tests with PEFT backend
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 4 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/lora/
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 4 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_models_lora_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/models/ -k "lora"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_${{ matrix.config.report }}_failures_short.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_models_lora_${{ matrix.config.report }}_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: pr_${{ matrix.config.report }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
34
.github/workflows/pr_tests.yml
vendored
34
.github/workflows/pr_tests.yml
vendored
@@ -40,11 +40,9 @@ jobs:
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install .[quality]
|
||||
- name: Check quality
|
||||
run: make quality
|
||||
- name: Check if failure
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "Quality check failed. Please ensure the right dependency versions are installed with 'pip install -e .[quality]' and run 'make style && make quality'" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
ruff check examples tests src utils scripts
|
||||
ruff format examples tests src utils scripts --check
|
||||
|
||||
check_repository_consistency:
|
||||
needs: check_code_quality
|
||||
@@ -59,15 +57,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install .[quality]
|
||||
- name: Check repo consistency
|
||||
- name: Check quality
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/check_copies.py
|
||||
python utils/check_dummies.py
|
||||
make deps_table_check_updated
|
||||
- name: Check if failure
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "Repo consistency check failed. Please ensure the right dependency versions are installed with 'pip install -e .[quality]' and run 'make fix-copies'" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_fast_tests:
|
||||
needs: [check_code_quality, check_repository_consistency]
|
||||
@@ -77,22 +71,22 @@ jobs:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- name: Fast PyTorch Pipeline CPU tests
|
||||
framework: pytorch_pipelines
|
||||
runner: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 32-cpu, 256-ram, ci ]
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_cpu_pipelines
|
||||
- name: Fast PyTorch Models & Schedulers CPU tests
|
||||
framework: pytorch_models
|
||||
runner: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_cpu_models_schedulers
|
||||
- name: Fast Flax CPU tests
|
||||
framework: flax
|
||||
runner: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-flax-cpu
|
||||
report: flax_cpu
|
||||
- name: PyTorch Example CPU tests
|
||||
framework: pytorch_examples
|
||||
runner: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_example_cpu
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -116,6 +110,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate
|
||||
@@ -129,7 +124,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'pytorch_pipelines' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/pipelines
|
||||
@@ -138,7 +133,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'pytorch_models' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 4 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx and not Dependency" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/models tests/schedulers tests/others
|
||||
@@ -147,7 +142,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'flax' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 4 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Flax" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests
|
||||
@@ -156,8 +151,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'pytorch_examples' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install peft timm
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 4 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
python -m uv pip install peft
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
examples
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -180,7 +175,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- name: Hub tests for models, schedulers, and pipelines
|
||||
framework: hub_tests_pytorch
|
||||
runner: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_hub
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -204,6 +199,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
78
.github/workflows/push_tests.yml
vendored
78
.github/workflows/push_tests.yml
vendored
@@ -21,9 +21,7 @@ env:
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
setup_torch_cuda_pipeline_matrix:
|
||||
name: Setup Torch Pipelines CUDA Slow Tests Matrix
|
||||
runs-on: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
pipeline_test_matrix: ${{ steps.fetch_pipeline_matrix.outputs.pipeline_test_matrix }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
@@ -31,13 +29,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.8"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
- name: Fetch Pipeline Matrix
|
||||
id: fetch_pipeline_matrix
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@@ -56,13 +55,12 @@ jobs:
|
||||
needs: setup_torch_cuda_pipeline_matrix
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
max-parallel: 8
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
module: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup_torch_cuda_pipeline_matrix.outputs.pipeline_test_matrix) }}
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface/diffusers:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
@@ -73,6 +71,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
@@ -81,7 +80,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
- name: Slow PyTorch CUDA checkpoint tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@@ -94,6 +93,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
@@ -103,16 +103,16 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
torch_cuda_tests:
|
||||
name: Torch CUDA Tests
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface/diffusers:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
module: [models, schedulers, lora, others, single_file]
|
||||
module: [models, schedulers, lora, others]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
@@ -121,6 +121,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
@@ -131,7 +132,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run slow PyTorch CUDA tests
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@@ -155,10 +156,10 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
peft_cuda_tests:
|
||||
name: PEFT CUDA Tests
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface/diffusers:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
@@ -170,10 +171,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
python -m pip install -U peft@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
|
||||
python -m uv pip install peft@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@@ -181,7 +183,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run slow PEFT CUDA tests
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@@ -189,17 +191,12 @@ jobs:
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx and not PEFTLoRALoading" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_peft_cuda \
|
||||
tests/lora/
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "lora and not Flax and not Onnx and not PEFTLoRALoading" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_peft_cuda_models_lora \
|
||||
tests/models/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_peft_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_peft_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_peft_cuda_models_lora_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
@@ -213,7 +210,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runs-on: docker-tpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-flax-tpu
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/ --privileged
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --privileged
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
@@ -225,6 +222,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
@@ -235,7 +233,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run slow Flax TPU tests
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 0 \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Flax" \
|
||||
@@ -257,10 +255,10 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
onnx_cuda_tests:
|
||||
name: ONNX CUDA Tests
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-onnxruntime-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
@@ -272,6 +270,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install accelerate@git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
@@ -282,7 +281,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run slow ONNXRuntime CUDA tests
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Onnx" \
|
||||
@@ -305,11 +304,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_torch_compile_tests:
|
||||
name: PyTorch Compile CUDA tests
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-compile-cuda
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
@@ -329,7 +328,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
- name: Run example tests on GPU
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s -v -k "compile" --make-reports=tests_torch_compile_cuda tests/
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
@@ -346,11 +345,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_xformers_tests:
|
||||
name: PyTorch xformers CUDA tests
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-xformers-cuda
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
@@ -370,7 +369,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
- name: Run example tests on GPU
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s -v -k "xformers" --make-reports=tests_torch_xformers_cuda tests/
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
@@ -387,11 +386,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_examples_tests:
|
||||
name: Examples PyTorch CUDA tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
@@ -415,10 +414,9 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run example tests on GPU
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install timm
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s -v --make-reports=examples_torch_cuda examples/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
@@ -432,4 +430,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: examples_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
19
.github/workflows/push_tests_fast.yml
vendored
19
.github/workflows/push_tests_fast.yml
vendored
@@ -29,22 +29,22 @@ jobs:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- name: Fast PyTorch CPU tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
runner: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_cpu
|
||||
- name: Fast Flax CPU tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: flax
|
||||
runner: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-flax-cpu
|
||||
report: flax_cpu
|
||||
- name: Fast ONNXRuntime CPU tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: onnxruntime
|
||||
runner: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-onnxruntime-cpu
|
||||
report: onnx_cpu
|
||||
- name: PyTorch Example CPU tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: pytorch_examples
|
||||
runner: [ self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci ]
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_example_cpu
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -68,6 +68,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -80,7 +81,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'pytorch' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 4 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
@@ -89,7 +90,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'flax' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 4 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Flax" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
@@ -98,7 +99,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'onnxruntime' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 4 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
@@ -107,8 +108,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'pytorch_examples' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install peft timm
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 4 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
python -m uv pip install peft
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
examples
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/workflows/push_tests_mps.yml
vendored
4
.github/workflows/push_tests_mps.yml
vendored
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ concurrency:
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_fast_tests_apple_m1:
|
||||
name: Fast PyTorch MPS tests on MacOS
|
||||
runs-on: macos-13-xlarge
|
||||
runs-on: [ self-hosted, apple-m1 ]
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
@@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
shell: arch -arch arm64 bash {0}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /System/Volumes/Data/mnt/cache
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
${CONDA_RUN} python -m pytest -n 0 -s -v --make-reports=tests_torch_mps tests/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
73
.github/workflows/run_tests_from_a_pr.yml
vendored
73
.github/workflows/run_tests_from_a_pr.yml
vendored
@@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Check running SLOW tests from a PR (only GPU)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
docker_image:
|
||||
default: 'diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda'
|
||||
description: 'Name of the Docker image'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
branch:
|
||||
description: 'PR Branch to test on'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
test:
|
||||
description: 'Tests to run (e.g.: `tests/models`).'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
DIFFUSERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
IS_GITHUB_CI: "1"
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
PYTEST_TIMEOUT: 600
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_tests:
|
||||
name: "Run a test on our runner from a PR"
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ github.event.inputs.docker_image }}
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --privileged --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Validate test files input
|
||||
id: validate_test_files
|
||||
env:
|
||||
PY_TEST: ${{ github.event.inputs.test }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [[ ! "$PY_TEST" =~ ^tests/ ]]; then
|
||||
echo "Error: The input string must start with 'tests/'."
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ ! "$PY_TEST" =~ ^tests/(models|pipelines) ]]; then
|
||||
echo "Error: The input string must contain either 'models' or 'pipelines' after 'tests/'."
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ "$PY_TEST" == *";"* ]]; then
|
||||
echo "Error: The input string must not contain ';'."
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
echo "$PY_TEST"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Checkout PR branch
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
ref: ${{ github.event.inputs.branch }}
|
||||
repository: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.repo.full_name }}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install pytest
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m venv /opt/venv && export PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
python -m uv pip install -e [quality,test]
|
||||
python -m uv pip install peft
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run tests
|
||||
env:
|
||||
PY_TEST: ${{ github.event.inputs.test }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pytest "$PY_TEST"
|
||||
46
.github/workflows/ssh-runner.yml
vendored
46
.github/workflows/ssh-runner.yml
vendored
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: SSH into runners
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
runner_type:
|
||||
description: 'Type of runner to test (a10 or t4)'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
docker_image:
|
||||
description: 'Name of the Docker image'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
IS_GITHUB_CI: "1"
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
DIFFUSERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
ssh_runner:
|
||||
name: "SSH"
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, "${{ github.event.inputs.runner_type }}", ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ github.event.inputs.docker_image }}
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface/diffusers:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0 --privileged
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Tailscale # In order to be able to SSH when a test fails
|
||||
uses: huggingface/tailscale-action@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
authkey: ${{ secrets.TAILSCALE_SSH_AUTHKEY }}
|
||||
slackChannel: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
slackToken: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
waitForSSH: true
|
||||
30
.github/workflows/update_metadata.yml
vendored
30
.github/workflows/update_metadata.yml
vendored
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Update Diffusers metadata
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
- update_diffusers_metadata*
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
update_metadata:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash -l {0}
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install datasets pandas
|
||||
pip install .[torch]
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update metadata
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SAYAK_HF_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/update_metadata.py --commit_sha ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
@@ -355,7 +355,7 @@ You will need basic `git` proficiency to be able to contribute to
|
||||
manual. Type `git --help` in a shell and enjoy. If you prefer books, [Pro
|
||||
Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2) is a very good reference.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow these steps to start contributing ([supported Python versions](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/42f25d601a910dceadaee6c44345896b4cfa9928/setup.py#L270)):
|
||||
Follow these steps to start contributing ([supported Python versions](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/setup.py#L265)):
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) by
|
||||
clicking on the 'Fork' button on the repository's page. This creates a copy of the code
|
||||
|
||||
2
Makefile
2
Makefile
@@ -42,7 +42,6 @@ repo-consistency:
|
||||
quality:
|
||||
ruff check $(check_dirs) setup.py
|
||||
ruff format --check $(check_dirs) setup.py
|
||||
doc-builder style src/diffusers docs/source --max_len 119 --check_only
|
||||
python utils/check_doc_toc.py
|
||||
|
||||
# Format source code automatically and check is there are any problems left that need manual fixing
|
||||
@@ -56,7 +55,6 @@ extra_style_checks:
|
||||
style:
|
||||
ruff check $(check_dirs) setup.py --fix
|
||||
ruff format $(check_dirs) setup.py
|
||||
doc-builder style src/diffusers docs/source --max_len 119
|
||||
${MAKE} autogenerate_code
|
||||
${MAKE} extra_style_checks
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ Please refer to the [How to use Stable Diffusion in Apple Silicon](https://huggi
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
Generating outputs is super easy with 🤗 Diffusers. To generate an image from text, use the `from_pretrained` method to load any pretrained diffusion model (browse the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads) for 25.000+ checkpoints):
|
||||
Generating outputs is super easy with 🤗 Diffusers. To generate an image from text, use the `from_pretrained` method to load any pretrained diffusion model (browse the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=downloads) for 22000+ checkpoints):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -219,7 +219,7 @@ Also, say 👋 in our public Discord channel <a href="https://discord.gg/G7tWnz9
|
||||
- https://github.com/deep-floyd/IF
|
||||
- https://github.com/bentoml/BentoML
|
||||
- https://github.com/bmaltais/kohya_ss
|
||||
- +11.000 other amazing GitHub repositories 💪
|
||||
- +9000 other amazing GitHub repositories 💪
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you for using us ❤️.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM ubuntu:20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get -y update \
|
||||
&& apt-get install -y software-properties-common \
|
||||
&& add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
python3.10 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
zip \
|
||||
wget \
|
||||
python3.10-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
invisible_watermark \
|
||||
--extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
hf-doc-builder \
|
||||
huggingface-hub \
|
||||
Jinja2 \
|
||||
librosa \
|
||||
numpy \
|
||||
scipy \
|
||||
tensorboard \
|
||||
transformers \
|
||||
matplotlib \
|
||||
setuptools==69.5.1
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
@@ -4,25 +4,21 @@ LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get -y update \
|
||||
&& apt-get install -y software-properties-common \
|
||||
&& add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.10 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.10-venv && \
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
python3.8 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.8-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
RUN python3 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,25 +4,21 @@ LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get -y update \
|
||||
&& apt-get install -y software-properties-common \
|
||||
&& add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.10 \
|
||||
python3.8 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.10-venv && \
|
||||
python3.8-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
RUN python3 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,25 +4,21 @@ LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get -y update \
|
||||
&& apt-get install -y software-properties-common \
|
||||
&& add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.10 \
|
||||
python3.8 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.10-venv && \
|
||||
python3.8-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
RUN python3 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,36 +4,32 @@ LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get -y update \
|
||||
&& apt-get install -y software-properties-common \
|
||||
&& add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.10 \
|
||||
python3.8 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.10-venv && \
|
||||
python3.8-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
RUN python3 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
"onnxruntime-gpu>=1.13.1" \
|
||||
--extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117 && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
python3 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
hf-doc-builder \
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,11 +4,8 @@ LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get -y update \
|
||||
&& apt-get install -y software-properties-common \
|
||||
&& add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
@@ -16,23 +13,24 @@ RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.10 \
|
||||
python3.9 \
|
||||
python3.9-dev \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.10-venv && \
|
||||
python3.9-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
RUN python3.9 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
RUN python3.9 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3.9 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
invisible_watermark && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
python3.9 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
hf-doc-builder \
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,36 +4,33 @@ LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get -y update \
|
||||
&& apt-get install -y software-properties-common \
|
||||
&& add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
python3.10 \
|
||||
python3.8 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.10-venv && \
|
||||
python3.8-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
RUN python3 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
invisible_watermark \
|
||||
--extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
python3 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
hf-doc-builder \
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,11 +4,8 @@ LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get -y update \
|
||||
&& apt-get install -y software-properties-common \
|
||||
&& add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
@@ -16,23 +13,23 @@ RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.10 \
|
||||
python3.8 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.10-venv && \
|
||||
python3.8-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
RUN python3 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
invisible_watermark && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
hf-doc-builder \
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,11 +4,8 @@ LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get -y update \
|
||||
&& apt-get install -y software-properties-common \
|
||||
&& add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
@@ -16,23 +13,23 @@ RUN apt install -y bash \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.10 \
|
||||
python3.8 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.10-venv && \
|
||||
python3.8-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
RUN python3 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
RUN python3.10 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip uv==0.1.11 && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
invisible_watermark && \
|
||||
python3.10 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
python3 -m uv pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
hf-doc-builder \
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -242,10 +242,10 @@ Here's an example of a tuple return, comprising several objects:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`tuple(torch.Tensor)` comprising various elements depending on the configuration ([`BertConfig`]) and inputs:
|
||||
- ** loss** (*optional*, returned when `masked_lm_labels` is provided) `torch.Tensor` of shape `(1,)` --
|
||||
`tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` comprising various elements depending on the configuration ([`BertConfig`]) and inputs:
|
||||
- ** loss** (*optional*, returned when `masked_lm_labels` is provided) `torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(1,)` --
|
||||
Total loss is the sum of the masked language modeling loss and the next sequence prediction (classification) loss.
|
||||
- **prediction_scores** (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)`) --
|
||||
- **prediction_scores** (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)`) --
|
||||
Prediction scores of the language modeling head (scores for each vocabulary token before SoftMax).
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,140 +23,154 @@
|
||||
title: Accelerate inference of text-to-image diffusion models
|
||||
title: Tutorials
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/loading
|
||||
title: Load pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Load community pipelines and components
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/schedulers
|
||||
title: Load schedulers and models
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/other-formats
|
||||
title: Model files and layouts
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/loading_adapters
|
||||
title: Load adapters
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/push_to_hub
|
||||
title: Push files to the Hub
|
||||
title: Load pipelines and adapters
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/unconditional_image_generation
|
||||
title: Unconditional image generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation
|
||||
title: Text-to-image
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/img2img
|
||||
title: Image-to-image
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/inpaint
|
||||
title: Inpainting
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/text-img2vid
|
||||
title: Text or image-to-video
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/depth2img
|
||||
title: Depth-to-image
|
||||
title: Generative tasks
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/overview_techniques
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: training/distributed_inference
|
||||
title: Distributed inference with multiple GPUs
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/merge_loras
|
||||
title: Merge LoRAs
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/scheduler_features
|
||||
title: Scheduler features
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/callback
|
||||
title: Pipeline callbacks
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/reusing_seeds
|
||||
title: Reproducible pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/image_quality
|
||||
title: Controlling image quality
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/weighted_prompts
|
||||
title: Prompt techniques
|
||||
title: Inference techniques
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: advanced_inference/outpaint
|
||||
title: Outpainting
|
||||
title: Advanced inference
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/sdxl
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/sdxl_turbo
|
||||
title: SDXL Turbo
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/kandinsky
|
||||
title: Kandinsky
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/ip_adapter
|
||||
title: IP-Adapter
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/controlnet
|
||||
title: ControlNet
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/t2i_adapter
|
||||
title: T2I-Adapter
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/inference_with_lcm
|
||||
title: Latent Consistency Model
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/textual_inversion_inference
|
||||
title: Textual inversion
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/shap-e
|
||||
title: Shap-E
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/diffedit
|
||||
title: DiffEdit
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/inference_with_tcd_lora
|
||||
title: Trajectory Consistency Distillation-LoRA
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/svd
|
||||
title: Stable Video Diffusion
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/marigold_usage
|
||||
title: Marigold Computer Vision
|
||||
title: Specific pipeline examples
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: training/create_dataset
|
||||
title: Create a dataset for training
|
||||
- local: training/adapt_a_model
|
||||
title: Adapt a model to a new task
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/unconditional_training
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/loading_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/loading
|
||||
title: Load pipelines, models, and schedulers
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/schedulers
|
||||
title: Load and compare different schedulers
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Load community pipelines and components
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/using_safetensors
|
||||
title: Load safetensors
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/other-formats
|
||||
title: Load different Stable Diffusion formats
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/loading_adapters
|
||||
title: Load adapters
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/push_to_hub
|
||||
title: Push files to the Hub
|
||||
title: Loading & Hub
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/unconditional_image_generation
|
||||
title: Unconditional image generation
|
||||
- local: training/text2image
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation
|
||||
title: Text-to-image
|
||||
- local: training/sdxl
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
- local: training/kandinsky
|
||||
title: Kandinsky 2.2
|
||||
- local: training/wuerstchen
|
||||
title: Wuerstchen
|
||||
- local: training/controlnet
|
||||
title: ControlNet
|
||||
- local: training/t2i_adapters
|
||||
title: T2I-Adapters
|
||||
- local: training/instructpix2pix
|
||||
title: InstructPix2Pix
|
||||
title: Models
|
||||
isExpanded: false
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/img2img
|
||||
title: Image-to-image
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/inpaint
|
||||
title: Inpainting
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/text-img2vid
|
||||
title: Text or image-to-video
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/depth2img
|
||||
title: Depth-to-image
|
||||
title: Tasks
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/text_inversion
|
||||
title: Textual Inversion
|
||||
- local: training/dreambooth
|
||||
title: DreamBooth
|
||||
- local: training/lora
|
||||
title: LoRA
|
||||
- local: training/custom_diffusion
|
||||
title: Custom Diffusion
|
||||
- local: training/lcm_distill
|
||||
title: Latent Consistency Distillation
|
||||
- local: training/ddpo
|
||||
title: Reinforcement learning training with DDPO
|
||||
title: Methods
|
||||
isExpanded: false
|
||||
title: Training
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/textual_inversion_inference
|
||||
title: Textual inversion
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/ip_adapter
|
||||
title: IP-Adapter
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/merge_loras
|
||||
title: Merge LoRAs
|
||||
- local: training/distributed_inference
|
||||
title: Distributed inference with multiple GPUs
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/reusing_seeds
|
||||
title: Improve image quality with deterministic generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/control_brightness
|
||||
title: Control image brightness
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/weighted_prompts
|
||||
title: Prompt weighting
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/freeu
|
||||
title: Improve generation quality with FreeU
|
||||
title: Techniques
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/sdxl
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/sdxl_turbo
|
||||
title: SDXL Turbo
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/kandinsky
|
||||
title: Kandinsky
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/controlnet
|
||||
title: ControlNet
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/shap-e
|
||||
title: Shap-E
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/diffedit
|
||||
title: DiffEdit
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/distilled_sd
|
||||
title: Distilled Stable Diffusion inference
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/callback
|
||||
title: Pipeline callbacks
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/reproducibility
|
||||
title: Create reproducible pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_examples
|
||||
title: Community pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/contribute_pipeline
|
||||
title: Contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/inference_with_lcm_lora
|
||||
title: Latent Consistency Model-LoRA
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/inference_with_lcm
|
||||
title: Latent Consistency Model
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/inference_with_tcd_lora
|
||||
title: Trajectory Consistency Distillation-LoRA
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/svd
|
||||
title: Stable Video Diffusion
|
||||
title: Specific pipeline examples
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: training/create_dataset
|
||||
title: Create a dataset for training
|
||||
- local: training/adapt_a_model
|
||||
title: Adapt a model to a new task
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/unconditional_training
|
||||
title: Unconditional image generation
|
||||
- local: training/text2image
|
||||
title: Text-to-image
|
||||
- local: training/sdxl
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
- local: training/kandinsky
|
||||
title: Kandinsky 2.2
|
||||
- local: training/wuerstchen
|
||||
title: Wuerstchen
|
||||
- local: training/controlnet
|
||||
title: ControlNet
|
||||
- local: training/t2i_adapters
|
||||
title: T2I-Adapters
|
||||
- local: training/instructpix2pix
|
||||
title: InstructPix2Pix
|
||||
title: Models
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/text_inversion
|
||||
title: Textual Inversion
|
||||
- local: training/dreambooth
|
||||
title: DreamBooth
|
||||
- local: training/lora
|
||||
title: LoRA
|
||||
- local: training/custom_diffusion
|
||||
title: Custom Diffusion
|
||||
- local: training/lcm_distill
|
||||
title: Latent Consistency Distillation
|
||||
- local: training/ddpo
|
||||
title: Reinforcement learning training with DDPO
|
||||
title: Methods
|
||||
title: Training
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/other-modalities
|
||||
title: Other Modalities
|
||||
title: Taking Diffusers Beyond Images
|
||||
title: Using Diffusers
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: optimization/fp16
|
||||
title: Speed up inference
|
||||
- local: optimization/memory
|
||||
title: Reduce memory usage
|
||||
- local: optimization/torch2.0
|
||||
title: PyTorch 2.0
|
||||
- local: optimization/xformers
|
||||
title: xFormers
|
||||
- local: optimization/tome
|
||||
title: Token merging
|
||||
- local: optimization/deepcache
|
||||
title: DeepCache
|
||||
- local: optimization/tgate
|
||||
title: TGATE
|
||||
- local: optimization/opt_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: optimization/fp16
|
||||
title: Speed up inference
|
||||
- local: optimization/memory
|
||||
title: Reduce memory usage
|
||||
- local: optimization/torch2.0
|
||||
title: PyTorch 2.0
|
||||
- local: optimization/xformers
|
||||
title: xFormers
|
||||
- local: optimization/tome
|
||||
title: Token merging
|
||||
- local: optimization/deepcache
|
||||
title: DeepCache
|
||||
title: General optimizations
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/stable_diffusion_jax_how_to
|
||||
title: JAX/Flax
|
||||
@@ -166,14 +180,14 @@
|
||||
title: OpenVINO
|
||||
- local: optimization/coreml
|
||||
title: Core ML
|
||||
title: Optimized model formats
|
||||
title: Optimized model types
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: optimization/mps
|
||||
title: Metal Performance Shaders (MPS)
|
||||
- local: optimization/habana
|
||||
title: Habana Gaudi
|
||||
title: Optimized hardware
|
||||
title: Accelerate inference and reduce memory
|
||||
title: Optimization
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: conceptual/philosophy
|
||||
title: Philosophy
|
||||
@@ -195,7 +209,6 @@
|
||||
- local: api/outputs
|
||||
title: Outputs
|
||||
title: Main Classes
|
||||
isExpanded: false
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/loaders/ip_adapter
|
||||
title: IP-Adapter
|
||||
@@ -210,7 +223,6 @@
|
||||
- local: api/loaders/peft
|
||||
title: PEFT
|
||||
title: Loaders
|
||||
isExpanded: false
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/models/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
@@ -237,21 +249,14 @@
|
||||
- local: api/models/consistency_decoder_vae
|
||||
title: ConsistencyDecoderVAE
|
||||
- local: api/models/transformer2d
|
||||
title: Transformer2DModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/pixart_transformer2d
|
||||
title: PixArtTransformer2DModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/dit_transformer2d
|
||||
title: DiTTransformer2DModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/hunyuan_transformer2d
|
||||
title: HunyuanDiT2DModel
|
||||
title: Transformer2D
|
||||
- local: api/models/transformer_temporal
|
||||
title: TransformerTemporalModel
|
||||
title: Transformer Temporal
|
||||
- local: api/models/prior_transformer
|
||||
title: PriorTransformer
|
||||
title: Prior Transformer
|
||||
- local: api/models/controlnet
|
||||
title: ControlNetModel
|
||||
title: ControlNet
|
||||
title: Models
|
||||
isExpanded: false
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
@@ -275,10 +280,6 @@
|
||||
title: ControlNet
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/controlnet_sdxl
|
||||
title: ControlNet with Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/controlnetxs
|
||||
title: ControlNet-XS
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/controlnetxs_sdxl
|
||||
title: ControlNet-XS with Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/dance_diffusion
|
||||
title: Dance Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/ddim
|
||||
@@ -291,8 +292,6 @@
|
||||
title: DiffEdit
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/dit
|
||||
title: DiT
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/hunyuandit
|
||||
title: Hunyuan-DiT
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/i2vgenxl
|
||||
title: I2VGen-XL
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pix2pix
|
||||
@@ -309,8 +308,6 @@
|
||||
title: Latent Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/ledits_pp
|
||||
title: LEDITS++
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/marigold
|
||||
title: Marigold
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/panorama
|
||||
title: MultiDiffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/musicldm
|
||||
@@ -321,8 +318,6 @@
|
||||
title: Personalized Image Animator (PIA)
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pixart
|
||||
title: PixArt-α
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pixart_sigma
|
||||
title: PixArt-Σ
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/self_attention_guidance
|
||||
title: Self-Attention Guidance
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion
|
||||
@@ -363,7 +358,7 @@
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/ldm3d_diffusion
|
||||
title: LDM3D Text-to-(RGB, Depth), Text-to-(RGB-pano, Depth-pano), LDM3D Upscaler
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/adapter
|
||||
title: T2I-Adapter
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion T2I-Adapter
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/gligen
|
||||
title: GLIGEN (Grounded Language-to-Image Generation)
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion
|
||||
@@ -382,7 +377,6 @@
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/wuerstchen
|
||||
title: Wuerstchen
|
||||
title: Pipelines
|
||||
isExpanded: false
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
@@ -443,7 +437,6 @@
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/vq_diffusion
|
||||
title: VQDiffusionScheduler
|
||||
title: Schedulers
|
||||
isExpanded: false
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/internal_classes_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
@@ -457,8 +450,5 @@
|
||||
title: Utilities
|
||||
- local: api/image_processor
|
||||
title: VAE Image Processor
|
||||
- local: api/video_processor
|
||||
title: Video Processor
|
||||
title: Internal classes
|
||||
isExpanded: false
|
||||
title: API
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,231 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Outpainting
|
||||
|
||||
Outpainting extends an image beyond its original boundaries, allowing you to add, replace, or modify visual elements in an image while preserving the original image. Like [inpainting](../using-diffusers/inpaint), you want to fill the white area (in this case, the area outside of the original image) with new visual elements while keeping the original image (represented by a mask of black pixels). There are a couple of ways to outpaint, such as with a [ControlNet](https://hf.co/blog/OzzyGT/outpainting-controlnet) or with [Differential Diffusion](https://hf.co/blog/OzzyGT/outpainting-differential-diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to outpaint with an inpainting model, ControlNet, and a ZoeDepth estimator.
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, make sure you have the [controlnet_aux](https://github.com/huggingface/controlnet_aux) library installed so you can use the ZoeDepth estimator.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
!pip install -q controlnet_aux
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Image preparation
|
||||
|
||||
Start by picking an image to outpaint with and remove the background with a Space like [BRIA-RMBG-1.4](https://hf.co/spaces/briaai/BRIA-RMBG-1.4).
