mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
synced 2025-12-07 04:54:47 +08:00
Compare commits
7 Commits
fix-schedu
...
v0.21.1
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
60ab8fad16 | ||
|
|
d17240457f | ||
|
|
7512fc4df5 | ||
|
|
0c2f1ccc97 | ||
|
|
47f2d2c7be | ||
|
|
af85591593 | ||
|
|
29f15673ed |
46
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
46
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
@@ -13,9 +13,8 @@ body:
|
||||
*Give your issue a fitting title. Assume that someone which very limited knowledge of diffusers can understand your issue. Add links to the source code, documentation other issues, pull requests etc...*
|
||||
- 2. If your issue is about something not working, **always** provide a reproducible code snippet. The reader should be able to reproduce your issue by **only copy-pasting your code snippet into a Python shell**.
|
||||
*The community cannot solve your issue if it cannot reproduce it. If your bug is related to training, add your training script and make everything needed to train public. Otherwise, just add a simple Python code snippet.*
|
||||
- 3. Add the **minimum** amount of code / context that is needed to understand, reproduce your issue.
|
||||
- 3. Add the **minimum amount of code / context that is needed to understand, reproduce your issue**.
|
||||
*Make the life of maintainers easy. `diffusers` is getting many issues every day. Make sure your issue is about one bug and one bug only. Make sure you add only the context, code needed to understand your issues - nothing more. Generally, every issue is a way of documenting this library, try to make it a good documentation entry.*
|
||||
- 4. For issues related to community pipelines (i.e., the pipelines located in the `examples/community` folder), please tag the author of the pipeline in your issue thread as those pipelines are not maintained.
|
||||
- type: markdown
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
value: |
|
||||
@@ -61,46 +60,21 @@ body:
|
||||
All issues are read by one of the core maintainers, so if you don't know who to tag, just leave this blank and
|
||||
a core maintainer will ping the right person.
|
||||
|
||||
Please tag a maximum of 2 people.
|
||||
Please tag fewer than 3 people.
|
||||
|
||||
General library related questions: @patrickvonplaten and @sayakpaul
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on DiffusionPipeline (Saving, Loading, From pretrained, ...):
|
||||
Questions on the training examples: @williamberman, @sayakpaul, @yiyixuxu
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on pipelines:
|
||||
- Stable Diffusion @yiyixuxu @DN6 @patrickvonplaten @sayakpaul @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- Stable Diffusion XL @yiyixuxu @sayakpaul @DN6 @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- Kandinsky @yiyixuxu @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- ControlNet @sayakpaul @yiyixuxu @DN6 @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- T2I Adapter @sayakpaul @yiyixuxu @DN6 @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- IF @DN6 @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- Text-to-Video / Video-to-Video @DN6 @sayakpaul @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- Wuerstchen @DN6 @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- Other: @yiyixuxu @DN6
|
||||
Questions on memory optimizations, LoRA, float16, etc.: @williamberman, @patrickvonplaten, and @sayakpaul
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on models:
|
||||
- UNet @DN6 @yiyixuxu @sayakpaul @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- VAE @sayakpaul @DN6 @yiyixuxu @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- Transformers/Attention @DN6 @yiyixuxu @sayakpaul @DN6 @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
Questions on schedulers: @patrickvonplaten and @williamberman
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on Schedulers: @yiyixuxu @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on LoRA: @sayakpaul @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on Textual Inversion: @sayakpaul @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on Training:
|
||||
- DreamBooth @sayakpaul @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- Text-to-Image Fine-tuning @sayakpaul @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- Textual Inversion @sayakpaul @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
- ControlNet @sayakpaul @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on Tests: @DN6 @sayakpaul @yiyixuxu
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on Documentation: @stevhliu
|
||||
Questions on models and pipelines: @patrickvonplaten, @sayakpaul, and @williamberman
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on JAX- and MPS-related things: @pcuenca
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on audio pipelines: @DN6 @patrickvonplaten
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Questions on audio pipelines: @patrickvonplaten, @kashif, and @sanchit-gandhi
|
||||
|
||||
Documentation: @stevhliu and @yiyixuxu
|
||||
placeholder: "@Username ..."
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/build_docker_images.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build_docker_images.yml
vendored
@@ -26,8 +26,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
image-name:
|
||||
- diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
- diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
- diffusers-pytorch-compile-cuda
|
||||
- diffusers-pytorch-xformers-cuda
|
||||
- diffusers-flax-cpu
|
||||
- diffusers-flax-tpu
|
||||
- diffusers-onnxruntime-cpu
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
install_libgl1: true
|
||||
package: diffusers
|
||||
notebook_folder: diffusers_doc
|
||||
languages: en ko zh ja pt
|
||||
languages: en ko zh
|
||||
|
||||
secrets:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.HUGGINGFACE_PUSH }}
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
@@ -15,4 +15,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
pr_number: ${{ github.event.number }}
|
||||
install_libgl1: true
|
||||
package: diffusers
|
||||
languages: en ko zh ja pt
|
||||
languages: en ko zh
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/pr_dependency_test.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/pr_dependency_test.yml
vendored
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.8"
|
||||
python-version: "3.7"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
34
.github/workflows/pr_flax_dependency_test.yml
vendored
34
.github/workflows/pr_flax_dependency_test.yml
vendored
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Run Flax dependency tests
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.run_id }}
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: true
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
check_flax_dependencies:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.8"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
pip install "jax[cpu]>=0.2.16,!=0.3.2"
|
||||
pip install "flax>=0.4.1"
|
||||
pip install "jaxlib>=0.1.65"
|
||||
pip install pytest
|
||||
- name: Check for soft dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pytest tests/others/test_dependencies.py
|
||||
4
.github/workflows/pr_quality.yml
vendored
4
.github/workflows/pr_quality.yml
vendored
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.8"
|
||||
python-version: "3.7"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.8"
|
||||
python-version: "3.7"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
67
.github/workflows/pr_test_peft_backend.yml
vendored
67
.github/workflows/pr_test_peft_backend.yml
vendored
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Fast tests for PRs - PEFT backend
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.run_id }}
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: true
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
DIFFUSERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 4
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 4
|
||||
PYTEST_TIMEOUT: 60
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_fast_tests:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- name: LoRA
|
||||
framework: lora
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_cpu_lora
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.config.name }}
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.config.runner }}
|
||||
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ matrix.config.image }}
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m pip install -e .[quality,test]
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
python -m pip install -U git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
python -m pip install -U git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run fast PyTorch LoRA CPU tests with PEFT backend
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'lora' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/lora/test_lora_layers_peft.py
|
||||
19
.github/workflows/pr_tests.yml
vendored
19
.github/workflows/pr_tests.yml
vendored
@@ -34,11 +34,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_cpu_models_schedulers
|
||||
- name: LoRA
|
||||
framework: lora
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu
|
||||
report: torch_cpu_lora
|
||||
- name: Fast Flax CPU tests
|
||||
framework: flax
|
||||
runner: docker-cpu
|
||||
@@ -72,7 +67,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m pip install -e .[quality,test]
|
||||
python -m pip install accelerate
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@@ -94,14 +89,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/models tests/schedulers tests/others
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run fast PyTorch LoRA CPU tests
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'lora' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx and not Dependency" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/lora
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run fast Flax TPU tests
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'flax' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@@ -115,7 +102,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
examples/test_examples.py
|
||||
examples/test_examples.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
@@ -183,4 +170,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: pr_${{ matrix.config.report }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
32
.github/workflows/pr_torch_dependency_test.yml
vendored
32
.github/workflows/pr_torch_dependency_test.yml
vendored
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Run Torch dependency tests
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.run_id }}
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: true
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
check_torch_dependencies:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.8"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio
|
||||
pip install pytest
|
||||
- name: Check for soft dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pytest tests/others/test_dependencies.py
|
||||
355
.github/workflows/push_tests.yml
vendored
355
.github/workflows/push_tests.yml
vendored
@@ -1,11 +1,10 @@
|
||||
name: Slow Tests on main
|
||||
name: Slow tests on main
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
DIFFUSERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
@@ -13,115 +12,53 @@ env:
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
PYTEST_TIMEOUT: 600
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
PIPELINE_USAGE_CUTOFF: 50000
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
setup_torch_cuda_pipeline_matrix:
|
||||
name: Setup Torch Pipelines CUDA Slow Tests Matrix
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cpu # this is a CPU image, but we need it to fetch the matrix
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
pipeline_test_matrix: ${{ steps.fetch_pipeline_matrix.outputs.pipeline_test_matrix }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m pip install -e .[quality,test]
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Fetch Pipeline Matrix
|
||||
id: fetch_pipeline_matrix
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
matrix=$(python utils/fetch_torch_cuda_pipeline_test_matrix.py)
|
||||
echo $matrix
|
||||
echo "pipeline_test_matrix=$matrix" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Pipeline Tests Artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: test-pipelines.json
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
torch_pipelines_cuda_tests:
|
||||
name: Torch Pipelines CUDA Slow Tests
|
||||
needs: setup_torch_cuda_pipeline_matrix
|
||||
run_slow_tests:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
max-parallel: 1
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
module: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup_torch_cuda_pipeline_matrix.outputs.pipeline_test_matrix) }}
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m pip install -e .[quality,test]
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
- name: Slow PyTorch CUDA checkpoint tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda \
|
||||
tests/pipelines/${{ matrix.module }}
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- name: Slow PyTorch CUDA tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
runner: docker-gpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
report: torch_cuda
|
||||
- name: Slow Flax TPU tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: flax
|
||||
runner: docker-tpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-flax-tpu
|
||||
report: flax_tpu
|
||||
- name: Slow ONNXRuntime CUDA tests on Ubuntu
|
||||
framework: onnxruntime
|
||||
runner: docker-gpu
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-onnxruntime-cuda
|
||||
report: onnx_cuda
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: pipeline_${{ matrix.module }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.config.name }}
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.config.runner }}
|
||||
|
||||
torch_cuda_tests:
|
||||
name: Torch CUDA Tests
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
image: ${{ matrix.config.image }}
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ ${{ matrix.config.runner == 'docker-tpu' && '--privileged' || '--gpus 0'}}
|
||||
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
module: [models, schedulers, lora, others]
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
if : ${{ matrix.config.runner == 'docker-gpu' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
@@ -133,251 +70,47 @@ jobs:
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run slow PyTorch CUDA tests
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'pytorch' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_torch_cuda \
|
||||
tests/${{ matrix.module }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_torch_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_torch_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: torch_cuda_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
peft_cuda_tests:
|
||||
name: PEFT CUDA Tests
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m pip install -e .[quality,test]
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run slow PEFT CUDA tests
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#avoiding-nondeterministic-algorithms
|
||||
CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG: :16:8
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "not Flax and not Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_peft_cuda \
|
||||
tests/lora/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_peft_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_peft_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: torch_peft_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
flax_tpu_tests:
|
||||
name: Flax TPU Tests
|
||||
runs-on: docker-tpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-flax-tpu
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --privileged
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m pip install -e .[quality,test]
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run slow Flax TPU tests
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'flax' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 0 \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Flax" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_flax_tpu \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_flax_tpu_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_flax_tpu_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: flax_tpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
onnx_cuda_tests:
|
||||
name: ONNX CUDA Tests
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-onnxruntime-cuda
|
||||
options: --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/ --gpus 0
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install libsndfile1-dev libgl1 -y
|
||||
python -m pip install -e .[quality,test]
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run slow ONNXRuntime CUDA tests
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.config.framework == 'onnxruntime' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile \
|
||||
-s -v -k "Onnx" \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_onnx_cuda \
|
||||
--make-reports=tests_${{ matrix.config.report }} \
|
||||
tests/
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/tests_onnx_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/tests_onnx_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_${{ matrix.config.report }}_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: onnx_cuda_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_torch_compile_tests:
|
||||
name: PyTorch Compile CUDA tests
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-compile-cuda
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install -e .[quality,test,training]
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
- name: Run example tests on GPU
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s -v -k "compile" --make-reports=tests_torch_compile_cuda tests/
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_compile_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: torch_compile_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_xformers_tests:
|
||||
name: PyTorch xformers CUDA tests
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: docker-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: diffusers/diffusers-pytorch-xformers-cuda
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/hf_cache:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout diffusers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install -e .[quality,test,training]
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
- name: Run example tests on GPU
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s -v -k "xformers" --make-reports=tests_torch_xformers_cuda tests/
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_xformers_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: torch_xformers_test_reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.config.report }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_examples_tests:
|
||||
@@ -415,13 +148,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat reports/examples_torch_cuda_stats.txt
|
||||
cat reports/examples_torch_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat reports/examples_torch_cuda_failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: examples_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/stale.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/stale.yml
vendored
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Setup Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: 3.8
|
||||
python-version: 3.7
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install requirements
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ In the following, we give an overview of different ways to contribute, ranked by
|
||||
As said before, **all contributions are valuable to the community**.
|
||||
In the following, we will explain each contribution a bit more in detail.
|
||||
|
||||
For all contributions 4.-9. you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in [Opening a pull request](#how-to-open-a-pr)
|
||||
For all contributions 4.-9. you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in [Opening a pull requst](#how-to-open-a-pr)
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Asking and answering questions on the Diffusers discussion forum or on the Diffusers Discord
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ In the same spirit, you are of immense help to the community by answering such q
|
||||
|
||||
**Please** keep in mind that the more effort you put into asking or answering a question, the higher
|
||||
the quality of the publicly documented knowledge. In the same way, well-posed and well-answered questions create a high-quality knowledge database accessible to everybody, while badly posed questions or answers reduce the overall quality of the public knowledge database.
|
||||
In short, a high quality question or answer is *precise*, *concise*, *relevant*, *easy-to-understand*, *accessible*, and *well-formated/well-posed*. For more information, please have a look through the [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue) section.
|
||||
In short, a high quality question or answer is *precise*, *concise*, *relevant*, *easy-to-understand*, *accesible*, and *well-formated/well-posed*. For more information, please have a look through the [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue) section.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE about channels**:
|
||||
[*The forum*](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) is much better indexed by search engines, such as Google. Posts are ranked by popularity rather than chronologically. Hence, it's easier to look up questions and answers that we posted some time ago.
|
||||
@@ -168,7 +168,7 @@ more precise, provide the link to a duplicated issue or redirect them to [the fo
|
||||
If you have verified that the issued bug report is correct and requires a correction in the source code,
|
||||
please have a look at the next sections.
|
||||
|
||||
For all of the following contributions, you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in the [Opening a pull request](#how-to-open-a-pr) section.
|
||||
For all of the following contributions, you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in the [Opening a pull requst](#how-to-open-a-pr) section.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Fixing a "Good first issue"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Pipelines should be used **only** for inference.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be very readable, self-explanatory, and easy to tweak.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be designed to build on top of each other and be easy to integrate into higher-level APIs.
|
||||
- Pipelines are **not** intended to be feature-complete user interfaces. For future complete user interfaces one should rather have a look at [InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI), [Diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers), and [lama-cleaner](https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner).
|
||||
- Pipelines are **not** intended to be feature-complete user interfaces. For future complete user interfaces one should rather have a look at [InvokeAI](https://github.com/invoke-ai/InvokeAI), [Diffuzers](https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/diffuzers), and [lama-cleaner](https://github.com/Sanster/lama-cleaner)
|
||||
- Every pipeline should have one and only one way to run it via a `__call__` method. The naming of the `__call__` arguments should be shared across all pipelines.
|
||||
- Pipelines should be named after the task they are intended to solve.
|
||||
- In almost all cases, novel diffusion pipelines shall be implemented in a new pipeline folder/file.
|
||||
@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Schedulers all inherit from `SchedulerMixin` and `ConfigMixin`.
|
||||
- Schedulers can be easily swapped out with the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/configuration#diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config) method as explained in detail [here](./using-diffusers/schedulers.md).
|
||||
- Every scheduler has to have a `set_num_inference_steps`, and a `step` function. `set_num_inference_steps(...)` has to be called before every denoising process, *i.e.* before `step(...)` is called.
|
||||
- Every scheduler exposes the timesteps to be "looped over" via a `timesteps` attribute, which is an array of timesteps the model will be called upon.
|
||||
- Every scheduler exposes the timesteps to be "looped over" via a `timesteps` attribute, which is an array of timesteps the model will be called upon
|
||||
- The `step(...)` function takes a predicted model output and the "current" sample (x_t) and returns the "previous", slightly more denoised sample (x_t-1).