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://briaai-bria-rmbg-1-4.hf.space"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="450"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
For example, remove the background from this image of a pair of shoes.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex flex-row gap-4">
|
||||
<div class="flex-1">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/stevhliu/testing-images/resolve/main/original-jordan.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">original image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="flex-1">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/stevhliu/testing-images/resolve/main/no-background-jordan.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">background removed</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
[Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL)](../using-diffusers/sdxl) models work best with 1024x1024 images, but you can resize the image to any size as long as your hardware has enough memory to support it. The transparent background in the image should also be replaced with a white background. Create a function (like the one below) that scales and pastes the image onto a white background.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from controlnet_aux import ZoeDetector
|
||||
from PIL import Image, ImageOps
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import (
|
||||
AutoencoderKL,
|
||||
ControlNetModel,
|
||||
StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline,
|
||||
StableDiffusionXLInpaintPipeline,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def scale_and_paste(original_image):
|
||||
aspect_ratio = original_image.width / original_image.height
|
||||
|
||||
if original_image.width > original_image.height:
|
||||
new_width = 1024
|
||||
new_height = round(new_width / aspect_ratio)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
new_height = 1024
|
||||
new_width = round(new_height * aspect_ratio)
|
||||
|
||||
resized_original = original_image.resize((new_width, new_height), Image.LANCZOS)
|
||||
white_background = Image.new("RGBA", (1024, 1024), "white")
|
||||
x = (1024 - new_width) // 2
|
||||
y = (1024 - new_height) // 2
|
||||
white_background.paste(resized_original, (x, y), resized_original)
|
||||
|
||||
return resized_original, white_background
|
||||
|
||||
original_image = Image.open(
|
||||
requests.get(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/stevhliu/testing-images/resolve/main/no-background-jordan.png",
|
||||
stream=True,
|
||||
).raw
|
||||
).convert("RGBA")
|
||||
resized_img, white_bg_image = scale_and_paste(original_image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To avoid adding unwanted extra details, use the ZoeDepth estimator to provide additional guidance during generation and to ensure the shoes remain consistent with the original image.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
zoe = ZoeDetector.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/Annotators")
|
||||
image_zoe = zoe(white_bg_image, detect_resolution=512, image_resolution=1024)
|
||||
image_zoe
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/stevhliu/testing-images/resolve/main/zoedepth-jordan.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Outpaint
|
||||
|
||||
Once your image is ready, you can generate content in the white area around the shoes with [controlnet-inpaint-dreamer-sdxl](https://hf.co/destitech/controlnet-inpaint-dreamer-sdxl), a SDXL ControlNet trained for inpainting.
|
||||
|
||||
Load the inpainting ControlNet, ZoeDepth model, VAE and pass them to the [`StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline`]. Then you can create an optional `generate_image` function (for convenience) to outpaint an initial image.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
controlnets = [
|
||||
ControlNetModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"destitech/controlnet-inpaint-dreamer-sdxl", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16"
|
||||
),
|
||||
ControlNetModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"diffusers/controlnet-zoe-depth-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
),
|
||||
]
|
||||
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained("madebyollin/sdxl-vae-fp16-fix", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"SG161222/RealVisXL_V4.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16", controlnet=controlnets, vae=vae
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
def generate_image(prompt, negative_prompt, inpaint_image, zoe_image, seed: int = None):
|
||||
if seed is None:
|
||||
seed = random.randint(0, 2**32 - 1)
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
|
||||
image=[inpaint_image, zoe_image],
|
||||
guidance_scale=6.5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
controlnet_conditioning_scale=[0.5, 0.8],
|
||||
control_guidance_end=[0.9, 0.6],
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "nike air jordans on a basketball court"
|
||||
negative_prompt = ""
|
||||
|
||||
temp_image = generate_image(prompt, negative_prompt, white_bg_image, image_zoe, 908097)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Paste the original image over the initial outpainted image. You'll improve the outpainted background in a later step.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
x = (1024 - resized_img.width) // 2
|
||||
y = (1024 - resized_img.height) // 2
|
||||
temp_image.paste(resized_img, (x, y), resized_img)
|
||||
temp_image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/stevhliu/testing-images/resolve/main/initial-outpaint.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Now is a good time to free up some memory if you're running low!
|
||||
>
|
||||
> ```py
|
||||
> pipeline=None
|
||||
> torch.cuda.empty_cache()
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you have an initial outpainted image, load the [`StableDiffusionXLInpaintPipeline`] with the [RealVisXL](https://hf.co/SG161222/RealVisXL_V4.0) model to generate the final outpainted image with better quality.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionXLInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"OzzyGT/RealVisXL_V4.0_inpainting",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
vae=vae,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Prepare a mask for the final outpainted image. To create a more natural transition between the original image and the outpainted background, blur the mask to help it blend better.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
mask = Image.new("L", temp_image.size)
|
||||
mask.paste(resized_img.split()[3], (x, y))
|
||||
mask = ImageOps.invert(mask)
|
||||
final_mask = mask.point(lambda p: p > 128 and 255)
|
||||
mask_blurred = pipeline.mask_processor.blur(final_mask, blur_factor=20)
|
||||
mask_blurred
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/stevhliu/testing-images/resolve/main/blurred-mask.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Create a better prompt and pass it to the `generate_outpaint` function to generate the final outpainted image. Again, paste the original image over the final outpainted background.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def generate_outpaint(prompt, negative_prompt, image, mask, seed: int = None):
|
||||
if seed is None:
|
||||
seed = random.randint(0, 2**32 - 1)
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
|
||||
image=image,
|
||||
mask_image=mask,
|
||||
guidance_scale=10.0,
|
||||
strength=0.8,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=30,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "high quality photo of nike air jordans on a basketball court, highly detailed"
|
||||
negative_prompt = ""
|
||||
|
||||
final_image = generate_outpaint(prompt, negative_prompt, temp_image, mask_blurred, 7688778)
|
||||
x = (1024 - resized_img.width) // 2
|
||||
y = (1024 - resized_img.height) // 2
|
||||
final_image.paste(resized_img, (x, y), resized_img)
|
||||
final_image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/stevhliu/testing-images/resolve/main/final-outpaint.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
@@ -55,6 +55,3 @@ An attention processor is a class for applying different types of attention mech
|
||||
|
||||
## XFormersAttnProcessor
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.attention_processor.XFormersAttnProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
## AttnProcessorNPU
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.attention_processor.AttnProcessorNPU
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,11 +25,3 @@ All pipelines with [`VaeImageProcessor`] accept PIL Image, PyTorch tensor, or Nu
|
||||
The [`VaeImageProcessorLDM3D`] accepts RGB and depth inputs and returns RGB and depth outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processor.VaeImageProcessorLDM3D
|
||||
|
||||
## PixArtImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processor.PixArtImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
## IPAdapterMaskProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processor.IPAdapterMaskProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,48 +12,26 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Single files
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~loaders.FromSingleFileMixin.from_single_file`] method allows you to load:
|
||||
Diffusers supports loading pretrained pipeline (or model) weights stored in a single file, such as a `ckpt` or `safetensors` file. These single file types are typically produced from community trained models. There are three classes for loading single file weights:
|
||||
|
||||
* a model stored in a single file, which is useful if you're working with models from the diffusion ecosystem, like Automatic1111, and commonly rely on a single-file layout to store and share models
|
||||
* a model stored in their originally distributed layout, which is useful if you're working with models finetuned with other services, and want to load it directly into Diffusers model objects and pipelines
|
||||
- [`FromSingleFileMixin`] supports loading pretrained pipeline weights stored in a single file, which can either be a `ckpt` or `safetensors` file.
|
||||
- [`FromOriginalVAEMixin`] supports loading a pretrained [`AutoencoderKL`] from pretrained ControlNet weights stored in a single file, which can either be a `ckpt` or `safetensors` file.
|
||||
- [`FromOriginalControlnetMixin`] supports loading pretrained ControlNet weights stored in a single file, which can either be a `ckpt` or `safetensors` file.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Read the [Model files and layouts](../../using-diffusers/other-formats) guide to learn more about the Diffusers-multifolder layout versus the single-file layout, and how to load models stored in these different layouts.
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported pipelines
|
||||
To learn more about how to load single file weights, see the [Load different Stable Diffusion formats](../../using-diffusers/other-formats) loading guide.
|
||||
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionControlNetImg2ImgPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionControlNetInpaintPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionUpscalePipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionXLPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionXLInpaintPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionXLInstructPix2PixPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionXLKDiffusionPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`LatentConsistencyModelPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`LatentConsistencyModelImg2ImgPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionControlNetXSPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionXLControlNetXSPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`LEditsPPPipelineStableDiffusion`]
|
||||
- [`LEditsPPPipelineStableDiffusionXL`]
|
||||
- [`PIAPipeline`]
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported models
|
||||
|
||||
- [`UNet2DConditionModel`]
|
||||
- [`StableCascadeUNet`]
|
||||
- [`AutoencoderKL`]
|
||||
- [`ControlNetModel`]
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## FromSingleFileMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] loaders.single_file.FromSingleFileMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## FromOriginalModelMixin
|
||||
## FromOriginalVAEMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] loaders.single_file_model.FromOriginalModelMixin
|
||||
[[autodoc]] loaders.autoencoder.FromOriginalVAEMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## FromOriginalControlnetMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] loaders.controlnet.FromOriginalControlNetMixin
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# ControlNetModel
|
||||
# ControlNet
|
||||
|
||||
The ControlNet model was introduced in [Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://huggingface.co/papers/2302.05543) by Lvmin Zhang, Anyi Rao, Maneesh Agrawala. It provides a greater degree of control over text-to-image generation by conditioning the model on additional inputs such as edge maps, depth maps, segmentation maps, and keypoints for pose detection.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# DiTTransformer2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
A Transformer model for image-like data from [DiT](https://huggingface.co/papers/2212.09748).
|
||||
|
||||
## DiTTransformer2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DiTTransformer2DModel
|
||||
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# HunyuanDiT2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
A Diffusion Transformer model for 2D data from [Hunyuan-DiT](https://github.com/Tencent/HunyuanDiT).
|
||||
|
||||
## HunyuanDiT2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HunyuanDiT2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PixArtTransformer2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
A Transformer model for image-like data from [PixArt-Alpha](https://huggingface.co/papers/2310.00426) and [PixArt-Sigma](https://huggingface.co/papers/2403.04692).
|
||||
|
||||
## PixArtTransformer2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PixArtTransformer2DModel
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PriorTransformer
|
||||
# Prior Transformer
|
||||
|
||||
The Prior Transformer was originally introduced in [Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://huggingface.co/papers/2204.06125) by Ramesh et al. It is used to predict CLIP image embeddings from CLIP text embeddings; image embeddings are predicted through a denoising diffusion process.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Transformer2DModel
|
||||
# Transformer2D
|
||||
|
||||
A Transformer model for image-like data from [CompVis](https://huggingface.co/CompVis) that is based on the [Vision Transformer](https://huggingface.co/papers/2010.11929) introduced by Dosovitskiy et al. The [`Transformer2DModel`] accepts discrete (classes of vector embeddings) or continuous (actual embeddings) inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# TransformerTemporalModel
|
||||
# Transformer Temporal
|
||||
|
||||
A Transformer model for video-like data.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,4 +24,4 @@ The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
## VQEncoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.autoencoders.vq_model.VQEncoderOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.vq_model.VQEncoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ aMUSEd was introduced in [aMUSEd: An Open MUSE Reproduction](https://huggingface
|
||||
|
||||
Amused is a lightweight text to image model based off of the [MUSE](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.00704) architecture. Amused is particularly useful in applications that require a lightweight and fast model such as generating many images quickly at once.
|
||||
|
||||
Amused is a vqvae token based transformer that can generate an image in fewer forward passes than many diffusion models. In contrast with muse, it uses the smaller text encoder CLIP-L/14 instead of t5-xxl. Due to its small parameter count and few forward pass generation process, amused can generate many images quickly. This benefit is seen particularly at larger batch sizes.
|
||||
Amused is a vqvae token based transformer that can generate an image in fewer forward passes than many diffusion models. In contrast with muse, it uses the smaller text encoder CLIP-L/14 instead of t5-xxl. Due to its small parameter count and few forward pass generation process, amused can generate many images quickly. This benefit is seen particularly at larger batch sizes.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -101,53 +101,6 @@ AnimateDiff tends to work better with finetuned Stable Diffusion models. If you
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### AnimateDiffSDXLPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
AnimateDiff can also be used with SDXL models. This is currently an experimental feature as only a beta release of the motion adapter checkpoint is available.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers.models import MotionAdapter
|
||||
from diffusers import AnimateDiffSDXLPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_gif
|
||||
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-sdxl-beta", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
|
||||
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id,
|
||||
subfolder="scheduler",
|
||||
clip_sample=False,
|
||||
timestep_spacing="linspace",
|
||||
beta_schedule="linear",
|
||||
steps_offset=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffSDXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id,
|
||||
motion_adapter=adapter,
|
||||
scheduler=scheduler,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# enable memory savings
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_tiling()
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipe(
|
||||
prompt="a panda surfing in the ocean, realistic, high quality",
|
||||
negative_prompt="low quality, worst quality",
|
||||
num_inference_steps=20,
|
||||
guidance_scale=8,
|
||||
width=1024,
|
||||
height=1024,
|
||||
num_frames=16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
frames = output.frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_gif(frames, "animation.gif")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### AnimateDiffVideoToVideoPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
AnimateDiff can also be used to generate visually similar videos or enable style/character/background or other edits starting from an initial video, allowing you to seamlessly explore creative possibilities.
|
||||
@@ -165,7 +118,7 @@ from PIL import Image
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5-2", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
# load SD 1.5 based finetuned model
|
||||
model_id = "SG161222/Realistic_Vision_V5.1_noVAE"
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffVideoToVideoPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, motion_adapter=adapter, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffVideoToVideoPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, motion_adapter=adapter, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id,
|
||||
subfolder="scheduler",
|
||||
@@ -569,12 +522,6 @@ export_to_gif(frames, "animatelcm-motion-lora.gif")
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## AnimateDiffSDXLPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AnimateDiffSDXLPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## AnimateDiffVideoToVideoPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AnimateDiffVideoToVideoPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,8 +20,7 @@ The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Although audio generation shares commonalities across different types of audio, such as speech, music, and sound effects, designing models for each type requires careful consideration of specific objectives and biases that can significantly differ from those of other types. To bring us closer to a unified perspective of audio generation, this paper proposes a framework that utilizes the same learning method for speech, music, and sound effect generation. Our framework introduces a general representation of audio, called "language of audio" (LOA). Any audio can be translated into LOA based on AudioMAE, a self-supervised pre-trained representation learning model. In the generation process, we translate any modalities into LOA by using a GPT-2 model, and we perform self-supervised audio generation learning with a latent diffusion model conditioned on LOA. The proposed framework naturally brings advantages such as in-context learning abilities and reusable self-supervised pretrained AudioMAE and latent diffusion models. Experiments on the major benchmarks of text-to-audio, text-to-music, and text-to-speech demonstrate state-of-the-art or competitive performance against previous approaches. Our code, pretrained model, and demo are available at [this https URL](https://audioldm.github.io/audioldm2).*
|
||||
|
||||
This pipeline was contributed by [sanchit-gandhi](https://huggingface.co/sanchit-gandhi) and [Nguyễn Công Tú Anh](https://github.com/tuanh123789). The original codebase can be
|
||||
found at [haoheliu/audioldm2](https://github.com/haoheliu/audioldm2).
|
||||
This pipeline was contributed by [sanchit-gandhi](https://huggingface.co/sanchit-gandhi). The original codebase can be found at [haoheliu/audioldm2](https://github.com/haoheliu/audioldm2).
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,8 +36,6 @@ See table below for details on the three checkpoints:
|
||||
| [audioldm2](https://huggingface.co/cvssp/audioldm2) | Text-to-audio | 350M | 1.1B | 1150k |
|
||||
| [audioldm2-large](https://huggingface.co/cvssp/audioldm2-large) | Text-to-audio | 750M | 1.5B | 1150k |
|
||||
| [audioldm2-music](https://huggingface.co/cvssp/audioldm2-music) | Text-to-music | 350M | 1.1B | 665k |
|
||||
| [audioldm2-gigaspeech](https://huggingface.co/anhnct/audioldm2_gigaspeech) | Text-to-speech | 350M | 1.1B |10k |
|
||||
| [audioldm2-ljspeech](https://huggingface.co/anhnct/audioldm2_ljspeech) | Text-to-speech | 350M | 1.1B | |
|
||||
|
||||
### Constructing a prompt
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -56,7 +53,7 @@ See table below for details on the three checkpoints:
|
||||
* The quality of the generated waveforms can vary significantly based on the seed. Try generating with different seeds until you find a satisfactory generation.
|
||||
* Multiple waveforms can be generated in one go: set `num_waveforms_per_prompt` to a value greater than 1. Automatic scoring will be performed between the generated waveforms and prompt text, and the audios ranked from best to worst accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
The following example demonstrates how to construct good music and speech generation using the aforementioned tips: [example](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/audioldm2#diffusers.AudioLDM2Pipeline.__call__.example).
|
||||
The following example demonstrates how to construct good music generation using the aforementioned tips: [example](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/audioldm2#diffusers.AudioLDM2Pipeline.__call__.example).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,10 +12,42 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# AutoPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
The `AutoPipeline` is designed to make it easy to load a checkpoint for a task without needing to know the specific pipeline class. Based on the task, the `AutoPipeline` automatically retrieves the correct pipeline class from the checkpoint `model_index.json` file.
|
||||
`AutoPipeline` is designed to:
|
||||
|
||||
1. make it easy for you to load a checkpoint for a task without knowing the specific pipeline class to use
|
||||
2. use multiple pipelines in your workflow
|
||||
|
||||
Based on the task, the `AutoPipeline` class automatically retrieves the relevant pipeline given the name or path to the pretrained weights with the `from_pretrained()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
To seamlessly switch between tasks with the same checkpoint without reallocating additional memory, use the `from_pipe()` method to transfer the components from the original pipeline to the new one.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=25).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [AutoPipeline](../../tutorials/autopipeline) tutorial to learn how to use this API!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
`AutoPipeline` supports text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting for the following diffusion models:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion/overview)
|
||||
- [ControlNet](./controlnet)
|
||||
- [Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL)](./stable_diffusion/stable_diffusion_xl)
|
||||
- [DeepFloyd IF](./deepfloyd_if)
|
||||
- [Kandinsky 2.1](./kandinsky)
|
||||
- [Kandinsky 2.2](./kandinsky_v22)
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Check out the [AutoPipeline](../../tutorials/autopipeline) tutorial to learn how to use this API!
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Hunyuan-DiT
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Hunyuan-DiT : A Powerful Multi-Resolution Diffusion Transformer with Fine-Grained Chinese Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.08748) from Tencent Hunyuan.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*We present Hunyuan-DiT, a text-to-image diffusion transformer with fine-grained understanding of both English and Chinese. To construct Hunyuan-DiT, we carefully design the transformer structure, text encoder, and positional encoding. We also build from scratch a whole data pipeline to update and evaluate data for iterative model optimization. For fine-grained language understanding, we train a Multimodal Large Language Model to refine the captions of the images. Finally, Hunyuan-DiT can perform multi-turn multimodal dialogue with users, generating and refining images according to the context. Through our holistic human evaluation protocol with more than 50 professional human evaluators, Hunyuan-DiT sets a new state-of-the-art in Chinese-to-image generation compared with other open-source models.*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can find the original codebase at [Tencent/HunyuanDiT](https://github.com/Tencent/HunyuanDiT) and all the available checkpoints at [Tencent-Hunyuan](https://huggingface.co/Tencent-Hunyuan/HunyuanDiT).
|
||||
|
||||
**Highlights**: HunyuanDiT supports Chinese/English-to-image, multi-resolution generation.
|
||||
|
||||
HunyuanDiT has the following components:
|
||||
* It uses a diffusion transformer as the backbone
|
||||
* It combines two text encoders, a bilingual CLIP and a multilingual T5 encoder
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers.md) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading.md#reuse-a-pipeline) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
You can optimize the pipeline's runtime and memory consumption with torch.compile and feed-forward chunking. To learn about other optimization methods, check out the [Speed up inference](../../optimization/fp16) and [Reduce memory usage](../../optimization/memory) guides.
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Use [`torch.compile`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/tutorials/fast_diffusion#torchcompile) to reduce the inference latency.
|
||||
|
||||
First, load the pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import HunyuanDiTPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = HunyuanDiTPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"Tencent-Hunyuan/HunyuanDiT-Diffusers", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then change the memory layout of the pipelines `transformer` and `vae` components to `torch.channels-last`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.transformer.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
pipeline.vae.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, compile the components and run inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.transformer = torch.compile(pipeline.transformer, mode="max-autotune", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
pipeline.vae.decode = torch.compile(pipeline.vae.decode, mode="max-autotune", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt="一个宇航员在骑马").images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The [benchmark](https://gist.github.com/sayakpaul/29d3a14905cfcbf611fe71ebd22e9b23) results on a 80GB A100 machine are:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
With torch.compile(): Average inference time: 12.470 seconds.
|
||||
Without torch.compile(): Average inference time: 20.570 seconds.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory optimization
|
||||
|
||||
By loading the T5 text encoder in 8 bits, you can run the pipeline in just under 6 GBs of GPU VRAM. Refer to [this script](https://gist.github.com/sayakpaul/3154605f6af05b98a41081aaba5ca43e) for details.
|
||||
|
||||
Furthermore, you can use the [`~HunyuanDiT2DModel.enable_forward_chunking`] method to reduce memory usage. Feed-forward chunking runs the feed-forward layers in a transformer block in a loop instead of all at once. This gives you a trade-off between memory consumption and inference runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
+ pipeline.transformer.enable_forward_chunking(chunk_size=1, dim=1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## HunyuanDiTPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HunyuanDiTPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,7 +47,6 @@ Sample output with I2VGenXL:
|
||||
* Unlike SVD, it additionally accepts text prompts as inputs.
|
||||
* It can generate higher resolution videos.
|
||||
* When using the [`DDIMScheduler`] (which is default for this pipeline), less than 50 steps for inference leads to bad results.
|
||||
* This implementation is 1-stage variant of I2VGenXL. The main figure in the [I2VGen-XL](https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.04145) paper shows a 2-stage variant, however, 1-stage variant works well. See [this discussion](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/discussions/7952) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
## I2VGenXLPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] I2VGenXLPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,12 +11,12 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
Kandinsky 3 is created by [Vladimir Arkhipkin](https://github.com/oriBetelgeuse),[Anastasia Maltseva](https://github.com/NastyaMittseva),[Igor Pavlov](https://github.com/boomb0om),[Andrei Filatov](https://github.com/anvilarth),[Arseniy Shakhmatov](https://github.com/cene555),[Andrey Kuznetsov](https://github.com/kuznetsoffandrey),[Denis Dimitrov](https://github.com/denndimitrov), [Zein Shaheen](https://github.com/zeinsh)
|
||||
|
||||
The description from it's Github page:
|
||||
The description from it's Github page:
|
||||
|
||||
*Kandinsky 3.0 is an open-source text-to-image diffusion model built upon the Kandinsky2-x model family. In comparison to its predecessors, enhancements have been made to the text understanding and visual quality of the model, achieved by increasing the size of the text encoder and Diffusion U-Net models, respectively.*
|
||||
|
||||
Its architecture includes 3 main components:
|
||||
1. [FLAN-UL2](https://huggingface.co/google/flan-ul2), which is an encoder decoder model based on the T5 architecture.
|
||||
1. [FLAN-UL2](https://huggingface.co/google/flan-ul2), which is an encoder decoder model based on the T5 architecture.
|
||||
2. New U-Net architecture featuring BigGAN-deep blocks doubles depth while maintaining the same number of parameters.
|
||||
3. Sber-MoVQGAN is a decoder proven to have superior results in image restoration.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,11 +25,11 @@ You can find additional information about LEDITS++ on the [project page](https:/
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
Due to some backward compatability issues with the current diffusers implementation of [`~schedulers.DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`] this implementation of LEdits++ can no longer guarantee perfect inversion.
|
||||
This issue is unlikely to have any noticeable effects on applied use-cases. However, we provide an alternative implementation that guarantees perfect inversion in a dedicated [GitHub repo](https://github.com/ml-research/ledits_pp).
|
||||
Due to some backward compatability issues with the current diffusers implementation of [`~schedulers.DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`] this implementation of LEdits++ can no longer guarantee perfect inversion.
|
||||
This issue is unlikely to have any noticeable effects on applied use-cases. However, we provide an alternative implementation that guarantees perfect inversion in a dedicated [GitHub repo](https://github.com/ml-research/ledits_pp).
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
We provide two distinct pipelines based on different pre-trained models.
|
||||
We provide two distinct pipelines based on different pre-trained models.
|
||||
|
||||
## LEditsPPPipelineStableDiffusion
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.ledits_pp.LEditsPPPipelineStableDiffusion
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 Marigold authors and The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Marigold Pipelines for Computer Vision Tasks
|
||||
|
||||
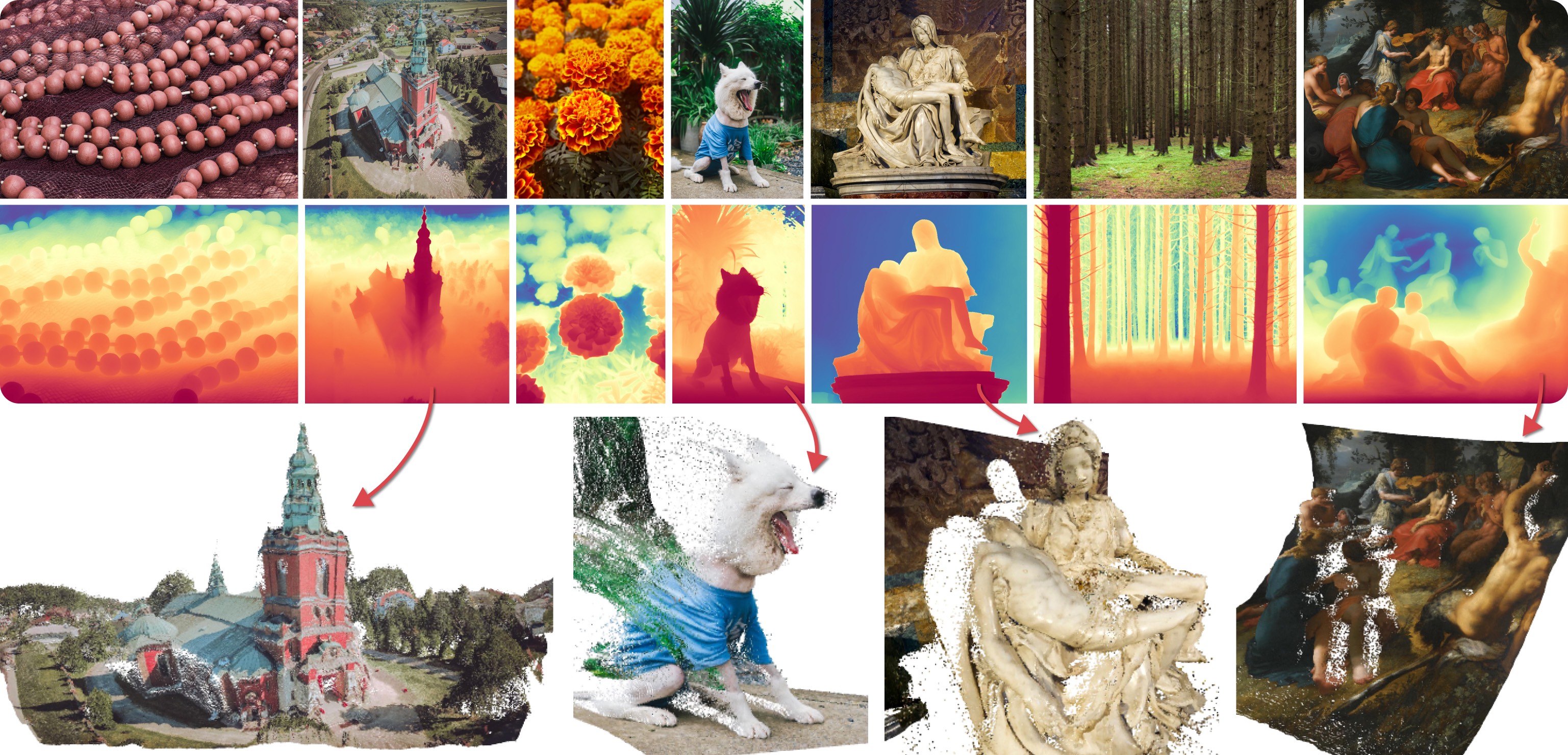

|
||||
|
||||
Marigold was proposed in [Repurposing Diffusion-Based Image Generators for Monocular Depth Estimation](https://huggingface.co/papers/2312.02145), a CVPR 2024 Oral paper by [Bingxin Ke](http://www.kebingxin.com/), [Anton Obukhov](https://www.obukhov.ai/), [Shengyu Huang](https://shengyuh.github.io/), [Nando Metzger](https://nandometzger.github.io/), [Rodrigo Caye Daudt](https://rcdaudt.github.io/), and [Konrad Schindler](https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=FZuNgqIAAAAJ&hl=en).
|
||||
The idea is to repurpose the rich generative prior of Text-to-Image Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) for traditional computer vision tasks.
|
||||
Initially, this idea was explored to fine-tune Stable Diffusion for Monocular Depth Estimation, as shown in the teaser above.
|
||||
Later,
|
||||
- [Tianfu Wang](https://tianfwang.github.io/) trained the first Latent Consistency Model (LCM) of Marigold, which unlocked fast single-step inference;
|
||||
- [Kevin Qu](https://www.linkedin.com/in/kevin-qu-b3417621b/?locale=en_US) extended the approach to Surface Normals Estimation;
|
||||
- [Anton Obukhov](https://www.obukhov.ai/) contributed the pipelines and documentation into diffusers (enabled and supported by [YiYi Xu](https://yiyixuxu.github.io/) and [Sayak Paul](https://sayak.dev/)).
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*Monocular depth estimation is a fundamental computer vision task. Recovering 3D depth from a single image is geometrically ill-posed and requires scene understanding, so it is not surprising that the rise of deep learning has led to a breakthrough. The impressive progress of monocular depth estimators has mirrored the growth in model capacity, from relatively modest CNNs to large Transformer architectures. Still, monocular depth estimators tend to struggle when presented with images with unfamiliar content and layout, since their knowledge of the visual world is restricted by the data seen during training, and challenged by zero-shot generalization to new domains. This motivates us to explore whether the extensive priors captured in recent generative diffusion models can enable better, more generalizable depth estimation. We introduce Marigold, a method for affine-invariant monocular depth estimation that is derived from Stable Diffusion and retains its rich prior knowledge. The estimator can be fine-tuned in a couple of days on a single GPU using only synthetic training data. It delivers state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of datasets, including over 20% performance gains in specific cases. Project page: https://marigoldmonodepth.github.io.*
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Each pipeline supports one Computer Vision task, which takes an input RGB image as input and produces a *prediction* of the modality of interest, such as a depth map of the input image.
|
||||
Currently, the following tasks are implemented:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Predicted Modalities | Demos |
|
||||
|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
|
||||
| [MarigoldDepthPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/marigold/pipeline_marigold_depth.py) | [Depth](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth_map), [Disparity](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binocular_disparity) | [Fast Demo (LCM)](https://huggingface.co/spaces/prs-eth/marigold-lcm), [Slow Original Demo (DDIM)](https://huggingface.co/spaces/prs-eth/marigold) |
|
||||
| [MarigoldNormalsPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/marigold/pipeline_marigold_normals.py) | [Surface normals](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal_mapping) | [Fast Demo (LCM)](https://huggingface.co/spaces/prs-eth/marigold-normals-lcm) |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
The original checkpoints can be found under the [PRS-ETH](https://huggingface.co/prs-eth/) Hugging Face organization.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines. Also, to know more about reducing the memory usage of this pipeline, refer to the ["Reduce memory usage"] section [here](../../using-diffusers/svd#reduce-memory-usage).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Marigold pipelines were designed and tested only with `DDIMScheduler` and `LCMScheduler`.
|
||||
Depending on the scheduler, the number of inference steps required to get reliable predictions varies, and there is no universal value that works best across schedulers.
|
||||
Because of that, the default value of `num_inference_steps` in the `__call__` method of the pipeline is set to `None` (see the API reference).
|
||||
Unless set explicitly, its value will be taken from the checkpoint configuration `model_index.json`.
|
||||
This is done to ensure high-quality predictions when calling the pipeline with just the `image` argument.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
See also Marigold [usage examples](marigold_usage).
|
||||
|
||||
## MarigoldDepthPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MarigoldDepthPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## MarigoldNormalsPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MarigoldNormalsPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## MarigoldDepthOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.marigold.pipeline_marigold_depth.MarigoldDepthOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## MarigoldNormalsOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.marigold.pipeline_marigold_normals.MarigoldNormalsOutput
|
||||
@@ -97,11 +97,6 @@ The table below lists all the pipelines currently available in 🤗 Diffusers an
|
||||
- to
|
||||
- components
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.StableDiffusionMixin.enable_freeu
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.StableDiffusionMixin.disable_freeu
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.pipeline_flax_utils.FlaxDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,13 +31,13 @@ Some notes about this pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers.md) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading.md#reuse-a-pipeline) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference with under 8GB GPU VRAM
|
||||
|
||||
Run the [`PixArtAlphaPipeline`] with under 8GB GPU VRAM by loading the text encoder in 8-bit precision. Let's walk through a full-fledged example.
|
||||
Run the [`PixArtAlphaPipeline`] with under 8GB GPU VRAM by loading the text encoder in 8-bit precision. Let's walk through a full-fledged example.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install the [bitsandbytes](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes) library:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -75,10 +75,10 @@ with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
prompt_embeds, prompt_attention_mask, negative_embeds, negative_prompt_attention_mask = pipe.encode_prompt(prompt)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Since text embeddings have been computed, remove the `text_encoder` and `pipe` from the memory, and free up some GPU VRAM:
|
||||
Since text embeddings have been computed, remove the `text_encoder` and `pipe` from the memory, and free up som GPU VRAM:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
|
||||
def flush():
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
@@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ pipe = PixArtAlphaPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
latents = pipe(
|
||||
negative_prompt=None,
|
||||
negative_prompt=None,
|
||||
prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds,
|
||||
negative_prompt_embeds=negative_embeds,
|
||||
prompt_attention_mask=prompt_attention_mask,
|
||||
@@ -146,3 +146,4 @@ While loading the `text_encoder`, you set `load_in_8bit` to `True`. You could al
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PixArtAlphaPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,149 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PixArt-Σ
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[PixArt-Σ: Weak-to-Strong Training of Diffusion Transformer for 4K Text-to-Image Generation](https://huggingface.co/papers/2403.04692) is Junsong Chen, Jincheng Yu, Chongjian Ge, Lewei Yao, Enze Xie, Yue Wu, Zhongdao Wang, James Kwok, Ping Luo, Huchuan Lu, and Zhenguo Li.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*In this paper, we introduce PixArt-Σ, a Diffusion Transformer model (DiT) capable of directly generating images at 4K resolution. PixArt-Σ represents a significant advancement over its predecessor, PixArt-α, offering images of markedly higher fidelity and improved alignment with text prompts. A key feature of PixArt-Σ is its training efficiency. Leveraging the foundational pre-training of PixArt-α, it evolves from the ‘weaker’ baseline to a ‘stronger’ model via incorporating higher quality data, a process we term “weak-to-strong training”. The advancements in PixArt-Σ are twofold: (1) High-Quality Training Data: PixArt-Σ incorporates superior-quality image data, paired with more precise and detailed image captions. (2) Efficient Token Compression: we propose a novel attention module within the DiT framework that compresses both keys and values, significantly improving efficiency and facilitating ultra-high-resolution image generation. Thanks to these improvements, PixArt-Σ achieves superior image quality and user prompt adherence capabilities with significantly smaller model size (0.6B parameters) than existing text-to-image diffusion models, such as SDXL (2.6B parameters) and SD Cascade (5.1B parameters). Moreover, PixArt-Σ’s capability to generate 4K images supports the creation of high-resolution posters and wallpapers, efficiently bolstering the production of highquality visual content in industries such as film and gaming.*
|
||||
|
||||
You can find the original codebase at [PixArt-alpha/PixArt-sigma](https://github.com/PixArt-alpha/PixArt-sigma) and all the available checkpoints at [PixArt-alpha](https://huggingface.co/PixArt-alpha).
|
||||
|
||||
Some notes about this pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
* It uses a Transformer backbone (instead of a UNet) for denoising. As such it has a similar architecture as [DiT](https://hf.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/dit).
|
||||
* It was trained using text conditions computed from T5. This aspect makes the pipeline better at following complex text prompts with intricate details.
|
||||
* It is good at producing high-resolution images at different aspect ratios. To get the best results, the authors recommend some size brackets which can be found [here](https://github.com/PixArt-alpha/PixArt-sigma/blob/master/diffusion/data/datasets/utils.py).
|
||||
* It rivals the quality of state-of-the-art text-to-image generation systems (as of this writing) such as PixArt-α, Stable Diffusion XL, Playground V2.0 and DALL-E 3, while being more efficient than them.
|
||||
* It shows the ability of generating super high resolution images, such as 2048px or even 4K.
|
||||
* It shows that text-to-image models can grow from a weak model to a stronger one through several improvements (VAEs, datasets, and so on.)
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-a-pipeline) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference with under 8GB GPU VRAM
|
||||
|
||||
Run the [`PixArtSigmaPipeline`] with under 8GB GPU VRAM by loading the text encoder in 8-bit precision. Let's walk through a full-fledged example.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install the [bitsandbytes](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes) library:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -U bitsandbytes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then load the text encoder in 8-bit:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import T5EncoderModel
|
||||
from diffusers import PixArtSigmaPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
text_encoder = T5EncoderModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"PixArt-alpha/PixArt-Sigma-XL-2-1024-MS",
|
||||
subfolder="text_encoder",
|
||||
load_in_8bit=True,
|
||||
device_map="auto",
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = PixArtSigmaPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"PixArt-alpha/PixArt-Sigma-XL-2-1024-MS",
|
||||
text_encoder=text_encoder,
|
||||
transformer=None,
|
||||
device_map="balanced"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, use the `pipe` to encode a prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
prompt = "cute cat"
|
||||
prompt_embeds, prompt_attention_mask, negative_embeds, negative_prompt_attention_mask = pipe.encode_prompt(prompt)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Since text embeddings have been computed, remove the `text_encoder` and `pipe` from the memory, and free up some GPU VRAM:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
|
||||
def flush():
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
|
||||
|
||||
del text_encoder
|
||||
del pipe
|
||||
flush()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then compute the latents with the prompt embeddings as inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe = PixArtSigmaPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"PixArt-alpha/PixArt-Sigma-XL-2-1024-MS",
|
||||
text_encoder=None,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
latents = pipe(
|
||||
negative_prompt=None,
|
||||
prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds,
|
||||
negative_prompt_embeds=negative_embeds,
|
||||
prompt_attention_mask=prompt_attention_mask,
|
||||
negative_prompt_attention_mask=negative_prompt_attention_mask,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt=1,
|
||||
output_type="latent",
|
||||
).images
|
||||
|
||||
del pipe.transformer
|
||||
flush()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that while initializing `pipe`, you're setting `text_encoder` to `None` so that it's not loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Once the latents are computed, pass it off to the VAE to decode into a real image:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
image = pipe.vae.decode(latents / pipe.vae.config.scaling_factor, return_dict=False)[0]
|
||||
image = pipe.image_processor.postprocess(image, output_type="pil")[0]
|
||||
image.save("cat.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By deleting components you aren't using and flushing the GPU VRAM, you should be able to run [`PixArtSigmaPipeline`] with under 8GB GPU VRAM.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you want a report of your memory-usage, run this [script](https://gist.github.com/sayakpaul/3ae0f847001d342af27018a96f467e4e).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Text embeddings computed in 8-bit can impact the quality of the generated images because of the information loss in the representation space caused by the reduced precision. It's recommended to compare the outputs with and without 8-bit.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
While loading the `text_encoder`, you set `load_in_8bit` to `True`. You could also specify `load_in_4bit` to bring your memory requirements down even further to under 7GB.
|
||||
|
||||
## PixArtSigmaPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PixArtSigmaPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,9 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# T2I-Adapter
|
||||
# Text-to-Image Generation with Adapter Conditioning
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[T2I-Adapter: Learning Adapters to Dig out More Controllable Ability for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.08453) by Chong Mou, Xintao Wang, Liangbin Xie, Jian Zhang, Zhongang Qi, Ying Shan, Xiaohu Qie.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,26 +24,236 @@ The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by the community contributor [HimariO](https://github.com/HimariO) ❤️ .
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Demo
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/t2i_adapter/pipeline_stable_diffusion_adapter.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation with T2I-Adapter Conditioning* | -
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/t2i_adapter/pipeline_stable_diffusion_xl_adapter.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation with T2I-Adapter Conditioning on StableDiffusion-XL* | -
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example with the base model of StableDiffusion-1.4/1.5
|
||||
|
||||
In the following we give a simple example of how to use a *T2I-Adapter* checkpoint with Diffusers for inference based on StableDiffusion-1.4/1.5.
|
||||
All adapters use the same pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Images are first converted into the appropriate *control image* format.
|
||||
2. The *control image* and *prompt* are passed to the [`StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
Let's have a look at a simple example using the [Color Adapter](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_color_sd14v1).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/color_ref.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Then we can create our color palette by simply resizing it to 8 by 8 pixels and then scaling it back to original size.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
color_palette = image.resize((8, 8))
|
||||
color_palette = color_palette.resize((512, 512), resample=Image.Resampling.NEAREST)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look at the processed image.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Next, create the adapter pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline, T2IAdapter
|
||||
|
||||
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2iadapter_color_sd14v1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
adapter=adapter,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, pass the prompt and control image to the pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# fix the random seed, so you will get the same result as the example
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(7)
|
||||
|
||||
out_image = pipe(
|
||||
"At night, glowing cubes in front of the beach",
|
||||
image=color_palette,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
make_image_grid([image, color_palette, out_image], rows=1, cols=3)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example with the base model of StableDiffusion-XL
|
||||
|
||||
In the following we give a simple example of how to use a *T2I-Adapter* checkpoint with Diffusers for inference based on StableDiffusion-XL.
|
||||
All adapters use the same pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Images are first downloaded into the appropriate *control image* format.
|
||||
2. The *control image* and *prompt* are passed to the [`StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
Let's have a look at a simple example using the [Sketch Adapter](https://huggingface.co/Adapter/t2iadapter/tree/main/sketch_sdxl_1.0).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
sketch_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/Adapter/t2iadapter/resolve/main/sketch.png").convert("L")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Then, create the adapter pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import (
|
||||
T2IAdapter,
|
||||
StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline,
|
||||
DDPMScheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
|
||||
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("Adapter/t2iadapter", subfolder="sketch_sdxl_1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, adapter_type="full_adapter_xl")
|
||||
scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained(model_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id, adapter=adapter, safety_checker=None, torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16", scheduler=scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, pass the prompt and control image to the pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# fix the random seed, so you will get the same result as the example
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator().manual_seed(42)
|
||||
|
||||
sketch_image_out = pipe(
|
||||
prompt="a photo of a dog in real world, high quality",
|
||||
negative_prompt="extra digit, fewer digits, cropped, worst quality, low quality",
|
||||
image=sketch_image,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
guidance_scale=7.5
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
make_image_grid([sketch_image, sketch_image_out], rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Available checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
Non-diffusers checkpoints can be found under [TencentARC/T2I-Adapter](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/T2I-Adapter/tree/main/models).
|
||||
|
||||
### T2I-Adapter with Stable Diffusion 1.4
|
||||
|
||||
| Model Name | Control Image Overview| Control Image Example | Generated Image Example |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_color_sd14v1](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_color_sd14v1)<br/> *Trained with spatial color palette* | An image with 8x8 color palette.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/color_sample_input.png"><img width="64" style="margin:0;padding:0;" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/color_sample_input.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/color_sample_output.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/color_sample_output.png"/></a>|
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_canny_sd14v1](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_canny_sd14v1)<br/> *Trained with canny edge detection* | A monochrome image with white edges on a black background.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/canny_sample_input.png"><img width="64" style="margin:0;padding:0;" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/canny_sample_input.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/canny_sample_output.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/canny_sample_output.png"/></a>|
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_sketch_sd14v1](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_sketch_sd14v1)<br/> *Trained with [PidiNet](https://github.com/zhuoinoulu/pidinet) edge detection* | A hand-drawn monochrome image with white outlines on a black background.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/sketch_sample_input.png"><img width="64" style="margin:0;padding:0;" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/sketch_sample_input.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/sketch_sample_output.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/sketch_sample_output.png"/></a>|
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_depth_sd14v1](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_depth_sd14v1)<br/> *Trained with Midas depth estimation* | A grayscale image with black representing deep areas and white representing shallow areas.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/depth_sample_input.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/depth_sample_input.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/depth_sample_output.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/depth_sample_output.png"/></a>|
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_openpose_sd14v1](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_openpose_sd14v1)<br/> *Trained with OpenPose bone image* | A [OpenPose bone](https://github.com/CMU-Perceptual-Computing-Lab/openpose) image.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/openpose_sample_input.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/openpose_sample_input.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/openpose_sample_output.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/openpose_sample_output.png"/></a>|
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_keypose_sd14v1](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_keypose_sd14v1)<br/> *Trained with mmpose skeleton image* | A [mmpose skeleton](https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmpose) image.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/keypose_sample_input.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/keypose_sample_input.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/keypose_sample_output.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/keypose_sample_output.png"/></a>|
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_seg_sd14v1](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_seg_sd14v1)<br/>*Trained with semantic segmentation* | An [custom](https://github.com/TencentARC/T2I-Adapter/discussions/25) segmentation protocol image.|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/seg_sample_input.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/seg_sample_input.png"/></a>|<a href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/seg_sample_output.png"><img width="64" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/seg_sample_output.png"/></a> |
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_canny_sd15v2](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_canny_sd15v2)||
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_depth_sd15v2](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_depth_sd15v2)||
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_sketch_sd15v2](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_sketch_sd15v2)||
|
||||
|[TencentARC/t2iadapter_zoedepth_sd15v1](https://huggingface.co/TencentARC/t2iadapter_zoedepth_sd15v1)||
|
||||
|[Adapter/t2iadapter, subfolder='sketch_sdxl_1.0'](https://huggingface.co/Adapter/t2iadapter/tree/main/sketch_sdxl_1.0)||
|
||||
|[Adapter/t2iadapter, subfolder='canny_sdxl_1.0'](https://huggingface.co/Adapter/t2iadapter/tree/main/canny_sdxl_1.0)||
|
||||
|[Adapter/t2iadapter, subfolder='openpose_sdxl_1.0'](https://huggingface.co/Adapter/t2iadapter/tree/main/openpose_sdxl_1.0)||
|
||||
|
||||
## Combining multiple adapters
|
||||
|
||||
[`MultiAdapter`] can be used for applying multiple conditionings at once.
|
||||
|
||||
Here we use the keypose adapter for the character posture and the depth adapter for creating the scene.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
cond_keypose = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/keypose_sample_input.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
cond_depth = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/t2i-adapter/depth_sample_input.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
cond = [cond_keypose, cond_depth]
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = ["A man walking in an office room with a nice view"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The two control images look as such:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
`MultiAdapter` combines keypose and depth adapters.
|
||||
|
||||
`adapter_conditioning_scale` balances the relative influence of the different adapters.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline, MultiAdapter, T2IAdapter
|
||||
|
||||
adapters = MultiAdapter(
|
||||
[
|
||||
T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2iadapter_keypose_sd14v1"),
|
||||
T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2iadapter_depth_sd14v1"),
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
adapters = adapters.to(torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
adapter=adapters,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, cond, adapter_conditioning_scale=[0.8, 0.8]).images[0]
|
||||
make_image_grid([cond_keypose, cond_depth, image], rows=1, cols=3)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## T2I-Adapter vs ControlNet
|
||||
|
||||
T2I-Adapter is similar to [ControlNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/controlnet).
|
||||
T2I-Adapter uses a smaller auxiliary network which is only run once for the entire diffusion process.
|
||||
However, T2I-Adapter performs slightly worse than ControlNet.
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- disable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- enable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- disable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- enable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- disable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- enable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- disable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- enable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -177,7 +177,7 @@ inpaint = StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline(**text2img.components)
|
||||
|
||||
The Stable Diffusion pipelines are automatically supported in [Gradio](https://github.com/gradio-app/gradio/), a library that makes creating beautiful and user-friendly machine learning apps on the web a breeze. First, make sure you have Gradio installed:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install -U gradio
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -209,4 +209,4 @@ gr.Interface.from_pipeline(pipe).launch()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the web demo runs on a local server. If you'd like to share it with others, you can generate a temporary public
|
||||
link by setting `share=True` in `launch()`. Or, you can host your demo on [Hugging Face Spaces](https://huggingface.co/spaces)https://huggingface.co/spaces for a permanent link.
|
||||
link by setting `share=True` in `launch()`. Or, you can host your demo on [Hugging Face Spaces](https://huggingface.co/spaces)https://huggingface.co/spaces for a permanent link.
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# EDMDPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
`EDMDPMSolverMultistepScheduler` is a [Karras formulation](https://huggingface.co/papers/2206.00364) of `DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`, a multistep scheduler from [DPM-Solver: A Fast ODE Solver for Diffusion Probabilistic Model Sampling in Around 10 Steps](https://huggingface.co/papers/2206.00927) and [DPM-Solver++: Fast Solver for Guided Sampling of Diffusion Probabilistic Models](https://huggingface.co/papers/2211.01095) by Cheng Lu, Yuhao Zhou, Fan Bao, Jianfei Chen, Chongxuan Li, and Jun Zhu.
|
||||
`EDMDPMSolverMultistepScheduler` is a [Karras formulation](https://huggingface.co/papers/2206.00364) of `DPMSolverMultistep`, a multistep scheduler from [DPM-Solver: A Fast ODE Solver for Diffusion Probabilistic Model Sampling in Around 10 Steps](https://huggingface.co/papers/2206.00927) and [DPM-Solver++: Fast Solver for Guided Sampling of Diffusion Probabilistic Models](https://huggingface.co/papers/2211.01095) by Cheng Lu, Yuhao Zhou, Fan Bao, Jianfei Chen, Chongxuan Li, and Jun Zhu.
|
||||
|
||||
DPMSolver (and the improved version DPMSolver++) is a fast dedicated high-order solver for diffusion ODEs with convergence order guarantee. Empirically, DPMSolver sampling with only 20 steps can generate high-quality
|
||||
samples, and it can generate quite good samples even in 10 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler` is a multistep scheduler from [DPM-Solver: A Fast ODE Solver for Diffusion Probabilistic Model Sampling in Around 10 Steps](https://huggingface.co/papers/2206.00927) and [DPM-Solver++: Fast Solver for Guided Sampling of Diffusion Probabilistic Models](https://huggingface.co/papers/2211.01095) by Cheng Lu, Yuhao Zhou, Fan Bao, Jianfei Chen, Chongxuan Li, and Jun Zhu.
|
||||
`DPMSolverMultistep` is a multistep scheduler from [DPM-Solver: A Fast ODE Solver for Diffusion Probabilistic Model Sampling in Around 10 Steps](https://huggingface.co/papers/2206.00927) and [DPM-Solver++: Fast Solver for Guided Sampling of Diffusion Probabilistic Models](https://huggingface.co/papers/2211.01095) by Cheng Lu, Yuhao Zhou, Fan Bao, Jianfei Chen, Chongxuan Li, and Jun Zhu.
|
||||
|
||||
DPMSolver (and the improved version DPMSolver++) is a fast dedicated high-order solver for diffusion ODEs with convergence order guarantee. Empirically, DPMSolver sampling with only 20 steps can generate high-quality
|
||||
samples, and it can generate quite good samples even in 10 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +37,3 @@ Utility and helper functions for working with 🤗 Diffusers.
|
||||
## make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
## randn_tensor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.torch_utils.randn_tensor
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Video Processor
|
||||
|
||||
The [`VideoProcessor`] provides a unified API for video pipelines to prepare inputs for VAE encoding and post-processing outputs once they're decoded. The class inherits [`VaeImageProcessor`] so it includes transformations such as resizing, normalization, and conversion between PIL Image, PyTorch, and NumPy arrays.
|
||||
|
||||
## VideoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] video_processor.VideoProcessor.preprocess_video
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] video_processor.VideoProcessor.postprocess_video
|
||||
@@ -198,81 +198,38 @@ Anything displayed on [the official Diffusers doc page](https://huggingface.co/d
|
||||
|
||||
Please have a look at [this page](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs) on how to verify changes made to the documentation locally.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Read the [Community pipelines](../using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview#community-pipelines) guide to learn more about the difference between a GitHub and Hugging Face Hub community pipeline. If you're interested in why we have community pipelines, take a look at GitHub Issue [#841](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841) (basically, we can't maintain all the possible ways diffusion models can be used for inference but we also don't want to prevent the community from building them).
|
||||
[Pipelines](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/overview) are usually the first point of contact between the Diffusers library and the user.
|
||||
Pipelines are examples of how to use Diffusers [models](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models/overview) and [schedulers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/schedulers/overview).
|
||||
We support two types of pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
Contributing a community pipeline is a great way to share your creativity and work with the community. It lets you build on top of the [`DiffusionPipeline`] so that anyone can load and use it by setting the `custom_pipeline` parameter. This section will walk you through how to create a simple pipeline where the UNet only does a single forward pass and calls the scheduler once (a "one-step" pipeline).
|
||||
- Official Pipelines
|
||||
- Community Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a one_step_unet.py file for your community pipeline. This file can contain whatever package you want to use as long as it's installed by the user. Make sure you only have one pipeline class that inherits from [`DiffusionPipeline`] to load model weights and the scheduler configuration from the Hub. Add a UNet and scheduler to the `__init__` function.
|
||||
Both official and community pipelines follow the same design and consist of the same type of components.
|
||||
|
||||
You should also add the `register_modules` function to ensure your pipeline and its components can be saved with [`~DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`].
|
||||
Official pipelines are tested and maintained by the core maintainers of Diffusers. Their code
|
||||
resides in [src/diffusers/pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines).
|
||||
In contrast, community pipelines are contributed and maintained purely by the **community** and are **not** tested.
|
||||
They reside in [examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) and while they can be accessed via the [PyPI diffusers package](https://pypi.org/project/diffusers/), their code is not part of the PyPI distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
The reason for the distinction is that the core maintainers of the Diffusers library cannot maintain and test all
|
||||
possible ways diffusion models can be used for inference, but some of them may be of interest to the community.
|
||||
Officially released diffusion pipelines,
|
||||
such as Stable Diffusion are added to the core src/diffusers/pipelines package which ensures
|
||||
high quality of maintenance, no backward-breaking code changes, and testing.
|
||||
More bleeding edge pipelines should be added as community pipelines. If usage for a community pipeline is high, the pipeline can be moved to the official pipelines upon request from the community. This is one of the ways we strive to be a community-driven library.
|
||||
|
||||
class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
To add a community pipeline, one should add a <name-of-the-community>.py file to [examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) and adapt the [examples/community/README.md](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community/README.md) to include an example of the new pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
|
||||
```
|
||||
An example can be seen [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/2400).
|
||||
|
||||
1. In the forward pass (which we recommend defining as `__call__`), you can add any feature you'd like. For the "one-step" pipeline, create a random image and call the UNet and scheduler once by setting `timestep=1`.
|
||||
Community pipeline PRs are only checked at a superficial level and ideally they should be maintained by their original authors.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
|
||||
self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self):
|
||||
image = torch.randn(
|
||||
(1, self.unet.config.in_channels, self.unet.config.sample_size, self.unet.config.sample_size),
|
||||
)
|
||||
timestep = 1
|
||||
|
||||
model_output = self.unet(image, timestep).sample
|
||||
scheduler_output = self.scheduler.step(model_output, timestep, image).prev_sample
|
||||
|
||||
return scheduler_output
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can run the pipeline by passing a UNet and scheduler to it or load pretrained weights if the pipeline structure is identical.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = DDPMScheduler()
|
||||
unet = UNet2DModel()
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
|
||||
output = pipeline()
|
||||
# load pretrained weights
|
||||
pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cifar10-32", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
output = pipeline()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can either share your pipeline as a GitHub community pipeline or Hub community pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="pipeline type">
|
||||
<hfoption id="GitHub pipeline">
|
||||
|
||||
Share your GitHub pipeline by opening a pull request on the Diffusers [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) and add the one_step_unet.py file to the [examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) subfolder.
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Hub pipeline">
|
||||
|
||||
Share your Hub pipeline by creating a model repository on the Hub and uploading the one_step_unet.py file to it.
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
Contributing a community pipeline is a great way to understand how Diffusers models and schedulers work. Having contributed a community pipeline is usually the first stepping stone to contributing an official pipeline to the
|
||||
core package.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Contribute to training examples
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Pipelines should be used **only** for inference.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be very readable, self-explanatory, and easy to tweak.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be designed to build on top of each other and be easy to integrate into higher-level APIs.
|
||||
- Pipelines are **not** intended to be feature-complete user interfaces. For feature-complete user interfaces one should rather have a look at [InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI), [Diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers), and [lama-cleaner](https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner).
|
||||
- Pipelines are **not** intended to be feature-complete user interfaces. For future complete user interfaces one should rather have a look at [InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI), [Diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers), and [lama-cleaner](https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner).
|
||||
- Every pipeline should have one and only one way to run it via a `__call__` method. The naming of the `__call__` arguments should be shared across all pipelines.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be named after the task they are intended to solve.
|
||||
- In almost all cases, novel diffusion pipelines shall be implemented in a new pipeline folder/file.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ pip install -e ".[flax]"
|
||||
|
||||
These commands will link the folder you cloned the repository to and your Python library paths.
|
||||
Python will now look inside the folder you cloned to in addition to the normal library paths.
|
||||
For example, if your Python packages are typically installed in `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.10/site-packages/`, Python will also search the `~/diffusers/` folder you cloned to.
|
||||
For example, if your Python packages are typically installed in `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.8/site-packages/`, Python will also search the `~/diffusers/` folder you cloned to.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ Then load and enable the [`DeepCacheSDHelper`](https://github.com/horseee/DeepCa
|
||||
image = pipe("a photo of an astronaut on a moon").images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `set_params` method accepts two arguments: `cache_interval` and `cache_branch_id`. `cache_interval` means the frequency of feature caching, specified as the number of steps between each cache operation. `cache_branch_id` identifies which branch of the network (ordered from the shallowest to the deepest layer) is responsible for executing the caching processes.
|
||||
The `set_params` method accepts two arguments: `cache_interval` and `cache_branch_id`. `cache_interval` means the frequency of feature caching, specified as the number of steps between each cache operation. `cache_branch_id` identifies which branch of the network (ordered from the shallowest to the deepest layer) is responsible for executing the caching processes.
|
||||
Opting for a lower `cache_branch_id` or a larger `cache_interval` can lead to faster inference speed at the expense of reduced image quality (ablation experiments of these two hyperparameters can be found in the [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.00858)). Once those arguments are set, use the `enable` or `disable` methods to activate or deactivate the `DeepCacheSDHelper`.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,23 +12,27 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Speed up inference
|
||||
|
||||
There are several ways to optimize Diffusers for inference speed, such as reducing the computational burden by lowering the data precision or using a lightweight distilled model. There are also memory-efficient attention implementations, [xFormers](xformers) and [scaled dot product attention](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html) in PyTorch 2.0, that reduce memory usage which also indirectly speeds up inference. Different speed optimizations can be stacked together to get the fastest inference times.
|
||||
There are several ways to optimize 🤗 Diffusers for inference speed. As a general rule of thumb, we recommend using either [xFormers](xformers) or `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention` in PyTorch 2.0 for their memory-efficient attention.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Optimizing for inference speed or reduced memory usage can lead to improved performance in the other category, so you should try to optimize for both whenever you can. This guide focuses on inference speed, but you can learn more about lowering memory usage in the [Reduce memory usage](memory) guide.
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The inference times below are obtained from generating a single 512x512 image from the prompt "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars" with 50 DDIM steps on a NVIDIA A100.
|
||||
In many cases, optimizing for speed or memory leads to improved performance in the other, so you should try to optimize for both whenever you can. This guide focuses on inference speed, but you can learn more about preserving memory in the [Reduce memory usage](memory) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
| setup | latency | speed-up |
|
||||
|----------|---------|----------|
|
||||
| baseline | 5.27s | x1 |
|
||||
| tf32 | 4.14s | x1.27 |
|
||||
| fp16 | 3.51s | x1.50 |
|
||||
| combined | 3.41s | x1.54 |
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## TensorFloat-32
|
||||
The results below are obtained from generating a single 512x512 image from the prompt `a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars` with 50 DDIM steps on a Nvidia Titan RTX, demonstrating the speed-up you can expect.
|
||||
|
||||
On Ampere and later CUDA devices, matrix multiplications and convolutions can use the [TensorFloat-32 (tf32)](https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2020/05/14/tensorfloat-32-precision-format/) mode for faster, but slightly less accurate computations. By default, PyTorch enables tf32 mode for convolutions but not matrix multiplications. Unless your network requires full float32 precision, we recommend enabling tf32 for matrix multiplications. It can significantly speed up computations with typically negligible loss in numerical accuracy.
|
||||
| | latency | speed-up |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------- |
|
||||
| original | 9.50s | x1 |
|
||||
| fp16 | 3.61s | x2.63 |
|
||||
| channels last | 3.30s | x2.88 |
|
||||
| traced UNet | 3.21s | x2.96 |
|
||||
| memory efficient attention | 2.63s | x3.61 |
|
||||
|
||||
## Use TensorFloat-32
|
||||
|
||||
On Ampere and later CUDA devices, matrix multiplications and convolutions can use the [TensorFloat-32 (TF32)](https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2020/05/14/tensorfloat-32-precision-format/) mode for faster, but slightly less accurate computations. By default, PyTorch enables TF32 mode for convolutions but not matrix multiplications. Unless your network requires full float32 precision, we recommend enabling TF32 for matrix multiplications. It can significantly speeds up computations with typically negligible loss in numerical accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -36,11 +40,11 @@ import torch
|
||||
torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Learn more about tf32 in the [Mixed precision training](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/perf_train_gpu_one#tf32) guide.
|
||||
You can learn more about TF32 in the [Mixed precision training](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/perf_train_gpu_one#tf32) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
## Half-precision weights
|
||||
|
||||
To save GPU memory and get more speed, set `torch_dtype=torch.float16` to load and run the model weights directly with half-precision weights.
|
||||
To save GPU memory and get more speed, try loading and running the model weights directly in half-precision or float16:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -52,76 +56,19 @@ pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Don't use [torch.autocast](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/amp.html#torch.autocast) in any of the pipelines as it can lead to black images and is always slower than pure float16 precision.