|
||||
- Given the complexity of diffusion schedulers, the `step` function does not expose all the complexity and can be a bit of a "black box".
|
||||
- In almost all cases, novel schedulers shall be implemented in a new scheduling file.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-runtime-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.9 \
|
||||
python3.9-dev \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.9-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3.9 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
RUN python3.9 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip && \
|
||||
python3.9 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
invisible_watermark && \
|
||||
python3.9 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
hf-doc-builder \
|
||||
huggingface-hub \
|
||||
Jinja2 \
|
||||
librosa \
|
||||
numpy \
|
||||
scipy \
|
||||
tensorboard \
|
||||
transformers \
|
||||
omegaconf
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-runtime-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:11.7.1-cudnn8-runtime-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,16 +6,16 @@ ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.8 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.8-venv && \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.8 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.8-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
@@ -25,22 +25,23 @@ ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
invisible_watermark && \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
invisible_watermark && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
hf-doc-builder \
|
||||
huggingface-hub \
|
||||
Jinja2 \
|
||||
librosa \
|
||||
numpy \
|
||||
scipy \
|
||||
tensorboard \
|
||||
transformers \
|
||||
omegaconf \
|
||||
pytorch-lightning
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
hf-doc-builder \
|
||||
huggingface-hub \
|
||||
Jinja2 \
|
||||
librosa \
|
||||
numpy \
|
||||
scipy \
|
||||
tensorboard \
|
||||
transformers \
|
||||
omegaconf \
|
||||
pytorch-lightning \
|
||||
xformers
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-runtime-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
LABEL repository="diffusers"
|
||||
|
||||
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y bash \
|
||||
build-essential \
|
||||
git \
|
||||
git-lfs \
|
||||
curl \
|
||||
ca-certificates \
|
||||
libsndfile1-dev \
|
||||
libgl1 \
|
||||
python3.8 \
|
||||
python3-pip \
|
||||
python3.8-venv && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to use venv
|
||||
RUN python3 -m venv /opt/venv
|
||||
ENV PATH="/opt/venv/bin:$PATH"
|
||||
|
||||
# pre-install the heavy dependencies (these can later be overridden by the deps from setup.py)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
torch \
|
||||
torchvision \
|
||||
torchaudio \
|
||||
invisible_watermark && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
datasets \
|
||||
hf-doc-builder \
|
||||
huggingface-hub \
|
||||
Jinja2 \
|
||||
librosa \
|
||||
numpy \
|
||||
scipy \
|
||||
tensorboard \
|
||||
transformers \
|
||||
omegaconf \
|
||||
xformers
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Generating the documentation
|
||||
|
||||
To generate the documentation, you first have to build it. Several packages are necessary to build the doc,
|
||||
To generate the documentation, you first have to build it. Several packages are necessary to build the doc,
|
||||
you can install them with the following command, at the root of the code repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
@@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ The `preview` command only works with existing doc files. When you add a complet
|
||||
Accepted files are Markdown (.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Create a file with its extension and put it in the source directory. You can then link it to the toc-tree by putting
|
||||
the filename without the extension in the [`_toctree.yml`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/docs/source/en/_toctree.yml) file.
|
||||
the filename without the extension in the [`_toctree.yml`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/docs/source/_toctree.yml) file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Renaming section headers and moving sections
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -81,14 +81,14 @@ Therefore, we simply keep a little map of moved sections at the end of the docum
|
||||
|
||||
So if you renamed a section from: "Section A" to "Section B", then you can add at the end of the file:
|
||||
|
||||
```md
|
||||
```
|
||||
Sections that were moved:
|
||||
|
||||
[ <a href="#section-b">Section A</a><a id="section-a"></a> ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
and of course, if you moved it to another file, then:
|
||||
|
||||
```md
|
||||
```
|
||||
Sections that were moved:
|
||||
|
||||
[ <a href="../new-file#section-b">Section A</a><a id="section-a"></a> ]
|
||||
@@ -109,8 +109,8 @@ although we can write them directly in Markdown.
|
||||
|
||||
Adding a new tutorial or section is done in two steps:
|
||||
|
||||
- Add a new Markdown (.md) file under `docs/source/<languageCode>`.
|
||||
- Link that file in `docs/source/<languageCode>/_toctree.yml` on the correct toc-tree.
|
||||
- Add a new file under `docs/source`. This file can either be ReStructuredText (.rst) or Markdown (.md).
|
||||
- Link that file in `docs/source/_toctree.yml` on the correct toc-tree.
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to put your new file under the proper section. It's unlikely to go in the first section (*Get Started*), so
|
||||
depending on the intended targets (beginners, more advanced users, or researchers) it should go in sections two, three, or four.
|
||||
@@ -119,7 +119,7 @@ depending on the intended targets (beginners, more advanced users, or researcher
|
||||
|
||||
When adding a new pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
- Create a file `xxx.md` under `docs/source/<languageCode>/api/pipelines` (don't hesitate to copy an existing file as template).
|
||||
- create a file `xxx.md` under `docs/source/api/pipelines` (don't hesitate to copy an existing file as template).
|
||||
- Link that file in (*Diffusers Summary*) section in `docs/source/api/pipelines/overview.md`, along with the link to the paper, and a colab notebook (if available).
|
||||
- Write a short overview of the diffusion model:
|
||||
- Overview with paper & authors
|
||||
@@ -129,6 +129,8 @@ When adding a new pipeline:
|
||||
- Add all the pipeline classes that should be linked in the diffusion model. These classes should be added using our Markdown syntax. By default as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
## XXXPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] XXXPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -142,11 +144,11 @@ This will include every public method of the pipeline that is documented, as wel
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- disable_attention_slicing
|
||||
- enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
- disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can follow the same process to create a new scheduler under the `docs/source/<languageCode>/api/schedulers` folder.
|
||||
You can follow the same process to create a new scheduler under the `docs/source/api/schedulers` folder
|
||||
|
||||
### Writing source documentation
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -154,7 +156,7 @@ Values that should be put in `code` should either be surrounded by backticks: \`
|
||||
and objects like True, None, or any strings should usually be put in `code`.
|
||||
|
||||
When mentioning a class, function, or method, it is recommended to use our syntax for internal links so that our tool
|
||||
adds a link to its documentation with this syntax: \[\`XXXClass\`\] or \[\`function\`\]. This requires the class or
|
||||
adds a link to its documentation with this syntax: \[\`XXXClass\`\] or \[\`function\`\]. This requires the class or
|
||||
function to be in the main package.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to create a link to some internal class or function, you need to
|
||||
@@ -162,7 +164,7 @@ provide its path. For instance: \[\`pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput\`\]. This will
|
||||
`pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput` in the description. To get rid of the path and only keep the name of the object you are
|
||||
linking to in the description, add a ~: \[\`~pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput\`\] will generate a link with `ImagePipelineOutput` in the description.
|
||||
|
||||
The same works for methods so you can either use \[\`XXXClass.method\`\] or \[\`~XXXClass.method\`\].
|
||||
The same works for methods so you can either use \[\`XXXClass.method\`\] or \[~\`XXXClass.method\`\].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Defining arguments in a method
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -194,8 +196,8 @@ Here's an example showcasing everything so far:
|
||||
For optional arguments or arguments with defaults we follow the following syntax: imagine we have a function with the
|
||||
following signature:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def my_function(x: str=None, a: float=3.14):
|
||||
```
|
||||
def my_function(x: str = None, a: float = 1):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
then its documentation should look like this:
|
||||
@@ -204,7 +206,7 @@ then its documentation should look like this:
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
x (`str`, *optional*):
|
||||
This argument controls ...
|
||||
a (`float`, *optional*, defaults to `3.14`):
|
||||
a (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
|
||||
This argument is used to ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -266,3 +268,4 @@ We have an automatic script running with the `make style` command that will make
|
||||
This script may have some weird failures if you made a syntax mistake or if you uncover a bug. Therefore, it's
|
||||
recommended to commit your changes before running `make style`, so you can revert the changes done by that script
|
||||
easily.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ Here, `LANG-ID` should be one of the ISO 639-1 or ISO 639-2 language codes -- se
|
||||
|
||||
The fun part comes - translating the text!
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing we recommend is translating the part of the `_toctree.yml` file that corresponds to your doc chapter. This file is used to render the table of contents on the website.
|
||||
The first thing we recommend is translating the part of the `_toctree.yml` file that corresponds to your doc chapter. This file is used to render the table of contents on the website.
|
||||
|
||||
> 🙋 If the `_toctree.yml` file doesn't yet exist for your language, you can create one by copy-pasting from the English version and deleting the sections unrelated to your chapter. Just make sure it exists in the `docs/source/LANG-ID/` directory!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,13 +12,11 @@
|
||||
- local: tutorials/tutorial_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/write_own_pipeline
|
||||
title: Understanding pipelines, models and schedulers
|
||||
title: Understanding models and schedulers
|
||||
- local: tutorials/autopipeline
|
||||
title: AutoPipeline
|
||||
- local: tutorials/basic_training
|
||||
title: Train a diffusion model
|
||||
- local: tutorials/using_peft_for_inference
|
||||
title: Inference with PEFT
|
||||
title: Tutorials
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
@@ -29,19 +27,15 @@
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/schedulers
|
||||
title: Load and compare different schedulers
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Load community pipelines and components
|
||||
title: Load community pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/using_safetensors
|
||||
title: Load safetensors
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/other-formats
|
||||
title: Load different Stable Diffusion formats
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/loading_adapters
|
||||
title: Load adapters
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/push_to_hub
|
||||
title: Push files to the Hub
|
||||
title: Loading & Hub
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/unconditional_image_generation
|
||||
title: Unconditional image generation
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/conditional_image_generation
|
||||
@@ -64,22 +58,14 @@
|
||||
title: Control image brightness
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/weighted_prompts
|
||||
title: Prompt weighting
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/freeu
|
||||
title: Improve generation quality with FreeU
|
||||
title: Techniques
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/pipeline_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/sdxl
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/lcm
|
||||
title: Latent Consistency Models
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/kandinsky
|
||||
title: Kandinsky
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/controlnet
|
||||
title: ControlNet
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/callback
|
||||
title: Callback
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/shap-e
|
||||
title: Shap-E
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/diffedit
|
||||
@@ -91,8 +77,8 @@
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/custom_pipeline_examples
|
||||
title: Community pipelines
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/contribute_pipeline
|
||||
title: Contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
title: Specific pipeline examples
|
||||
title: How to contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
title: Pipelines for Inference
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: training/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
@@ -118,8 +104,6 @@
|
||||
title: Custom Diffusion
|
||||
- local: training/t2i_adapters
|
||||
title: T2I-Adapters
|
||||
- local: training/ddpo
|
||||
title: Reinforcement learning training with DDPO
|
||||
title: Training
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/other-modalities
|
||||
@@ -129,35 +113,27 @@
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: optimization/opt_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: optimization/fp16
|
||||
title: Speed up inference
|
||||
- local: optimization/memory
|
||||
title: Reduce memory usage
|
||||
- local: optimization/torch2.0
|
||||
title: PyTorch 2.0
|
||||
- local: optimization/xformers
|
||||
title: xFormers
|
||||
- local: optimization/tome
|
||||
title: Token merging
|
||||
title: General optimizations
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/stable_diffusion_jax_how_to
|
||||
title: JAX/Flax
|
||||
- local: optimization/onnx
|
||||
title: ONNX
|
||||
- local: optimization/open_vino
|
||||
title: OpenVINO
|
||||
- local: optimization/coreml
|
||||
title: Core ML
|
||||
title: Optimized model types
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: optimization/mps
|
||||
title: Metal Performance Shaders (MPS)
|
||||
- local: optimization/habana
|
||||
title: Habana Gaudi
|
||||
title: Optimized hardware
|
||||
title: Optimization
|
||||
- local: optimization/fp16
|
||||
title: Memory and Speed
|
||||
- local: optimization/torch2.0
|
||||
title: Torch2.0 support
|
||||
- local: using-diffusers/stable_diffusion_jax_how_to
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion in JAX/Flax
|
||||
- local: optimization/xformers
|
||||
title: xFormers
|
||||
- local: optimization/onnx
|
||||
title: ONNX
|
||||
- local: optimization/open_vino
|
||||
title: OpenVINO
|
||||
- local: optimization/coreml
|
||||
title: Core ML
|
||||
- local: optimization/mps
|
||||
title: MPS
|
||||
- local: optimization/habana
|
||||
title: Habana Gaudi
|
||||
- local: optimization/tome
|
||||
title: Token Merging
|
||||
title: Optimization/Special Hardware
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: conceptual/philosophy
|
||||
title: Philosophy
|
||||
@@ -172,14 +148,22 @@
|
||||
title: Conceptual Guides
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/configuration
|
||||
title: Configuration
|
||||
- local: api/loaders
|
||||
title: Loaders
|
||||
- local: api/attnprocessor
|
||||
title: Attention Processor
|
||||
- local: api/diffusion_pipeline
|
||||
title: Diffusion Pipeline
|
||||
- local: api/logging
|
||||
title: Logging
|
||||
- local: api/configuration
|
||||
title: Configuration
|
||||
- local: api/outputs
|
||||
title: Outputs
|
||||
- local: api/loaders
|
||||
title: Loaders
|
||||
- local: api/utilities
|
||||
title: Utilities
|
||||
- local: api/image_processor
|
||||
title: VAE Image Processor
|
||||
title: Main Classes
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/models/overview
|
||||
@@ -192,8 +176,6 @@
|
||||
title: UNet2DConditionModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/unet3d-cond
|
||||
title: UNet3DConditionModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/unet-motion
|
||||
title: UNetMotionModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/vq
|
||||
title: VQModel
|
||||
- local: api/models/autoencoderkl
|
||||
@@ -202,8 +184,6 @@
|
||||
title: AsymmetricAutoencoderKL
|
||||
- local: api/models/autoencoder_tiny
|
||||
title: Tiny AutoEncoder
|
||||
- local: api/models/consistency_decoder_vae
|
||||
title: ConsistencyDecoderVAE
|
||||
- local: api/models/transformer2d
|
||||
title: Transformer2D
|
||||
- local: api/models/transformer_temporal
|
||||
@@ -218,8 +198,6 @@
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/alt_diffusion
|
||||
title: AltDiffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/animatediff
|
||||
title: AnimateDiff
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/attend_and_excite
|
||||
title: Attend-and-Excite
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/audio_diffusion
|
||||
@@ -230,8 +208,6 @@
|
||||
title: AudioLDM 2
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/auto_pipeline
|
||||
title: AutoPipeline
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/blip_diffusion
|
||||
title: BLIP Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/consistency_models
|
||||
title: Consistency Models
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/controlnet
|
||||
@@ -255,11 +231,9 @@
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pix2pix
|
||||
title: InstructPix2Pix
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/kandinsky
|
||||
title: Kandinsky 2.1
|
||||
title: Kandinsky
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/kandinsky_v22
|
||||
title: Kandinsky 2.2
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/latent_consistency_models
|
||||
title: Latent Consistency Models
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/latent_diffusion
|
||||
title: Latent Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/panorama
|
||||
@@ -267,13 +241,11 @@
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/musicldm
|
||||
title: MusicLDM
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/paint_by_example
|
||||
title: Paint By Example
|
||||
title: PaintByExample
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/paradigms
|
||||
title: Parallel Sampling of Diffusion Models
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pix2pix_zero
|
||||
title: Pix2Pix Zero
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pixart
|
||||
title: PixArt
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/pndm
|
||||
title: PNDM
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/repaint
|
||||
@@ -314,7 +286,7 @@
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/ldm3d_diffusion
|
||||
title: LDM3D Text-to-(RGB, Depth)
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/adapter
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion T2I-Adapter
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion T2I-adapter
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/gligen
|
||||
title: GLIGEN (Grounded Language-to-Image Generation)
|
||||
title: Stable Diffusion
|
||||
@@ -329,7 +301,7 @@
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/text_to_video_zero
|
||||
title: Text2Video-Zero
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/unclip
|
||||
title: unCLIP
|
||||
title: UnCLIP
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond
|
||||
title: Unconditional Latent Diffusion
|
||||
- local: api/pipelines/unidiffuser
|
||||
@@ -348,8 +320,6 @@
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/cm_stochastic_iterative
|
||||
title: CMStochasticIterativeScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/consistency_decoder
|
||||
title: ConsistencyDecoderScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/ddim_inverse
|
||||
title: DDIMInverseScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/ddim
|
||||
@@ -380,8 +350,6 @@
|
||||
title: KDPM2AncestralDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/dpm_discrete
|
||||
title: KDPM2DiscreteScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/lcm
|
||||
title: LCMScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/lms_discrete
|
||||
title: LMSDiscreteScheduler
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/pndm
|
||||
@@ -397,18 +365,4 @@
|
||||
- local: api/schedulers/vq_diffusion
|
||||
title: VQDiffusionScheduler
|
||||
title: Schedulers
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: api/internal_classes_overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: api/attnprocessor
|
||||
title: Attention Processor
|
||||
- local: api/activations
|
||||
title: Custom activation functions
|
||||
- local: api/normalization
|
||||
title: Custom normalization layers
|
||||
- local: api/utilities
|
||||
title: Utilities
|
||||
- local: api/image_processor
|
||||
title: VAE Image Processor
|
||||
title: Internal classes
|
||||
title: API
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Activation functions
|
||||
|
||||
Customized activation functions for supporting various models in 🤗 Diffusers.