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Don't use [`torch.autocast`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/amp.html#torch.autocast) in any of the pipelines as it can lead to black images and is always slower than pure float16 precision.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Distilled model
|
||||
|
||||
You could also use a distilled Stable Diffusion model and autoencoder to speed up inference. During distillation, many of the UNet's residual and attention blocks are shed to reduce the model size by 51% and improve latency on CPU/GPU by 43%. The distilled model is faster and uses less memory while generating images of comparable quality to the full Stable Diffusion model.
|
||||
You could also use a distilled Stable Diffusion model and autoencoder to speed up inference. During distillation, many of the UNet's residual and attention blocks are shed to reduce the model size. The distilled model is faster and uses less memory while generating images of comparable quality to the full Stable Diffusion model.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Read the [Open-sourcing Knowledge Distillation Code and Weights of SD-Small and SD-Tiny](https://huggingface.co/blog/sd_distillation) blog post to learn more about how knowledge distillation training works to produce a faster, smaller, and cheaper generative model.
|
||||
|
||||
The inference times below are obtained from generating 4 images from the prompt "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars" with 25 PNDM steps on a NVIDIA A100. Each generation is repeated 3 times with the distilled Stable Diffusion v1.4 model by [Nota AI](https://hf.co/nota-ai).
|
||||
|
||||
| setup | latency | speed-up |
|
||||
|------------------------------|---------|----------|
|
||||
| baseline | 6.37s | x1 |
|
||||
| distilled | 4.18s | x1.52 |
|
||||
| distilled + tiny autoencoder | 3.83s | x1.66 |
|
||||
|
||||
Let's load the distilled Stable Diffusion model and compare it against the original Stable Diffusion model.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
distilled = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"nota-ai/bk-sdm-small", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
prompt = "a golden vase with different flowers"
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(2023)
|
||||
image = distilled("a golden vase with different flowers", num_inference_steps=25, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/original_sd.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">original Stable Diffusion</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/distilled_sd.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">distilled Stable Diffusion</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### Tiny AutoEncoder
|
||||
|
||||
To speed inference up even more, replace the autoencoder with a [distilled version](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/taesdxl-diffusers) of it.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoencoderTiny, StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
distilled = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"nota-ai/bk-sdm-small", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
distilled.vae = AutoencoderTiny.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"sayakpaul/taesd-diffusers", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a golden vase with different flowers"
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(2023)
|
||||
image = distilled("a golden vase with different flowers", num_inference_steps=25, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/distilled_sd_vae.png" />
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">distilled Stable Diffusion + Tiny AutoEncoder</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
Learn more about in the [Distilled Stable Diffusion inference](../using-diffusers/distilled_sd) guide!
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -261,7 +261,7 @@ from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class UNet2DConditionOutput:
|
||||
sample: torch.Tensor
|
||||
sample: torch.FloatTensor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
|
||||
17
docs/source/en/optimization/opt_overview.md
Normal file
17
docs/source/en/optimization/opt_overview.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Generating high-quality outputs is computationally intensive, especially during each iterative step where you go from a noisy output to a less noisy output. One of 🤗 Diffuser's goals is to make this technology widely accessible to everyone, which includes enabling fast inference on consumer and specialized hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
This section will cover tips and tricks - like half-precision weights and sliced attention - for optimizing inference speed and reducing memory-consumption. You'll also learn how to speed up your PyTorch code with [`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html) or [ONNX Runtime](https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/), and enable memory-efficient attention with [xFormers](https://facebookresearch.github.io/xformers/). There are also guides for running inference on specific hardware like Apple Silicon, and Intel or Habana processors.
|
||||
@@ -1,182 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# T-GATE
|
||||
|
||||
[T-GATE](https://github.com/HaozheLiu-ST/T-GATE/tree/main) accelerates inference for [Stable Diffusion](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview), [PixArt](../api/pipelines/pixart), and [Latency Consistency Model](../api/pipelines/latent_consistency_models.md) pipelines by skipping the cross-attention calculation once it converges. This method doesn't require any additional training and it can speed up inference from 10-50%. T-GATE is also compatible with other optimization methods like [DeepCache](./deepcache).
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, make sure you install T-GATE.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install tgate
|
||||
pip install -U torch diffusers transformers accelerate DeepCache
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To use T-GATE with a pipeline, you need to use its corresponding loader.
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | T-GATE Loader |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| PixArt | TgatePixArtLoader |
|
||||
| Stable Diffusion XL | TgateSDXLLoader |
|
||||
| Stable Diffusion XL + DeepCache | TgateSDXLDeepCacheLoader |
|
||||
| Stable Diffusion | TgateSDLoader |
|
||||
| Stable Diffusion + DeepCache | TgateSDDeepCacheLoader |
|
||||
|
||||
Next, create a `TgateLoader` with a pipeline, the gate step (the time step to stop calculating the cross attention), and the number of inference steps. Then call the `tgate` method on the pipeline with a prompt, gate step, and the number of inference steps.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's see how to enable this for several different pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="pipelines">
|
||||
<hfoption id="PixArt">
|
||||
|
||||
Accelerate `PixArtAlphaPipeline` with T-GATE:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import PixArtAlphaPipeline
|
||||
from tgate import TgatePixArtLoader
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = PixArtAlphaPipeline.from_pretrained("PixArt-alpha/PixArt-XL-2-1024-MS", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
gate_step = 8
|
||||
inference_step = 25
|
||||
pipe = TgatePixArtLoader(
|
||||
pipe,
|
||||
gate_step=gate_step,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=inference_step,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe.tgate(
|
||||
"An alpaca made of colorful building blocks, cyberpunk.",
|
||||
gate_step=gate_step,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=inference_step,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Stable Diffusion XL">
|
||||
|
||||
Accelerate `StableDiffusionXLPipeline` with T-GATE:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
from tgate import TgateSDXLLoader
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
gate_step = 10
|
||||
inference_step = 25
|
||||
pipe = TgateSDXLLoader(
|
||||
pipe,
|
||||
gate_step=gate_step,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=inference_step,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe.tgate(
|
||||
"Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k.",
|
||||
gate_step=gate_step,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=inference_step
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="StableDiffusionXL with DeepCache">
|
||||
|
||||
Accelerate `StableDiffusionXLPipeline` with [DeepCache](https://github.com/horseee/DeepCache) and T-GATE:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
from tgate import TgateSDXLDeepCacheLoader
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
gate_step = 10
|
||||
inference_step = 25
|
||||
pipe = TgateSDXLDeepCacheLoader(
|
||||
pipe,
|
||||
cache_interval=3,
|
||||
cache_branch_id=0,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe.tgate(
|
||||
"Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k.",
|
||||
gate_step=gate_step,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=inference_step
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Latent Consistency Model">
|
||||
|
||||
Accelerate `latent-consistency/lcm-sdxl` with T-GATE:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import UNet2DConditionModel, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
from tgate import TgateSDXLLoader
|
||||
|
||||
unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"latent-consistency/lcm-sdxl",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
unet=unet,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
gate_step = 1
|
||||
inference_step = 4
|
||||
pipe = TgateSDXLLoader(
|
||||
pipe,
|
||||
gate_step=gate_step,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=inference_step,
|
||||
lcm=True
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe.tgate(
|
||||
"Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k.",
|
||||
gate_step=gate_step,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=inference_step
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
T-GATE also supports [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] and [PixArt-alpha/PixArt-LCM-XL-2-1024-MS](https://hf.co/PixArt-alpha/PixArt-LCM-XL-2-1024-MS).
|
||||
|
||||
## Benchmarks
|
||||
| Model | MACs | Param | Latency | Zero-shot 10K-FID on MS-COCO |
|
||||
|-----------------------|----------|-----------|---------|---------------------------|
|
||||
| SD-1.5 | 16.938T | 859.520M | 7.032s | 23.927 |
|
||||
| SD-1.5 w/ T-GATE | 9.875T | 815.557M | 4.313s | 20.789 |
|
||||
| SD-2.1 | 38.041T | 865.785M | 16.121s | 22.609 |
|
||||
| SD-2.1 w/ T-GATE | 22.208T | 815.433 M | 9.878s | 19.940 |
|
||||
| SD-XL | 149.438T | 2.570B | 53.187s | 24.628 |
|
||||
| SD-XL w/ T-GATE | 84.438T | 2.024B | 27.932s | 22.738 |
|
||||
| Pixart-Alpha | 107.031T | 611.350M | 61.502s | 38.669 |
|
||||
| Pixart-Alpha w/ T-GATE | 65.318T | 462.585M | 37.867s | 35.825 |
|
||||
| DeepCache (SD-XL) | 57.888T | - | 19.931s | 23.755 |
|
||||
| DeepCache w/ T-GATE | 43.868T | - | 14.666s | 23.999 |
|
||||
| LCM (SD-XL) | 11.955T | 2.570B | 3.805s | 25.044 |
|
||||
| LCM w/ T-GATE | 11.171T | 2.024B | 3.533s | 25.028 |
|
||||
| LCM (Pixart-Alpha) | 8.563T | 611.350M | 4.733s | 36.086 |
|
||||
| LCM w/ T-GATE | 7.623T | 462.585M | 4.543s | 37.048 |
|
||||
|
||||
The latency is tested on an NVIDIA 1080TI, MACs and Params are calculated with [calflops](https://github.com/MrYxJ/calculate-flops.pytorch), and the FID is calculated with [PytorchFID](https://github.com/mseitzer/pytorch-fid).
|
||||
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ One of the simplest ways to speed up inference is to place the pipeline on a GPU
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To make sure you can use the same image and improve on it, use a [`Generator`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html) and set a seed for [reproducibility](./using-diffusers/reusing_seeds):
|
||||
To make sure you can use the same image and improve on it, use a [`Generator`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.Generator.html) and set a seed for [reproducibility](./using-diffusers/reproducibility):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
@@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ Many of the basic parameters are described in the [DreamBooth](dreambooth#script
|
||||
- `--freeze_model`: freezes the key and value parameters in the cross-attention layer; the default is `crossattn_kv`, but you can set it to `crossattn` to train all the parameters in the cross-attention layer
|
||||
- `--concepts_list`: to learn multiple concepts, provide a path to a JSON file containing the concepts
|
||||
- `--modifier_token`: a special word used to represent the learned concept
|
||||
- `--initializer_token`: a special word used to initialize the embeddings of the `modifier_token`
|
||||
- `--initializer_token`:
|
||||
|
||||
### Prior preservation loss
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -52,76 +52,6 @@ To learn more, take a look at the [Distributed Inference with 🤗 Accelerate](h
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Device placement
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> This feature is experimental and its APIs might change in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
With Accelerate, you can use the `device_map` to determine how to distribute the models of a pipeline across multiple devices. This is useful in situations where you have more than one GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you have two 8GB GPUs, then using [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload`] may not work so well because:
|
||||
|
||||
* it only works on a single GPU
|
||||
* a single model might not fit on a single GPU ([`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_sequential_cpu_offload`] might work but it will be extremely slow and it is also limited to a single GPU)
|
||||
|
||||
To make use of both GPUs, you can use the "balanced" device placement strategy which splits the models across all available GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Only the "balanced" strategy is supported at the moment, and we plan to support additional mapping strategies in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
- "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
+ "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True, device_map="balanced"
|
||||
)
|
||||
image = pipeline("a dog").images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also pass a dictionary to enforce the maximum GPU memory that can be used on each device:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
max_memory = {0:"1GB", 1:"1GB"}
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
device_map="balanced",
|
||||
+ max_memory=max_memory
|
||||
)
|
||||
image = pipeline("a dog").images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If a device is not present in `max_memory`, then it will be completely ignored and will not participate in the device placement.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Diffusers uses the maximum memory of all devices. If the models don't fit on the GPUs, they are offloaded to the CPU. If the CPU doesn't have enough memory, then you might see an error. In that case, you could defer to using [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_sequential_cpu_offload`] and [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload`].
|
||||
|
||||
Call [`~DiffusionPipeline.reset_device_map`] to reset the `device_map` of a pipeline. This is also necessary if you want to use methods like `to()`, [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_sequential_cpu_offload`], and [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload`] on a pipeline that was device-mapped.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.reset_device_map()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once a pipeline has been device-mapped, you can also access its device map via `hf_device_map`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
print(pipeline.hf_device_map)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
An example device map would look like so:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
{'unet': 1, 'vae': 1, 'safety_checker': 0, 'text_encoder': 0}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## PyTorch Distributed
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch supports [`DistributedDataParallel`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel.html) which enables data parallelism.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
@@ -180,7 +180,7 @@ elif args.pretrained_model_name_or_path:
|
||||
revision=args.revision,
|
||||
use_fast=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Load scheduler and models
|
||||
noise_scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained(args.pretrained_model_name_or_path, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
text_encoder = text_encoder_cls.from_pretrained(
|
||||
@@ -440,198 +440,6 @@ Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL) is a powerful text-to-image model that generates high
|
||||
|
||||
The SDXL training script is discussed in more detail in the [SDXL training](sdxl) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
## DeepFloyd IF
|
||||
|
||||
DeepFloyd IF is a cascading pixel diffusion model with three stages. The first stage generates a base image and the second and third stages progressively upscales the base image into a high-resolution 1024x1024 image. Use the [train_dreambooth_lora.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth_lora.py) or [train_dreambooth.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py) scripts to train a DeepFloyd IF model with LoRA or the full model.
|
||||
|
||||
DeepFloyd IF uses predicted variance, but the Diffusers training scripts uses predicted error so the trained DeepFloyd IF models are switched to a fixed variance schedule. The training scripts will update the scheduler config of the fully trained model for you. However, when you load the saved LoRA weights you must also update the pipeline's scheduler config.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("DeepFloyd/IF-I-XL-v1.0", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("<lora weights path>")
|
||||
|
||||
# Update scheduler config to fixed variance schedule
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = pipe.scheduler.__class__.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config, variance_type="fixed_small")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The stage 2 model requires additional validation images to upscale. You can download and use a downsized version of the training images for this.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
|
||||
|
||||
local_dir = "./dog_downsized"
|
||||
snapshot_download(
|
||||
"diffusers/dog-example-downsized",
|
||||
local_dir=local_dir,
|
||||
repo_type="dataset",
|
||||
ignore_patterns=".gitattributes",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The code samples below provide a brief overview of how to train a DeepFloyd IF model with a combination of DreamBooth and LoRA. Some important parameters to note are:
|
||||
|
||||
* `--resolution=64`, a much smaller resolution is required because DeepFloyd IF is a pixel diffusion model and to work on uncompressed pixels, the input images must be smaller
|
||||
* `--pre_compute_text_embeddings`, compute the text embeddings ahead of time to save memory because the [`~transformers.T5Model`] can take up a lot of memory
|
||||
* `--tokenizer_max_length=77`, you can use a longer default text length with T5 as the text encoder but the default model encoding procedure uses a shorter text length
|
||||
* `--text_encoder_use_attention_mask`, to pass the attention mask to the text encoder
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="IF-DreamBooth">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Stage 1 LoRA DreamBooth">
|
||||
|
||||
Training stage 1 of DeepFloyd IF with LoRA and DreamBooth requires ~28GB of memory.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="DeepFloyd/IF-I-XL-v1.0"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="dog"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="dreambooth_dog_lora"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_dreambooth_lora.py \
|
||||
--report_to wandb \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--instance_prompt="a sks dog" \
|
||||
--resolution=64 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=4 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=1 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=5e-6 \
|
||||
--scale_lr \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=1200 \
|
||||
--validation_prompt="a sks dog" \
|
||||
--validation_epochs=25 \
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=100 \
|
||||
--pre_compute_text_embeddings \
|
||||
--tokenizer_max_length=77 \
|
||||
--text_encoder_use_attention_mask
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Stage 2 LoRA DreamBooth">
|
||||
|
||||
For stage 2 of DeepFloyd IF with LoRA and DreamBooth, pay attention to these parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
* `--validation_images`, the images to upscale during validation
|
||||
* `--class_labels_conditioning=timesteps`, to additionally conditional the UNet as needed in stage 2
|
||||
* `--learning_rate=1e-6`, a lower learning rate is used compared to stage 1
|
||||
* `--resolution=256`, the expected resolution for the upscaler
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="DeepFloyd/IF-II-L-v1.0"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="dog"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="dreambooth_dog_upscale"
|
||||
export VALIDATION_IMAGES="dog_downsized/image_1.png dog_downsized/image_2.png dog_downsized/image_3.png dog_downsized/image_4.png"
|
||||
|
||||
python train_dreambooth_lora.py \
|
||||
--report_to wandb \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--instance_prompt="a sks dog" \
|
||||
--resolution=256 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=4 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=1 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-6 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=2000 \
|
||||
--validation_prompt="a sks dog" \
|
||||
--validation_epochs=100 \
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=500 \
|
||||
--pre_compute_text_embeddings \
|
||||
--tokenizer_max_length=77 \
|
||||
--text_encoder_use_attention_mask \
|
||||
--validation_images $VALIDATION_IMAGES \
|
||||
--class_labels_conditioning=timesteps
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Stage 1 DreamBooth">
|
||||
|
||||
For stage 1 of DeepFloyd IF with DreamBooth, pay attention to these parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
* `--skip_save_text_encoder`, to skip saving the full T5 text encoder with the finetuned model
|
||||
* `--use_8bit_adam`, to use 8-bit Adam optimizer to save memory due to the size of the optimizer state when training the full model
|
||||
* `--learning_rate=1e-7`, a really low learning rate should be used for full model training otherwise the model quality is degraded (you can use a higher learning rate with a larger batch size)
|
||||
|
||||
Training with 8-bit Adam and a batch size of 4, the full model can be trained with ~48GB of memory.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="DeepFloyd/IF-I-XL-v1.0"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="dog"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="dreambooth_if"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--instance_prompt="a photo of sks dog" \
|
||||
--resolution=64 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=4 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=1 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-7 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=150 \
|
||||
--validation_prompt "a photo of sks dog" \
|
||||
--validation_steps 25 \
|
||||
--text_encoder_use_attention_mask \
|
||||
--tokenizer_max_length 77 \
|
||||
--pre_compute_text_embeddings \
|
||||
--use_8bit_adam \
|
||||
--set_grads_to_none \
|
||||
--skip_save_text_encoder \
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Stage 2 DreamBooth">
|
||||
|
||||
For stage 2 of DeepFloyd IF with DreamBooth, pay attention to these parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
* `--learning_rate=5e-6`, use a lower learning rate with a smaller effective batch size
|
||||
* `--resolution=256`, the expected resolution for the upscaler
|
||||
* `--train_batch_size=2` and `--gradient_accumulation_steps=6`, to effectively train on images wiht faces requires larger batch sizes
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="DeepFloyd/IF-II-L-v1.0"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="dog"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="dreambooth_dog_upscale"
|
||||
export VALIDATION_IMAGES="dog_downsized/image_1.png dog_downsized/image_2.png dog_downsized/image_3.png dog_downsized/image_4.png"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--report_to wandb \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--instance_prompt="a sks dog" \
|
||||
--resolution=256 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=2 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=6 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=5e-6 \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=2000 \
|
||||
--validation_prompt="a sks dog" \
|
||||
--validation_steps=150 \
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=500 \
|
||||
--pre_compute_text_embeddings \
|
||||
--tokenizer_max_length=77 \
|
||||
--text_encoder_use_attention_mask \
|
||||
--validation_images $VALIDATION_IMAGES \
|
||||
--class_labels_conditioning timesteps \
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
### Training tips
|
||||
|
||||
Training the DeepFloyd IF model can be challenging, but here are some tips that we've found helpful:
|
||||
|
||||
- LoRA is sufficient for training the stage 1 model because the model's low resolution makes representing finer details difficult regardless.
|
||||
- For common or simple objects, you don't necessarily need to finetune the upscaler. Make sure the prompt passed to the upscaler is adjusted to remove the new token from the instance prompt. For example, if your stage 1 prompt is "a sks dog" then your stage 2 prompt should be "a dog".
|
||||
- For finer details like faces, fully training the stage 2 upscaler is better than training the stage 2 model with LoRA. It also helps to use lower learning rates with larger batch sizes.
|
||||
- Lower learning rates should be used to train the stage 2 model.
|
||||
- The [`DDPMScheduler`] works better than the DPMSolver used in the training scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
Congratulations on training your DreamBooth model! To learn more about how to use your new model, the following guide may be helpful:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
@@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ The dataset preprocessing code and training loop are found in the [`main()`](htt
|
||||
|
||||
As with the script parameters, a walkthrough of the training script is provided in the [Text-to-image](text2image#training-script) training guide. Instead, this guide takes a look at the InstructPix2Pix relevant parts of the script.
|
||||
|
||||
The script begins by modifying the [number of input channels](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/64603389da01082055a901f2883c4810d1144edb/examples/instruct_pix2pix/train_instruct_pix2pix.py#L445) in the first convolutional layer of the UNet to account for InstructPix2Pix's additional conditioning image:
|
||||
The script begins by modifing the [number of input channels](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/64603389da01082055a901f2883c4810d1144edb/examples/instruct_pix2pix/train_instruct_pix2pix.py#L445) in the first convolutional layer of the UNet to account for InstructPix2Pix's additional conditioning image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
in_channels = 8
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
@@ -205,7 +205,7 @@ model_pred = unet(noisy_latents, timesteps, None, added_cond_kwargs=added_cond_k
|
||||
|
||||
Once you’ve made all your changes or you’re okay with the default configuration, you’re ready to launch the training script! 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
You'll train on the [Naruto BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions) dataset to generate your own Naruto characters, but you can also create and train on your own dataset by following the [Create a dataset for training](create_dataset) guide. Set the environment variable `DATASET_NAME` to the name of the dataset on the Hub or if you're training on your own files, set the environment variable `TRAIN_DIR` to a path to your dataset.
|
||||
You'll train on the [Pokémon BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions) dataset to generate your own Pokémon, but you can also create and train on your own dataset by following the [Create a dataset for training](create_dataset) guide. Set the environment variable `DATASET_NAME` to the name of the dataset on the Hub or if you're training on your own files, set the environment variable `TRAIN_DIR` to a path to your dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re training on more than one GPU, add the `--multi_gpu` parameter to the `accelerate launch` command.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -219,7 +219,7 @@ To monitor training progress with Weights & Biases, add the `--report_to=wandb`
|
||||
<hfoption id="prior model">
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions"
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image_prior.py \
|
||||
--dataset_name=$DATASET_NAME \
|
||||
@@ -232,17 +232,17 @@ accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image_prior.py \
|
||||
--checkpoints_total_limit=3 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler="constant" \
|
||||
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--validation_prompts="A robot naruto, 4k photo" \
|
||||
--validation_prompts="A robot pokemon, 4k photo" \
|
||||
--report_to="wandb" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub \
|
||||
--output_dir="kandi2-prior-naruto-model"
|
||||
--output_dir="kandi2-prior-pokemon-model"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="decoder model">
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions"
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image_decoder.py \
|
||||
--dataset_name=$DATASET_NAME \
|
||||
@@ -256,10 +256,10 @@ accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image_decoder.py \
|
||||
--checkpoints_total_limit=3 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler="constant" \
|
||||
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--validation_prompts="A robot naruto, 4k photo" \
|
||||
--validation_prompts="A robot pokemon, 4k photo" \
|
||||
--report_to="wandb" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub \
|
||||
--output_dir="kandi2-decoder-naruto-model"
|
||||
--output_dir="kandi2-decoder-pokemon-model"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
@@ -279,7 +279,7 @@ prior_components = {"prior_" + k: v for k,v in prior_pipeline.components.items()
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", **prior_components, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
prompt="A robot naruto, 4k photo"
|
||||
prompt="A robot pokemon, 4k photo"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -299,7 +299,7 @@ import torch
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("path/to/saved/model", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt="A robot naruto, 4k photo"
|
||||
prompt="A robot pokemon, 4k photo"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt=prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -313,7 +313,7 @@ unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained("path/to/saved/model" + "/checkpoint
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", unet=unet, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt="A robot naruto, 4k photo").images[0]
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt="A robot pokemon, 4k photo").images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
@@ -252,4 +252,4 @@ The SDXL training script is discussed in more detail in the [SDXL training](sdxl
|
||||
Congratulations on distilling a LCM model! To learn more about LCM, the following may be helpful:
|
||||
|
||||
- Learn how to use [LCMs for inference](../using-diffusers/lcm) for text-to-image, image-to-image, and with LoRA checkpoints.
|
||||
- Read the [SDXL in 4 steps with Latent Consistency LoRAs](https://huggingface.co/blog/lcm_lora) blog post to learn more about SDXL LCM-LoRA's for super fast inference, quality comparisons, benchmarks, and more.
|
||||
- Read the [SDXL in 4 steps with Latent Consistency LoRAs](https://huggingface.co/blog/lcm_lora) blog post to learn more about SDXL LCM-LoRA's for super fast inference, quality comparisons, benchmarks, and more.
|
||||
@@ -170,7 +170,7 @@ Aside from setting up the LoRA layers, the training script is more or less the s
|
||||
|
||||
Once you've made all your changes or you're okay with the default configuration, you're ready to launch the training script! 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
Let's train on the [Naruto BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions) dataset to generate your own Naruto characters. Set the environment variables `MODEL_NAME` and `DATASET_NAME` to the model and dataset respectively. You should also specify where to save the model in `OUTPUT_DIR`, and the name of the model to save to on the Hub with `HUB_MODEL_ID`. The script creates and saves the following files to your repository:
|
||||
Let's train on the [Pokémon BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions) dataset to generate our own Pokémon. Set the environment variables `MODEL_NAME` and `DATASET_NAME` to the model and dataset respectively. You should also specify where to save the model in `OUTPUT_DIR`, and the name of the model to save to on the Hub with `HUB_MODEL_ID`. The script creates and saves the following files to your repository:
|
||||
|
||||
- saved model checkpoints
|
||||
- `pytorch_lora_weights.safetensors` (the trained LoRA weights)
|
||||
@@ -185,9 +185,9 @@ A full training run takes ~5 hours on a 2080 Ti GPU with 11GB of VRAM.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="/sddata/finetune/lora/naruto"
|
||||
export HUB_MODEL_ID="naruto-lora"
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="/sddata/finetune/lora/pokemon"
|
||||
export HUB_MODEL_ID="pokemon-lora"
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image_lora.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
@@ -208,7 +208,7 @@ accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image_lora.py \
|
||||
--hub_model_id=${HUB_MODEL_ID} \
|
||||
--report_to=wandb \
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=500 \
|
||||
--validation_prompt="A naruto with blue eyes." \
|
||||
--validation_prompt="A pokemon with blue eyes." \
|
||||
--seed=1337
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -220,7 +220,7 @@ import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights("path/to/lora/model", weight_name="pytorch_lora_weights.safetensors")
|
||||
image = pipeline("A naruto with blue eyes").images[0]
|
||||
image = pipeline("A pokemon with blue eyes").images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
@@ -176,7 +176,7 @@ If you want to learn more about how the training loop works, check out the [Unde
|
||||
|
||||
Once you’ve made all your changes or you’re okay with the default configuration, you’re ready to launch the training script! 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s train on the [Naruto BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions) dataset to generate your own Naruto characters. Set the environment variables `MODEL_NAME` and `DATASET_NAME` to the model and the dataset (either from the Hub or a local path). You should also specify a VAE other than the SDXL VAE (either from the Hub or a local path) with `VAE_NAME` to avoid numerical instabilities.
|
||||
Let’s train on the [Pokémon BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions) dataset to generate your own Pokémon. Set the environment variables `MODEL_NAME` and `DATASET_NAME` to the model and the dataset (either from the Hub or a local path). You should also specify a VAE other than the SDXL VAE (either from the Hub or a local path) with `VAE_NAME` to avoid numerical instabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -187,7 +187,7 @@ To monitor training progress with Weights & Biases, add the `--report_to=wandb`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
|
||||
export VAE_NAME="madebyollin/sdxl-vae-fp16-fix"
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions"
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_text_to_image_sdxl.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
@@ -211,7 +211,7 @@ accelerate launch train_text_to_image_sdxl.py \
|
||||
--validation_prompt="a cute Sundar Pichai creature" \
|
||||
--validation_epochs 5 \
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps=5000 \
|
||||
--output_dir="sdxl-naruto-model" \
|
||||
--output_dir="sdxl-pokemon-model" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -226,9 +226,9 @@ import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("path/to/your/model", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A naruto with green eyes and red legs."
|
||||
prompt = "A pokemon with green eyes and red legs."
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=30, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
image.save("naruto.png")
|
||||
image.save("pokemon.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
@@ -244,11 +244,11 @@ import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
|
||||
device = xm.xla_device()
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A naruto with green eyes and red legs."
|
||||
prompt = "A pokemon with green eyes and red legs."
|
||||
start = time()
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=inference_steps).images[0]
|
||||
print(f'Compilation time is {time()-start} sec')
|
||||
image.save("naruto.png")
|
||||
image.save("pokemon.png")
|
||||
|
||||
start = time()
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=inference_steps).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
@@ -158,7 +158,7 @@ Once you've made all your changes or you're okay with the default configuration,
|
||||
<hfoptions id="training-inference">
|
||||
<hfoption id="PyTorch">
|
||||
|
||||
Let's train on the [Naruto BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions) dataset to generate your own Naruto characters. Set the environment variables `MODEL_NAME` and `dataset_name` to the model and the dataset (either from the Hub or a local path). If you're training on more than one GPU, add the `--multi_gpu` parameter to the `accelerate launch` command.
|
||||
Let's train on the [Pokémon BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions) dataset to generate your own Pokémon. Set the environment variables `MODEL_NAME` and `dataset_name` to the model and the dataset (either from the Hub or a local path). If you're training on more than one GPU, add the `--multi_gpu` parameter to the `accelerate launch` command.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -168,7 +168,7 @@ To train on a local dataset, set the `TRAIN_DIR` and `OUTPUT_DIR` environment va
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export dataset_name="lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions"
|
||||
export dataset_name="lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
@@ -183,7 +183,7 @@ accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image.py \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm=1 \
|
||||
--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
--lr_scheduler="constant" --lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--output_dir="sd-naruto-model" \
|
||||
--output_dir="sd-pokemon-model" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -202,7 +202,7 @@ To train on a local dataset, set the `TRAIN_DIR` and `OUTPUT_DIR` environment va
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME="runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
export dataset_name="lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions"
|
||||
export dataset_name="lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions"
|
||||
|
||||
python train_text_to_image_flax.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
@@ -212,7 +212,7 @@ python train_text_to_image_flax.py \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=15000 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-05 \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm=1 \
|
||||
--output_dir="sd-naruto-model" \
|
||||
--output_dir="sd-pokemon-model" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -231,7 +231,7 @@ import torch
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("path/to/saved_model", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt="yoda").images[0]
|
||||
image.save("yoda-naruto.png")
|
||||
image.save("yoda-pokemon.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
@@ -246,7 +246,7 @@ from diffusers import FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline, params = FlaxStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("path/to/saved_model", dtype=jax.numpy.bfloat16)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "yoda naruto"
|
||||
prompt = "yoda pokemon"
|
||||
prng_seed = jax.random.PRNGKey(0)
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 50
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -261,7 +261,7 @@ prompt_ids = shard(prompt_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(prompt_ids, params, prng_seed, num_inference_steps, jit=True).images
|
||||
images = pipeline.numpy_to_pil(np.asarray(images.reshape((num_samples,) + images.shape[-3:])))
|
||||
image.save("yoda-naruto.png")
|
||||
image.save("yoda-pokemon.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ accelerate config default
|
||||
|
||||
Or if your environment doesn't support an interactive shell, like a notebook, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_config()
|
||||
@@ -131,7 +131,7 @@ If you want to learn more about how the training loop works, check out the [Unde
|
||||
|
||||
Once you’ve made all your changes or you’re okay with the default configuration, you’re ready to launch the training script! 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
Set the `DATASET_NAME` environment variable to the dataset name from the Hub. This guide uses the [Naruto BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions) dataset, but you can create and train on your own datasets as well (see the [Create a dataset for training](create_dataset) guide).
|
||||
Set the `DATASET_NAME` environment variable to the dataset name from the Hub. This guide uses the [Pokémon BLIP captions](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions) dataset, but you can create and train on your own datasets as well (see the [Create a dataset for training](create_dataset) guide).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ To monitor training progress with Weights & Biases, add the `--report_to=wandb`
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/naruto-blip-captions"
|
||||
export DATASET_NAME="lambdalabs/pokemon-blip-captions"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_text_to_image_prior.py \
|
||||
--mixed_precision="fp16" \
|
||||
@@ -156,10 +156,10 @@ accelerate launch train_text_to_image_prior.py \
|
||||
--checkpoints_total_limit=3 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler="constant" \
|
||||
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--validation_prompts="A robot naruto, 4k photo" \
|
||||
--validation_prompts="A robot pokemon, 4k photo" \
|
||||
--report_to="wandb" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub \
|
||||
--output_dir="wuerstchen-prior-naruto-model"
|
||||
--output_dir="wuerstchen-prior-pokemon-model"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once training is complete, you can use your newly trained model for inference!
|
||||
@@ -171,9 +171,9 @@ from diffusers.pipelines.wuerstchen import DEFAULT_STAGE_C_TIMESTEPS
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("path/to/saved/model", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
caption = "A cute bird naruto holding a shield"
|
||||
caption = "A cute bird pokemon holding a shield"
|
||||
images = pipeline(
|
||||
caption,
|
||||
caption,
|
||||
width=1024,
|
||||
height=1536,
|
||||
prior_timesteps=DEFAULT_STAGE_C_TIMESTEPS,
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,74 +12,75 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# AutoPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers provides many pipelines for basic tasks like generating images, videos, audio, and inpainting. On top of these, there are specialized pipelines for adapters and features like upscaling, super-resolution, and more. Different pipeline classes can even use the same checkpoint because they share the same pretrained model! With so many different pipelines, it can be overwhelming to know which pipeline class to use.
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is able to complete many different tasks, and you can often reuse the same pretrained weights for multiple tasks such as text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting. If you're new to the library and diffusion models though, it may be difficult to know which pipeline to use for a task. For example, if you're using the [runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) checkpoint for text-to-image, you might not know that you could also use it for image-to-image and inpainting by loading the checkpoint with the [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`] and [`StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline`] classes respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
The [AutoPipeline](../api/pipelines/auto_pipeline) class is designed to simplify the variety of pipelines in Diffusers. It is a generic *task-first* pipeline that lets you focus on a task ([`AutoPipelineForText2Image`], [`AutoPipelineForImage2Image`], and [`AutoPipelineForInpainting`]) without needing to know the specific pipeline class. The [AutoPipeline](../api/pipelines/auto_pipeline) automatically detects the correct pipeline class to use.
|
||||
The `AutoPipeline` class is designed to simplify the variety of pipelines in 🤗 Diffusers. It is a generic, *task-first* pipeline that lets you focus on the task. The `AutoPipeline` automatically detects the correct pipeline class to use, which makes it easier to load a checkpoint for a task without knowing the specific pipeline class name.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let's use the [dreamlike-art/dreamlike-photoreal-2.0](https://hf.co/dreamlike-art/dreamlike-photoreal-2.0) checkpoint.
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Under the hood, [AutoPipeline](../api/pipelines/auto_pipeline):
|
||||
Take a look at the [AutoPipeline](../api/pipelines/auto_pipeline) reference to see which tasks are supported. Currently, it supports text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Detects a `"stable-diffusion"` class from the [model_index.json](https://hf.co/dreamlike-art/dreamlike-photoreal-2.0/blob/main/model_index.json) file.
|
||||
2. Depending on the task you're interested in, it loads the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`], or [`StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline`]. Any parameter (`strength`, `num_inference_steps`, etc.) you would pass to these specific pipelines can also be passed to the [AutoPipeline](../api/pipelines/auto_pipeline).
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="autopipeline">
|
||||
<hfoption id="text-to-image">
|
||||
This tutorial shows you how to use an `AutoPipeline` to automatically infer the pipeline class to load for a specific task, given the pretrained weights.
|
||||
|
||||
## Choose an AutoPipeline for your task
|
||||
|
||||
Start by picking a checkpoint. For example, if you're interested in text-to-image with the [runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) checkpoint, use [`AutoPipelineForText2Image`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_txt2img = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"dreamlike-art/dreamlike-photoreal-2.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
prompt = "peasant and dragon combat, wood cutting style, viking era, bevel with rune"
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "cinematic photo of Godzilla eating sushi with a cat in a izakaya, 35mm photograph, film, professional, 4k, highly detailed"
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(37)
|
||||
image = pipe_txt2img(prompt, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, num_inference_steps=25).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/autopipeline-text2img.png"/>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/autopipeline-text2img.png" alt="generated image of peasant fighting dragon in wood cutting style"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="image-to-image">
|
||||
Under the hood, [`AutoPipelineForText2Image`]:
|
||||
|
||||
1. automatically detects a `"stable-diffusion"` class from the [`model_index.json`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/blob/main/model_index.json) file
|
||||
2. loads the corresponding text-to-image [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] based on the `"stable-diffusion"` class name
|
||||
|
||||
Likewise, for image-to-image, [`AutoPipelineForImage2Image`] detects a `"stable-diffusion"` checkpoint from the `model_index.json` file and it'll load the corresponding [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`] behind the scenes. You can also pass any additional arguments specific to the pipeline class such as `strength`, which determines the amount of noise or variation added to an input image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_img2img = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"dreamlike-art/dreamlike-photoreal-2.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
prompt = "a portrait of a dog wearing a pearl earring"
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/autopipeline-text2img.png")
|
||||
url = "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0f/1665_Girl_with_a_Pearl_Earring.jpg/800px-1665_Girl_with_a_Pearl_Earring.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "cinematic photo of Godzilla eating burgers with a cat in a fast food restaurant, 35mm photograph, film, professional, 4k, highly detailed"
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(53)
|
||||
image = pipe_img2img(prompt, image=init_image, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
image.thumbnail((768, 768))
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, image, num_inference_steps=200, strength=0.75, guidance_scale=10.5).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice how the [dreamlike-art/dreamlike-photoreal-2.0](https://hf.co/dreamlike-art/dreamlike-photoreal-2.0) checkpoint is used for both text-to-image and image-to-image tasks? To save memory and avoid loading the checkpoint twice, use the [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipe_img2img = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pipe(pipe_txt2img).to("cuda")
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, image=init_image, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about the [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`] method in the [Reuse a pipeline](../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-a-pipeline) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/autopipeline-img2img.png"/>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/autopipeline-img2img.png" alt="generated image of a vermeer portrait of a dog wearing a pearl earring"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="inpainting">
|
||||
And if you want to do inpainting, then [`AutoPipelineForInpainting`] loads the underlying [`StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline`] class in the same way:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForInpainting
|
||||
@@ -90,27 +91,22 @@ pipeline = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/autopipeline-img2img.png")
|
||||
mask_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/autopipeline-mask.png")
|
||||
img_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo.png"
|
||||
mask_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo_mask.png"
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "cinematic photo of a owl, 35mm photograph, film, professional, 4k, highly detailed"
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(38)
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image, generator=generator, strength=0.4).images[0]
|
||||
init_image = load_image(img_url).convert("RGB")
|
||||
mask_image = load_image(mask_url).convert("RGB")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A majestic tiger sitting on a bench"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image, num_inference_steps=50, strength=0.80).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/autopipeline-inpaint.png"/>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/autopipeline-inpaint.png" alt="generated image of a tiger sitting on a bench"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## Unsupported checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
The [AutoPipeline](../api/pipelines/auto_pipeline) supports [Stable Diffusion](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview), [Stable Diffusion XL](../api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/stable_diffusion_xl), [ControlNet](../api/pipelines/controlnet), [Kandinsky 2.1](../api/pipelines/kandinsky.md), [Kandinsky 2.2](../api/pipelines/kandinsky_v22), and [DeepFloyd IF](../api/pipelines/deepfloyd_if) checkpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
If you try to load an unsupported checkpoint, you'll get an error.
|
||||
If you try to load an unsupported checkpoint, it'll throw an error:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
@@ -121,3 +117,54 @@ pipeline = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
)
|
||||
"ValueError: AutoPipeline can't find a pipeline linked to ShapEImg2ImgPipeline for None"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Use multiple pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
For some workflows or if you're loading many pipelines, it is more memory-efficient to reuse the same components from a checkpoint instead of reloading them which would unnecessarily consume additional memory. For example, if you're using a checkpoint for text-to-image and you want to use it again for image-to-image, use the [`~AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pipe`] method. This method creates a new pipeline from the components of a previously loaded pipeline at no additional memory cost.
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pipe`] method detects the original pipeline class and maps it to the new pipeline class corresponding to the task you want to do. For example, if you load a `"stable-diffusion"` class pipeline for text-to-image:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image, AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline_text2img = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(type(pipeline_text2img))
|
||||
"<class 'diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.pipeline_stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipeline'>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then [`~AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pipe`] maps the original `"stable-diffusion"` pipeline class to [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline_img2img = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pipe(pipeline_text2img)
|
||||
print(type(pipeline_img2img))
|
||||
"<class 'diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.pipeline_stable_diffusion_img2img.StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline'>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you passed an optional argument - like disabling the safety checker - to the original pipeline, this argument is also passed on to the new pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image, AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline_text2img = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
requires_safety_checker=False,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline_img2img = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pipe(pipeline_text2img)
|
||||
print(pipeline_img2img.config.requires_safety_checker)
|
||||
"False"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can overwrite any of the arguments and even configuration from the original pipeline if you want to change the behavior of the new pipeline. For example, to turn the safety checker back on and add the `strength` argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline_img2img = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pipe(pipeline_text2img, requires_safety_checker=True, strength=0.3)
|
||||
print(pipeline_img2img.config.requires_safety_checker)
|
||||
"True"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -260,7 +260,7 @@ Then, you'll need a way to evaluate the model. For evaluation, you can use the [
|
||||
... # The default pipeline output type is `List[PIL.Image]`
|
||||
... images = pipeline(
|
||||
... batch_size=config.eval_batch_size,
|
||||
... generator=torch.Generator(device='cpu').manual_seed(config.seed), # Use a separate torch generator to avoid rewinding the random state of the main training loop
|
||||
... generator=torch.manual_seed(config.seed),
|
||||
... ).images
|
||||
|
||||
... # Make a grid out of the images
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -133,62 +133,6 @@ image
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Customize adapters strength
|
||||
For even more customization, you can control how strongly the adapter affects each part of the pipeline. For this, pass a dictionary with the control strengths (called "scales") to [`~diffusers.loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.set_adapters`].
|
||||
|
||||
For example, here's how you can turn on the adapter for the `down` parts, but turn it off for the `mid` and `up` parts:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe.enable_lora() # enable lora again, after we disabled it above
|
||||
prompt = "toy_face of a hacker with a hoodie, pixel art"
|
||||
adapter_weight_scales = { "unet": { "down": 1, "mid": 0, "up": 0} }
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters("pixel", adapter_weight_scales)
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30, generator=torch.manual_seed(0)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Let's see how turning off the `down` part and turning on the `mid` and `up` part respectively changes the image.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
adapter_weight_scales = { "unet": { "down": 0, "mid": 1, "up": 0} }
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters("pixel", adapter_weight_scales)
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30, generator=torch.manual_seed(0)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
adapter_weight_scales = { "unet": { "down": 0, "mid": 0, "up": 1} }
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters("pixel", adapter_weight_scales)
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30, generator=torch.manual_seed(0)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Looks cool!
|
||||
|
||||
This is a really powerful feature. You can use it to control the adapter strengths down to per-transformer level. And you can even use it for multiple adapters.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
adapter_weight_scales_toy = 0.5
|
||||
adapter_weight_scales_pixel = {
|
||||
"unet": {
|
||||
"down": 0.9, # all transformers in the down-part will use scale 0.9
|
||||
# "mid" # because, in this example, "mid" is not given, all transformers in the mid part will use the default scale 1.0
|
||||
"up": {
|
||||
"block_0": 0.6, # all 3 transformers in the 0th block in the up-part will use scale 0.6
|
||||
"block_1": [0.4, 0.8, 1.0], # the 3 transformers in the 1st block in the up-part will use scales 0.4, 0.8 and 1.0 respectively
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters(["toy", "pixel"], [adapter_weight_scales_toy, adapter_weight_scales_pixel])
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30, generator=torch.manual_seed(0)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Manage active adapters
|
||||
|
||||
You have attached multiple adapters in this tutorial, and if you're feeling a bit lost on what adapters have been attached to the pipeline's components, use the [`~diffusers.loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.get_active_adapters`] method to check the list of active adapters:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,74 +19,13 @@ The denoising loop of a pipeline can be modified with custom defined functions u
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will demonstrate how callbacks work by a few features you can implement with them.
|
||||
|
||||
## Official callbacks
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a list of callbacks you can plug into an existing pipeline and modify the denoising loop. This is the current list of official callbacks:
|
||||
|
||||
- `SDCFGCutoffCallback`: Disables the CFG after a certain number of steps for all SD 1.5 pipelines, including text-to-image, image-to-image, inpaint, and controlnet.
|
||||
- `SDXLCFGCutoffCallback`: Disables the CFG after a certain number of steps for all SDXL pipelines, including text-to-image, image-to-image, inpaint, and controlnet.
|
||||
- `IPAdapterScaleCutoffCallback`: Disables the IP Adapter after a certain number of steps for all pipelines supporting IP-Adapter.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> If you want to add a new official callback, feel free to open a [feature request](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose) or [submit a PR](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/conceptual/contribution#how-to-open-a-pr).
|
||||
|
||||
To set up a callback, you need to specify the number of denoising steps after which the callback comes into effect. You can do so by using either one of these two arguments
|
||||
|
||||
- `cutoff_step_ratio`: Float number with the ratio of the steps.
|
||||
- `cutoff_step_index`: Integer number with the exact number of the step.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler, StableDiffusionXLPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.callbacks import SDXLCFGCutoffCallback
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
callback = SDXLCFGCutoffCallback(cutoff_step_ratio=0.4)
|
||||
# can also be used with cutoff_step_index
|
||||
# callback = SDXLCFGCutoffCallback(cutoff_step_ratio=None, cutoff_step_index=10)
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config, use_karras_sigmas=True)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a sports car at the road, best quality, high quality, high detail, 8k resolution"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(2628670641)
|
||||
|
||||
out = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
negative_prompt="",
|
||||
guidance_scale=6.5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
callback_on_step_end=callback,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
out.images[0].save("official_callback.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/without_cfg_callback.png" alt="generated image of a sports car at the road" />
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">without SDXLCFGCutoffCallback</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/with_cfg_callback.png" alt="generated image of a a sports car at the road with cfg callback" />
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">with SDXLCFGCutoffCallback</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Dynamic classifier-free guidance
|
||||
|
||||
Dynamic classifier-free guidance (CFG) is a feature that allows you to disable CFG after a certain number of inference steps which can help you save compute with minimal cost to performance. The callback function for this should have the following arguments:
|
||||
|
||||
- `pipeline` (or the pipeline instance) provides access to important properties such as `num_timesteps` and `guidance_scale`. You can modify these properties by updating the underlying attributes. For this example, you'll disable CFG by setting `pipeline._guidance_scale=0.0`.
|
||||
- `step_index` and `timestep` tell you where you are in the denoising loop. Use `step_index` to turn off CFG after reaching 40% of `num_timesteps`.
|
||||
- `callback_kwargs` is a dict that contains tensor variables you can modify during the denoising loop. It only includes variables specified in the `callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs` argument, which is passed to the pipeline's `__call__` method. Different pipelines may use different sets of variables, so please check a pipeline's `_callback_tensor_inputs` attribute for the list of variables you can modify. Some common variables include `latents` and `prompt_embeds`. For this function, change the batch size of `prompt_embeds` after setting `guidance_scale=0.0` in order for it to work properly.
|
||||
* `pipeline` (or the pipeline instance) provides access to important properties such as `num_timesteps` and `guidance_scale`. You can modify these properties by updating the underlying attributes. For this example, you'll disable CFG by setting `pipeline._guidance_scale=0.0`.
|
||||
* `step_index` and `timestep` tell you where you are in the denoising loop. Use `step_index` to turn off CFG after reaching 40% of `num_timesteps`.
|
||||
* `callback_kwargs` is a dict that contains tensor variables you can modify during the denoising loop. It only includes variables specified in the `callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs` argument, which is passed to the pipeline's `__call__` method. Different pipelines may use different sets of variables, so please check a pipeline's `_callback_tensor_inputs` attribute for the list of variables you can modify. Some common variables include `latents` and `prompt_embeds`. For this function, change the batch size of `prompt_embeds` after setting `guidance_scale=0.0` in order for it to work properly.
|
||||
|
||||
Your callback function should look something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -188,7 +127,7 @@ def latents_to_rgb(latents):
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def decode_tensors(pipe, step, timestep, callback_kwargs):
|
||||
latents = callback_kwargs["latents"]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
image = latents_to_rgb(latents)
|
||||
image.save(f"{step}.png")
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -209,9 +148,9 @@ pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
use_safetensors=True
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt="A croissant shaped like a cute bear.",
|
||||
negative_prompt="Deformed, ugly, bad anatomy",
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt = "A croissant shaped like a cute bear."
|
||||
negative_prompt = "Deformed, ugly, bad anatomy"
|
||||
callback_on_step_end=decode_tensors,
|
||||
callback_on_step_end_tensor_inputs=["latents"],
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
184
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/contribute_pipeline.md
Normal file
184
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/contribute_pipeline.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Take a look at GitHub Issue [#841](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841) for more context about why we're adding community pipelines to help everyone easily share their work without being slowed down.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipelines allow you to add any additional features you'd like on top of the [`DiffusionPipeline`]. The main benefit of building on top of the `DiffusionPipeline` is anyone can load and use your pipeline by only adding one more argument, making it super easy for the community to access.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to create a community pipeline and explain how they work. To keep things simple, you'll create a "one-step" pipeline where the `UNet` does a single forward pass and calls the scheduler once.
|
||||
|
||||
## Initialize the pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
You should start by creating a `one_step_unet.py` file for your community pipeline. In this file, create a pipeline class that inherits from the [`DiffusionPipeline`] to be able to load model weights and the scheduler configuration from the Hub. The one-step pipeline needs a `UNet` and a scheduler, so you'll need to add these as arguments to the `__init__` function:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To ensure your pipeline and its components (`unet` and `scheduler`) can be saved with [`~DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`], add them to the `register_modules` function:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
|
||||
+ self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Cool, the `__init__` step is done and you can move to the forward pass now! 🔥
|
||||
|
||||
## Define the forward pass
|
||||
|
||||
In the forward pass, which we recommend defining as `__call__`, you have complete creative freedom to add whatever feature you'd like. For our amazing one-step pipeline, create a random image and only call the `unet` and `scheduler` once by setting `timestep=1`:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
class UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(DiffusionPipeline):
|
||||
def __init__(self, unet, scheduler):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
|
||||
self.register_modules(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
|
||||
|
||||
+ def __call__(self):
|
||||
+ image = torch.randn(
|
||||
+ (1, self.unet.config.in_channels, self.unet.config.sample_size, self.unet.config.sample_size),
|
||||
+ )
|
||||
+ timestep = 1
|
||||
|
||||
+ model_output = self.unet(image, timestep).sample
|
||||
+ scheduler_output = self.scheduler.step(model_output, timestep, image).prev_sample
|
||||
|
||||
+ return scheduler_output
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That's it! 🚀 You can now run this pipeline by passing a `unet` and `scheduler` to it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DDPMScheduler, UNet2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = DDPMScheduler()
|
||||
unet = UNet2DModel()
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline(unet=unet, scheduler=scheduler)
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipeline()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
But what's even better is you can load pre-existing weights into the pipeline if the pipeline structure is identical. For example, you can load the [`google/ddpm-cifar10-32`](https://huggingface.co/google/ddpm-cifar10-32) weights into the one-step pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline = UnetSchedulerOneForwardPipeline.from_pretrained("google/ddpm-cifar10-32", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipeline()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Share your pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Open a Pull Request on the 🧨 Diffusers [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers) to add your awesome pipeline in `one_step_unet.py` to the [examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) subfolder.
|
||||
|
||||
Once it is merged, anyone with `diffusers >= 0.4.0` installed can use this pipeline magically 🪄 by specifying it in the `custom_pipeline` argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"google/ddpm-cifar10-32", custom_pipeline="one_step_unet", use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to share your community pipeline is to upload the `one_step_unet.py` file directly to your preferred [model repository](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/models-uploading) on the Hub. Instead of specifying the `one_step_unet.py` file, pass the model repository id to the `custom_pipeline` argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"google/ddpm-cifar10-32", custom_pipeline="stevhliu/one_step_unet", use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the following table to compare the two sharing workflows to help you decide the best option for you:
|
||||
|
||||
| | GitHub community pipeline | HF Hub community pipeline |
|
||||
|----------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| usage | same | same |
|
||||
| review process | open a Pull Request on GitHub and undergo a review process from the Diffusers team before merging; may be slower | upload directly to a Hub repository without any review; this is the fastest workflow |
|
||||
| visibility | included in the official Diffusers repository and documentation | included on your HF Hub profile and relies on your own usage/promotion to gain visibility |
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 You can use whatever package you want in your community pipeline file - as long as the user has it installed, everything will work fine. Make sure you have one and only one pipeline class that inherits from `DiffusionPipeline` because this is automatically detected.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## How do community pipelines work?
|
||||
|
||||
A community pipeline is a class that inherits from [`DiffusionPipeline`] which means:
|
||||
|
||||
- It can be loaded with the [`custom_pipeline`] argument.
|
||||
- The model weights and scheduler configuration are loaded from [`pretrained_model_name_or_path`].
|
||||
- The code that implements a feature in the community pipeline is defined in a `pipeline.py` file.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you can't load all the pipeline components weights from an official repository. In this case, the other components should be passed directly to the pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPImageProcessor, CLIPModel
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
|
||||
clip_model_id = "laion/CLIP-ViT-B-32-laion2B-s34B-b79K"
|
||||
|
||||
feature_extractor = CLIPImageProcessor.from_pretrained(clip_model_id)
|
||||
clip_model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained(clip_model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id,
|
||||
custom_pipeline="clip_guided_stable_diffusion",
|
||||
clip_model=clip_model,
|
||||
feature_extractor=feature_extractor,
|
||||
scheduler=scheduler,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The magic behind community pipelines is contained in the following code. It allows the community pipeline to be loaded from GitHub or the Hub, and it'll be available to all 🧨 Diffusers packages.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 2. Load the pipeline class, if using custom module then load it from the Hub
|
||||
# if we load from explicit class, let's use it
|
||||
if custom_pipeline is not None:
|
||||
pipeline_class = get_class_from_dynamic_module(
|
||||
custom_pipeline, module_file=CUSTOM_PIPELINE_FILE_NAME, cache_dir=custom_pipeline
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif cls != DiffusionPipeline:
|
||||
pipeline_class = cls
|
||||
else:
|
||||
diffusers_module = importlib.import_module(cls.__module__.split(".")[0])
|
||||
pipeline_class = getattr(diffusers_module, config_dict["_class_name"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
58
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/control_brightness.md
Normal file
58
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/control_brightness.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Control image brightness
|
||||
|
||||
The Stable Diffusion pipeline is mediocre at generating images that are either very bright or dark as explained in the [Common Diffusion Noise Schedules and Sample Steps are Flawed](https://huggingface.co/papers/2305.08891) paper. The solutions proposed in the paper are currently implemented in the [`DDIMScheduler`] which you can use to improve the lighting in your images.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Take a look at the paper linked above for more details about the proposed solutions!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
One of the solutions is to train a model with *v prediction* and *v loss*. Add the following flag to the [`train_text_to_image.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/text_to_image/train_text_to_image.py) or [`train_text_to_image_lora.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/text_to_image/train_text_to_image_lora.py) scripts to enable `v_prediction`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--prediction_type="v_prediction"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let's use the [`ptx0/pseudo-journey-v2`](https://huggingface.co/ptx0/pseudo-journey-v2) checkpoint which has been finetuned with `v_prediction`.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, configure the following parameters in the [`DDIMScheduler`]:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `rescale_betas_zero_snr=True`, rescales the noise schedule to zero terminal signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
|
||||
2. `timestep_spacing="trailing"`, starts sampling from the last timestep
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("ptx0/pseudo-journey-v2", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# switch the scheduler in the pipeline to use the DDIMScheduler
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_config(
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler.config, rescale_betas_zero_snr=True, timestep_spacing="trailing"
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, in your call to the pipeline, set `guidance_rescale` to prevent overexposure:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A lion in galaxies, spirals, nebulae, stars, smoke, iridescent, intricate detail, octane render, 8k"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, guidance_rescale=0.7).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/zero_snr.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
119
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_examples.md
Normal file
119
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_examples.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Community pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For more context about the design choices behind community pipelines, please have a look at [this issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipelines allow you to get creative and build your own unique pipelines to share with the community. You can find all community pipelines in the [diffusers/examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) folder along with inference and training examples for how to use them. This guide showcases some of the community pipelines and hopefully it'll inspire you to create your own (feel free to open a PR with your own pipeline and we will merge it!).
|
||||
|
||||
To load a community pipeline, use the `custom_pipeline` argument in [`DiffusionPipeline`] to specify one of the files in [diffusers/examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", custom_pipeline="filename_in_the_community_folder", use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If a community pipeline doesn't work as expected, please open a GitHub issue and mention the author.
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about community pipelines in the how to [load community pipelines](custom_pipeline_overview) and how to [contribute a community pipeline](contribute_pipeline) guides.
|
||||
|
||||
## Multilingual Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
The multilingual Stable Diffusion pipeline uses a pretrained [XLM-RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/papluca/xlm-roberta-base-language-detection) to identify a language and the [mBART-large-50](https://huggingface.co/facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-one-mmt) model to handle the translation. This allows you to generate images from text in 20 languages.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
pipeline,
|
||||
MBart50TokenizerFast,
|
||||
MBartForConditionalGeneration,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
device_dict = {"cuda": 0, "cpu": -1}
|
||||
|
||||
# add language detection pipeline
|
||||
language_detection_model_ckpt = "papluca/xlm-roberta-base-language-detection"
|
||||
language_detection_pipeline = pipeline("text-classification",
|
||||
model=language_detection_model_ckpt,
|
||||
device=device_dict[device])
|
||||
|
||||
# add model for language translation
|
||||
translation_tokenizer = MBart50TokenizerFast.from_pretrained("facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-one-mmt")
|
||||
translation_model = MBartForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-one-mmt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
diffuser_pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="multilingual_stable_diffusion",
|
||||
detection_pipeline=language_detection_pipeline,
|
||||
translation_model=translation_model,
|
||||
translation_tokenizer=translation_tokenizer,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
diffuser_pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
diffuser_pipeline = diffuser_pipeline.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = ["a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse",
|
||||
"Una casa en la playa",
|
||||
"Ein Hund, der Orange isst",
|
||||
"Un restaurant parisien"]
|
||||
|
||||
images = diffuser_pipeline(prompt).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, rows=2, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/4313860/198328706-295824a4-9856-4ce5-8e66-278ceb42fd29.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## MagicMix
|
||||
|
||||
[MagicMix](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.16056) is a pipeline that can mix an image and text prompt to generate a new image that preserves the image structure. The `mix_factor` determines how much influence the prompt has on the layout generation, `kmin` controls the number of steps during the content generation process, and `kmax` determines how much information is kept in the layout of the original image.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="magic_mix",
|
||||
scheduler=DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", subfolder="scheduler"),
|
||||
).to('cuda')
|
||||
|
||||
img = load_image("https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/59410571/209578593-141467c7-d831-4792-8b9a-b17dc5e47816.jpg")
|
||||
mix_img = pipeline(img, prompt="bed", kmin=0.3, kmax=0.5, mix_factor=0.5)
|
||||
make_image_grid([img, mix_img], rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/59410571/209578593-141467c7-d831-4792-8b9a-b17dc5e47816.jpg" />
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">original image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/59410571/209578602-70f323fa-05b7-4dd6-b055-e40683e37914.jpg" />
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">image and text prompt mix</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
@@ -16,27 +16,17 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
## Community pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP] Take a look at GitHub Issue [#841](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/841) for more context about why we're adding community pipelines to help everyone easily share their work without being slowed down.
|
||||
Community pipelines are any [`DiffusionPipeline`] class that are different from the original implementation as specified in their paper (for example, the [`StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline`] corresponds to the [Text-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) paper). They provide additional functionality or extend the original implementation of a pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipelines are any [`DiffusionPipeline`] class that are different from the original paper implementation (for example, the [`StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline`] corresponds to the [Text-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) paper). They provide additional functionality or extend the original implementation of a pipeline.
|
||||
There are many cool community pipelines like [Speech to Image](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community#speech-to-image) or [Composable Stable Diffusion](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community#composable-stable-diffusion), and you can find all the official community pipelines [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community).
|
||||
|
||||
There are many cool community pipelines like [Marigold Depth Estimation](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community#marigold-depth-estimation) or [InstantID](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community#instantid-pipeline), and you can find all the official community pipelines [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community).
|
||||
To load any community pipeline on the Hub, pass the repository id of the community pipeline to the `custom_pipeline` argument and the model repository where you'd like to load the pipeline weights and components from. For example, the example below loads a dummy pipeline from [`hf-internal-testing/diffusers-dummy-pipeline`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-dummy-pipeline/blob/main/pipeline.py) and the pipeline weights and components from [`google/ddpm-cifar10-32`](https://huggingface.co/google/ddpm-cifar10-32):
|
||||
|
||||
There are two types of community pipelines, those stored on the Hugging Face Hub and those stored on Diffusers GitHub repository. Hub pipelines are completely customizable (scheduler, models, pipeline code, etc.) while Diffusers GitHub pipelines are only limited to custom pipeline code.
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
| | GitHub community pipeline | HF Hub community pipeline |
|
||||
|----------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| usage | same | same |
|
||||
| review process | open a Pull Request on GitHub and undergo a review process from the Diffusers team before merging; may be slower | upload directly to a Hub repository without any review; this is the fastest workflow |
|
||||
| visibility | included in the official Diffusers repository and documentation | included on your HF Hub profile and relies on your own usage/promotion to gain visibility |
|
||||
🔒 By loading a community pipeline from the Hugging Face Hub, you are trusting that the code you are loading is safe. Make sure to inspect the code online before loading and running it automatically!