|
||||
|
||||
## GELU
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.activations.GELU
|
||||
|
||||
## GEGLU
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.activations.GEGLU
|
||||
|
||||
## ApproximateGELU
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.activations.ApproximateGELU
|
||||
@@ -17,9 +17,6 @@ An attention processor is a class for applying different types of attention mech
|
||||
## CustomDiffusionAttnProcessor
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.attention_processor.CustomDiffusionAttnProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
## CustomDiffusionAttnProcessor2_0
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.attention_processor.CustomDiffusionAttnProcessor2_0
|
||||
|
||||
## AttnAddedKVProcessor
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.attention_processor.AttnAddedKVProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -42,4 +39,4 @@ An attention processor is a class for applying different types of attention mech
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.attention_processor.SlicedAttnProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
## SlicedAttnAddedKVProcessor
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.attention_processor.SlicedAttnAddedKVProcessor
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.attention_processor.SlicedAttnAddedKVProcessor
|
||||
36
docs/source/en/api/diffusion_pipeline.md
Normal file
36
docs/source/en/api/diffusion_pipeline.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
The [`DiffusionPipeline`] is the quickest way to load any pretrained diffusion pipeline from the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?library=diffusers) for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You shouldn't use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] class for training or finetuning a diffusion model. Individual
|
||||
components (for example, [`UNet2DModel`] and [`UNet2DConditionModel`]) of diffusion pipelines are usually trained individually, so we suggest directly working with them instead.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The pipeline type (for example [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]) of any diffusion pipeline loaded with [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] is automatically
|
||||
detected and pipeline components are loaded and passed to the `__init__` function of the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
Any pipeline object can be saved locally with [`~DiffusionPipeline.save_pretrained`].
|
||||
|
||||
## DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- device
|
||||
- to
|
||||
- components
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The APIs in this section are more experimental and prone to breaking changes. Most of them are used internally for development, but they may also be useful to you if you're interested in building a diffusion model with some custom parts or if you're interested in some of our helper utilities for working with 🤗 Diffusers.
|
||||
@@ -28,10 +28,6 @@ Adapters (textual inversion, LoRA, hypernetworks) allow you to modify a diffusio
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] loaders.TextualInversionLoaderMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionXLLoraLoaderMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] loaders.StableDiffusionXLLoraLoaderMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## LoraLoaderMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] loaders.LoraLoaderMixin
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -67,30 +67,30 @@ By default, `tqdm` progress bars are displayed during model download. [`logging.
|
||||
|
||||
## Base setters
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.set_verbosity_error
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_error
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.set_verbosity_warning
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_warning
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.set_verbosity_info
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_info
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.set_verbosity_debug
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_debug
|
||||
|
||||
## Other functions
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.get_verbosity
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.get_verbosity
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.set_verbosity
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.get_logger
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.enable_default_handler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.enable_default_handler
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.disable_default_handler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.disable_default_handler
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.enable_explicit_format
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.enable_explicit_format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.reset_format
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.reset_format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.enable_progress_bar
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.enable_progress_bar
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.logging.disable_progress_bar
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.disable_progress_bar
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Consistency Decoder
|
||||
|
||||
Consistency decoder can be used to decode the latents from the denoising UNet in the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]. This decoder was introduced in the [DALL-E 3 technical report](https://openai.com/dall-e-3).
|
||||
|
||||
The original codebase can be found at [openai/consistencydecoder](https://github.com/openai/consistencydecoder).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Inference is only supported for 2 iterations as of now.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The pipeline could not have been contributed without the help of [madebyollin](https://github.com/madebyollin) and [mrsteyk](https://github.com/mrsteyk) from [this issue](https://github.com/openai/consistencydecoder/issues/1).
|
||||
|
||||
## ConsistencyDecoderVAE
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ConsistencyDecoderVAE
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- decode
|
||||
@@ -12,13 +12,13 @@ By default the [`ControlNetModel`] should be loaded with [`~ModelMixin.from_pret
|
||||
from the original format using [`FromOriginalControlnetMixin.from_single_file`] as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline, ControlNetModel
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlnetPipeline, ControlNetModel
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/lllyasviel/ControlNet-v1-1/blob/main/control_v11p_sd15_canny.pth" # can also be a local path
|
||||
controlnet = ControlNetModel.from_single_file(url)
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5/blob/main/v1-5-pruned.safetensors" # can also be a local path
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline.from_single_file(url, controlnet=controlnet)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionControlnetPipeline.from_single_file(url, controlnet=controlnet)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ControlNetModel
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# UNetMotionModel
|
||||
|
||||
The [UNet](https://huggingface.co/papers/1505.04597) model was originally introduced by Ronneberger et al for biomedical image segmentation, but it is also commonly used in 🤗 Diffusers because it outputs images that are the same size as the input. It is one of the most important components of a diffusion system because it facilitates the actual diffusion process. There are several variants of the UNet model in 🤗 Diffusers, depending on it's number of dimensions and whether it is a conditional model or not. This is a 2D UNet model.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*There is large consent that successful training of deep networks requires many thousand annotated training samples. In this paper, we present a network and training strategy that relies on the strong use of data augmentation to use the available annotated samples more efficiently. The architecture consists of a contracting path to capture context and a symmetric expanding path that enables precise localization. We show that such a network can be trained end-to-end from very few images and outperforms the prior best method (a sliding-window convolutional network) on the ISBI challenge for segmentation of neuronal structures in electron microscopic stacks. Using the same network trained on transmitted light microscopy images (phase contrast and DIC) we won the ISBI cell tracking challenge 2015 in these categories by a large margin. Moreover, the network is fast. Segmentation of a 512x512 image takes less than a second on a recent GPU. The full implementation (based on Caffe) and the trained networks are available at http://lmb.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/people/ronneber/u-net.*
|
||||
|
||||
## UNetMotionModel
|
||||
[[autodoc]] UNetMotionModel
|
||||
|
||||
## UNet3DConditionOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.unet_3d_condition.UNet3DConditionOutput
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Normalization layers
|
||||
|
||||
Customized normalization layers for supporting various models in 🤗 Diffusers.
|
||||
|
||||
## AdaLayerNorm
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.normalization.AdaLayerNorm
|
||||
|
||||
## AdaLayerNormZero
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.normalization.AdaLayerNormZero
|
||||
|
||||
## AdaGroupNorm
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.normalization.AdaGroupNorm
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,230 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Text-to-Video Generation with AnimateDiff
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[AnimateDiff: Animate Your Personalized Text-to-Image Diffusion Models without Specific Tuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.04725) by Yuwei Guo, Ceyuan Yang*, Anyi Rao, Yaohui Wang, Yu Qiao, Dahua Lin, Bo Dai
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
With the advance of text-to-image models (e.g., Stable Diffusion) and corresponding personalization techniques such as DreamBooth and LoRA, everyone can manifest their imagination into high-quality images at an affordable cost. Subsequently, there is a great demand for image animation techniques to further combine generated static images with motion dynamics. In this report, we propose a practical framework to animate most of the existing personalized text-to-image models once and for all, saving efforts in model-specific tuning. At the core of the proposed framework is to insert a newly initialized motion modeling module into the frozen text-to-image model and train it on video clips to distill reasonable motion priors. Once trained, by simply injecting this motion modeling module, all personalized versions derived from the same base T2I readily become text-driven models that produce diverse and personalized animated images. We conduct our evaluation on several public representative personalized text-to-image models across anime pictures and realistic photographs, and demonstrate that our proposed framework helps these models generate temporally smooth animation clips while preserving the domain and diversity of their outputs. Code and pre-trained weights will be publicly available at this https URL .
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Demo
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [AnimateDiffPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/animatediff/pipeline_animatediff.py) | *Text-to-Video Generation with AnimateDiff* |
|
||||
|
||||
## Available checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
Motion Adapter checkpoints can be found under [guoyww](https://huggingface.co/guoyww/). These checkpoints are meant to work with any model based on Stable Diffusion 1.4/1.5
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
AnimateDiff works with a MotionAdapter checkpoint and a Stable Diffusion model checkpoint. The MotionAdapter is a collection of Motion Modules that are responsible for adding coherent motion across image frames. These modules are applied after the Resnet and Attention blocks in Stable Diffusion UNet.
|
||||
|
||||
The following example demonstrates how to use a *MotionAdapter* checkpoint with Diffusers for inference based on StableDiffusion-1.4/1.5.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import MotionAdapter, AnimateDiffPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_gif
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the motion adapter
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5-2")
|
||||
# load SD 1.5 based finetuned model
|
||||
model_id = "SG161222/Realistic_Vision_V5.1_noVAE"
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, motion_adapter=adapter)
|
||||
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id, subfolder="scheduler", clip_sample=False, timestep_spacing="linspace", steps_offset=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
# enable memory savings
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=(
|
||||
"masterpiece, bestquality, highlydetailed, ultradetailed, sunset, "
|
||||
"orange sky, warm lighting, fishing boats, ocean waves seagulls, "
|
||||
"rippling water, wharf, silhouette, serene atmosphere, dusk, evening glow, "
|
||||
"golden hour, coastal landscape, seaside scenery"
|
||||
),
|
||||
negative_prompt="bad quality, worse quality",
|
||||
num_frames=16,
|
||||
guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
generator=torch.Generator("cpu").manual_seed(42),
|
||||
)
|
||||
frames = output.frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_gif(frames, "animation.gif")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><center>
|
||||
masterpiece, bestquality, sunset.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/animatediff-realistic-doc.gif"
|
||||
alt="masterpiece, bestquality, sunset"
|
||||
style="width: 300px;" />
|
||||
</center></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
AnimateDiff tends to work better with finetuned Stable Diffusion models. If you plan on using a scheduler that can clip samples, make sure to disable it by setting `clip_sample=False` in the scheduler as this can also have an adverse effect on generated samples.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Motion LoRAs
|
||||
|
||||
Motion LoRAs are a collection of LoRAs that work with the `guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5-2` checkpoint. These LoRAs are responsible for adding specific types of motion to the animations.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import MotionAdapter, AnimateDiffPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_gif
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the motion adapter
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5-2")
|
||||
# load SD 1.5 based finetuned model
|
||||
model_id = "SG161222/Realistic_Vision_V5.1_noVAE"
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, motion_adapter=adapter)
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("guoyww/animatediff-motion-lora-zoom-out", adapter_name="zoom-out")
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id, subfolder="scheduler", clip_sample=False, timestep_spacing="linspace", steps_offset=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
# enable memory savings
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=(
|
||||
"masterpiece, bestquality, highlydetailed, ultradetailed, sunset, "
|
||||
"orange sky, warm lighting, fishing boats, ocean waves seagulls, "
|
||||
"rippling water, wharf, silhouette, serene atmosphere, dusk, evening glow, "
|
||||
"golden hour, coastal landscape, seaside scenery"
|
||||
),
|
||||
negative_prompt="bad quality, worse quality",
|
||||
num_frames=16,
|
||||
guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
generator=torch.Generator("cpu").manual_seed(42),
|
||||
)
|
||||
frames = output.frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_gif(frames, "animation.gif")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><center>
|
||||
masterpiece, bestquality, sunset.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/animatediff-zoom-out-lora.gif"
|
||||
alt="masterpiece, bestquality, sunset"
|
||||
style="width: 300px;" />
|
||||
</center></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Motion LoRAs with PEFT
|
||||
|
||||
You can also leverage the [PEFT](https://github.com/huggingface/peft) backend to combine Motion LoRA's and create more complex animations.
|
||||
|
||||
First install PEFT with
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install peft
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can use the following code to combine Motion LoRAs.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import MotionAdapter, AnimateDiffPipeline, DDIMScheduler
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import export_to_gif
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the motion adapter
|
||||
adapter = MotionAdapter.from_pretrained("guoyww/animatediff-motion-adapter-v1-5-2")
|
||||
# load SD 1.5 based finetuned model
|
||||
model_id = "SG161222/Realistic_Vision_V5.1_noVAE"
|
||||
pipe = AnimateDiffPipeline.from_pretrained(model_id, motion_adapter=adapter)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("diffusers/animatediff-motion-lora-zoom-out", adapter_name="zoom-out")
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("diffusers/animatediff-motion-lora-pan-left", adapter_name="pan-left")
|
||||
pipe.set_adapters(["zoom-out", "pan-left"], adapter_weights=[1.0, 1.0])
|
||||
|
||||
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id, subfolder="scheduler", clip_sample=False, timestep_spacing="linspace", steps_offset=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
# enable memory savings
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
output = pipe(
|
||||
prompt=(
|
||||
"masterpiece, bestquality, highlydetailed, ultradetailed, sunset, "
|
||||
"orange sky, warm lighting, fishing boats, ocean waves seagulls, "
|
||||
"rippling water, wharf, silhouette, serene atmosphere, dusk, evening glow, "
|
||||
"golden hour, coastal landscape, seaside scenery"
|
||||
),
|
||||
negative_prompt="bad quality, worse quality",
|
||||
num_frames=16,
|
||||
guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
generator=torch.Generator("cpu").manual_seed(42),
|
||||
)
|
||||
frames = output.frames[0]
|
||||
export_to_gif(frames, "animation.gif")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><center>
|
||||
masterpiece, bestquality, sunset.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/diffusers/animatediff-zoom-out-pan-left-lora.gif"
|
||||
alt="masterpiece, bestquality, sunset"
|
||||
style="width: 300px;" />
|
||||
</center></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## AnimateDiffPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AnimateDiffPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_freeu
|
||||
- disable_freeu
|
||||
- enable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_vae_tiling
|
||||
- disable_vae_tiling
|
||||
|
||||
## AnimateDiffPipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.animatediff.AnimateDiffPipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ You can find additional information about Attend-and-Excite on the [project page
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ The original codebase, training scripts and example notebooks can be found at [t
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ During inference:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -70,7 +70,9 @@ The following example demonstrates how to construct good music generation using
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between
|
||||
scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines)
|
||||
section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ Check out the [AutoPipeline](/tutorials/autopipeline) tutorial to learn how to u
|
||||
`AutoPipeline` supports text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting for the following diffusion models:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion)
|
||||
- [ControlNet](./controlnet)
|
||||
- [ControlNet](./api/pipelines/controlnet)
|
||||
- [Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL)](./stable_diffusion/stable_diffusion_xl)
|
||||
- [DeepFloyd IF](./if)
|
||||
- [Kandinsky](./kandinsky)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Blip Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
Blip Diffusion was proposed in [BLIP-Diffusion: Pre-trained Subject Representation for Controllable Text-to-Image Generation and Editing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.14720). It enables zero-shot subject-driven generation and control-guided zero-shot generation.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*Subject-driven text-to-image generation models create novel renditions of an input subject based on text prompts. Existing models suffer from lengthy fine-tuning and difficulties preserving the subject fidelity. To overcome these limitations, we introduce BLIP-Diffusion, a new subject-driven image generation model that supports multimodal control which consumes inputs of subject images and text prompts. Unlike other subject-driven generation models, BLIP-Diffusion introduces a new multimodal encoder which is pre-trained to provide subject representation. We first pre-train the multimodal encoder following BLIP-2 to produce visual representation aligned with the text. Then we design a subject representation learning task which enables a diffusion model to leverage such visual representation and generates new subject renditions. Compared with previous methods such as DreamBooth, our model enables zero-shot subject-driven generation, and efficient fine-tuning for customized subject with up to 20x speedup. We also demonstrate that BLIP-Diffusion can be flexibly combined with existing techniques such as ControlNet and prompt-to-prompt to enable novel subject-driven generation and editing applications.*
|
||||
|
||||
The original codebase can be found at [salesforce/LAVIS](https://github.com/salesforce/LAVIS/tree/main/projects/blip-diffusion). You can find the official BLIP Diffusion checkpoints under the [hf.co/SalesForce](https://hf.co/SalesForce) organization.