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="community">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Hub pipelines">
|
||||
|
||||
To load a Hugging Face Hub community pipeline, pass the repository id of the community pipeline to the `custom_pipeline` argument and the model repository where you'd like to load the pipeline weights and components from. For example, the example below loads a dummy pipeline from [hf-internal-testing/diffusers-dummy-pipeline](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-dummy-pipeline/blob/main/pipeline.py) and the pipeline weights and components from [google/ddpm-cifar10-32](https://huggingface.co/google/ddpm-cifar10-32):
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> By loading a community pipeline from the Hugging Face Hub, you are trusting that the code you are loading is safe. Make sure to inspect the code online before loading and running it automatically!
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -46,10 +36,7 @@ pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="GitHub pipelines">
|
||||
|
||||
To load a GitHub community pipeline, pass the repository id of the community pipeline to the `custom_pipeline` argument and the model repository where you you'd like to load the pipeline weights and components from. You can also load model components directly. The example below loads the community [CLIP Guided Stable Diffusion](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community#clip-guided-stable-diffusion) pipeline and the CLIP model components.
|
||||
Loading an official community pipeline is similar, but you can mix loading weights from an official repository id and pass pipeline components directly. The example below loads the community [CLIP Guided Stable Diffusion](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community#clip-guided-stable-diffusion) pipeline, and you can pass the CLIP model components directly to it:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -69,12 +56,9 @@ pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
### Load from a local file
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipelines can also be loaded from a local file if you pass a file path instead. The path to the passed directory must contain a pipeline.py file that contains the pipeline class.
|
||||
Community pipelines can also be loaded from a local file if you pass a file path instead. The path to the passed directory must contain a `pipeline.py` file that contains the pipeline class in order to successfully load it.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
@@ -93,7 +77,7 @@ By default, community pipelines are loaded from the latest stable version of Dif
|
||||
<hfoptions id="version">
|
||||
<hfoption id="main">
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to load from the main branch:
|
||||
For example, to load from the `main` branch:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
@@ -109,7 +93,7 @@ pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="older version">
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to load from a previous version of Diffusers like v0.25.0:
|
||||
For example, to load from a previous version of Diffusers like `v0.25.0`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
@@ -125,140 +109,8 @@ pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
### Load with from_pipe
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipelines can also be loaded with the [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`] method which allows you to load and reuse multiple pipelines without any additional memory overhead (learn more in the [Reuse a pipeline](./loading#reuse-a-pipeline) guide). The memory requirement is determined by the largest single pipeline loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let's load a community pipeline that supports [long prompts with weighting](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community#long-prompt-weighting-stable-diffusion) from a Stable Diffusion pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_sd = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("emilianJR/CyberRealistic_V3", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe_sd.to("cuda")
|
||||
# load long prompt weighting pipeline
|
||||
pipe_lpw = DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe(
|
||||
pipe_sd,
|
||||
custom_pipeline="lpw_stable_diffusion",
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "cat, hiding in the leaves, ((rain)), zazie rainyday, beautiful eyes, macro shot, colorful details, natural lighting, amazing composition, subsurface scattering, amazing textures, filmic, soft light, ultra-detailed eyes, intricate details, detailed texture, light source contrast, dramatic shadows, cinematic light, depth of field, film grain, noise, dark background, hyperrealistic dslr film still, dim volumetric cinematic lighting"
|
||||
neg_prompt = "(deformed iris, deformed pupils, semi-realistic, cgi, 3d, render, sketch, cartoon, drawing, anime, mutated hands and fingers:1.4), (deformed, distorted, disfigured:1.3), poorly drawn, bad anatomy, wrong anatomy, extra limb, missing limb, floating limbs, disconnected limbs, mutation, mutated, ugly, disgusting, amputation"
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(20)
|
||||
out_lpw = pipe_lpw(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
negative_prompt=neg_prompt,
|
||||
width=512,
|
||||
height=512,
|
||||
max_embeddings_multiples=3,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
out_lpw
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/from_pipe_lpw.png" />
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">Stable Diffusion with long prompt weighting</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/from_pipe_non_lpw.png" />
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">Stable Diffusion</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Example community pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Community pipelines are a really fun and creative way to extend the capabilities of the original pipeline with new and unique features. You can find all community pipelines in the [diffusers/examples/community](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community) folder with inference and training examples for how to use them.
|
||||
|
||||
This section showcases a couple of the community pipelines and hopefully it'll inspire you to create your own (feel free to open a PR for your community pipeline and ping us for a review)!
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> The [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`] method is particularly useful for loading community pipelines because many of them don't have pretrained weights and add a feature on top of an existing pipeline like Stable Diffusion or Stable Diffusion XL. You can learn more about the [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`] method in the [Load with from_pipe](custom_pipeline_overview#load-with-from_pipe) section.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="community">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Marigold">
|
||||
|
||||
[Marigold](https://marigoldmonodepth.github.io/) is a depth estimation diffusion pipeline that uses the rich existing and inherent visual knowledge in diffusion models. It takes an input image and denoises and decodes it into a depth map. Marigold performs well even on images it hasn't seen before.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"prs-eth/marigold-lcm-v1-0",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="marigold_depth_estimation",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/community-marigold.png")
|
||||
output = pipeline(
|
||||
image,
|
||||
denoising_steps=4,
|
||||
ensemble_size=5,
|
||||
processing_res=768,
|
||||
match_input_res=True,
|
||||
batch_size=0,
|
||||
seed=33,
|
||||
color_map="Spectral",
|
||||
show_progress_bar=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
depth_colored: Image.Image = output.depth_colored
|
||||
depth_colored.save("./depth_colored.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex flex-row gap-4">
|
||||
<div class="flex-1">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/community-marigold.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">original image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="flex-1">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/marigold-depth.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">colorized depth image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="HD-Painter">
|
||||
|
||||
[HD-Painter](https://hf.co/papers/2312.14091) is a high-resolution inpainting pipeline. It introduces a *Prompt-Aware Introverted Attention (PAIntA)* layer to better align a prompt with the area to be inpainted, and *Reweighting Attention Score Guidance (RASG)* to keep the latents more prompt-aligned and within their trained domain to generate realistc images.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"Lykon/dreamshaper-8-inpainting",
|
||||
custom_pipeline="hd_painter"
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)
|
||||
init_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/hd-painter.jpg")
|
||||
mask_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/hd-painter-mask.png")
|
||||
prompt = "football"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, init_image, mask_image, use_rasg=True, use_painta=True, generator=torch.manual_seed(0)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex flex-row gap-4">
|
||||
<div class="flex-1">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/hd-painter.jpg"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">original image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="flex-1">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/hd-painter-output.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">generated image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
For more information about community pipelines, take a look at the [Community pipelines](custom_pipeline_examples) guide for how to use them and if you're interested in adding a community pipeline check out the [How to contribute a community pipeline](contribute_pipeline) guide!
|
||||
|
||||
## Community components
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -266,7 +118,7 @@ Community components allow users to build pipelines that may have customized com
|
||||
|
||||
This section shows how users should use community components to build a community pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
You'll use the [showlab/show-1-base](https://huggingface.co/showlab/show-1-base) pipeline checkpoint as an example.
|
||||
You'll use the [showlab/show-1-base](https://huggingface.co/showlab/show-1-base) pipeline checkpoint as an example. So, let's start loading the components:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Import and load the text encoder from Transformers:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -300,17 +152,17 @@ In steps 4 and 5, the custom [UNet](https://github.com/showlab/Show-1/blob/main/
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
4. Now you'll load a [custom UNet](https://github.com/showlab/Show-1/blob/main/showone/models/unet_3d_condition.py), which in this example, has already been implemented in [showone_unet_3d_condition.py](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/unet/showone_unet_3d_condition.py) for your convenience. You'll notice the [`UNet3DConditionModel`] class name is changed to `ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel` because [`UNet3DConditionModel`] already exists in Diffusers. Any components needed for the `ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel` class should be placed in showone_unet_3d_condition.py.
|
||||
4. Now you'll load a [custom UNet](https://github.com/showlab/Show-1/blob/main/showone/models/unet_3d_condition.py), which in this example, has already been implemented in the `showone_unet_3d_condition.py` [script](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/unet/showone_unet_3d_condition.py) for your convenience. You'll notice the `UNet3DConditionModel` class name is changed to `ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel` because [`UNet3DConditionModel`] already exists in Diffusers. Any components needed for the `ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel` class should be placed in the `showone_unet_3d_condition.py` script.
|
||||
|
||||
Once this is done, you can initialize the UNet:
|
||||
Once this is done, you can initialize the UNet:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from showone_unet_3d_condition import ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from showone_unet_3d_condition import ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel
|
||||
|
||||
unet = ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel.from_pretrained(pipe_id, subfolder="unet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
unet = ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel.from_pretrained(pipe_id, subfolder="unet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Finally, you'll load the custom pipeline code. For this example, it has already been created for you in [pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py). This script contains a custom `TextToVideoIFPipeline` class for generating videos from text. Just like the custom UNet, any code needed for the custom pipeline to work should go in pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py.
|
||||
5. Finally, you'll load the custom pipeline code. For this example, it has already been created for you in the `pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py` [script](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py). This script contains a custom `TextToVideoIFPipeline` class for generating videos from text. Just like the custom UNet, any code needed for the custom pipeline to work should go in the `pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py` script.
|
||||
|
||||
Once everything is in place, you can initialize the `TextToVideoIFPipeline` with the `ShowOneUNet3DConditionModel`:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -335,16 +187,13 @@ Push the pipeline to the Hub to share with the community!
|
||||
pipeline.push_to_hub("custom-t2v-pipeline")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After the pipeline is successfully pushed, you need to make a few changes:
|
||||
After the pipeline is successfully pushed, you need a couple of changes:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Change the `_class_name` attribute in [model_index.json](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/model_index.json#L2) to `"pipeline_t2v_base_pixel"` and `"TextToVideoIFPipeline"`.
|
||||
2. Upload `showone_unet_3d_condition.py` to the [unet](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/unet/showone_unet_3d_condition.py) subfolder.
|
||||
3. Upload `pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py` to the pipeline [repository](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/tree/main).
|
||||
1. Change the `_class_name` attribute in [`model_index.json`](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/model_index.json#L2) to `"pipeline_t2v_base_pixel"` and `"TextToVideoIFPipeline"`.
|
||||
2. Upload `showone_unet_3d_condition.py` to the `unet` [directory](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/unet/showone_unet_3d_condition.py).
|
||||
3. Upload `pipeline_t2v_base_pixel.py` to the pipeline base [directory](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/show-1-base-with-code/blob/main/unet/showone_unet_3d_condition.py).
|
||||
|
||||
To run inference, add the `trust_remote_code` argument while initializing the pipeline to handle all the "magic" behind the scenes.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> As an additional precaution with `trust_remote_code=True`, we strongly encourage you to pass a commit hash to the `revision` parameter in [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] to make sure the code hasn't been updated with some malicious new lines of code (unless you fully trust the model owners).
|
||||
To run inference, simply add the `trust_remote_code` argument while initializing the pipeline to handle all the "magic" behind the scenes.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -372,9 +221,10 @@ video_frames = pipeline(
|
||||
).frames
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As an additional reference, take a look at the repository structure of [stabilityai/japanese-stable-diffusion-xl](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/japanese-stable-diffusion-xl/) which also uses the `trust_remote_code` feature.
|
||||
As an additional reference example, you can refer to the repository structure of [stabilityai/japanese-stable-diffusion-xl](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/japanese-stable-diffusion-xl/), that makes use of the `trust_remote_code` feature:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -382,4 +232,14 @@ pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/japanese-stable-diffusion-xl", trust_remote_code=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipeline.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# if using torch < 2.0
|
||||
# pipeline.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "柴犬、カラフルアート"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt=prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> When using `trust_remote_code=True`, it is also strongly encouraged to pass a commit hash as a `revision` to make sure the author of the models did not update the code with some malicious new lines (unless you fully trust the authors of the models).
|
||||
133
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/distilled_sd.md
Normal file
133
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/distilled_sd.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Distilled Stable Diffusion inference
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Stable Diffusion inference can be a computationally intensive process because it must iteratively denoise the latents to generate an image. To reduce the computational burden, you can use a *distilled* version of the Stable Diffusion model from [Nota AI](https://huggingface.co/nota-ai). The distilled version of their Stable Diffusion model eliminates some of the residual and attention blocks from the UNet, reducing the model size by 51% and improving latency on CPU/GPU by 43%.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Read this [blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/sd_distillation) to learn more about how knowledge distillation training works to produce a faster, smaller, and cheaper generative model.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Let's load the distilled Stable Diffusion model and compare it against the original Stable Diffusion model:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
distilled = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"nota-ai/bk-sdm-small", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
original = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Given a prompt, get the inference time for the original model:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
seed = 2023
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
NUM_ITERS_TO_RUN = 3
|
||||
NUM_INFERENCE_STEPS = 25
|
||||
NUM_IMAGES_PER_PROMPT = 4
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a golden vase with different flowers"
|
||||
|
||||
start = time.time_ns()
|
||||
for _ in range(NUM_ITERS_TO_RUN):
|
||||
images = original(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=NUM_INFERENCE_STEPS,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt=NUM_IMAGES_PER_PROMPT
|
||||
).images
|
||||
end = time.time_ns()
|
||||
original_sd = f"{(end - start) / 1e6:.1f}"
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"Execution time -- {original_sd} ms\n")
|
||||
"Execution time -- 45781.5 ms"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Time the distilled model inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
start = time.time_ns()
|
||||
for _ in range(NUM_ITERS_TO_RUN):
|
||||
images = distilled(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=NUM_INFERENCE_STEPS,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt=NUM_IMAGES_PER_PROMPT
|
||||
).images
|
||||
end = time.time_ns()
|
||||
|
||||
distilled_sd = f"{(end - start) / 1e6:.1f}"
|
||||
print(f"Execution time -- {distilled_sd} ms\n")
|
||||
"Execution time -- 29884.2 ms"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/original_sd.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">original Stable Diffusion (45781.5 ms)</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/distilled_sd.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">distilled Stable Diffusion (29884.2 ms)</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Tiny AutoEncoder
|
||||
|
||||
To speed inference up even more, use a tiny distilled version of the [Stable Diffusion VAE](https://huggingface.co/sayakpaul/taesdxl-diffusers) to denoise the latents into images. Replace the VAE in the distilled Stable Diffusion model with the tiny VAE:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoencoderTiny
|
||||
|
||||
distilled.vae = AutoencoderTiny.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"sayakpaul/taesd-diffusers", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Time the distilled model and distilled VAE inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
start = time.time_ns()
|
||||
for _ in range(NUM_ITERS_TO_RUN):
|
||||
images = distilled(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=NUM_INFERENCE_STEPS,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt=NUM_IMAGES_PER_PROMPT
|
||||
).images
|
||||
end = time.time_ns()
|
||||
|
||||
distilled_tiny_sd = f"{(end - start) / 1e6:.1f}"
|
||||
print(f"Execution time -- {distilled_tiny_sd} ms\n")
|
||||
"Execution time -- 27165.7 ms"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/distilled_sd_vae.png" />
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">distilled Stable Diffusion + Tiny AutoEncoder (27165.7 ms)</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
135
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/freeu.md
Normal file
135
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/freeu.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Improve generation quality with FreeU
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
The UNet is responsible for denoising during the reverse diffusion process, and there are two distinct features in its architecture:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Backbone features primarily contribute to the denoising process
|
||||
2. Skip features mainly introduce high-frequency features into the decoder module and can make the network overlook the semantics in the backbone features
|
||||
|
||||
However, the skip connection can sometimes introduce unnatural image details. [FreeU](https://hf.co/papers/2309.11497) is a technique for improving image quality by rebalancing the contributions from the UNet’s skip connections and backbone feature maps.
|
||||
|
||||
FreeU is applied during inference and it does not require any additional training. The technique works for different tasks such as text-to-image, image-to-image, and text-to-video.
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, you will apply FreeU to the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], [`StableDiffusionXLPipeline`], and [`TextToVideoSDPipeline`]. You need to install Diffusers from source to run the examples below.
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Load the pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, safety_checker=None
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then enable the FreeU mechanism with the FreeU-specific hyperparameters. These values are scaling factors for the backbone and skip features.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.enable_freeu(s1=0.9, s2=0.2, b1=1.2, b2=1.4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The values above are from the official FreeU [code repository](https://github.com/ChenyangSi/FreeU) where you can also find [reference hyperparameters](https://github.com/ChenyangSi/FreeU#range-for-more-parameters) for different models.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Disable the FreeU mechanism by calling `disable_freeu()` on a pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
And then run inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A squirrel eating a burger"
|
||||
seed = 2023
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=torch.manual_seed(seed)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The figure below compares non-FreeU and FreeU results respectively for the same hyperparameters used above (`prompt` and `seed`):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Let's see how Stable Diffusion 2 results are impacted:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16, safety_checker=None
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A squirrel eating a burger"
|
||||
seed = 2023
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline.enable_freeu(s1=0.9, s2=0.2, b1=1.1, b2=1.2)
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=torch.manual_seed(seed)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, let's take a look at how FreeU affects Stable Diffusion XL results:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A squirrel eating a burger"
|
||||
seed = 2023
|
||||
|
||||
# Comes from
|
||||
# https://wandb.ai/nasirk24/UNET-FreeU-SDXL/reports/FreeU-SDXL-Optimal-Parameters--Vmlldzo1NDg4NTUw
|
||||
pipeline.enable_freeu(s1=0.6, s2=0.4, b1=1.1, b2=1.2)
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=torch.manual_seed(seed)).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Text-to-video generation
|
||||
|
||||
FreeU can also be used to improve video quality:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_video
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "cerspense/zeroscope_v2_576w"
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
seed = 2023
|
||||
|
||||
# The values come from
|
||||
# https://github.com/lyn-rgb/FreeU_Diffusers#video-pipelines
|
||||
pipe.enable_freeu(b1=1.2, b2=1.4, s1=0.9, s2=0.2)
|
||||
video_frames = pipe(prompt, height=320, width=576, num_frames=30, generator=torch.manual_seed(seed)).frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_video(video_frames, "astronaut_rides_horse.mp4")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks to [kadirnar](https://github.com/kadirnar/) for helping to integrate the feature, and to [justindujardin](https://github.com/justindujardin) for the helpful discussions.
|
||||
@@ -1,146 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Controlling image quality
|
||||
|
||||
The components of a diffusion model, like the UNet and scheduler, can be optimized to improve the quality of generated images leading to better details. These techniques are especially useful if you don't have the resources to simply use a larger model for inference. You can enable these techniques during inference without any additional training.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to turn these techniques on in your pipeline and how to configure them to improve the quality of your generated images.
|
||||
|
||||
## Details
|
||||
|
||||
[FreeU](https://hf.co/papers/2309.11497) improves image details by rebalancing the UNet's backbone and skip connection weights. The skip connections can cause the model to overlook some of the backbone semantics which may lead to unnatural image details in the generated image. This technique does not require any additional training and can be applied on the fly during inference for tasks like image-to-image and text-to-video.
|
||||
|
||||
Use the [`~pipelines.StableDiffusionMixin.enable_freeu`] method on your pipeline and configure the scaling factors for the backbone (`b1` and `b2`) and skip connections (`s1` and `s2`). The number after each scaling factor corresponds to the stage in the UNet where the factor is applied. Take a look at the [FreeU](https://github.com/ChenyangSi/FreeU#parameters) repository for reference hyperparameters for different models.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="freeu">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Stable Diffusion v1-5">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, safety_checker=None
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_freeu(s1=0.9, s2=0.2, b1=1.5, b2=1.6)
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(33)
|
||||
prompt = ""
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/sdv15-no-freeu.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">FreeU disabled</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/sdv15-freeu.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">FreeU enabled</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Stable Diffusion v2-1">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16, safety_checker=None
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_freeu(s1=0.9, s2=0.2, b1=1.4, b2=1.6)
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(80)
|
||||
prompt = "A squirrel eating a burger"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/sdv21-no-freeu.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">FreeU disabled</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/sdv21-freeu.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">FreeU enabled</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Stable Diffusion XL">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_freeu(s1=0.9, s2=0.2, b1=1.3, b2=1.4)
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(13)
|
||||
prompt = "A squirrel eating a burger"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/sdxl-no-freeu.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">FreeU disabled</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/sdxl-freeu.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">FreeU enabled</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Zeroscope">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_video
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
# values come from https://github.com/lyn-rgb/FreeU_Diffusers#video-pipelines
|
||||
pipeline.enable_freeu(b1=1.2, b2=1.4, s1=0.9, s2=0.2)
|
||||
prompt = "Confident teddy bear surfer rides the wave in the tropics"
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(47)
|
||||
video_frames = pipeline(prompt, generator=generator).frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_video(video_frames, "teddy_bear.mp4", fps=10)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/video-no-freeu.gif"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">FreeU disabled</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/video-freeu.gif"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">FreeU enabled</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
Call the [`pipelines.StableDiffusionMixin.disable_freeu`] method to disable FreeU.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.disable_freeu()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -10,30 +10,29 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Latent Consistency Model
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
[Latent Consistency Models (LCMs)](https://hf.co/papers/2310.04378) enable fast high-quality image generation by directly predicting the reverse diffusion process in the latent rather than pixel space. In other words, LCMs try to predict the noiseless image from the noisy image in contrast to typical diffusion models that iteratively remove noise from the noisy image. By avoiding the iterative sampling process, LCMs are able to generate high-quality images in 2-4 steps instead of 20-30 steps.
|
||||
# Latent Consistency Model
|
||||
|
||||
LCMs are distilled from pretrained models which requires ~32 hours of A100 compute. To speed this up, [LCM-LoRAs](https://hf.co/papers/2311.05556) train a [LoRA adapter](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/conceptual_guides/adapter#low-rank-adaptation-lora) which have much fewer parameters to train compared to the full model. The LCM-LoRA can be plugged into a diffusion model once it has been trained.
|
||||
Latent Consistency Models (LCM) enable quality image generation in typically 2-4 steps making it possible to use diffusion models in almost real-time settings.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to use LCMs and LCM-LoRAs for fast inference on tasks and how to use them with other adapters like ControlNet or T2I-Adapter.
|
||||
From the [official website](https://latent-consistency-models.github.io/):
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> LCMs and LCM-LoRAs are available for Stable Diffusion v1.5, Stable Diffusion XL, and the SSD-1B model. You can find their checkpoints on the [Latent Consistency](https://hf.co/collections/latent-consistency/latent-consistency-models-weights-654ce61a95edd6dffccef6a8) Collections.
|
||||
> LCMs can be distilled from any pre-trained Stable Diffusion (SD) in only 4,000 training steps (~32 A100 GPU Hours) for generating high quality 768 x 768 resolution images in 2~4 steps or even one step, significantly accelerating text-to-image generation. We employ LCM to distill the Dreamshaper-V7 version of SD in just 4,000 training iterations.
|
||||
|
||||
For a more technical overview of LCMs, refer to [the paper](https://huggingface.co/papers/2310.04378).
|
||||
|
||||
LCM distilled models are available for [stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), [stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0), and the [SSD-1B](https://huggingface.co/segmind/SSD-1B) model. All the checkpoints can be found in this [collection](https://huggingface.co/collections/latent-consistency/latent-consistency-models-weights-654ce61a95edd6dffccef6a8).
|
||||
|
||||
This guide shows how to perform inference with LCMs for
|
||||
- text-to-image
|
||||
- image-to-image
|
||||
- combined with style LoRAs
|
||||
- ControlNet/T2I-Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
## Text-to-image
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="lcm-text2img">
|
||||
<hfoption id="LCM">
|
||||
|
||||
To use LCMs, you need to load the LCM checkpoint for your supported model into [`UNet2DConditionModel`] and replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`]. Then you can use the pipeline as usual, and pass a text prompt to generate an image in just 4 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
A couple of notes to keep in mind when using LCMs are:
|
||||
|
||||
* Typically, batch size is doubled inside the pipeline for classifier-free guidance. But LCM applies guidance with guidance embeddings and doesn't need to double the batch size, which leads to faster inference. The downside is that negative prompts don't work with LCM because they don't have any effect on the denoising process.
|
||||
* The ideal range for `guidance_scale` is [3., 13.] because that is what the UNet was trained with. However, disabling `guidance_scale` with a value of 1.0 is also effective in most cases.
|
||||
You'll use the [`StableDiffusionXLPipeline`] pipeline with the [`LCMScheduler`] and then load the LCM-LoRA. Together with the LCM-LoRA and the scheduler, the pipeline enables a fast inference workflow, overcoming the slow iterative nature of diffusion models.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline, UNet2DConditionModel, LCMScheduler
|
||||
@@ -50,69 +49,31 @@ pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Self-portrait oil painting, a beautiful cyborg with golden hair, 8k"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt, num_inference_steps=4, generator=generator, guidance_scale=8.0
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm/lcm_full_sdxl_t2i.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="LCM-LoRA">
|
||||
Notice that we use only 4 steps for generation which is way less than what's typically used for standard SDXL.
|
||||
|
||||
To use LCM-LoRAs, you need to replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`] and load the LCM-LoRA weights with the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method. Then you can use the pipeline as usual, and pass a text prompt to generate an image in just 4 steps.
|
||||
Some details to keep in mind:
|
||||
|
||||
A couple of notes to keep in mind when using LCM-LoRAs are:
|
||||
* To perform classifier-free guidance, batch size is usually doubled inside the pipeline. LCM, however, applies guidance using guidance embeddings, so the batch size does not have to be doubled in this case. This leads to a faster inference time, with the drawback that negative prompts don't have any effect on the denoising process.
|
||||
* The UNet was trained using the [3., 13.] guidance scale range. So, that is the ideal range for `guidance_scale`. However, disabling `guidance_scale` using a value of 1.0 is also effective in most cases.
|
||||
|
||||
* Typically, batch size is doubled inside the pipeline for classifier-free guidance. But LCM applies guidance with guidance embeddings and doesn't need to double the batch size, which leads to faster inference. The downside is that negative prompts don't work with LCM because they don't have any effect on the denoising process.
|
||||
* You could use guidance with LCM-LoRAs, but it is very sensitive to high `guidance_scale` values and can lead to artifacts in the generated image. The best values we've found are between [1.0, 2.0].
|
||||
* Replace [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://hf.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0) with any finetuned model. For example, try using the [animagine-xl](https://huggingface.co/Linaqruf/animagine-xl) checkpoint to generate anime images with SDXL.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, LCMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdxl")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Self-portrait oil painting, a beautiful cyborg with golden hair, 8k"
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(42)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt, num_inference_steps=4, generator=generator, guidance_scale=1.0
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm/lcm_sdxl_t2i.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## Image-to-image
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="lcm-img2img">
|
||||
<hfoption id="LCM">
|
||||
|
||||
To use LCMs for image-to-image, you need to load the LCM checkpoint for your supported model into [`UNet2DConditionModel`] and replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`]. Then you can use the pipeline as usual, and pass a text prompt and initial image to generate an image in just 4 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Experiment with different values for `num_inference_steps`, `strength`, and `guidance_scale` to get the best results.
|
||||
LCMs can be applied to image-to-image tasks too. For this example, we'll use the [LCM_Dreamshaper_v7](https://huggingface.co/SimianLuo/LCM_Dreamshaper_v7) model, but the same steps can be applied to other LCM models as well.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image, UNet2DConditionModel, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid, load_image
|
||||
|
||||
unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"SimianLuo/LCM_Dreamshaper_v7",
|
||||
@@ -128,8 +89,12 @@ pipe = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/img2img-init.png")
|
||||
# prepare image
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/img2img-init.png"
|
||||
init_image = load_image(url)
|
||||
prompt = "Astronauts in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
|
||||
|
||||
# pass prompt and image to pipeline
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
@@ -139,130 +104,22 @@ image = pipe(
|
||||
strength=0.5,
|
||||
generator=generator
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
make_image_grid([init_image, image], rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/img2img-init.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">initial image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm-img2img.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">generated image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="LCM-LoRA">
|
||||
|
||||
To use LCM-LoRAs for image-to-image, you need to replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`] and load the LCM-LoRA weights with the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method. Then you can use the pipeline as usual, and pass a text prompt and initial image to generate an image in just 4 steps.
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Experiment with different values for `num_inference_steps`, `strength`, and `guidance_scale` to get the best results.
|
||||
You can get different results based on your prompt and the image you provide. To get the best results, we recommend trying different values for `num_inference_steps`, `strength`, and `guidance_scale` parameters and choose the best one.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid, load_image
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"Lykon/dreamshaper-7",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
## Combine with style LoRAs
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdv1-5")
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/img2img-init.png")
|
||||
prompt = "Astronauts in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=init_image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=1,
|
||||
strength=0.6,
|
||||
generator=generator
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/img2img-init.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">initial image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm-lora-img2img.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">generated image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## Inpainting
|
||||
|
||||
To use LCM-LoRAs for inpainting, you need to replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`] and load the LCM-LoRA weights with the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method. Then you can use the pipeline as usual, and pass a text prompt, initial image, and mask image to generate an image in just 4 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForInpainting, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdv1-5")
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/inpaint.png")
|
||||
mask_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/inpaint_mask.png")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "concept art digital painting of an elven castle, inspired by lord of the rings, highly detailed, 8k"
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
image=init_image,
|
||||
mask_image=mask_image,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=4,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex gap-4">
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/inpaint.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">initial image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm-lora-inpaint.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">generated image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Adapters
|
||||
|
||||
LCMs are compatible with adapters like LoRA, ControlNet, T2I-Adapter, and AnimateDiff. You can bring the speed of LCMs to these adapters to generate images in a certain style or condition the model on another input like a canny image.
|
||||
|
||||
### LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
[LoRA](../using-diffusers/loading_adapters#lora) adapters can be rapidly finetuned to learn a new style from just a few images and plugged into a pretrained model to generate images in that style.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="lcm-lora">
|
||||
<hfoption id="LCM">
|
||||
|
||||
Load the LCM checkpoint for your supported model into [`UNet2DConditionModel`] and replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`]. Then you can use the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method to load the LoRA weights into the LCM and generate a styled image in a few steps.
|
||||
LCMs can be used with other styled LoRAs to generate styled-images in very few steps (4-8). In the following example, we'll use the [papercut LoRA](TheLastBen/Papercut_SDXL).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline, UNet2DConditionModel, LCMScheduler
|
||||
@@ -277,9 +134,11 @@ pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", unet=unet, torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16",
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("TheLastBen/Papercut_SDXL", weight_name="papercut.safetensors", adapter_name="papercut")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "papercut, a cute fox"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt, num_inference_steps=4, generator=generator, guidance_scale=8.0
|
||||
@@ -287,58 +146,15 @@ image = pipe(
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm/lcm_full_sdx_lora_mix.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="LCM-LoRA">
|
||||
|
||||
Replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`]. Then you can use the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method to load the LCM-LoRA weights and the style LoRA you want to use. Combine both LoRA adapters with the [`~loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.set_adapters`] method and generate a styled image in a few steps.
|
||||
## ControlNet/T2I-Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, LCMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdxl", adapter_name="lcm")
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("TheLastBen/Papercut_SDXL", weight_name="papercut.safetensors", adapter_name="papercut")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters(["lcm", "papercut"], adapter_weights=[1.0, 0.8])
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "papercut, a cute fox"
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=4, guidance_scale=1, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm/lcm_sdx_lora_mix.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
Let's look at how we can perform inference with ControlNet/T2I-Adapter and a LCM.
|
||||
|
||||
### ControlNet
|
||||
|
||||
[ControlNet](./controlnet) are adapters that can be trained on a variety of inputs like canny edge, pose estimation, or depth. The ControlNet can be inserted into the pipeline to provide additional conditioning and control to the model for more accurate generation.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find additional ControlNet models trained on other inputs in [lllyasviel's](https://hf.co/lllyasviel) repository.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="lcm-controlnet">
|
||||
<hfoption id="LCM">
|
||||
|
||||
Load a ControlNet model trained on canny images and pass it to the [`ControlNetModel`]. Then you can load a LCM model into [`StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline`] and replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`]. Now pass the canny image to the pipeline and generate an image.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Experiment with different values for `num_inference_steps`, `controlnet_conditioning_scale`, `cross_attention_kwargs`, and `guidance_scale` to get the best results.
|
||||
For this example, we'll use the [LCM_Dreamshaper_v7](https://huggingface.co/SimianLuo/LCM_Dreamshaper_v7) model with canny ControlNet, but the same steps can be applied to other LCM models as well.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -370,6 +186,8 @@ pipe = StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
safety_checker=None,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# set scheduler
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
@@ -382,84 +200,16 @@ image = pipe(
|
||||
make_image_grid([canny_image, image], rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm/lcm_full_sdv1-5_controlnet.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="LCM-LoRA">
|
||||
|
||||
Load a ControlNet model trained on canny images and pass it to the [`ControlNetModel`]. Then you can load a Stable Diffusion v1.5 model into [`StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline`] and replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`]. Use the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method to load the LCM-LoRA weights, and pass the canny image to the pipeline and generate an image.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Experiment with different values for `num_inference_steps`, `controlnet_conditioning_scale`, `cross_attention_kwargs`, and `guidance_scale` to get the best results.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline, ControlNetModel, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://hf.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/input_image_vermeer.png"
|
||||
).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
|
||||
low_threshold = 100
|
||||
high_threshold = 200
|
||||
|
||||
image = cv2.Canny(image, low_threshold, high_threshold)
|
||||
image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
canny_image = Image.fromarray(image)
|
||||
|
||||
controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-canny", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
controlnet=controlnet,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
safety_checker=None,
|
||||
variant="fp16"
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdv1-5")
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
"the mona lisa",
|
||||
image=canny_image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=1.5,
|
||||
controlnet_conditioning_scale=0.8,
|
||||
cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 1},
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm/lcm_sdv1-5_controlnet.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
The inference parameters in this example might not work for all examples, so we recommend trying different values for the `num_inference_steps`, `guidance_scale`, `controlnet_conditioning_scale`, and `cross_attention_kwargs` parameters and choosing the best one.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### T2I-Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
[T2I-Adapter](./t2i_adapter) is an even more lightweight adapter than ControlNet, that provides an additional input to condition a pretrained model with. It is faster than ControlNet but the results may be slightly worse.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find additional T2I-Adapter checkpoints trained on other inputs in [TencentArc's](https://hf.co/TencentARC) repository.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="lcm-t2i">
|
||||
<hfoption id="LCM">
|
||||
|
||||
Load a T2IAdapter trained on canny images and pass it to the [`StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline`]. Then load a LCM checkpoint into [`UNet2DConditionModel`] and replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`]. Now pass the canny image to the pipeline and generate an image.
|
||||
This example shows how to use the `lcm-sdxl` with the [Canny T2I-Adapter](TencentARC/t2i-adapter-canny-sdxl-1.0).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -470,9 +220,10 @@ from PIL import Image
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline, UNet2DConditionModel, T2IAdapter, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
# detect the canny map in low resolution to avoid high-frequency details
|
||||
# Prepare image
|
||||
# Detect the canny map in low resolution to avoid high-frequency details
|
||||
image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://hf.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/input_image_vermeer.png"
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/Adapter/t2iadapter/resolve/main/figs_SDXLV1.0/org_canny.jpg"
|
||||
).resize((384, 384))
|
||||
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
@@ -485,6 +236,7 @@ image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
canny_image = Image.fromarray(image).resize((1024, 1216))
|
||||
|
||||
# load adapter
|
||||
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-canny-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, varient="fp16").to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
unet = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
@@ -502,7 +254,7 @@ pipe = StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "the mona lisa, 4k picture, high quality"
|
||||
prompt = "Mystical fairy in real, magic, 4k picture, high quality"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "extra digit, fewer digits, cropped, worst quality, low quality, glitch, deformed, mutated, ugly, disfigured"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
@@ -516,116 +268,7 @@ image = pipe(
|
||||
adapter_conditioning_factor=1,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
grid = make_image_grid([canny_image, image], rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm-t2i.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="LCM-LoRA">
|
||||
|
||||
Load a T2IAdapter trained on canny images and pass it to the [`StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline`]. Replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`], and use the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] method to load the LCM-LoRA weights. Pass the canny image to the pipeline and generate an image.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline, UNet2DConditionModel, T2IAdapter, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
# detect the canny map in low resolution to avoid high-frequency details
|
||||
image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://hf.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/input_image_vermeer.png"
|
||||
).resize((384, 384))
|
||||
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
|
||||
low_threshold = 100
|
||||
high_threshold = 200
|
||||
|
||||
image = cv2.Canny(image, low_threshold, high_threshold)
|
||||
image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
canny_image = Image.fromarray(image).resize((1024, 1024))
|
||||
|
||||
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-canny-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, varient="fp16").to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
adapter=adapter,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdxl")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "the mona lisa, 4k picture, high quality"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "extra digit, fewer digits, cropped, worst quality, low quality, glitch, deformed, mutated, ugly, disfigured"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
|
||||
image=canny_image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=1.5,
|
||||
adapter_conditioning_scale=0.8,
|
||||
adapter_conditioning_factor=1,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm-lora-t2i.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
### AnimateDiff
|
||||
|
||||
[AnimateDiff](../api/pipelines/animatediff) is an adapter that adds motion to an image. It can be used with most Stable Diffusion models, effectively turning them into "video generation" models. Generating good results with a video model usually requires generating multiple frames (16-24), which can be very slow with a regular Stable Diffusion model. LCM-LoRA can speed up this process by only taking 4-8 steps for each frame.
|
||||
|
||||
Load a [`AnimateDiffPipeline`] and pass a [`MotionAdapter`] to it. Then replace the scheduler with the [`LCMScheduler`], and combine both LoRA adapters with the [`~loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.set_adapters`] method. Now you can pass a prompt to the pipeline and generate an animated image.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import MotionAdapter, AnimateDiffPipeline, DDIMScheduler, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_gif
|
||||
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5")
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"frankjoshua/toonyou_beta6",
|
||||
motion_adapter=adapter,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# set scheduler
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
# load LCM-LoRA
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdv1-5", adapter_name="lcm")
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("guoyww/animatediff-motion-lora-zoom-in", weight_name="diffusion_pytorch_model.safetensors", adapter_name="motion-lora")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters(["lcm", "motion-lora"], adapter_weights=[0.55, 1.2])
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "best quality, masterpiece, 1girl, looking at viewer, blurry background, upper body, contemporary, dress"
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
frames = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=5,
|
||||
guidance_scale=1.25,
|
||||
cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 1},
|
||||
num_frames=24,
|
||||
generator=generator
|
||||
).frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_gif(frames, "animation.gif")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/lcm-lora-animatediff.gif"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
422
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/inference_with_lcm_lora.md
Normal file
422
docs/source/en/using-diffusers/inference_with_lcm_lora.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,422 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
# Performing inference with LCM-LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
Latent Consistency Models (LCM) enable quality image generation in typically 2-4 steps making it possible to use diffusion models in almost real-time settings.
|
||||
|
||||
From the [official website](https://latent-consistency-models.github.io/):
|
||||
|
||||
> LCMs can be distilled from any pre-trained Stable Diffusion (SD) in only 4,000 training steps (~32 A100 GPU Hours) for generating high quality 768 x 768 resolution images in 2~4 steps or even one step, significantly accelerating text-to-image generation. We employ LCM to distill the Dreamshaper-V7 version of SD in just 4,000 training iterations.
|
||||
|
||||
For a more technical overview of LCMs, refer to [the paper](https://huggingface.co/papers/2310.04378).
|
||||
|
||||
However, each model needs to be distilled separately for latent consistency distillation. The core idea with LCM-LoRA is to train just a few adapter layers, the adapter being LoRA in this case.
|
||||
This way, we don't have to train the full model and keep the number of trainable parameters manageable. The resulting LoRAs can then be applied to any fine-tuned version of the model without distilling them separately.
|
||||
Additionally, the LoRAs can be applied to image-to-image, ControlNet/T2I-Adapter, inpainting, AnimateDiff etc.
|
||||
The LCM-LoRA can also be combined with other LoRAs to generate styled images in very few steps (4-8).
|
||||
|
||||
LCM-LoRAs are available for [stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5), [stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0), and the [SSD-1B](https://huggingface.co/segmind/SSD-1B) model. All the checkpoints can be found in this [collection](https://huggingface.co/collections/latent-consistency/latent-consistency-models-loras-654cdd24e111e16f0865fba6).
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about LCM-LoRA, refer to [the technical report](https://huggingface.co/papers/2311.05556).
|
||||
|
||||
This guide shows how to perform inference with LCM-LoRAs for
|
||||
- text-to-image
|
||||
- image-to-image
|
||||
- combined with styled LoRAs
|
||||
- ControlNet/T2I-Adapter
|
||||
- inpainting
|
||||
- AnimateDiff
|
||||
|
||||
Before going through this guide, we'll take a look at the general workflow for performing inference with LCM-LoRAs.
|
||||
LCM-LoRAs are similar to other Stable Diffusion LoRAs so they can be used with any [`DiffusionPipeline`] that supports LoRAs.
|
||||
|
||||
- Load the task specific pipeline and model.
|
||||
- Set the scheduler to [`LCMScheduler`].
|
||||
- Load the LCM-LoRA weights for the model.
|
||||
- Reduce the `guidance_scale` between `[1.0, 2.0]` and set the `num_inference_steps` between [4, 8].
|
||||
- Perform inference with the pipeline with the usual parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's look at how we can perform inference with LCM-LoRAs for different tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure you have [peft](https://github.com/huggingface/peft) installed, for better LoRA support.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -U peft
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Text-to-image
|
||||
|
||||
You'll use the [`StableDiffusionXLPipeline`] with the scheduler: [`LCMScheduler`] and then load the LCM-LoRA. Together with the LCM-LoRA and the scheduler, the pipeline enables a fast inference workflow overcoming the slow iterative nature of diffusion models.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, LCMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# set scheduler
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
# load LCM-LoRA
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdxl")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Self-portrait oil painting, a beautiful cyborg with golden hair, 8k"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(42)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt, num_inference_steps=4, generator=generator, guidance_scale=1.0
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Notice that we use only 4 steps for generation which is way less than what's typically used for standard SDXL.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You may have noticed that we set `guidance_scale=1.0`, which disables classifer-free-guidance. This is because the LCM-LoRA is trained with guidance, so the batch size does not have to be doubled in this case. This leads to a faster inference time, with the drawback that negative prompts don't have any effect on the denoising process.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use guidance with LCM-LoRA, but due to the nature of training the model is very sensitve to the `guidance_scale` values, high values can lead to artifacts in the generated images. In our experiments, we found that the best values are in the range of [1.0, 2.0].
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference with a fine-tuned model
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned above, the LCM-LoRA can be applied to any fine-tuned version of the model without having to distill them separately. Let's look at how we can perform inference with a fine-tuned model. In this example, we'll use the [animagine-xl](https://huggingface.co/Linaqruf/animagine-xl) model, which is a fine-tuned version of the SDXL model for generating anime.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, LCMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"Linaqruf/animagine-xl",
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# set scheduler
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
# load LCM-LoRA
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdxl")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "face focus, cute, masterpiece, best quality, 1girl, green hair, sweater, looking at viewer, upper body, beanie, outdoors, night, turtleneck"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt, num_inference_steps=4, generator=generator, guidance_scale=1.0
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Image-to-image
|
||||
|
||||
LCM-LoRA can be applied to image-to-image tasks too. Let's look at how we can perform image-to-image generation with LCMs. For this example we'll use the [dreamshaper-7](https://huggingface.co/Lykon/dreamshaper-7) model and the LCM-LoRA for `stable-diffusion-v1-5 `.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid, load_image
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"Lykon/dreamshaper-7",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# set scheduler
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
# load LCM-LoRA
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdv1-5")
|
||||
|
||||
# prepare image
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/img2img-init.png"
|
||||
init_image = load_image(url)
|
||||
prompt = "Astronauts in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
|
||||
|
||||
# pass prompt and image to pipeline
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=init_image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=1,
|
||||
strength=0.6,
|
||||
generator=generator
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
make_image_grid([init_image, image], rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You can get different results based on your prompt and the image you provide. To get the best results, we recommend trying different values for `num_inference_steps`, `strength`, and `guidance_scale` parameters and choose the best one.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Combine with styled LoRAs
|
||||
|
||||
LCM-LoRA can be combined with other LoRAs to generate styled-images in very few steps (4-8). In the following example, we'll use the LCM-LoRA with the [papercut LoRA](TheLastBen/Papercut_SDXL).
|
||||
To learn more about how to combine LoRAs, refer to [this guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/tutorials/using_peft_for_inference#combine-multiple-adapters).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, LCMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# set scheduler
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
# load LoRAs
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdxl", adapter_name="lcm")
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("TheLastBen/Papercut_SDXL", weight_name="papercut.safetensors", adapter_name="papercut")
|
||||
|
||||
# Combine LoRAs
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters(["lcm", "papercut"], adapter_weights=[1.0, 0.8])
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "papercut, a cute fox"
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=4, guidance_scale=1, generator=generator).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## ControlNet/T2I-Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
Let's look at how we can perform inference with ControlNet/T2I-Adapter and LCM-LoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
### ControlNet
|
||||
For this example, we'll use the SD-v1-5 model and the LCM-LoRA for SD-v1-5 with canny ControlNet.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline, ControlNetModel, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://hf.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/input_image_vermeer.png"
|
||||
).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
|
||||
low_threshold = 100
|
||||
high_threshold = 200
|
||||
|
||||
image = cv2.Canny(image, low_threshold, high_threshold)
|
||||
image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
canny_image = Image.fromarray(image)
|
||||
|
||||
controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained("lllyasviel/sd-controlnet-canny", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
controlnet=controlnet,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
safety_checker=None,
|
||||
variant="fp16"
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# set scheduler
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
# load LCM-LoRA
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdv1-5")
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
"the mona lisa",
|
||||
image=canny_image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=1.5,
|
||||
controlnet_conditioning_scale=0.8,
|
||||
cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 1},
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
make_image_grid([canny_image, image], rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
The inference parameters in this example might not work for all examples, so we recommend you to try different values for `num_inference_steps`, `guidance_scale`, `controlnet_conditioning_scale` and `cross_attention_kwargs` parameters and choose the best one.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### T2I-Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
This example shows how to use the LCM-LoRA with the [Canny T2I-Adapter](TencentARC/t2i-adapter-canny-sdxl-1.0) and SDXL.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline, T2IAdapter, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
# Prepare image
|
||||
# Detect the canny map in low resolution to avoid high-frequency details
|
||||
image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/Adapter/t2iadapter/resolve/main/figs_SDXLV1.0/org_canny.jpg"
|
||||
).resize((384, 384))
|
||||
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
|
||||
low_threshold = 100
|
||||
high_threshold = 200
|
||||
|
||||
image = cv2.Canny(image, low_threshold, high_threshold)
|
||||
image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
canny_image = Image.fromarray(image).resize((1024, 1024))
|
||||
|
||||
# load adapter
|
||||
adapter = T2IAdapter.from_pretrained("TencentARC/t2i-adapter-canny-sdxl-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16, varient="fp16").to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
adapter=adapter,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# set scheduler
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
# load LCM-LoRA
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdxl")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Mystical fairy in real, magic, 4k picture, high quality"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "extra digit, fewer digits, cropped, worst quality, low quality, glitch, deformed, mutated, ugly, disfigured"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
|
||||
image=canny_image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=1.5,
|
||||
adapter_conditioning_scale=0.8,
|
||||
adapter_conditioning_factor=1,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
make_image_grid([canny_image, image], rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Inpainting
|
||||
|
||||
LCM-LoRA can be used for inpainting as well.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForInpainting, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# set scheduler
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
# load LCM-LoRA
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdv1-5")
|
||||
|
||||
# load base and mask image
|
||||
init_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/inpaint.png")
|
||||
mask_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/inpaint_mask.png")
|
||||
|
||||
# generator = torch.Generator("cuda").manual_seed(92)
|
||||
prompt = "concept art digital painting of an elven castle, inspired by lord of the rings, highly detailed, 8k"
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
image=init_image,
|
||||
mask_image=mask_image,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=4,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
make_image_grid([init_image, mask_image, image], rows=1, cols=3)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## AnimateDiff
|
||||
|
||||
[`AnimateDiff`] allows you to animate images using Stable Diffusion models. To get good results, we need to generate multiple frames (16-24), and doing this with standard SD models can be very slow.
|
||||
LCM-LoRA can be used to speed up the process significantly, as you just need to do 4-8 steps for each frame. Let's look at how we can perform animation with LCM-LoRA and AnimateDiff.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import MotionAdapter, AnimateDiffPipeline, DDIMScheduler, LCMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_gif
|
||||
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("diffusers/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5")
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"frankjoshua/toonyou_beta6",
|
||||
motion_adapter=adapter,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# set scheduler
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = LCMScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
|
||||
# load LCM-LoRA
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("latent-consistency/lcm-lora-sdv1-5", adapter_name="lcm")
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("guoyww/animatediff-motion-lora-zoom-in", weight_name="diffusion_pytorch_model.safetensors", adapter_name="motion-lora")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters(["lcm", "motion-lora"], adapter_weights=[0.55, 1.2])
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "best quality, masterpiece, 1girl, looking at viewer, blurry background, upper body, contemporary, dress"
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
frames = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=5,
|
||||
guidance_scale=1.25,
|
||||
cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 1},
|
||||
num_frames=24,
|
||||
generator=generator
|
||||
).frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_gif(frames, "animation.gif")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -78,7 +78,7 @@ image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=0,
|
||||
eta=0.3,
|
||||
eta=0.3,
|
||||
generator=torch.Generator(device=device).manual_seed(0),
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -156,14 +156,14 @@ image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=8,
|
||||
guidance_scale=0,
|
||||
eta=0.3,
|
||||
eta=0.3,
|
||||
generator=torch.Generator(device=device).manual_seed(0),
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
TCD-LoRA also supports other LoRAs trained on different styles. For example, let's load the [TheLastBen/Papercut_SDXL](https://huggingface.co/TheLastBen/Papercut_SDXL) LoRA and fuse it with the TCD-LoRA with the [`~loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.set_adapters`] method.
|
||||
TCD-LoRA also supports other LoRAs trained on different styles. For example, let's load the [TheLastBen/Papercut_SDXL](https://huggingface.co/TheLastBen/Papercut_SDXL) LoRA and fuse it with the TCD-LoRA with the [`~loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.set_adapters`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Check out the [Merge LoRAs](merge_loras) guide to learn more about efficient merging methods.
|
||||
@@ -171,7 +171,7 @@ TCD-LoRA also supports other LoRAs trained on different styles. For example, let
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
|
||||
from scheduling_tcd import TCDScheduler
|
||||
from scheduling_tcd import TCDScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
base_model_id = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
|
||||
@@ -191,7 +191,7 @@ image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=0,
|
||||
eta=0.3,
|
||||
eta=0.3,
|
||||
generator=torch.Generator(device=device).manual_seed(0),
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -215,7 +215,7 @@ from PIL import Image
|
||||
from transformers import DPTFeatureExtractor, DPTForDepthEstimation
|
||||
from diffusers import ControlNetModel, StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
from scheduling_tcd import TCDScheduler
|
||||
from scheduling_tcd import TCDScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
depth_estimator = DPTForDepthEstimation.from_pretrained("Intel/dpt-hybrid-midas").to(device)
|
||||
@@ -249,13 +249,13 @@ controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
controlnet_id,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
)
|
||||
).to(device)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
base_model_id,
|
||||
controlnet=controlnet,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
)
|
||||
).to(device)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = TCDScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
@@ -271,9 +271,9 @@ depth_image = get_depth_map(image)
|
||||
controlnet_conditioning_scale = 0.5 # recommended for good generalization
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=depth_image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=depth_image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=0,
|
||||
eta=0.3,
|
||||
controlnet_conditioning_scale=controlnet_conditioning_scale,
|
||||
@@ -290,7 +290,7 @@ grid_image = make_image_grid([depth_image, image], rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import ControlNetModel, StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
from scheduling_tcd import TCDScheduler
|
||||
from scheduling_tcd import TCDScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
base_model_id = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
|
||||
@@ -301,13 +301,13 @@ controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
controlnet_id,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
)
|
||||
).to(device)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionXLControlNetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
base_model_id,
|
||||
controlnet=controlnet,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
)
|
||||
).to(device)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = TCDScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
@@ -322,9 +322,9 @@ canny_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/di
|
||||
controlnet_conditioning_scale = 0.5 # recommended for good generalization
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=canny_image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=canny_image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=0,
|
||||
eta=0.3,
|
||||
controlnet_conditioning_scale=controlnet_conditioning_scale,
|
||||
@@ -336,7 +336,7 @@ grid_image = make_image_grid([canny_image, image], rows=1, cols=2)
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
The inference parameters in this example might not work for all examples, so we recommend you to try different values for `num_inference_steps`, `guidance_scale`, `controlnet_conditioning_scale` and `cross_attention_kwargs` parameters and choose the best one.
|
||||
The inference parameters in this example might not work for all examples, so we recommend you to try different values for `num_inference_steps`, `guidance_scale`, `controlnet_conditioning_scale` and `cross_attention_kwargs` parameters and choose the best one.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
@@ -350,7 +350,7 @@ from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
from ip_adapter import IPAdapterXL
|
||||
from scheduling_tcd import TCDScheduler
|
||||
from scheduling_tcd import TCDScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
base_model_path = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
|
||||
@@ -359,8 +359,8 @@ ip_ckpt = "sdxl_models/ip-adapter_sdxl.bin"
|
||||
tcd_lora_id = "h1t/TCD-SDXL-LoRA"
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
base_model_path,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
base_model_path,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16"
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = TCDScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
@@ -375,13 +375,13 @@ ref_image = load_image("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tencent-ailab/IP-Adapt
|
||||
prompt = "best quality, high quality, wearing sunglasses"
|
||||
|
||||
image = ip_model.generate(
|
||||
pil_image=ref_image,
|
||||
pil_image=ref_image,
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
scale=0.5,
|
||||
num_samples=1,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
num_samples=1,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=4,
|
||||
guidance_scale=0,
|
||||
eta=0.3,
|
||||
eta=0.3,
|
||||
seed=0,
|
||||
)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -230,7 +230,7 @@ from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16"
|
||||
)
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
# remove following line if xFormers is not installed or you have PyTorch 2.0 or higher installed
|
||||
pipeline.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
@@ -255,7 +255,7 @@ from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16"
|
||||
)
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
# remove following line if xFormers is not installed or you have PyTorch 2.0 or higher installed
|
||||
pipeline.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
@@ -296,7 +296,7 @@ from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16"
|
||||
)
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
# remove following line if xFormers is not installed or you have PyTorch 2.0 or higher installed
|
||||
pipeline.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
@@ -319,7 +319,7 @@ from diffusers.utils import load_image, make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16"
|
||||
)
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
# remove following line if xFormers is not installed or you have PyTorch 2.0 or higher installed
|
||||
pipeline.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -277,7 +277,7 @@ images = pipeline(
|
||||
|
||||
### IP-Adapter masking
|
||||
|
||||
Binary masks specify which portion of the output image should be assigned to an IP-Adapter. This is useful for composing more than one IP-Adapter image. For each input IP-Adapter image, you must provide a binary mask.
|
||||
Binary masks specify which portion of the output image should be assigned to an IP-Adapter. This is useful for composing more than one IP-Adapter image. For each input IP-Adapter image, you must provide a binary mask an an IP-Adapter.
|
||||
|
||||
To start, preprocess the input IP-Adapter images with the [`~image_processor.IPAdapterMaskProcessor.preprocess()`] to generate their masks. For optimal results, provide the output height and width to [`~image_processor.IPAdapterMaskProcessor.preprocess()`]. This ensures masks with different aspect ratios are appropriately stretched. If the input masks already match the aspect ratio of the generated image, you don't have to set the `height` and `width`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -305,18 +305,13 @@ masks = processor.preprocess([mask1, mask2], height=output_height, width=output_
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
When there is more than one input IP-Adapter image, load them as a list and provide the IP-Adapter scale list. Each of the input IP-Adapter images here corresponds to one of the masks generated above.
|
||||
When there is more than one input IP-Adapter image, load them as a list to ensure each image is assigned to a different IP-Adapter. Each of the input IP-Adapter images here correspond to the masks generated above.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.load_ip_adapter("h94/IP-Adapter", subfolder="sdxl_models", weight_name=["ip-adapter-plus-face_sdxl_vit-h.safetensors"])
|
||||
pipeline.set_ip_adapter_scale([[0.7, 0.7]]) # one scale for each image-mask pair
|
||||
|
||||
face_image1 = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/ip_mask_girl1.png")
|
||||
face_image2 = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/ip_mask_girl2.png")
|
||||
|
||||
ip_images = [[face_image1, face_image2]]
|
||||
|
||||
masks = [masks.reshape(1, masks.shape[0], masks.shape[2], masks.shape[3])]
|
||||
ip_images = [[face_image1], [face_image2]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex flex-row gap-4">
|
||||
@@ -333,6 +328,8 @@ masks = [masks.reshape(1, masks.shape[0], masks.shape[2], masks.shape[3])]
|
||||
Now pass the preprocessed masks to `cross_attention_kwargs` in the pipeline call.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.load_ip_adapter("h94/IP-Adapter", subfolder="sdxl_models", weight_name=["ip-adapter-plus-face_sdxl_vit-h.safetensors"] * 2)
|
||||
pipeline.set_ip_adapter_scale([0.7] * 2)
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(0)
|
||||
num_images = 1
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -365,12 +362,14 @@ IP-Adapter's image prompting and compatibility with other adapters and models ma
|
||||
|
||||
### Face model
|
||||
|
||||
Generating accurate faces is challenging because they are complex and nuanced. Diffusers supports two IP-Adapter checkpoints specifically trained to generate faces from the [h94/IP-Adapter](https://huggingface.co/h94/IP-Adapter) repository:
|
||||
Generating accurate faces is challenging because they are complex and nuanced. Diffusers supports two IP-Adapter checkpoints specifically trained to generate faces:
|
||||
|
||||
* [ip-adapter-full-face_sd15.safetensors](https://huggingface.co/h94/IP-Adapter/blob/main/models/ip-adapter-full-face_sd15.safetensors) is conditioned with images of cropped faces and removed backgrounds
|
||||
* [ip-adapter-plus-face_sd15.safetensors](https://huggingface.co/h94/IP-Adapter/blob/main/models/ip-adapter-plus-face_sd15.safetensors) uses patch embeddings and is conditioned with images of cropped faces
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, Diffusers supports all IP-Adapter checkpoints trained with face embeddings extracted by `insightface` face models. Supported models are from the [h94/IP-Adapter-FaceID](https://huggingface.co/h94/IP-Adapter-FaceID) repository.