|
||||
|
||||
`BlipDiffusionPipeline` and `BlipDiffusionControlNetPipeline` were contributed by [`ayushtues`](https://github.com/ayushtues/).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## BlipDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BlipDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## BlipDiffusionControlNetPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BlipDiffusionControlNetPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [lllyasviel/ControlNet](https://github.com
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ If you don't see a checkpoint you're interested in, you can train your own SDXL
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,15 +41,6 @@ Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers)
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionXLControlNetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StableDiffusionXLControlNetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionXLControlNetInpaintPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StableDiffusionXLControlNetInpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
## StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The original codebase of this implementation can be found at [Harmonai-org](http
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [hohonathanho/diffusion](https://github.co
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ this in the generated mask, you simply have to set the embeddings related to the
|
||||
`source_prompt` and "dog" to `target_prompt`.
|
||||
* When generating partially inverted latents using `invert`, assign a caption or text embedding describing the
|
||||
overall image to the `prompt` argument to help guide the inverse latent sampling process. In most cases, the
|
||||
source concept is sufficiently descriptive to yield good results, but feel free to explore alternatives.
|
||||
source concept is sufficently descriptive to yield good results, but feel free to explore alternatives.
|
||||
* When calling the pipeline to generate the final edited image, assign the source concept to `negative_prompt`
|
||||
and the target concept to `prompt`. Taking the above example, you simply have to set the embeddings related to
|
||||
the phrases including "cat" to `negative_prompt` and "dog" to `prompt`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [facebookresearch/dit](https://github.com/
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,60 +7,462 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Kandinsky 2.1
|
||||
# Kandinsky
|
||||
|
||||
Kandinsky 2.1 is created by [Arseniy Shakhmatov](https://github.com/cene555), [Anton Razzhigaev](https://github.com/razzant), [Aleksandr Nikolich](https://github.com/AlexWortega), [Igor Pavlov](https://github.com/boomb0om), [Andrey Kuznetsov](https://github.com/kuznetsoffandrey) and [Denis Dimitrov](https://github.com/denndimitrov).
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The description from it's GitHub page is:
|
||||
Kandinsky inherits best practices from [DALL-E 2](https://huggingface.co/papers/2204.06125) and [Latent Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/latent_diffusion), while introducing some new ideas.
|
||||
|
||||
*Kandinsky 2.1 inherits best practicies from Dall-E 2 and Latent diffusion, while introducing some new ideas. As text and image encoder it uses CLIP model and diffusion image prior (mapping) between latent spaces of CLIP modalities. This approach increases the visual performance of the model and unveils new horizons in blending images and text-guided image manipulation.*
|
||||
It uses [CLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip) for encoding images and text, and a diffusion image prior (mapping) between latent spaces of CLIP modalities. This approach enhances the visual performance of the model and unveils new horizons in blending images and text-guided image manipulation.
|
||||
|
||||
The original codebase can be found at [ai-forever/Kandinsky-2](https://github.com/ai-forever/Kandinsky-2).
|
||||
The Kandinsky model is created by [Arseniy Shakhmatov](https://github.com/cene555), [Anton Razzhigaev](https://github.com/razzant), [Aleksandr Nikolich](https://github.com/AlexWortega), [Igor Pavlov](https://github.com/boomb0om), [Andrey Kuznetsov](https://github.com/kuznetsoffandrey) and [Denis Dimitrov](https://github.com/denndimitrov). The original codebase can be found [here](https://github.com/ai-forever/Kandinsky-2)
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [Kandinsky Community](https://huggingface.co/kandinsky-community) organization on the Hub for the official model checkpoints for tasks like text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting.
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we will walk you through some examples of how to use the Kandinsky pipelines to create some visually aesthetic artwork.
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-to-Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
For text-to-image generation, we need to use both [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`] and [`KandinskyPipeline`].
|
||||
The first step is to encode text prompts with CLIP and then diffuse the CLIP text embeddings to CLIP image embeddings,
|
||||
as first proposed in [DALL-E 2](https://cdn.openai.com/papers/dall-e-2.pdf).
|
||||
Let's throw a fun prompt at Kandinsky to see what it comes up with.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's instantiate the prior pipeline and the text-to-image pipeline. Both
|
||||
pipelines are diffusion models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the text-to-image pipeline use [`DDIMScheduler`], you can change the scheduler to [`DDPMScheduler`]
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", subfolder="ddpm_scheduler")
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", scheduler=scheduler, torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
Now we pass the prompt through the prior to generate image embeddings. The prior
|
||||
returns both the image embeddings corresponding to the prompt and negative/unconditional image
|
||||
embeddings corresponding to an empty string.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, guidance_scale=1.0).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The text-to-image pipeline expects both `image_embeds`, `negative_image_embeds` and the original
|
||||
`prompt` as the text-to-image pipeline uses another text encoder to better guide the second diffusion
|
||||
process of `t2i_pipe`.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the prior returns unconditioned negative image embeddings corresponding to the negative prompt of `""`.
|
||||
For better results, you can also pass a `negative_prompt` to the prior. This will increase the effective batch size
|
||||
of the prior by a factor of 2.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, negative_prompt, guidance_scale=1.0).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we can pass the embeddings as well as the prompt to the text-to-image pipeline. Remember that
|
||||
in case you are using a customized negative prompt, that you should pass this one also to the text-to-image pipelines
|
||||
with `negative_prompt=negative_prompt`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = t2i_pipe(
|
||||
prompt, image_embeds=image_embeds, negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds, height=768, width=768
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
image.save("cheeseburger_monster.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
One cheeseburger monster coming up! Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
We also provide an end-to-end Kandinsky pipeline [`KandinskyCombinedPipeline`], which combines both the prior pipeline and text-to-image pipeline, and lets you perform inference in a single step. You can create the combined pipeline with the [`~AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained`] method
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Under the hood, it will automatically load both [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`] and [`KandinskyPipeline`]. To generate images, you no longer need to call both pipelines and pass the outputs from one to another. You only need to call the combined pipeline once. You can set different `guidance_scale` and `num_inference_steps` for the prior pipeline with the `prior_guidance_scale` and `prior_num_inference_steps` arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, prior_guidance_scale =1.0, guidance_scacle = 4.0, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The Kandinsky model works extremely well with creative prompts. Here is some of the amazing art that can be created using the exact same process but with different prompts.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "bird eye view shot of a full body woman with cyan light orange magenta makeup, digital art, long braided hair her face separated by makeup in the style of yin Yang surrealism, symmetrical face, real image, contrasting tone, pastel gradient background"
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "A car exploding into colorful dust"
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "editorial photography of an organic, almost liquid smoke style armchair"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "birds eye view of a quilted paper style alien planet landscape, vibrant colours, Cinematic lighting"
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Text Guided Image-to-Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
The same Kandinsky model weights can be used for text-guided image-to-image translation. In this case, just make sure to load the weights using the [`KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline`] pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: You can also directly move the weights of the text-to-image pipelines to the image-to-image pipelines
|
||||
without loading them twice by making use of the [`~DiffusionPipeline.components`] function as explained [here](#converting-between-different-pipelines).
|
||||
|
||||
Let's download an image.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
# download image
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
original_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
original_image = original_image.resize((768, 512))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline, KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
# create prior
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# create img2img pipeline
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, Cinematic lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, negative_prompt).to_tuple()
|
||||
|
||||
out = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=original_image,
|
||||
image_embeds=image_embeds,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
strength=0.3,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
out.images[0].save("fantasy_land.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the [`KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline`] for end-to-end image-to-image generation with Kandinsky 2.1
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForImage2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForImage2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A fantasy landscape, Cinematic lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
original_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
original_image.thumbnail((768, 768))
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=original_image, strength=0.3).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Text Guided Inpainting Generation
|
||||
|
||||
You can use [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`] to edit images. In this example, we will add a hat to the portrait of a cat.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyInpaintPipeline, KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a hat"
|
||||
prior_output = pipe_prior(prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-inpaint", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinsky/cat.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
mask = np.zeros((768, 768), dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
# Let's mask out an area above the cat's head
|
||||
mask[:250, 250:-250] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
out = pipe(
|
||||
prompt,
|
||||
image=init_image,
|
||||
mask_image=mask,
|
||||
**prior_output,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=150,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
image = out.images[0]
|
||||
image.save("cat_with_hat.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To use the [`KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline`] to perform end-to-end image inpainting generation, you can run below code instead
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForInpainting
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForInpainting.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-inpaint", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=original_image, mask_image=mask).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
🚨🚨🚨 __Breaking change for Kandinsky Mask Inpainting__ 🚨🚨🚨
|
||||
|
||||
We introduced a breaking change for Kandinsky inpainting pipeline in the following pull request: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/4207. Previously we accepted a mask format where black pixels represent the masked-out area. This is inconsistent with all other pipelines in diffusers. We have changed the mask format in Knaindsky and now using white pixels instead.
|
||||
Please upgrade your inpainting code to follow the above. If you are using Kandinsky Inpaint in production. You now need to change the mask to:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# For PIL input
|
||||
import PIL.ImageOps
|
||||
mask = PIL.ImageOps.invert(mask)
|
||||
|
||||
# For PyTorch and Numpy input
|
||||
mask = 1 - mask
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Interpolate
|
||||
|
||||
The [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`] also comes with a cool utility function that will allow you to interpolate the latent space of different images and texts super easily. Here is an example of how you can create an Impressionist-style portrait for your pet based on "The Starry Night".
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you can interpolate between texts and images - in the below example, we passed a text prompt "a cat" and two images to the `interplate` function, along with a `weights` variable containing the corresponding weights for each condition we interplate.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyPriorPipeline, KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyPriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
img1 = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinsky/cat.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
img2 = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinsky/starry_night.jpeg"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# add all the conditions we want to interpolate, can be either text or image
|
||||
images_texts = ["a cat", img1, img2]
|
||||
|
||||
# specify the weights for each condition in images_texts
|
||||
weights = [0.3, 0.3, 0.4]
|
||||
|
||||
# We can leave the prompt empty
|
||||
prompt = ""
|
||||
prior_out = pipe_prior.interpolate(images_texts, weights)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, **prior_out, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
image.save("starry_cat.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
Running Kandinsky in inference requires running both a first prior pipeline: [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`]
|
||||
and a second image decoding pipeline which is one of [`KandinskyPipeline`], [`KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline`], or [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
The bulk of the computation time will always be the second image decoding pipeline, so when looking
|
||||
into optimizing the model, one should look into the second image decoding pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
When running with PyTorch < 2.0, we strongly recommend making use of [`xformers`](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers)
|
||||
to speed-up the optimization. This can be done by simply running:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When running on PyTorch >= 2.0, PyTorch's SDPA attention will automatically be used. For more information on
|
||||
PyTorch's SDPA, feel free to have a look at [this blog post](https://pytorch.org/blog/accelerated-diffusers-pt-20/).
|
||||
|
||||
To have explicit control , you can also manually set the pipeline to use PyTorch's 2.0 efficient attention:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The slowest and most memory intense attention processor is the default `AttnAddedKVProcessor` processor.
|
||||
We do **not** recommend using it except for testing purposes or cases where very high determistic behaviour is desired.
|
||||
You can set it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With PyTorch >= 2.0, you can also use Kandinsky with `torch.compile` which depending
|
||||
on your hardware can signficantly speed-up your inference time once the model is compiled.
|
||||
To use Kandinsksy with `torch.compile`, you can do:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet = torch.compile(t2i_pipe.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After compilation you should see a very fast inference time. For more information,
|
||||
feel free to have a look at [Our PyTorch 2.0 benchmark](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/optimization/torch2.0).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To generate images directly from a single pipeline, you can use [`KandinskyCombinedPipeline`], [`KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline`], [`KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline`].
|
||||
These combined pipelines wrap the [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`] and [`KandinskyPipeline`], [`KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline`], [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`] respectively into a single
|
||||
pipeline for a simpler user experience
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky_combined.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky_combined.py) | *End-to-end Text-to-Image, image-to-image, Inpainting Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky_inpaint.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky_inpaint.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky_img2img.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky/pipeline_kandinsky_img2img.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyPriorPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- interpolate
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
### KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
### KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
### KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyInpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
### KandinskyCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyImg2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyInpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,77 +9,348 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Kandinsky 2.2
|
||||
|
||||
Kandinsky 2.1 is created by [Arseniy Shakhmatov](https://github.com/cene555), [Anton Razzhigaev](https://github.com/razzant), [Aleksandr Nikolich](https://github.com/AlexWortega), [Igor Pavlov](https://github.com/boomb0om), [Andrey Kuznetsov](https://github.com/kuznetsoffandrey) and [Denis Dimitrov](https://github.com/denndimitrov).
|
||||
The Kandinsky 2.2 release includes robust new text-to-image models that support text-to-image generation, image-to-image generation, image interpolation, and text-guided image inpainting. The general workflow to perform these tasks using Kandinsky 2.2 is the same as in Kandinsky 2.1. First, you will need to use a prior pipeline to generate image embeddings based on your text prompt, and then use one of the image decoding pipelines to generate the output image. The only difference is that in Kandinsky 2.2, all of the decoding pipelines no longer accept the `prompt` input, and the image generation process is conditioned with only `image_embeds` and `negative_image_embeds`.
|
||||
|
||||
The description from it's GitHub page is:
|
||||
Same as with Kandinsky 2.1, the easiest way to perform text-to-image generation is to use the combined Kandinsky pipeline. This process is exactly the same as Kandinsky 2.1. All you need to do is to replace the Kandinsky 2.1 checkpoint with 2.2.
|
||||
|
||||
*Kandinsky 2.2 brings substantial improvements upon its predecessor, Kandinsky 2.1, by introducing a new, more powerful image encoder - CLIP-ViT-G and the ControlNet support. The switch to CLIP-ViT-G as the image encoder significantly increases the model's capability to generate more aesthetic pictures and better understand text, thus enhancing the model's overall performance. The addition of the ControlNet mechanism allows the model to effectively control the process of generating images. This leads to more accurate and visually appealing outputs and opens new possibilities for text-guided image manipulation.*
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoPipelineForText2Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
The original codebase can be found at [ai-forever/Kandinsky-2](https://github.com/ai-forever/Kandinsky-2).
|
||||
pipe = AutoPipelineForText2Image.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A alien cheeseburger creature eating itself, claymation, cinematic, moody lighting"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prompt, prior_guidance_scale =1.0, height=768, width=768).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's look at an example where we take separate steps to run the prior pipeline and text-to-image pipeline. This way, we can understand what's happening under the hood and how Kandinsky 2.2 differs from Kandinsky 2.1.
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's create the prior pipeline and text-to-image pipeline with Kandinsky 2.2 checkpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-decoder", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can then use `pipe_prior` to generate image embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "portrait of a women, blue eyes, cinematic"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "low quality, bad quality"
|
||||
|
||||
image_embeds, negative_image_embeds = pipe_prior(prompt, guidance_scale=1.0).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can pass these embeddings to the text-to-image pipeline. When using Kandinsky 2.2 you don't need to pass the `prompt` (but you do with the previous version, Kandinsky 2.1).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
image = t2i_pipe(image_embeds=image_embeds, negative_image_embeds=negative_image_embeds, height=768, width=768).images[
|
||||
0
|
||||
]
|
||||
image.save("portrait.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We used the text-to-image pipeline as an example, but the same process applies to all decoding pipelines in Kandinsky 2.2. For more information, please refer to our API section for each pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
### Text-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we give a simple example of how to use [`KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline`] to add control to the text-to-image generation with a depth image.
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's take an image and extract its depth map.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
img = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main/kandinskyv22/cat.png"
|
||||
).resize((768, 768))
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We can use the `depth-estimation` pipeline from transformers to process the image and retrieve its depth map.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def make_hint(image, depth_estimator):
|
||||
image = depth_estimator(image)["depth"]
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
detected_map = torch.from_numpy(image).float() / 255.0
|
||||
hint = detected_map.permute(2, 0, 1)
|
||||
return hint
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
depth_estimator = pipeline("depth-estimation")
|
||||
hint = make_hint(img, depth_estimator).unsqueeze(0).half().to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
Now, we load the prior pipeline and the text-to-image controlnet pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyV22PriorPipeline, KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyV22PriorPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior = pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-controlnet-depth", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We pass the prompt and negative prompt through the prior to generate image embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "A robot, 4k photo"
|
||||
|
||||
negative_prior_prompt = "lowres, text, error, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, ugly, duplicate, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, extra fingers, mutated hands, poorly drawn hands, poorly drawn face, mutation, deformed, blurry, dehydrated, bad anatomy, bad proportions, extra limbs, cloned face, disfigured, gross proportions, malformed limbs, missing arms, missing legs, extra arms, extra legs, fused fingers, too many fingers, long neck, username, watermark, signature"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(43)
|
||||
image_emb, zero_image_emb = pipe_prior(
|
||||
prompt=prompt, negative_prompt=negative_prior_prompt, generator=generator
|
||||
).to_tuple()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can pass the image embeddings and the depth image we extracted to the controlnet pipeline. With Kandinsky 2.2, only prior pipelines accept `prompt` input. You do not need to pass the prompt to the controlnet pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
images = pipe(
|
||||
image_embeds=image_emb,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds=zero_image_emb,
|
||||
hint=hint,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
).images
|
||||
|
||||
images[0].save("robot_cat.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The output image looks as follow:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Image-to-Image Generation with ControlNet Conditioning
|
||||
|
||||
Kandinsky 2.2 also includes a [`KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline`] that will allow you to add control to the image generation process with both the image and its depth map. This pipeline works really well with [`KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline`], which generates image embeddings based on both a text prompt and an image.
|
||||
|
||||
For our robot cat example, we will pass the prompt and cat image together to the prior pipeline to generate an image embedding. We will then use that image embedding and the depth map of the cat to further control the image generation process.
|
||||
|
||||
We can use the same cat image and its depth map from the last example.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from diffusers import KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline, KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
img = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/hf-internal-testing/diffusers-images/resolve/main" "/kandinskyv22/cat.png"
|
||||
).resize((768, 768))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def make_hint(image, depth_estimator):
|
||||
image = depth_estimator(image)["depth"]
|
||||
image = np.array(image)
|
||||
image = image[:, :, None]
|
||||
image = np.concatenate([image, image, image], axis=2)
|
||||
detected_map = torch.from_numpy(image).float() / 255.0
|
||||
hint = detected_map.permute(2, 0, 1)
|
||||
return hint
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
depth_estimator = pipeline("depth-estimation")
|
||||
hint = make_hint(img, depth_estimator).unsqueeze(0).half().to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_prior = KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-prior", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe_prior = pipe_prior.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-2-controlnet-depth", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "A robot, 4k photo"
|
||||
negative_prior_prompt = "lowres, text, error, cropped, worst quality, low quality, jpeg artifacts, ugly, duplicate, morbid, mutilated, out of frame, extra fingers, mutated hands, poorly drawn hands, poorly drawn face, mutation, deformed, blurry, dehydrated, bad anatomy, bad proportions, extra limbs, cloned face, disfigured, gross proportions, malformed limbs, missing arms, missing legs, extra arms, extra legs, fused fingers, too many fingers, long neck, username, watermark, signature"
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(43)
|
||||
|
||||
# run prior pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
img_emb = pipe_prior(prompt=prompt, image=img, strength=0.85, generator=generator)
|
||||
negative_emb = pipe_prior(prompt=negative_prior_prompt, image=img, strength=1, generator=generator)
|
||||
|
||||
# run controlnet img2img pipeline
|
||||
images = pipe(
|
||||
image=img,
|
||||
strength=0.5,
|
||||
image_embeds=img_emb.image_embeds,
|
||||
negative_image_embeds=negative_emb.image_embeds,
|
||||
hint=hint,
|
||||
num_inference_steps=50,
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
height=768,
|
||||
width=768,
|
||||
).images
|
||||
|
||||
images[0].save("robot_cat.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the output. Compared with the output from our text-to-image controlnet example, it kept a lot more cat facial details from the original image and worked into the robot style we asked for.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
Running Kandinsky in inference requires running both a first prior pipeline: [`KandinskyPriorPipeline`]
|
||||
and a second image decoding pipeline which is one of [`KandinskyPipeline`], [`KandinskyImg2ImgPipeline`], or [`KandinskyInpaintPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
The bulk of the computation time will always be the second image decoding pipeline, so when looking
|
||||
into optimizing the model, one should look into the second image decoding pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
When running with PyTorch < 2.0, we strongly recommend making use of [`xformers`](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers)
|
||||
to speed-up the optimization. This can be done by simply running:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("kandinsky-community/kandinsky-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When running on PyTorch >= 2.0, PyTorch's SDPA attention will automatically be used. For more information on
|
||||
PyTorch's SDPA, feel free to have a look at [this blog post](https://pytorch.org/blog/accelerated-diffusers-pt-20/).
|
||||
|
||||
To have explicit control , you can also manually set the pipeline to use PyTorch's 2.0 efficient attention:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor2_0())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The slowest and most memory intense attention processor is the default `AttnAddedKVProcessor` processor.
|
||||
We do **not** recommend using it except for testing purposes or cases where very high determistic behaviour is desired.
|
||||
You can set it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnAddedKVProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnAddedKVProcessor())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With PyTorch >= 2.0, you can also use Kandinsky with `torch.compile` which depending
|
||||
on your hardware can signficantly speed-up your inference time once the model is compiled.
|
||||
To use Kandinsksy with `torch.compile`, you can do:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
t2i_pipe.unet = torch.compile(t2i_pipe.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After compilation you should see a very fast inference time. For more information,
|
||||
feel free to have a look at [Our PyTorch 2.0 benchmark](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/optimization/torch2.0).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [Kandinsky Community](https://huggingface.co/kandinsky-community) organization on the Hub for the official model checkpoints for tasks like text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting.
|
||||
To generate images directly from a single pipeline, you can use [`KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline`], [`KandinskyV22Img2ImgCombinedPipeline`], [`KandinskyV22InpaintCombinedPipeline`].
|
||||
These combined pipelines wrap the [`KandinskyV22PriorPipeline`] and [`KandinskyV22Pipeline`], [`KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline`], [`KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline`] respectively into a single
|
||||
pipeline for a simpler user experience
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22PriorPipeline
|
||||
## Available Pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2_combined.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2_combined.py) | *End-to-end Text-to-Image, image-to-image, Inpainting Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2_inpaint.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2_inpaint.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2_img2img.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2_img2img.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2_controlnet.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2_controlnet.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
| [pipeline_kandinsky2_2_controlnet_img2img.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/kandinsky2_2/pipeline_kandinsky2_2_controlnet_img2img.py) | *Image-Guided Image Generation* |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22Pipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
### KandinskyV22PriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22PriorPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- interpolate
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22Pipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22ControlnetPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline
|
||||
### KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22PriorEmb2EmbPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- interpolate
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline
|
||||
### KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22Img2ImgPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22CombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22Img2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
### KandinskyV22Img2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22Img2ImgCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22ControlnetImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22InpaintPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## KandinskyV22InpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
### KandinskyV22InpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KandinskyV22InpaintCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Latent Consistency Models
|
||||
|
||||
Latent Consistency Models (LCMs) were proposed in [Latent Consistency Models: Synthesizing High-Resolution Images with Few-Step Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.04378) by Simian Luo, Yiqin Tan, Longbo Huang, Jian Li, and Hang Zhao.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the [paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2310.04378.pdf) is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
*Latent Diffusion models (LDMs) have achieved remarkable results in synthesizing high-resolution images. However, the iterative sampling process is computationally intensive and leads to slow generation. Inspired by Consistency Models (song et al.), we propose Latent Consistency Models (LCMs), enabling swift inference with minimal steps on any pre-trained LDMs, including Stable Diffusion (rombach et al). Viewing the guided reverse diffusion process as solving an augmented probability flow ODE (PF-ODE), LCMs are designed to directly predict the solution of such ODE in latent space, mitigating the need for numerous iterations and allowing rapid, high-fidelity sampling. Efficiently distilled from pre-trained classifier-free guided diffusion models, a high-quality 768 x 768 2~4-step LCM takes only 32 A100 GPU hours for training. Furthermore, we introduce Latent Consistency Fine-tuning (LCF), a novel method that is tailored for fine-tuning LCMs on customized image datasets. Evaluation on the LAION-5B-Aesthetics dataset demonstrates that LCMs achieve state-of-the-art text-to-image generation performance with few-step inference.*
|
||||
|
||||
A demo for the [SimianLuo/LCM_Dreamshaper_v7](https://huggingface.co/SimianLuo/LCM_Dreamshaper_v7) checkpoint can be found [here](https://huggingface.co/spaces/SimianLuo/Latent_Consistency_Model).
|
||||
|
||||
The pipelines were contributed by [luosiallen](https://luosiallen.github.io/), [nagolinc](https://github.com/nagolinc), and [dg845](https://github.com/dg845).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## LatentConsistencyModelPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LatentConsistencyModelPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_freeu
|
||||
- disable_freeu
|
||||
- enable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_vae_tiling
|
||||
- disable_vae_tiling
|
||||
|
||||
## LatentConsistencyModelImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LatentConsistencyModelImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- enable_freeu
|
||||
- disable_freeu
|
||||
- enable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- disable_vae_slicing
|
||||
- enable_vae_tiling
|
||||
- disable_vae_tiling
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [Compvis/latent-diffusion](https://github.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [CompVis/latent-diffusion](https://github.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ You can find additional information about model editing on the [project page](ht
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -45,7 +45,9 @@ During inference:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between
|
||||
scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines)
|
||||
section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,74 +12,16 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines provide a simple way to run state-of-the-art diffusion models in inference by bundling all of the necessary components (multiple independently-trained models, schedulers, and processors) into a single end-to-end class. Pipelines are flexible and they can be adapted to use different schedulers or even model components.
|
||||
Pipelines provide a simple way to run state-of-the-art diffusion models in inference by bundling all of the necessary components (multiple independently-trained models, schedulers, and processors) into a single end-to-end class. Pipelines are flexible and they can be adapted to use different scheduler or even model components.
|
||||
|
||||
All pipelines are built from the base [`DiffusionPipeline`] class which provides basic functionality for loading, downloading, and saving all the components. Specific pipeline types (for example [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]) loaded with [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] are automatically detected and the pipeline components are loaded and passed to the `__init__` function of the pipeline.
|
||||
All pipelines are built from the base [`DiffusionPipeline`] class which provides basic functionality for loading, downloading, and saving all the components.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
You shouldn't use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] class for training. Individual components (for example, [`UNet2DModel`] and [`UNet2DConditionModel`]) of diffusion pipelines are usually trained individually, so we suggest directly working with them instead.
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines do not offer any training functionality. You'll notice PyTorch's autograd is disabled by decorating the [`~DiffusionPipeline.__call__`] method with a [`torch.no_grad`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.no_grad.html) decorator because pipelines should not be used for training. If you're interested in training, please take a look at the [Training](../../training/overview) guides instead!
|
||||
Pipelines do not offer any training functionality. You'll notice PyTorch's autograd is disabled by decorating the [`~DiffusionPipeline.__call__`] method with a [`torch.no_grad`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.no_grad.html) decorator because pipelines should not be used for training. If you're interested in training, please take a look at the [Training](../traininig/overview) guides instead!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The table below lists all the pipelines currently available in 🤗 Diffusers and the tasks they support. Click on a pipeline to view its abstract and published paper.
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| [AltDiffusion](alt_diffusion) | image2image |
|
||||
| [Attend-and-Excite](attend_and_excite) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Audio Diffusion](audio_diffusion) | image2audio |
|
||||
| [AudioLDM](audioldm) | text2audio |
|
||||
| [AudioLDM2](audioldm2) | text2audio |
|
||||
| [BLIP Diffusion](blip_diffusion) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Consistency Models](consistency_models) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [ControlNet](controlnet) | text2image, image2image, inpainting |
|
||||
| [ControlNet with Stable Diffusion XL](controlnet_sdxl) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Cycle Diffusion](cycle_diffusion) | image2image |
|
||||
| [Dance Diffusion](dance_diffusion) | unconditional audio generation |
|
||||
| [DDIM](ddim) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [DDPM](ddpm) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [DeepFloyd IF](deepfloyd_if) | text2image, image2image, inpainting, super-resolution |
|
||||
| [DiffEdit](diffedit) | inpainting |
|
||||
| [DiT](dit) | text2image |
|
||||
| [GLIGEN](gligen) | text2image |
|
||||
| [InstructPix2Pix](pix2pix) | image editing |
|
||||
| [Kandinsky](kandinsky) | text2image, image2image, inpainting, interpolation |
|
||||
| [Kandinsky 2.2](kandinsky_v22) | text2image, image2image, inpainting |
|
||||
| [Latent Diffusion](latent_diffusion) | text2image, super-resolution |
|
||||
| [LDM3D](ldm3d_diffusion) | text2image, text-to-3D |
|
||||
| [MultiDiffusion](panorama) | text2image |
|
||||
| [MusicLDM](musicldm) | text2audio |
|
||||
| [PaintByExample](paint_by_example) | inpainting |
|
||||
| [ParaDiGMS](paradigms) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Pix2Pix Zero](pix2pix_zero) | image editing |
|
||||
| [PNDM](pndm) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [RePaint](repaint) | inpainting |
|
||||
| [ScoreSdeVe](score_sde_ve) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [Self-Attention Guidance](self_attention_guidance) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Semantic Guidance](semantic_stable_diffusion) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Shap-E](shap_e) | text-to-3D, image-to-3D |
|
||||
| [Spectrogram Diffusion](spectrogram_diffusion) | |
|
||||
| [Stable Diffusion](stable_diffusion/overview) | text2image, image2image, depth2image, inpainting, image variation, latent upscaler, super-resolution |
|
||||
| [Stable Diffusion Model Editing](model_editing) | model editing |
|
||||
| [Stable Diffusion XL](stable_diffusion_xl) | text2image, image2image, inpainting |
|
||||
| [Stable unCLIP](stable_unclip) | text2image, image variation |
|
||||
| [KarrasVe](karras_ve) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [T2I Adapter](adapter) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Text2Video](text_to_video) | text2video, video2video |
|
||||
| [Text2Video Zero](text_to_video_zero) | text2video |
|
||||
| [UnCLIP](unclip) | text2image, image variation |
|
||||
| [Unconditional Latent Diffusion](latent_diffusion_uncond) | unconditional image generation |
|
||||
| [UniDiffuser](unidiffuser) | text2image, image2text, image variation, text variation, unconditional image generation, unconditional audio generation |
|
||||
| [Value-guided planning](value_guided_sampling) | value guided sampling |
|
||||
| [Versatile Diffusion](versatile_diffusion) | text2image, image variation |
|
||||
| [VQ Diffusion](vq_diffusion) | text2image |
|
||||
| [Wuerstchen](wuerstchen) | text2image |
|
||||
|
||||
## DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Paint By Example
|
||||
# PaintByExample
|
||||
|
||||
[Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models](https://huggingface.co/papers/2211.13227) is by Binxin Yang, Shuyang Gu, Bo Zhang, Ting Zhang, Xuejin Chen, Xiaoyan Sun, Dong Chen, Fang Wen.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ PaintByExample is supported by the official [Fantasy-Studio/Paint-by-Example](ht
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ But with circular padding, the right and the left parts are matching (`circular_
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ in parallel on multiple GPUs. But [`StableDiffusionParadigmsPipeline`] is design
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ You can find additional information about InstructPix2Pix on the [project page](
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -34,7 +34,13 @@ Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers)
|
||||
- load_lora_weights
|
||||
- save_lora_weights
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.stable_diffusion.StableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionXLInstructPix2PixPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StableDiffusionXLInstructPix2PixPipeline
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionXLPipelineOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.stable_diffusion_xl.StableDiffusionXLPipelineOutput
|
||||
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PixArt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[PixArt-α: Fast Training of Diffusion Transformer for Photorealistic Text-to-Image Synthesis](https://huggingface.co/papers/2310.00426) is Junsong Chen, Jincheng Yu, Chongjian Ge, Lewei Yao, Enze Xie, Yue Wu, Zhongdao Wang, James Kwok, Ping Luo, Huchuan Lu, and Zhenguo Li.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*The most advanced text-to-image (T2I) models require significant training costs (e.g., millions of GPU hours), seriously hindering the fundamental innovation for the AIGC community while increasing CO2 emissions. This paper introduces PIXART-α, a Transformer-based T2I diffusion model whose image generation quality is competitive with state-of-the-art image generators (e.g., Imagen, SDXL, and even Midjourney), reaching near-commercial application standards. Additionally, it supports high-resolution image synthesis up to 1024px resolution with low training cost, as shown in Figure 1 and 2. To achieve this goal, three core designs are proposed: (1) Training strategy decomposition: We devise three distinct training steps that separately optimize pixel dependency, text-image alignment, and image aesthetic quality; (2) Efficient T2I Transformer: We incorporate cross-attention modules into Diffusion Transformer (DiT) to inject text conditions and streamline the computation-intensive class-condition branch; (3) High-informative data: We emphasize the significance of concept density in text-image pairs and leverage a large Vision-Language model to auto-label dense pseudo-captions to assist text-image alignment learning. As a result, PIXART-α's training speed markedly surpasses existing large-scale T2I models, e.g., PIXART-α only takes 10.8% of Stable Diffusion v1.5's training time (675 vs. 6,250 A100 GPU days), saving nearly $300,000 ($26,000 vs. $320,000) and reducing 90% CO2 emissions. Moreover, compared with a larger SOTA model, RAPHAEL, our training cost is merely 1%. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PIXART-α excels in image quality, artistry, and semantic control. We hope PIXART-α will provide new insights to the AIGC community and startups to accelerate building their own high-quality yet low-cost generative models from scratch.*
|
||||
|
||||
You can find the original codebase at [PixArt-alpha/PixArt-alpha](https://github.com/PixArt-alpha/PixArt-alpha) and all the available checkpoints at [PixArt-alpha](https://huggingface.co/PixArt-alpha).