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> [IP-Adapter-FaceID](https://huggingface.co/h94/IP-Adapter-FaceID) is a face-specific IP-Adapter trained with face ID embeddings instead of CLIP image embeddings, allowing you to generate more consistent faces in different contexts and styles. Try out this popular [community pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/community#ip-adapter-face-id) and see how it compares to the other face IP-Adapters.
|
||||
|
||||
For face models, use the [h94/IP-Adapter](https://huggingface.co/h94/IP-Adapter) checkpoint. It is also recommended to use [`DDIMScheduler`] or [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`] for face models.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -412,71 +411,6 @@ image
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
To use IP-Adapter FaceID models, first extract face embeddings with `insightface`. Then pass the list of tensors to the pipeline as `ip_adapter_image_embeds`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
from insightface.app import FaceAnalysis
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_config(pipeline.scheduler.config)
|
||||
pipeline.load_ip_adapter("h94/IP-Adapter-FaceID", subfolder=None, weight_name="ip-adapter-faceid_sd15.bin", image_encoder_folder=None)
|
||||
pipeline.set_ip_adapter_scale(0.6)
|
||||
|
||||
image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/ip_mask_girl1.png")
|
||||
|
||||
ref_images_embeds = []
|
||||
app = FaceAnalysis(name="buffalo_l", providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider', 'CPUExecutionProvider'])
|
||||
app.prepare(ctx_id=0, det_size=(640, 640))
|
||||
image = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(image), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
|
||||
faces = app.get(image)
|
||||
image = torch.from_numpy(faces[0].normed_embedding)
|
||||
ref_images_embeds.append(image.unsqueeze(0))
|
||||
ref_images_embeds = torch.stack(ref_images_embeds, dim=0).unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
neg_ref_images_embeds = torch.zeros_like(ref_images_embeds)
|
||||
id_embeds = torch.cat([neg_ref_images_embeds, ref_images_embeds]).to(dtype=torch.float16, device="cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(42)
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt="A photo of a girl",
|
||||
ip_adapter_image_embeds=[id_embeds],
|
||||
negative_prompt="monochrome, lowres, bad anatomy, worst quality, low quality",
|
||||
num_inference_steps=20, num_images_per_prompt=1,
|
||||
generator=generator
|
||||
).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Both IP-Adapter FaceID Plus and Plus v2 models require CLIP image embeddings. You can prepare face embeddings as shown previously, then you can extract and pass CLIP embeddings to the hidden image projection layers.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from insightface.utils import face_align
|
||||
|
||||
ref_images_embeds = []
|
||||
ip_adapter_images = []
|
||||
app = FaceAnalysis(name="buffalo_l", providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider', 'CPUExecutionProvider'])
|
||||
app.prepare(ctx_id=0, det_size=(640, 640))
|
||||
image = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(image), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
|
||||
faces = app.get(image)
|
||||
ip_adapter_images.append(face_align.norm_crop(image, landmark=faces[0].kps, image_size=224))
|
||||
image = torch.from_numpy(faces[0].normed_embedding)
|
||||
ref_images_embeds.append(image.unsqueeze(0))
|
||||
ref_images_embeds = torch.stack(ref_images_embeds, dim=0).unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
neg_ref_images_embeds = torch.zeros_like(ref_images_embeds)
|
||||
id_embeds = torch.cat([neg_ref_images_embeds, ref_images_embeds]).to(dtype=torch.float16, device="cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
clip_embeds = pipeline.prepare_ip_adapter_image_embeds(
|
||||
[ip_adapter_images], None, torch.device("cuda"), num_images, True)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline.unet.encoder_hid_proj.image_projection_layers[0].clip_embeds = clip_embeds.to(dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipeline.unet.encoder_hid_proj.image_projection_layers[0].shortcut = False # True if Plus v2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Multi IP-Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
More than one IP-Adapter can be used at the same time to generate specific images in more diverse styles. For example, you can use IP-Adapter-Face to generate consistent faces and characters, and IP-Adapter Plus to generate those faces in a specific style.
|
||||
@@ -658,87 +592,3 @@ image
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/YiYiXu/testing-images/resolve/main/ipa-controlnet-out.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### Style & layout control
|
||||
|
||||
[InstantStyle](https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.02733) is a plug-and-play method on top of IP-Adapter, which disentangles style and layout from image prompt to control image generation. This way, you can generate images following only the style or layout from image prompt, with significantly improved diversity. This is achieved by only activating IP-Adapters to specific parts of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
By default IP-Adapters are inserted to all layers of the model. Use the [`~loaders.IPAdapterMixin.set_ip_adapter_scale`] method with a dictionary to assign scales to IP-Adapter at different layers.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.load_ip_adapter("h94/IP-Adapter", subfolder="sdxl_models", weight_name="ip-adapter_sdxl.bin")
|
||||
|
||||
scale = {
|
||||
"down": {"block_2": [0.0, 1.0]},
|
||||
"up": {"block_0": [0.0, 1.0, 0.0]},
|
||||
}
|
||||
pipeline.set_ip_adapter_scale(scale)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will activate IP-Adapter at the second layer in the model's down-part block 2 and up-part block 0. The former is the layer where IP-Adapter injects layout information and the latter injects style. Inserting IP-Adapter to these two layers you can generate images following both the style and layout from image prompt, but with contents more aligned to text prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
style_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/0052a70beed5bf71b92610a43a52df6d286cd5f3/diffusers/rabbit.jpg")
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(26)
|
||||
image = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt="a cat, masterpiece, best quality, high quality",
|
||||
ip_adapter_image=style_image,
|
||||
negative_prompt="text, watermark, lowres, low quality, worst quality, deformed, glitch, low contrast, noisy, saturation, blurry",
|
||||
guidance_scale=5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=30,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex flex-row gap-4">
|
||||
<div class="flex-1">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/0052a70beed5bf71b92610a43a52df6d286cd5f3/diffusers/rabbit.jpg"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">IP-Adapter image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="flex-1">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/datasets/cat_style_layout.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">generated image</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
In contrast, inserting IP-Adapter to all layers will often generate images that overly focus on image prompt and diminish diversity.
|
||||
|
||||
Activate IP-Adapter only in the style layer and then call the pipeline again.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
scale = {
|
||||
"up": {"block_0": [0.0, 1.0, 0.0]},
|
||||
}
|
||||
pipeline.set_ip_adapter_scale(scale)
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(26)
|
||||
image = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt="a cat, masterpiece, best quality, high quality",
|
||||
ip_adapter_image=style_image,
|
||||
negative_prompt="text, watermark, lowres, low quality, worst quality, deformed, glitch, low contrast, noisy, saturation, blurry",
|
||||
guidance_scale=5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=30,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex flex-row gap-4">
|
||||
<div class="flex-1">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/datasets/cat_style_only.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">IP-Adapter only in style layer</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="flex-1">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/datasets/cat_ip_adapter.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">IP-Adapter in all layers</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you don't have to specify all layers in the dictionary. Those not included in the dictionary will be set to scale 0 which means disable IP-Adapter by default.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,75 +10,57 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Load pipelines
|
||||
# Load pipelines, models, and schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusion systems consist of multiple components like parameterized models and schedulers that interact in complex ways. That is why we designed the [`DiffusionPipeline`] to wrap the complexity of the entire diffusion system into an easy-to-use API. At the same time, the [`DiffusionPipeline`] is entirely customizable so you can modify each component to build a diffusion system for your use case.
|
||||
Having an easy way to use a diffusion system for inference is essential to 🧨 Diffusers. Diffusion systems often consist of multiple components like parameterized models, tokenizers, and schedulers that interact in complex ways. That is why we designed the [`DiffusionPipeline`] to wrap the complexity of the entire diffusion system into an easy-to-use API, while remaining flexible enough to be adapted for other use cases, such as loading each component individually as building blocks to assemble your own diffusion system.
|
||||
|
||||
Everything you need for inference or training is accessible with the `from_pretrained()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to load:
|
||||
|
||||
- pipelines from the Hub and locally
|
||||
- different components into a pipeline
|
||||
- multiple pipelines without increasing memory usage
|
||||
- checkpoint variants such as different floating point types or non-exponential mean averaged (EMA) weights
|
||||
- models and schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
## Load a pipeline
|
||||
## Diffusion Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Skip to the [DiffusionPipeline explained](#diffusionpipeline-explained) section if you're interested in an explanation about how the [`DiffusionPipeline`] class works.
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
There are two ways to load a pipeline for a task:
|
||||
💡 Skip to the [DiffusionPipeline explained](#diffusionpipeline-explained) section if you are interested in learning in more detail about how the [`DiffusionPipeline`] class works.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Load the generic [`DiffusionPipeline`] class and allow it to automatically detect the correct pipeline class from the checkpoint.
|
||||
2. Load a specific pipeline class for a specific task.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="pipelines">
|
||||
<hfoption id="generic pipeline">
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] class is a simple and generic way to load the latest trending diffusion model from the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=trending). It uses the [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method to automatically detect the correct pipeline class for a task from the checkpoint, downloads and caches all the required configuration and weight files, and returns a pipeline ready for inference.
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] class is the simplest and most generic way to load the latest trending diffusion model from the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers&sort=trending). The [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method automatically detects the correct pipeline class from the checkpoint, downloads, and caches all the required configuration and weight files, and returns a pipeline instance ready for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This same checkpoint can also be used for an image-to-image task. The [`DiffusionPipeline`] class can handle any task as long as you provide the appropriate inputs. For example, for an image-to-image task, you need to pass an initial image to the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/img2img-init.png")
|
||||
prompt = "Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k"
|
||||
image = pipeline("Astronaut in a jungle, cold color palette, muted colors, detailed, 8k", image=init_image).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="specific pipeline">
|
||||
|
||||
Checkpoints can be loaded by their specific pipeline class if you already know it. For example, to load a Stable Diffusion model, use the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] class.
|
||||
You can also load a checkpoint with its specific pipeline class. The example above loaded a Stable Diffusion model; to get the same result, use the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] class:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This same checkpoint may also be used for another task like image-to-image. To differentiate what task you want to use the checkpoint for, you have to use the corresponding task-specific pipeline class. For example, to use the same checkpoint for image-to-image, use the [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`] class.
|
||||
A checkpoint (such as [`CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4`](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4) or [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)) may also be used for more than one task, like text-to-image or image-to-image. To differentiate what task you want to use the checkpoint for, you have to load it directly with its corresponding task-specific pipeline class:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
Use the Space below to gauge a pipeline's memory requirements before you download and load it to see if it runs on your hardware.
|
||||
You can use the Space below to gauge the memory requirements of a pipeline you want to load beforehand without downloading the pipeline checkpoints:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="block dark:hidden">
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
@@ -97,310 +79,264 @@ Use the Space below to gauge a pipeline's memory requirements before you downloa
|
||||
|
||||
### Local pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
To load a pipeline locally, use [git-lfs](https://git-lfs.github.com/) to manually download a checkpoint to your local disk.
|
||||
To load a diffusion pipeline locally, use [`git-lfs`](https://git-lfs.github.com/) to manually download the checkpoint (in this case, [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)) to your local disk. This creates a local folder, `./stable-diffusion-v1-5`, on your disk:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git-lfs install
|
||||
git clone https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This creates a local folder, ./stable-diffusion-v1-5, on your disk and you should pass its path to [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`].
|
||||
Then pass the local path to [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
repo_id = "./stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method won't download files from the Hub when it detects a local path, but this also means it won't download and cache the latest changes to a checkpoint.
|
||||
The [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method won't download any files from the Hub when it detects a local path, but this also means it won't download and cache the latest changes to a checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
## Customize a pipeline
|
||||
### Swap components in a pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize a pipeline by loading different components into it. This is important because you can:
|
||||
You can customize the default components of any pipeline with another compatible component. Customization is important because:
|
||||
|
||||
- change to a scheduler with faster generation speed or higher generation quality depending on your needs (call the `scheduler.compatibles` method on your pipeline to see compatible schedulers)
|
||||
- change a default pipeline component to a newer and better performing one
|
||||
- Changing the scheduler is important for exploring the trade-off between generation speed and quality.
|
||||
- Different components of a model are typically trained independently and you can swap out a component with a better-performing one.
|
||||
- During finetuning, usually only some components - like the UNet or text encoder - are trained.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let's customize the default [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://hf.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0) checkpoint with:
|
||||
|
||||
- The [`HeunDiscreteScheduler`] to generate higher quality images at the expense of slower generation speed. You must pass the `subfolder="scheduler"` parameter in [`~HeunDiscreteScheduler.from_pretrained`] to load the scheduler configuration into the correct [subfolder](https://hf.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0/tree/main/scheduler) of the pipeline repository.
|
||||
- A more stable VAE that runs in fp16.
|
||||
To find out which schedulers are compatible for customization, you can use the `compatibles` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline, HeunDiscreteScheduler, AutoencoderKL
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = HeunDiscreteScheduler.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained("madebyollin/sdxl-vae-fp16-fix", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
stable_diffusion.scheduler.compatibles
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now pass the new scheduler and VAE to the [`StableDiffusionXLPipeline`].
|
||||
Let's use the [`SchedulerMixin.from_pretrained`] method to replace the default [`PNDMScheduler`] with a more performant scheduler, [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`]. The `subfolder="scheduler"` argument is required to load the scheduler configuration from the correct [subfolder](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main/scheduler) of the pipeline repository.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
scheduler=scheduler,
|
||||
vae=vae,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
variant="fp16",
|
||||
use_safetensors=True
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Reuse a pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
When you load multiple pipelines that share the same model components, it makes sense to reuse the shared components instead of reloading everything into memory again, especially if your hardware is memory-constrained. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
1. You generated an image with the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] but you want to improve its quality with the [`StableDiffusionSAGPipeline`]. Both of these pipelines share the same pretrained model, so it'd be a waste of memory to load the same model twice.
|
||||
2. You want to add a model component, like a [`MotionAdapter`](../api/pipelines/animatediff#animatediffpipeline), to [`AnimateDiffPipeline`] which was instantiated from an existing [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]. Again, both pipelines share the same pretrained model, so it'd be a waste of memory to load an entirely new pipeline again.
|
||||
|
||||
With the [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`] API, you can switch between multiple pipelines to take advantage of their different features without increasing memory-usage. It is similar to turning on and off a feature in your pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> To switch between tasks (rather than features), use the [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`] method with the [AutoPipeline](../api/pipelines/auto_pipeline) class, which automatically identifies the pipeline class based on the task (learn more in the [AutoPipeline](../tutorials/autopipeline) tutorial).
|
||||
|
||||
Let's start with a [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] and then reuse the loaded model components to create a [`StableDiffusionSAGPipeline`] to increase generation quality. You'll use the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] with an [IP-Adapter](./ip_adapter) to generate a bear eating pizza.
|
||||
Then you can pass the new [`EulerDiscreteScheduler`] instance to the `scheduler` argument in [`DiffusionPipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, StableDiffusionSAGPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import compute_module_sizes
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline, EulerDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
image = load_image("https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/load_neg_embed.png")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_sd = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("SG161222/Realistic_Vision_V6.0_B1_noVAE", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe_sd.load_ip_adapter("h94/IP-Adapter", subfolder="models", weight_name="ip-adapter_sd15.bin")
|
||||
pipe_sd.set_ip_adapter_scale(0.6)
|
||||
pipe_sd.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(33)
|
||||
out_sd = pipe_sd(
|
||||
prompt="bear eats pizza",
|
||||
negative_prompt="wrong white balance, dark, sketches,worst quality,low quality",
|
||||
ip_adapter_image=image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
out_sd
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
scheduler = EulerDiscreteScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, scheduler=scheduler, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/YiYiXu/testing-images/resolve/main/from_pipe_out_sd_0.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
### Safety checker
|
||||
|
||||
For reference, you can check how much memory this process consumed.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def bytes_to_giga_bytes(bytes):
|
||||
return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
|
||||
print(f"Max memory allocated: {bytes_to_giga_bytes(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated())} GB")
|
||||
"Max memory allocated: 4.406213283538818 GB"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, reuse the same pipeline components from [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] in [`StableDiffusionSAGPipeline`] with the [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Some pipeline methods may not function properly on new pipelines created with [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`]. For instance, the [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload`] method installs hooks on the model components based on a unique offloading sequence for each pipeline. If the models are executed in a different order in the new pipeline, the CPU offloading may not work correctly.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> To ensure everything works as expected, we recommend re-applying a pipeline method on a new pipeline created with [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`].
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe_sag = StableDiffusionSAGPipeline.from_pipe(
|
||||
pipe_sd
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(33)
|
||||
out_sag = pipe_sag(
|
||||
prompt="bear eats pizza",
|
||||
negative_prompt="wrong white balance, dark, sketches,worst quality,low quality",
|
||||
ip_adapter_image=image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
guidance_scale=1.0,
|
||||
sag_scale=0.75
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
out_sag
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/YiYiXu/testing-images/resolve/main/from_pipe_out_sag_1.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
If you check the memory usage, you'll see it remains the same as before because [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] and [`StableDiffusionSAGPipeline`] are sharing the same pipeline components. This allows you to use them interchangeably without any additional memory overhead.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
print(f"Max memory allocated: {bytes_to_giga_bytes(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated())} GB")
|
||||
"Max memory allocated: 4.406213283538818 GB"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's animate the image with the [`AnimateDiffPipeline`] and also add a [`MotionAdapter`] module to the pipeline. For the [`AnimateDiffPipeline`], you need to unload the IP-Adapter first and reload it *after* you've created your new pipeline (this only applies to the [`AnimateDiffPipeline`]).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import AnimateDiffPipeline, MotionAdapter, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_gif
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_sag.unload_ip_adapter()
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5-2", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_animate = AnimateDiffPipeline.from_pipe(pipe_sd, motion_adapter=adapter)
|
||||
pipe_animate.scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_config(pipe_animate.scheduler.config, beta_schedule="linear")
|
||||
# load IP-Adapter and LoRA weights again
|
||||
pipe_animate.load_ip_adapter("h94/IP-Adapter", subfolder="models", weight_name="ip-adapter_sd15.bin")
|
||||
pipe_animate.load_lora_weights("guoyww/animatediff-motion-lora-zoom-out", adapter_name="zoom-out")
|
||||
pipe_animate.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(33)
|
||||
pipe_animate.set_adapters("zoom-out", adapter_weights=0.75)
|
||||
out = pipe_animate(
|
||||
prompt="bear eats pizza",
|
||||
num_frames=16,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
ip_adapter_image=image,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_gif(out, "out_animate.gif")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img class="rounded-xl" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/YiYiXu/testing-images/resolve/main/from_pipe_out_animate_3.gif"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
The [`AnimateDiffPipeline`] is more memory-intensive and consumes 15GB of memory (see the [Memory-usage of from_pipe](#memory-usage-of-from_pipe) section to learn what this means for your memory-usage).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
print(f"Max memory allocated: {bytes_to_giga_bytes(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated())} GB")
|
||||
"Max memory allocated: 15.178664207458496 GB"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Modify from_pipe components
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines loaded with [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`] can be customized with different model components or methods. However, whenever you modify the *state* of the model components, it affects all the other pipelines that share the same components. For example, if you call [`~diffusers.loaders.IPAdapterMixin.unload_ip_adapter`] on the [`StableDiffusionSAGPipeline`], you won't be able to use IP-Adapter with the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] because it's been removed from their shared components.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipe.sag_unload_ip_adapter()
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(33)
|
||||
out_sd = pipe_sd(
|
||||
prompt="bear eats pizza",
|
||||
negative_prompt="wrong white balance, dark, sketches,worst quality,low quality",
|
||||
ip_adapter_image=image,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
"AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'image_projection_layers'"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory usage of from_pipe
|
||||
|
||||
The memory requirement of loading multiple pipelines with [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pipe`] is determined by the pipeline with the highest memory-usage regardless of the number of pipelines you create.
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Memory usage (GB) |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| StableDiffusionPipeline | 4.400 |
|
||||
| StableDiffusionSAGPipeline | 4.400 |
|
||||
| AnimateDiffPipeline | 15.178 |
|
||||
|
||||
The [`AnimateDiffPipeline`] has the highest memory requirement, so the *total memory-usage* is based only on the [`AnimateDiffPipeline`]. Your memory-usage will not increase if you create additional pipelines as long as their memory requirements doesn't exceed that of the [`AnimateDiffPipeline`]. Each pipeline can be used interchangeably without any additional memory overhead.
|
||||
|
||||
## Safety checker
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers implements a [safety checker](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py) for Stable Diffusion models which can generate harmful content. The safety checker screens the generated output against known hardcoded not-safe-for-work (NSFW) content. If for whatever reason you'd like to disable the safety checker, pass `safety_checker=None` to the [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] method.
|
||||
Diffusion models like Stable Diffusion can generate harmful content, which is why 🧨 Diffusers has a [safety checker](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py) to check generated outputs against known hardcoded NSFW content. If you'd like to disable the safety checker for whatever reason, pass `None` to the `safety_checker` argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", safety_checker=None, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, safety_checker=None, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
You have disabled the safety checker for <class 'diffusers.pipelines.stable_diffusion.pipeline_stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipeline'> by passing `safety_checker=None`. Ensure that you abide by the conditions of the Stable Diffusion license and do not expose unfiltered results in services or applications open to the public. Both the diffusers team and Hugging Face strongly recommend keeping the safety filter enabled in all public-facing circumstances, disabling it only for use cases that involve analyzing network behavior or auditing its results. For more information, please have a look at https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/254 .
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Reuse components across pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
You can also reuse the same components in multiple pipelines to avoid loading the weights into RAM twice. Use the [`~DiffusionPipeline.components`] method to save the components:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion_txt2img = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
|
||||
components = stable_diffusion_txt2img.components
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can pass the `components` to another pipeline without reloading the weights into RAM:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
stable_diffusion_img2img = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline(**components)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also pass the components individually to the pipeline if you want more flexibility over which components to reuse or disable. For example, to reuse the same components in the text-to-image pipeline, except for the safety checker and feature extractor, in the image-to-image pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
stable_diffusion_txt2img = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
stable_diffusion_img2img = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline(
|
||||
vae=stable_diffusion_txt2img.vae,
|
||||
text_encoder=stable_diffusion_txt2img.text_encoder,
|
||||
tokenizer=stable_diffusion_txt2img.tokenizer,
|
||||
unet=stable_diffusion_txt2img.unet,
|
||||
scheduler=stable_diffusion_txt2img.scheduler,
|
||||
safety_checker=None,
|
||||
feature_extractor=None,
|
||||
requires_safety_checker=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Checkpoint variants
|
||||
|
||||
A checkpoint variant is usually a checkpoint whose weights are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Stored in a different floating point type, such as [torch.float16](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html#data-types), because it only requires half the bandwidth and storage to download. You can't use this variant if you're continuing training or using a CPU.
|
||||
- Non-exponential mean averaged (EMA) weights which shouldn't be used for inference. You should use this variant to continue finetuning a model.
|
||||
- Stored in a different floating point type for lower precision and lower storage, such as [`torch.float16`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/tensors.html#data-types), because it only requires half the bandwidth and storage to download. You can't use this variant if you're continuing training or using a CPU.
|
||||
- Non-exponential mean averaged (EMA) weights, which shouldn't be used for inference. You should use these to continue fine-tuning a model.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> When the checkpoints have identical model structures, but they were trained on different datasets and with a different training setup, they should be stored in separate repositories. For example, [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2](https://hf.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2) and [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1](https://hf.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1) are stored in separate repositories.
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Otherwise, a variant is **identical** to the original checkpoint. They have exactly the same serialization format (like [safetensors](./using_safetensors)), model structure, and their weights have identical tensor shapes.
|
||||
💡 When the checkpoints have identical model structures, but they were trained on different datasets and with a different training setup, they should be stored in separate repositories instead of variations (for example, [`stable-diffusion-v1-4`] and [`stable-diffusion-v1-5`]).
|
||||
|
||||
| **checkpoint type** | **weight name** | **argument for loading weights** |
|
||||
|---------------------|---------------------------------------------|----------------------------------|
|
||||
| original | diffusion_pytorch_model.safetensors | |
|
||||
| floating point | diffusion_pytorch_model.fp16.safetensors | `variant`, `torch_dtype` |
|
||||
| non-EMA | diffusion_pytorch_model.non_ema.safetensors | `variant` |
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
There are two important arguments for loading variants:
|
||||
Otherwise, a variant is **identical** to the original checkpoint. They have exactly the same serialization format (like [Safetensors](./using_safetensors)), model structure, and weights that have identical tensor shapes.
|
||||
|
||||
- `torch_dtype` specifies the floating point precision of the loaded checkpoint. For example, if you want to save bandwidth by loading a fp16 variant, you should set `variant="fp16"` and `torch_dtype=torch.float16` to *convert the weights* to fp16. Otherwise, the fp16 weights are converted to the default fp32 precision.
|
||||
| **checkpoint type** | **weight name** | **argument for loading weights** |
|
||||
|---------------------|-------------------------------------|----------------------------------|
|
||||
| original | diffusion_pytorch_model.bin | |
|
||||
| floating point | diffusion_pytorch_model.fp16.bin | `variant`, `torch_dtype` |
|
||||
| non-EMA | diffusion_pytorch_model.non_ema.bin | `variant` |
|
||||
|
||||
If you only set `torch_dtype=torch.float16`, the default fp32 weights are downloaded first and then converted to fp16.
|
||||
There are two important arguments to know for loading variants:
|
||||
|
||||
- `variant` specifies which files should be loaded from the repository. For example, if you want to load a non-EMA variant of a UNet from [runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5](https://hf.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main/unet), set `variant="non_ema"` to download the `non_ema` file.
|
||||
- `torch_dtype` defines the floating point precision of the loaded checkpoints. For example, if you want to save bandwidth by loading a `fp16` variant, you should specify `torch_dtype=torch.float16` to *convert the weights* to `fp16`. Otherwise, the `fp16` weights are converted to the default `fp32` precision. You can also load the original checkpoint without defining the `variant` argument, and convert it to `fp16` with `torch_dtype=torch.float16`. In this case, the default `fp32` weights are downloaded first, and then they're converted to `fp16` after loading.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="variants">
|
||||
<hfoption id="fp16">
|
||||
- `variant` defines which files should be loaded from the repository. For example, if you want to load a `non_ema` variant from the [`diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants`](https://huggingface.co/diffusers/stable-diffusion-variants/tree/main/unet) repository, you should specify `variant="non_ema"` to download the `non_ema` files.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
# load fp16 variant
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="fp16", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="non-EMA">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
# load non_ema variant
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="non_ema", use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
Use the `variant` parameter in the [`DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`] method to save a checkpoint as a different floating point type or as a non-EMA variant. You should try save a variant to the same folder as the original checkpoint, so you have the option of loading both from the same folder.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="save">
|
||||
<hfoption id="fp16">
|
||||
To save a checkpoint stored in a different floating-point type or as a non-EMA variant, use the [`DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`] method and specify the `variant` argument. You should try and save a variant to the same folder as the original checkpoint, so you can load both from the same folder:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline.save_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="fp16")
|
||||
# save as fp16 variant
|
||||
stable_diffusion.save_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="fp16")
|
||||
# save as non-ema variant
|
||||
stable_diffusion.save_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="non_ema")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="non_ema">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.save_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="non_ema")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't save the variant to an existing folder, you must specify the `variant` argument otherwise it'll throw an `Exception` because it can't find the original checkpoint.
|
||||
If you don't save the variant to an existing folder, you must specify the `variant` argument otherwise it'll throw an `Exception` because it can't find the original checkpoint:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# 👎 this won't work
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"./stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
# 👍 this works
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
stable_diffusion = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"./stable-diffusion-v1-5", variant="fp16", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
TODO(Patrick) - Make sure to uncomment this part as soon as things are deprecated.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using `revision` to load pipeline variants is deprecated
|
||||
|
||||
Previously the `revision` argument of [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] was heavily used to
|
||||
load model variants, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4", revision="fp16", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
However, this behavior is now deprecated since the "revision" argument should (just as it's done in GitHub) better be used to load model checkpoints from a specific commit or branch in development.
|
||||
|
||||
The above example is therefore deprecated and won't be supported anymore for `diffusers >= 1.0.0`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
If you load diffusers pipelines or models with `revision="fp16"` or `revision="non_ema"`,
|
||||
please make sure to update the code and use `variant="fp16"` or `variation="non_ema"` respectively
|
||||
instead.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
## Models
|
||||
|
||||
Models are loaded from the [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] method, which downloads and caches the latest version of the model weights and configurations. If the latest files are available in the local cache, [`~ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] reuses files in the cache instead of re-downloading them.
|
||||
|
||||
Models can be loaded from a subfolder with the `subfolder` argument. For example, the model weights for `runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5` are stored in the [`unet`](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/tree/main/unet) subfolder:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
model = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="unet", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or directly from a repository's [directory](https://huggingface.co/google/ddpm-cifar10-32/tree/main):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import UNet2DModel
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "google/ddpm-cifar10-32"
|
||||
model = UNet2DModel.from_pretrained(repo_id, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also load and save model variants by specifying the `variant` argument in [`ModelMixin.from_pretrained`] and [`ModelMixin.save_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
|
||||
model = UNet2DConditionModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", subfolder="unet", variant="non_ema", use_safetensors=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.save_pretrained("./local-unet", variant="non_ema")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
Schedulers are loaded from the [`SchedulerMixin.from_pretrained`] method, and unlike models, schedulers are **not parameterized** or **trained**; they are defined by a configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
Loading schedulers does not consume any significant amount of memory and the same configuration file can be used for a variety of different schedulers.
|
||||
For example, the following schedulers are compatible with [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], which means you can load the same scheduler configuration file in any of these classes:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers import (
|
||||
DDPMScheduler,
|
||||
DDIMScheduler,
|
||||
PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
LMSDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
EulerDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
DPMSolverMultistepScheduler,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
repo_id = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
|
||||
ddpm = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
ddim = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
pndm = PNDMScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
lms = LMSDiscreteScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
euler_anc = EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
euler = EulerDiscreteScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
dpm = DPMSolverMultistepScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id, subfolder="scheduler")
|
||||
|
||||
# replace `dpm` with any of `ddpm`, `ddim`, `pndm`, `lms`, `euler_anc`, `euler`
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(repo_id, scheduler=dpm, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## DiffusionPipeline explained
|
||||
|
||||
As a class method, [`DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] is responsible for two things:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -153,43 +153,18 @@ image
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/load_attn_proc.png" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For both [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] and [`~loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.load_attn_procs`], you can pass the `cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 0.5}` parameter to adjust how much of the LoRA weights to use. A value of `0` is the same as only using the base model weights, and a value of `1` is equivalent to using the fully finetuned LoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To unload the LoRA weights, use the [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.unload_lora_weights`] method to discard the LoRA weights and restore the model to its original weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.unload_lora_weights()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Adjust LoRA weight scale
|
||||
|
||||
For both [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights`] and [`~loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.load_attn_procs`], you can pass the `cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 0.5}` parameter to adjust how much of the LoRA weights to use. A value of `0` is the same as only using the base model weights, and a value of `1` is equivalent to using the fully finetuned LoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
For more granular control on the amount of LoRA weights used per layer, you can use [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.set_adapters`] and pass a dictionary specifying by how much to scale the weights in each layer by.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe = ... # create pipeline
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights(..., adapter_name="my_adapter")
|
||||
scales = {
|
||||
"text_encoder": 0.5,
|
||||
"text_encoder_2": 0.5, # only usable if pipe has a 2nd text encoder
|
||||
"unet": {
|
||||
"down": 0.9, # all transformers in the down-part will use scale 0.9
|
||||
# "mid" # in this example "mid" is not given, therefore all transformers in the mid part will use the default scale 1.0
|
||||
"up": {
|
||||
"block_0": 0.6, # all 3 transformers in the 0th block in the up-part will use scale 0.6
|
||||
"block_1": [0.4, 0.8, 1.0], # the 3 transformers in the 1st block in the up-part will use scales 0.4, 0.8 and 1.0 respectively
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters("my_adapter", scales)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This also works with multiple adapters - see [this guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/tutorials/using_peft_for_inference#customize-adapters-strength) for how to do it.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, [`~loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.set_adapters`] only supports scaling attention weights. If a LoRA has other parts (e.g., resnets or down-/upsamplers), they will keep a scale of 1.0.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Kohya and TheLastBen
|
||||
|
||||
Other popular LoRA trainers from the community include those by [Kohya](https://github.com/kohya-ss/sd-scripts/) and [TheLastBen](https://github.com/TheLastBen/fast-stable-diffusion). These trainers create different LoRA checkpoints than those trained by 🤗 Diffusers, but they can still be loaded in the same way.
|
||||
@@ -320,40 +295,3 @@ pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline.load_ip_adapter("h94/IP-Adapter", subfolder="sdxl_models", weight_name="ip-adapter-plus_sdxl_vit-h.safetensors")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### IP-Adapter Face ID models
|
||||
|
||||
The IP-Adapter FaceID models are experimental IP Adapters that use image embeddings generated by `insightface` instead of CLIP image embeddings. Some of these models also use LoRA to improve ID consistency.
|
||||
You need to install `insightface` and all its requirements to use these models.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
As InsightFace pretrained models are available for non-commercial research purposes, IP-Adapter-FaceID models are released exclusively for research purposes and are not intended for commercial use.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline.load_ip_adapter("h94/IP-Adapter-FaceID", subfolder=None, weight_name="ip-adapter-faceid_sdxl.bin", image_encoder_folder=None)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use one of the two IP-Adapter FaceID Plus models, you must also load the CLIP image encoder, as this models use both `insightface` and CLIP image embeddings to achieve better photorealism.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import CLIPVisionModelWithProjection
|
||||
|
||||
image_encoder = CLIPVisionModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"laion/CLIP-ViT-H-14-laion2B-s32B-b79K",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
image_encoder=image_encoder,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline.load_ip_adapter("h94/IP-Adapter-FaceID", subfolder=None, weight_name="ip-adapter-faceid-plus_sd15.bin")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user