|
||||
|
||||
Some notes about this pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
* It uses a Transformer backbone (instead of a UNet) for denoising. As such it has a similar architecture as [DiT](./dit.md).
|
||||
* It was trained using text conditions computed from T5. This aspect makes the pipeline better at following complex text prompts with intricate details.
|
||||
* It is good at producing high-resolution images at different aspect ratios. To get the best results, the authors recommend some size brackets which can be found [here](https://github.com/PixArt-alpha/PixArt-alpha/blob/08fbbd281ec96866109bdd2cdb75f2f58fb17610/diffusion/data/datasets/utils.py).
|
||||
* It rivals the quality of state-of-the-art text-to-image generation systems (as of this writing) such as Stable Diffusion XL, Imagen, and DALL-E 2, while being more efficient than them.
|
||||
|
||||
## PixArtAlphaPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PixArtAlphaPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [luping-liu/PNDM](https://github.com/lupin
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [andreas128/RePaint](https://github.com/an
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [yang-song/score_sde_pytorch](https://gith
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ You can find additional information about Self-Attention Guidance on the [projec
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,5 +31,5 @@ Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers)
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## StableDiffusionSafePipelineOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.semantic_stable_diffusion.pipeline_output.SemanticStableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
- all
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.semantic_stable_diffusion.SemanticStableDiffusionPipelineOutput
|
||||
- all
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [openai/shap-e](https://github.com/openai/
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
See the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
See the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ As depicted above the model takes as input a MIDI file and tokenizes it into a s
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -28,8 +28,8 @@ This model was contributed by the community contributor [HimariO](https://github
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Tasks | Demo
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/t2i_adapter/pipeline_stable_diffusion_adapter.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation with T2I-Adapter Conditioning* | -
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/t2i_adapter/pipeline_stable_diffusion_xl_adapter.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation with T2I-Adapter Conditioning on StableDiffusion-XL* | -
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionAdapterPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_adapter.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation with T2I-Adapter Conditioning* | -
|
||||
| [StableDiffusionXLAdapterPipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pipeline_stable_diffusion_xl_adapter.py) | *Text-to-Image Generation with T2I-Adapter Conditioning on StableDiffusion-XL* | -
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example with the base model of StableDiffusion-1.4/1.5
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Text-to-(RGB, depth)
|
||||
|
||||
LDM3D was proposed in [LDM3D: Latent Diffusion Model for 3D](https://huggingface.co/papers/2305.10853) by Gabriela Ben Melech Stan, Diana Wofk, Scottie Fox, Alex Redden, Will Saxton, Jean Yu, Estelle Aflalo, Shao-Yen Tseng, Fabio Nonato, Matthias Muller, and Vasudev Lal. LDM3D generates an image and a depth map from a given text prompt unlike the existing text-to-image diffusion models such as [Stable Diffusion](./overview) which only generates an image. With almost the same number of parameters, LDM3D achieves to create a latent space that can compress both the RGB images and the depth maps.
|
||||
LDM3D was proposed in [LDM3D: Latent Diffusion Model for 3D](https://huggingface.co/papers/2305.10853) by Gabriela Ben Melech Stan, Diana Wofk, Scottie Fox, Alex Redden, Will Saxton, Jean Yu, Estelle Aflalo, Shao-Yen Tseng, Fabio Nonato, Matthias Muller, and Vasudev Lal. LDM3D generates an image and a depth map from a given text prompt unlike the existing text-to-image diffusion models such as [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion/overview) which only generates an image. With almost the same number of parameters, LDM3D achieves to create a latent space that can compress both the RGB images and the depth maps.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,8 +36,10 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<th class="px-4 py-2 font-medium text-gray-900 text-left">
|
||||
Space
|
||||
</th>
|
||||
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
|
||||
<tbody class="divide-y divide-gray-200">
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
@@ -47,6 +49,7 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/stabilityai/stable-diffusion"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./img2img">StableDiffusionImg2Img</a>
|
||||
@@ -55,6 +58,7 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface/diffuse-the-rest"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./inpaint">StableDiffusionInpaint</a>
|
||||
@@ -63,6 +67,7 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./depth2img">StableDiffusionDepth2Img</a>
|
||||
@@ -71,6 +76,7 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/radames/stable-diffusion-depth2img"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./image_variation">StableDiffusionImageVariation</a>
|
||||
@@ -79,6 +85,7 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/lambdalabs/stable-diffusion-image-variations"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./stable_diffusion_safe">StableDiffusionPipelineSafe</a>
|
||||
@@ -87,6 +94,7 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/AIML-TUDA/unsafe-vs-safe-stable-diffusion"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./stable_diffusion_2">StableDiffusion2</a>
|
||||
@@ -95,6 +103,7 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/stabilityai/stable-diffusion"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./stable_diffusion_xl">StableDiffusionXL</a>
|
||||
@@ -103,6 +112,7 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/RamAnanth1/stable-diffusion-xl"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./latent_upscale">StableDiffusionLatentUpscale</a>
|
||||
@@ -111,12 +121,14 @@ The table below summarizes the available Stable Diffusion pipelines, their suppo
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2"><a href="https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-projects/stable-diffusion-latent-upscaler"><img src="https://img.shields.io/badge/%F0%9F%A4%97%20Hugging%20Face-Spaces-blue"/></a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./upscale">StableDiffusionUpscale</a>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">super-resolution</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td class="px-4 py-2 text-gray-700">
|
||||
<a href="./ldm3d_diffusion">StableDiffusionLDM3D</a>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,9 +20,6 @@ The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips
|
||||
|
||||
- Using SDXL with a DPM++ scheduler for less than 50 steps is known to produce [visual artifacts](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/5433) because the solver becomes numerically unstable. To fix this issue, take a look at this [PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/5541) which recommends for ODE/SDE solvers:
|
||||
- set `use_karras_sigmas=True` or `lu_lambdas=True` to improve image quality
|
||||
- set `euler_at_final=True` if you're using a solver with uniform step sizes (DPM++2M or DPM++2M SDE)
|
||||
- Most SDXL checkpoints work best with an image size of 1024x1024. Image sizes of 768x768 and 512x512 are also supported, but the results aren't as good. Anything below 512x512 is not recommended and likely won't for for default checkpoints like [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0).
|
||||
- SDXL can pass a different prompt for each of the text encoders it was trained on. We can even pass different parts of the same prompt to the text encoders.
|
||||
- SDXL output images can be improved by making use of a refiner model in an image-to-image setting.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The abstract from the paper:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,9 +7,9 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# unCLIP
|
||||
# UnCLIP
|
||||
|
||||
[Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://huggingface.co/papers/2204.06125) is by Aditya Ramesh, Prafulla Dhariwal, Alex Nichol, Casey Chu, Mark Chen. The unCLIP model in 🤗 Diffusers comes from kakaobrain's [karlo]((https://github.com/kakaobrain/karlo)).
|
||||
[Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://huggingface.co/papers/2204.06125) is by Aditya Ramesh, Prafulla Dhariwal, Alex Nichol, Casey Chu, Mark Chen. The UnCLIP model in 🤗 Diffusers comes from kakaobrain's [karlo]((https://github.com/kakaobrain/karlo)).
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is following:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ You can find lucidrains DALL-E 2 recreation at [lucidrains/DALLE2-pytorch](https
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -34,4 +34,4 @@ Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers)
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## ImagePipelineOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.ImagePipelineOutput
|
||||
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ You can load the more memory intensive "all-in-one" [`VersatileDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The original codebase can be found at [microsoft/VQ-Diffusion](https://github.co
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](../../using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](../../using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
Make sure to check out the Schedulers [guide](/using-diffusers/schedulers) to learn how to explore the tradeoff between scheduler speed and quality, and see the [reuse components across pipelines](/using-diffusers/loading#reuse-components-across-pipelines) section to learn how to efficiently load the same components into multiple pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,18 +2,15 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/dome272/Wuerstchen/assets/61938694/0617c863-165a-43ee-9303-2a17299a0cf9">
|
||||
|
||||
[Würstchen: Efficient Pretraining of Text-to-Image Models](https://huggingface.co/papers/2306.00637) is by Pablo Pernias, Dominic Rampas, Mats L. Richter and Christopher Pal and Marc Aubreville.
|
||||
[Würstchen: Efficient Pretraining of Text-to-Image Models](https://huggingface.co/papers/2306.00637) is by Pablo Pernias, Dominic Rampas, and Marc Aubreville.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*We introduce Würstchen, a novel technique for text-to-image synthesis that unites competitive performance with unprecedented cost-effectiveness and ease of training on constrained hardware. Building on recent advancements in machine learning, our approach, which utilizes latent diffusion strategies at strong latent image compression rates, significantly reduces the computational burden, typically associated with state-of-the-art models, while preserving, if not enhancing, the quality of generated images. Wuerstchen achieves notable speed improvements at inference time, thereby rendering real-time applications more viable. One of the key advantages of our method lies in its modest training requirements of only 9,200 GPU hours, slashing the usual costs significantly without compromising the end performance. In a comparison against the state-of-the-art, we found the approach to yield strong competitiveness. This paper opens the door to a new line of research that prioritizes both performance and computational accessibility, hence democratizing the use of sophisticated AI technologies. Through Wuerstchen, we demonstrate a compelling stride forward in the realm of text-to-image synthesis, offering an innovative path to explore in future research.*
|
||||
|
||||
## Würstchen Overview
|
||||
Würstchen is a diffusion model, whose text-conditional model works in a highly compressed latent space of images. Why is this important? Compressing data can reduce computational costs for both training and inference by magnitudes. Training on 1024x1024 images is way more expensive than training on 32x32. Usually, other works make use of a relatively small compression, in the range of 4x - 8x spatial compression. Würstchen takes this to an extreme. Through its novel design, we achieve a 42x spatial compression. This was unseen before because common methods fail to faithfully reconstruct detailed images after 16x spatial compression. Würstchen employs a two-stage compression, what we call Stage A and Stage B. Stage A is a VQGAN, and Stage B is a Diffusion Autoencoder (more details can be found in the [paper](https://huggingface.co/papers/2306.00637) ). A third model, Stage C, is learned in that highly compressed latent space. This training requires fractions of the compute used for current top-performing models, while also allowing cheaper and faster inference.
|
||||
|
||||
## Würstchen v2 comes to Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
After the initial paper release, we have improved numerous things in the architecture, training and sampling, making Würstchen competitive to current state-of-the-art models in many ways. We are excited to release this new version together with Diffusers. Here is a list of the improvements.
|
||||
After the initial paper release, we have improved numerous things in the architecture, training and sampling, making Würstchen competetive to current state-of-the-art models in many ways. We are excited to release this new version together with Diffusers. Here is a list of the improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
- Higher resolution (1024x1024 up to 2048x2048)
|
||||
- Faster inference
|
||||
@@ -25,16 +22,16 @@ We are releasing 3 checkpoints for the text-conditional image generation model (
|
||||
|
||||
- v2-base
|
||||
- v2-aesthetic
|
||||
- **(default)** v2-interpolated (50% interpolation between v2-base and v2-aesthetic)
|
||||
- v2-interpolated (50% interpolation between v2-base and v2-aesthetic)
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend using v2-interpolated, as it has a nice touch of both photorealism and aesthetics. Use v2-base for finetunings as it does not have a style bias and use v2-aesthetic for very artistic generations.
|
||||
We recommend to use v2-interpolated, as it has a nice touch of both photorealism and aesthetic. Use v2-base for finetunings as it does not have a style bias and use v2-aesthetic for very artistic generations.
|
||||
A comparison can be seen here:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/dome272/Wuerstchen/assets/61938694/2914830f-cbd3-461c-be64-d50734f4b49d" width=500>
|
||||
|
||||
## Text-to-Image Generation
|
||||
|
||||
For the sake of usability, Würstchen can be used with a single pipeline. This pipeline can be used as follows:
|
||||
For the sake of usability Würstchen can be used with a single pipeline. This pipeline is called `WuerstchenCombinedPipeline` and can be used as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -88,6 +85,7 @@ decoder_output = decoder_pipeline(
|
||||
image_embeddings=prior_output.image_embeddings,
|
||||
prompt=caption,
|
||||
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt=num_images_per_prompt,
|
||||
guidance_scale=0.0,
|
||||
output_type="pil",
|
||||
).images
|
||||
@@ -97,8 +95,8 @@ decoder_output = decoder_pipeline(
|
||||
You can make use of `torch.compile` function and gain a speed-up of about 2-3x:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prior_pipeline.prior = torch.compile(prior_pipeline.prior, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
decoder_pipeline.decoder = torch.compile(decoder_pipeline.decoder, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
pipeline.prior = torch.compile(pipeline.prior, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
pipeline.decoder = torch.compile(pipeline.decoder, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Limitations
|
||||
@@ -113,7 +111,7 @@ after 1024x1024 is 1152x1152
|
||||
|
||||
The original codebase, as well as experimental ideas, can be found at [dome272/Wuerstchen](https://github.com/dome272/Wuerstchen).
|
||||
|
||||
## WuerstchenCombinedPipeline
|
||||
## WuerschenPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] WuerstchenCombinedPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
@@ -121,7 +119,8 @@ The original codebase, as well as experimental ideas, can be found at [dome272/W
|
||||
|
||||
## WuerstchenPriorPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] WuerstchenPriorPipeline
|
||||
[[autodoc]] WuerstchenDecoderPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -134,16 +133,3 @@ The original codebase, as well as experimental ideas, can be found at [dome272/W
|
||||
[[autodoc]] WuerstchenDecoderPipeline
|
||||
- all
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## Citation
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@misc{pernias2023wuerstchen,
|
||||
title={Wuerstchen: Efficient Pretraining of Text-to-Image Models},
|
||||
author={Pablo Pernias and Dominic Rampas and Mats L. Richter and Christopher Pal and Marc Aubreville},
|
||||
year={2023},
|
||||
eprint={2306.00637},
|
||||
archivePrefix={arXiv},
|
||||
primaryClass={cs.CV}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# ConsistencyDecoderScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
This scheduler is a part of the [`ConsistencyDecoderPipeline`] and was introduced in [DALL-E 3](https://openai.com/dall-e-3).
|
||||
|
||||
The original codebase can be found at [openai/consistency_models](https://github.com/openai/consistency_models).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## ConsistencyDecoderScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] schedulers.scheduling_consistency_decoder.ConsistencyDecoderScheduler
|
||||
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Latent Consistency Model Multistep Scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Multistep and onestep scheduler (Algorithm 3) introduced alongside latent consistency models in the paper [Latent Consistency Models: Synthesizing High-Resolution Images with Few-Step Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.04378) by Simian Luo, Yiqin Tan, Longbo Huang, Jian Li, and Hang Zhao.
|
||||
This scheduler should be able to generate good samples from [`LatentConsistencyModelPipeline`] in 1-8 steps.
|
||||
|
||||
## LCMScheduler
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LCMScheduler
|
||||
@@ -28,11 +28,11 @@ the core library.
|
||||
In the following, we give an overview of different ways to contribute, ranked by difficulty in ascending order. All of them are valuable to the community.
|
||||
|
||||
* 1. Asking and answering questions on [the Diffusers discussion forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers) or on [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR).
|
||||
* 2. Opening new issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose).
|
||||
* 3. Answering issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues).
|
||||
* 2. Opening new issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose)
|
||||
* 3. Answering issues on [the GitHub Issues tab](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues)
|
||||
* 4. Fix a simple issue, marked by the "Good first issue" label, see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22).
|
||||
* 5. Contribute to the [documentation](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/docs/source).
|
||||
* 6. Contribute a [Community Pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3Acommunity-examples).
|
||||
* 6. Contribute a [Community Pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3Acommunity-examples)
|
||||
* 7. Contribute to the [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples).
|
||||
* 8. Fix a more difficult issue, marked by the "Good second issue" label, see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22).
|
||||
* 9. Add a new pipeline, model, or scheduler, see ["New Pipeline/Model"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22) and ["New scheduler"](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22) issues. For this contribution, please have a look at [Design Philosophy](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/PHILOSOPHY.md).
|
||||
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ In the following, we give an overview of different ways to contribute, ranked by
|
||||
As said before, **all contributions are valuable to the community**.
|
||||
In the following, we will explain each contribution a bit more in detail.
|
||||
|
||||
For all contributions 4 - 9, you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in [Opening a pull request](#how-to-open-a-pr).
|
||||
For all contributions 4.-9. you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in [Opening a pull requst](#how-to-open-a-pr)
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Asking and answering questions on the Diffusers discussion forum or on the Diffusers Discord
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,13 +57,13 @@ Any question or comment related to the Diffusers library can be asked on the [di
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
|
||||
Every question that is asked on the forum or on Discord actively encourages the community to publicly
|
||||
share knowledge and might very well help a beginner in the future who has the same question you're
|
||||
share knowledge and might very well help a beginner in the future that has the same question you're
|
||||
having. Please do pose any questions you might have.
|
||||
In the same spirit, you are of immense help to the community by answering such questions because this way you are publicly documenting knowledge for everybody to learn from.
|
||||
|
||||
**Please** keep in mind that the more effort you put into asking or answering a question, the higher
|
||||
the quality of the publicly documented knowledge. In the same way, well-posed and well-answered questions create a high-quality knowledge database accessible to everybody, while badly posed questions or answers reduce the overall quality of the public knowledge database.
|
||||
In short, a high quality question or answer is *precise*, *concise*, *relevant*, *easy-to-understand*, *accessible*, and *well-formated/well-posed*. For more information, please have a look through the [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue) section.
|
||||
In short, a high quality question or answer is *precise*, *concise*, *relevant*, *easy-to-understand*, *accesible*, and *well-formated/well-posed*. For more information, please have a look through the [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue) section.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE about channels**:
|
||||
[*The forum*](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) is much better indexed by search engines, such as Google. Posts are ranked by popularity rather than chronologically. Hence, it's easier to look up questions and answers that we posted some time ago.
|
||||
@@ -91,12 +91,12 @@ open a new issue nevertheless and link to the related issue.
|
||||
|
||||
New issues usually include the following.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.1. Reproducible, minimal bug reports
|
||||
#### 2.1. Reproducible, minimal bug reports.
|
||||
|
||||
A bug report should always have a reproducible code snippet and be as minimal and concise as possible.
|
||||
This means in more detail:
|
||||
- Narrow the bug down as much as you can, **do not just dump your whole code file**.
|
||||
- Format your code.
|
||||
- Narrow the bug down as much as you can, **do not just dump your whole code file**
|
||||
- Format your code
|
||||
- Do not include any external libraries except for Diffusers depending on them.
|
||||
- **Always** provide all necessary information about your environment; for this, you can run: `diffusers-cli env` in your shell and copy-paste the displayed information to the issue.
|
||||
- Explain the issue. If the reader doesn't know what the issue is and why it is an issue, she cannot solve it.
|
||||
@@ -105,9 +105,9 @@ This means in more detail:
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, please have a look through the [How to write a good issue](#how-to-write-a-good-issue) section.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a bug report [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&projects=&template=bug-report.yml).
|
||||
You can open a bug report [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.2. Feature requests
|
||||
#### 2.2. Feature requests.
|
||||
|
||||
A world-class feature request addresses the following points:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -125,26 +125,26 @@ Awesome! Tell us what problem it solved for you.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a feature request [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feature_request.md&title=).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.3 Feedback
|
||||
#### 2.3 Feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
Feedback about the library design and why it is good or not good helps the core maintainers immensely to build a user-friendly library. To understand the philosophy behind the current design philosophy, please have a look [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/conceptual/philosophy). If you feel like a certain design choice does not fit with the current design philosophy, please explain why and how it should be changed. If a certain design choice follows the design philosophy too much, hence restricting use cases, explain why and how it should be changed.
|
||||
If a certain design choice is very useful for you, please also leave a note as this is great feedback for future design decisions.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open an issue about feedback [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.4 Technical questions
|
||||
#### 2.4 Technical questions.
|
||||
|
||||
Technical questions are mainly about why certain code of the library was written in a certain way, or what a certain part of the code does. Please make sure to link to the code in question and please provide details on
|
||||
Technical questions are mainly about why certain code of the library was written in a certain way, or what a certain part of the code does. Please make sure to link to the code in question and please provide detail on
|
||||
why this part of the code is difficult to understand.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open an issue about a technical question [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&template=bug-report.yml).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2.5 Proposal to add a new model, scheduler, or pipeline
|
||||
#### 2.5 Proposal to add a new model, scheduler, or pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
If the diffusion model community released a new model, pipeline, or scheduler that you would like to see in the Diffusers library, please provide the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
* Short description of the diffusion pipeline, model, or scheduler and link to the paper or public release.
|
||||
* Link to any of its open-source implementation(s).
|
||||
* Link to any of its open-source implementation.
|
||||
* Link to the model weights if they are available.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are willing to contribute to the model yourself, let us know so we can best guide you. Also, don't forget
|
||||
@@ -156,21 +156,21 @@ You can open a request for a model/pipeline/scheduler [here](https://github.com/
|
||||
|
||||
Answering issues on GitHub might require some technical knowledge of Diffusers, but we encourage everybody to give it a try even if you are not 100% certain that your answer is correct.
|
||||
Some tips to give a high-quality answer to an issue:
|
||||
- Be as concise and minimal as possible.
|
||||
- Be as concise and minimal as possible
|
||||
- Stay on topic. An answer to the issue should concern the issue and only the issue.
|
||||
- Provide links to code, papers, or other sources that prove or encourage your point.
|
||||
- Answer in code. If a simple code snippet is the answer to the issue or shows how the issue can be solved, please provide a fully reproducible code snippet.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, many issues tend to be simply off-topic, duplicates of other issues, or irrelevant. It is of great
|
||||
help to the maintainers if you can answer such issues, encouraging the author of the issue to be
|
||||
more precise, provide the link to a duplicated issue or redirect them to [the forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) or [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR).
|
||||
more precise, provide the link to a duplicated issue or redirect them to [the forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/discussion-related-to-httpsgithubcomhuggingfacediffusers/63) or [Discord](https://discord.gg/G7tWnz98XR)
|
||||
|
||||
If you have verified that the issued bug report is correct and requires a correction in the source code,
|
||||
please have a look at the next sections.
|
||||
|
||||
For all of the following contributions, you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in the [Opening a pull request](#how-to-open-a-pr) section.
|
||||
For all of the following contributions, you will need to open a PR. It is explained in detail how to do so in the [Opening a pull requst](#how-to-open-a-pr) section.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Fixing a "Good first issue"
|
||||
### 4. Fixing a `Good first issue`
|
||||
|
||||
*Good first issues* are marked by the [Good first issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22) label. Usually, the issue already
|
||||
explains how a potential solution should look so that it is easier to fix.
|
||||
@@ -188,7 +188,7 @@ valuable contribution**.
|
||||
Contributing to the library can have many forms:
|
||||
|
||||
- Correcting spelling or grammatical errors.
|
||||
- Correct incorrect formatting of the docstring. If you see that the official documentation is weirdly displayed or a link is broken, we would be very happy if you take some time to correct it.
|
||||
- Correct incorrect formatting of the docstring. If you see that the official documentation is weirdly displayed or a link is broken, we are very happy if you take some time to correct it.
|
||||
- Correct the shape or dimensions of a docstring input or output tensor.
|
||||
- Clarify documentation that is hard to understand or incorrect.
|
||||
- Update outdated code examples.
|
||||
@@ -202,7 +202,7 @@ Please have a look at [this page](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/
|
||||
### 6. Contribute a community pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[Pipelines](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/overview) are usually the first point of contact between the Diffusers library and the user.
|
||||
Pipelines are examples of how to use Diffusers [models](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models/overview) and [schedulers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/schedulers/overview).
|
||||
Pipelines are examples of how to use Diffusers [models](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models) and [schedulers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/schedulers/overview).
|
||||
We support two types of pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
- Official Pipelines
|
||||
@@ -242,46 +242,46 @@ We support two types of training examples:
|
||||
|
||||
Research training examples are located in [examples/research_projects](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects) whereas official training examples include all folders under [examples](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples) except the `research_projects` and `community` folders.
|
||||
The official training examples are maintained by the Diffusers' core maintainers whereas the research training examples are maintained by the community.
|
||||
This is because of the same reasons put forward in [6. Contribute a community pipeline](#6-contribute-a-community-pipeline) for official pipelines vs. community pipelines: It is not feasible for the core maintainers to maintain all possible training methods for diffusion models.
|
||||
This is because of the same reasons put forward in [6. Contribute a community pipeline](#contribute-a-community-pipeline) for official pipelines vs. community pipelines: It is not feasible for the core maintainers to maintain all possible training methods for diffusion models.
|
||||
If the Diffusers core maintainers and the community consider a certain training paradigm to be too experimental or not popular enough, the corresponding training code should be put in the `research_projects` folder and maintained by the author.
|
||||
|
||||
Both official training and research examples consist of a directory that contains one or more training scripts, a requirements.txt file, and a README.md file. In order for the user to make use of the
|
||||
training examples, it is required to clone the repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
as well as to install all additional dependencies required for training:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install -r /examples/<your-example-folder>/requirements.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore when adding an example, the `requirements.txt` file shall define all pip dependencies required for your training example so that once all those are installed, the user can run the example's training script. See, for example, the [DreamBooth `requirements.txt` file](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/requirements.txt).
|
||||
|
||||
Training examples of the Diffusers library should adhere to the following philosophy:
|
||||
- All the code necessary to run the examples should be found in a single Python file.
|
||||
- One should be able to run the example from the command line with `python <your-example>.py --args`.
|
||||
- All the code necessary to run the examples should be found in a single Python file
|
||||
- One should be able to run the example from the command line with `python <your-example>.py --args`
|
||||
- Examples should be kept simple and serve as **an example** on how to use Diffusers for training. The purpose of example scripts is **not** to create state-of-the-art diffusion models, but rather to reproduce known training schemes without adding too much custom logic. As a byproduct of this point, our examples also strive to serve as good educational materials.
|
||||
|
||||
To contribute an example, it is highly recommended to look at already existing examples such as [dreambooth](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py) to get an idea of how they should look like.
|
||||
We strongly advise contributors to make use of the [Accelerate library](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate) as it's tightly integrated
|
||||
with Diffusers.
|
||||
Once an example script works, please make sure to add a comprehensive `README.md` that states how to use the example exactly. This README should include:
|
||||
- An example command on how to run the example script as shown [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#running-locally-with-pytorch).
|
||||
- A link to some training results (logs, models, etc.) that show what the user can expect as shown [here](https://api.wandb.ai/report/patrickvonplaten/xm6cd5q5).
|
||||
- An example command on how to run the example script as shown [here e.g.](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#running-locally-with-pytorch).
|
||||
- A link to some training results (logs, models, ...) that show what the user can expect as shown [here e.g.](https://api.wandb.ai/report/patrickvonplaten/xm6cd5q5).
|
||||
- If you are adding a non-official/research training example, **please don't forget** to add a sentence that you are maintaining this training example which includes your git handle as shown [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/intel_opts#diffusers-examples-with-intel-optimizations).
|
||||
|
||||
If you are contributing to the official training examples, please also make sure to add a test to [examples/test_examples.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/examples/test_examples.py). This is not necessary for non-official training examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Fixing a "Good second issue"
|
||||
### 8. Fixing a `Good second issue`
|
||||
|
||||
*Good second issues* are marked by the [Good second issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22) label. Good second issues are
|
||||
usually more complicated to solve than [Good first issues](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22good+first+issue%22).
|
||||
The issue description usually gives less guidance on how to fix the issue and requires
|
||||
a decent understanding of the library by the interested contributor.
|
||||
If you are interested in tackling a good second issue, feel free to open a PR to fix it and link the PR to the issue. If you see that a PR has already been opened for this issue but did not get merged, have a look to understand why it wasn't merged and try to open an improved PR.
|
||||
If you are interested in tackling a second good issue, feel free to open a PR to fix it and link the PR to the issue. If you see that a PR has already been opened for this issue but did not get merged, have a look to understand why it wasn't merged and try to open an improved PR.
|
||||
Good second issues are usually more difficult to get merged compared to good first issues, so don't hesitate to ask for help from the core maintainers. If your PR is almost finished the core maintainers can also jump into your PR and commit to it in order to get it merged.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Adding pipelines, models, schedulers
|
||||
@@ -297,7 +297,7 @@ if you don't know yet what specific component you would like to add:
|
||||
- [Model or pipeline](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+pipeline%2Fmodel%22)
|
||||
- [Scheduler](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22New+scheduler%22)
|
||||
|
||||
Before adding any of the three components, it is strongly recommended that you give the [Philosophy guide](philosophy) a read to better understand the design of any of the three components. Please be aware that
|
||||
Before adding any of the three components, it is strongly recommended that you give the [Philosophy guide](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues?q=is%3Aopen+is%3Aissue+label%3A%22Good+second+issue%22) a read to better understand the design of any of the three components. Please be aware that
|
||||
we cannot merge model, scheduler, or pipeline additions that strongly diverge from our design philosophy
|
||||
as it will lead to API inconsistencies. If you fundamentally disagree with a design choice, please
|
||||
open a [Feedback issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=) instead so that it can be discussed whether a certain design
|
||||
@@ -337,8 +337,8 @@ to be merged;
|
||||
9. Add high-coverage tests. No quality testing = no merge.
|
||||
- If you are adding new `@slow` tests, make sure they pass using
|
||||
`RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest tests/test_my_new_model.py`.
|
||||
CircleCI does not run the slow tests, but GitHub Actions does every night!
|
||||
10. All public methods must have informative docstrings that work nicely with markdown. See [`pipeline_latent_diffusion.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/latent_diffusion/pipeline_latent_diffusion.py) for an example.
|
||||
CircleCI does not run the slow tests, but GitHub actions does every night!
|
||||
10. All public methods must have informative docstrings that work nicely with markdown. See `[pipeline_latent_diffusion.py](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/latent_diffusion/pipeline_latent_diffusion.py)` for an example.
|
||||
11. Due to the rapidly growing repository, it is important to make sure that no files that would significantly weigh down the repository are added. This includes images, videos, and other non-text files. We prefer to leverage a hf.co hosted `dataset` like
|
||||
[`hf-internal-testing`](https://huggingface.co/hf-internal-testing) or [huggingface/documentation-images](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images) to place these files.
|
||||
If an external contribution, feel free to add the images to your PR and ask a Hugging Face member to migrate your images
|
||||
@@ -364,7 +364,7 @@ under your GitHub user account.
|
||||
2. Clone your fork to your local disk, and add the base repository as a remote:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git clone git@github.com:<your GitHub handle>/diffusers.git
|
||||
$ git clone git@github.com:<your Github handle>/diffusers.git
|
||||
$ cd diffusers
|
||||
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -395,14 +395,7 @@ passes. You should run the tests impacted by your changes like this:
|
||||
$ pytest tests/<TEST_TO_RUN>.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Before you run the tests, please make sure you install the dependencies required for testing. You can do so
|
||||
with this command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pip install -e ".[test]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also run the full test suite with the following command, but it takes
|
||||
You can also run the full suite with the following command, but it takes
|
||||
a beefy machine to produce a result in a decent amount of time now that
|
||||
Diffusers has grown a lot. Here is the command for it:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -430,7 +423,7 @@ make a commit with `git commit` to record your changes locally:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ git add modified_file.py
|
||||
$ git commit -m "A descriptive message about your changes."
|
||||
$ git commit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is a good idea to sync your copy of the code with the original
|
||||
@@ -450,7 +443,7 @@ Push the changes to your account using:
|
||||
webpage of your fork on GitHub. Click on 'Pull request' to send your changes
|
||||
to the project maintainers for review.
|
||||
|
||||
7. It's OK if maintainers ask you for changes. It happens to core contributors
|
||||
7. It's ok if maintainers ask you for changes. It happens to core contributors
|
||||
too! So everyone can see the changes in the Pull request, work in your local
|
||||
branch and push the changes to your fork. They will automatically appear in
|
||||
the pull request.
|
||||
@@ -493,7 +486,7 @@ To avoid pinging the upstream repository which adds reference notes to each upst
|
||||
when syncing the main branch of a forked repository, please, follow these steps:
|
||||
1. When possible, avoid syncing with the upstream using a branch and PR on the forked repository. Instead, merge directly into the forked main.
|
||||
2. If a PR is absolutely necessary, use the following steps after checking out your branch:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git checkout -b your-branch-for-syncing
|
||||
$ git pull --squash --no-commit upstream main
|
||||
$ git commit -m '<your message without GitHub references>'
|
||||
@@ -502,4 +495,4 @@ $ git push --set-upstream origin your-branch-for-syncing
|
||||
|
||||
### Style guide
|
||||
|
||||
For documentation strings, 🧨 Diffusers follows the [Google style](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html).
|
||||
For documentation strings, 🧨 Diffusers follows the [google style](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,20 +1,8 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 🧨 Diffusers’ Ethical Guidelines
|
||||
|
||||
## Preamble
|
||||
|
||||
[Diffusers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index) provides pre-trained diffusion models and serves as a modular toolbox for inference and training.
|
||||
[Diffusers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index) provides pre-trained diffusion models and serves as a modular toolbox for inference and training.
|
||||
|
||||
Given its real case applications in the world and potential negative impacts on society, we think it is important to provide the project with ethical guidelines to guide the development, users’ contributions, and usage of the Diffusers library.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -46,7 +34,7 @@ The following ethical guidelines apply generally, but we will primarily implemen
|
||||
|
||||
## Examples of implementations: Safety features and Mechanisms
|
||||
|
||||
The team works daily to make the technical and non-technical tools available to deal with the potential ethical and social risks associated with diffusion technology. Moreover, the community's input is invaluable in ensuring these features' implementation and raising awareness with us.
|
||||
The team works daily to make the technical and non-technical tools available to deal with the potential ethical and social risks associated with diffusion technology. Moreover, the community's input is invaluable in ensuring these features' implementation and raising awareness with us.
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Community tab**](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/repositories-pull-requests-discussions): it enables the community to discuss and better collaborate on a project.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -54,10 +42,10 @@ The team works daily to make the technical and non-technical tools available to
|
||||
|
||||
- **Encouraging safety in deployment**
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Safe Stable Diffusion**](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/stable_diffusion_safe): It mitigates the well-known issue that models, like Stable Diffusion, that are trained on unfiltered, web-crawled datasets tend to suffer from inappropriate degeneration. Related paper: [Safe Latent Diffusion: Mitigating Inappropriate Degeneration in Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105).
|
||||
- [**Safe Stable Diffusion**](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe): It mitigates the well-known issue that models, like Stable Diffusion, that are trained on unfiltered, web-crawled datasets tend to suffer from inappropriate degeneration. Related paper: [Safe Latent Diffusion: Mitigating Inappropriate Degeneration in Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105).
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Safety Checker**](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/pipelines/stable_diffusion/safety_checker.py): It checks and compares the class probability of a set of hard-coded harmful concepts in the embedding space against an image after it has been generated. The harmful concepts are intentionally hidden to prevent reverse engineering of the checker.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Staged released on the Hub**: in particularly sensitive situations, access to some repositories should be restricted. This staged release is an intermediary step that allows the repository’s authors to have more control over its use.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Licensing**: [OpenRAILs](https://huggingface.co/blog/open_rail), a new type of licensing, allow us to ensure free access while having a set of restrictions that ensure more responsible use.
|
||||
- **Licensing**: [OpenRAILs](https://huggingface.co/blog/open_rail), a new type of licensing, allow us to ensure free access while having a set of restrictions that ensure more responsible use.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,9 +12,9 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Evaluating Diffusion Models
|
||||
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/evaluation.ipynb">
|
||||
<img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/evaluation.ipynb">
|
||||
<img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Evaluation of generative models like [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/stable_diffusion) is subjective in nature. But as practitioners and researchers, we often have to make careful choices amongst many different possibilities. So, when working with different generative models (like GANs, Diffusion, etc.), how do we choose one over the other?
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ However, quantitative metrics don't necessarily correspond to image quality. So,
|
||||
of both qualitative and quantitative evaluations provides a stronger signal when choosing one model
|
||||
over the other.
|
||||
|
||||
In this document, we provide a non-exhaustive overview of qualitative and quantitative methods to evaluate Diffusion models. For quantitative methods, we specifically focus on how to implement them alongside `diffusers`.
|
||||
In this document, we provide a non-exhaustive overview of qualitative and quantitative methods to evaluate Diffusion models. For quantitative methods, we specifically focus on how to implement them alongside `diffusers`.
|
||||
|
||||
The methods shown in this document can also be used to evaluate different [noise schedulers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/schedulers/overview) keeping the underlying generation model fixed.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,15 +32,15 @@ The methods shown in this document can also be used to evaluate different [noise
|
||||
We cover Diffusion models with the following pipelines:
|
||||
|
||||
- Text-guided image generation (such as the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img)).
|
||||
- Text-guided image generation, additionally conditioned on an input image (such as the [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) and [`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/pix2pix)).
|
||||
- Text-guided image generation, additionally conditioned on an input image (such as the [`StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img), and [`StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix)).
|
||||
- Class-conditioned image generation models (such as the [`DiTPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/dit)).
|
||||
|
||||
## Qualitative Evaluation
|
||||
|
||||
Qualitative evaluation typically involves human assessment of generated images. Quality is measured across aspects such as compositionality, image-text alignment, and spatial relations. Common prompts provide a degree of uniformity for subjective metrics.
|
||||
DrawBench and PartiPrompts are prompt datasets used for qualitative benchmarking. DrawBench and PartiPrompts were introduced by [Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/) and [Parti](https://parti.research.google/) respectively.
|
||||
DrawBench and PartiPrompts are prompt datasets used for qualitative benchmarking. DrawBench and PartiPrompts were introduced by [Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/) and [Parti](https://parti.research.google/) respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
From the [official Parti website](https://parti.research.google/):
|
||||
From the [official Parti website](https://parti.research.google/):
|
||||
|
||||
> PartiPrompts (P2) is a rich set of over 1600 prompts in English that we release as part of this work. P2 can be used to measure model capabilities across various categories and challenge aspects.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -52,13 +52,13 @@ PartiPrompts has the following columns:
|
||||
- Category of the prompt (such as “Abstract”, “World Knowledge”, etc.)
|
||||
- Challenge reflecting the difficulty (such as “Basic”, “Complex”, “Writing & Symbols”, etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
These benchmarks allow for side-by-side human evaluation of different image generation models.
|
||||
These benchmarks allow for side-by-side human evaluation of different image generation models.
|
||||
|
||||
For this, the 🧨 Diffusers team has built **Open Parti Prompts**, which is a community-driven qualitative benchmark based on Parti Prompts to compare state-of-the-art open-source diffusion models:
|
||||
- [Open Parti Prompts Game](https://huggingface.co/spaces/OpenGenAI/open-parti-prompts): For 10 parti prompts, 4 generated images are shown and the user selects the image that suits the prompt best.
|
||||
- [Open Parti Prompts Leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/spaces/OpenGenAI/parti-prompts-leaderboard): The leaderboard comparing the currently best open-sourced diffusion models to each other.
|
||||
|
||||
To manually compare images, let’s see how we can use `diffusers` on a couple of PartiPrompts.
|
||||
To manually compare images, let’s see how we can use `diffusers` on a couple of PartiPrompts.
|
||||
|
||||
Below we show some prompts sampled across different challenges: Basic, Complex, Linguistic Structures, Imagination, and Writing & Symbols. Here we are using PartiPrompts as a [dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/nateraw/parti-prompts).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -87,21 +87,21 @@ import torch
|
||||
seed = 0
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(sample_prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator).images
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(sample_prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We can also set `num_images_per_prompt` accordingly to compare different images for the same prompt. Running the same pipeline but with a different checkpoint ([v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)), yields:
|
||||
We can also set `num_images_per_prompt` accordingly to compare different images for the same prompt. Running the same pipeline but with a different checkpoint ([v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)), yields:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once several images are generated from all the prompts using multiple models (under evaluation), these results are presented to human evaluators for scoring. For
|
||||
more details on the DrawBench and PartiPrompts benchmarks, refer to their respective papers.
|
||||
more details on the DrawBench and PartiPrompts benchmarks, refer to their respective papers.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
It is useful to look at some inference samples while a model is training to measure the
|
||||
It is useful to look at some inference samples while a model is training to measure the
|
||||
training progress. In our [training scripts](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/), we support this utility with additional support for
|
||||
logging to TensorBoard and Weights & Biases.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -141,7 +141,7 @@ prompts = [
|
||||
"A small cabin on top of a snowy mountain in the style of Disney, artstation",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, output_type="np").images
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
|
||||
print(images.shape)
|
||||
# (6, 512, 512, 3)
|
||||
@@ -155,11 +155,13 @@ from functools import partial
|
||||
|
||||
clip_score_fn = partial(clip_score, model_name_or_path="openai/clip-vit-base-patch16")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def calculate_clip_score(images, prompts):
|
||||
images_int = (images * 255).astype("uint8")
|
||||
clip_score = clip_score_fn(torch.from_numpy(images_int).permute(0, 3, 1, 2), prompts).detach()
|
||||
return round(float(clip_score), 4)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sd_clip_score = calculate_clip_score(images, prompts)
|
||||
print(f"CLIP score: {sd_clip_score}")
|
||||
# CLIP score: 35.7038
|
||||
@@ -174,16 +176,16 @@ fixed seed with the [v1-4 Stable Diffusion checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/Co
|
||||
seed = 0
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="np").images
|
||||
images = sd_pipeline(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we load the [v1-5 checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) to generate images:
|
||||
Then we load the [v1-5 checkpoint](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) to generate images:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model_ckpt_1_5 = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
sd_pipeline_1_5 = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(model_ckpt_1_5, torch_dtype=weight_dtype).to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
images_1_5 = sd_pipeline_1_5(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="np").images
|
||||
images_1_5 = sd_pipeline_1_5(prompts, num_images_per_prompt=1, generator=generator, output_type="numpy").images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And finally, we compare their CLIP scores:
|
||||
@@ -205,7 +207,7 @@ It seems like the [v1-5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5)
|
||||
By construction, there are some limitations in this score. The captions in the training dataset
|
||||
were crawled from the web and extracted from `alt` and similar tags associated an image on the internet.
|
||||
They are not necessarily representative of what a human being would use to describe an image. Hence we
|
||||
had to "engineer" some prompts here.
|
||||
had to "engineer" some prompts here.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -293,11 +295,12 @@ def edit_image(input_image, instruction):
|
||||
image = instruct_pix2pix_pipeline(
|
||||
instruction,
|
||||
image=input_image,
|
||||
output_type="np",
|
||||
output_type="numpy",
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
return image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
input_images = []
|
||||
original_captions = []
|
||||
modified_captions = []
|
||||
@@ -414,7 +417,7 @@ It should be noted that the `StableDiffusionInstructPix2PixPipeline` exposes t
|
||||
|
||||
We can extend the idea of this metric to measure how similar the original image and edited version are. To do that, we can just do `F.cosine_similarity(img_feat_two, img_feat_one)`. For these kinds of edits, we would still want the primary semantics of the images to be preserved as much as possible, i.e., a high similarity score.
|
||||
|
||||
We can use these metrics for similar pipelines such as the [`StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/pix2pix_zero#diffusers.StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline).
|
||||
We can use these metrics for similar pipelines such as the [`StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero#diffusers.StableDiffusionPix2PixZeroPipeline).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -424,7 +427,7 @@ Both CLIP score and CLIP direction similarity rely on the CLIP model, which can
|
||||
|
||||
***Extending metrics like IS, FID (discussed later), or KID can be difficult*** when the model under evaluation was pre-trained on a large image-captioning dataset (such as the [LAION-5B dataset](https://laion.ai/blog/laion-5b/)). This is because underlying these metrics is an InceptionNet (pre-trained on the ImageNet-1k dataset) used for extracting intermediate image features. The pre-training dataset of Stable Diffusion may have limited overlap with the pre-training dataset of InceptionNet, so it is not a good candidate here for feature extraction.
|
||||
|
||||
***Using the above metrics helps evaluate models that are class-conditioned. For example, [DiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/dit). It was pre-trained being conditioned on the ImageNet-1k classes.***
|
||||
***Using the above metrics helps evaluate models that are class-conditioned. For example, [DiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview). It was pre-trained being conditioned on the ImageNet-1k classes.***
|
||||
|
||||
### Class-conditioned image generation
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -449,6 +452,7 @@ def download(url, local_filepath):
|
||||
f.write(r.content)
|
||||
return local_filepath
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dummy_dataset_url = "https://hf.co/datasets/sayakpaul/sample-datasets/resolve/main/sample-imagenet-images.zip"
|
||||
local_filepath = download(dummy_dataset_url, dummy_dataset_url.split("/")[-1])
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -466,7 +470,7 @@ image_paths = sorted([os.path.join(dataset_path, x) for x in os.listdir(dataset_
|
||||
real_images = [np.array(Image.open(path).convert("RGB")) for path in image_paths]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These are 10 images from the following ImageNet-1k classes: "cassette_player", "chain_saw" (x2), "church", "gas_pump" (x3), "parachute" (x2), and "tench".
|
||||
These are 10 images from the following Imagenet-1k classes: "cassette_player", "chain_saw" (x2), "church", "gas_pump" (x3), "parachute" (x2), and "tench".
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/evaluation_diffusion_models/real-images.png" alt="real-images"><br>
|
||||
@@ -484,6 +488,7 @@ def preprocess_image(image):
|
||||
image = image.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) / 255.0
|
||||
return F.center_crop(image, (256, 256))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
real_images = torch.cat([preprocess_image(image) for image in real_images])
|
||||
print(real_images.shape)
|
||||
# torch.Size([10, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
@@ -512,7 +517,7 @@ words = [
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
class_ids = dit_pipeline.get_label_ids(words)
|
||||
output = dit_pipeline(class_labels=class_ids, generator=generator, output_type="np")
|
||||
output = dit_pipeline(class_labels=class_ids, generator=generator, output_type="numpy")
|
||||
|
||||
fake_images = output.images
|
||||
fake_images = torch.tensor(fake_images)
|
||||
@@ -551,15 +556,15 @@ FID results tend to be fragile as they depend on a lot of factors:
|
||||
* The implementation accuracy of the computation.
|
||||
* The image format (not the same if we start from PNGs vs JPGs).
|
||||
|
||||
Keeping that in mind, FID is often most useful when comparing similar runs, but it is
|
||||
hard to reproduce paper results unless the authors carefully disclose the FID
|
||||
Keeping that in mind, FID is often most useful when comparing similar runs, but it is
|
||||
hard to reproduce paper results unless the authors carefully disclose the FID
|
||||
measurement code.
|
||||
|
||||
These points apply to other related metrics too, such as KID and IS.
|
||||
These points apply to other related metrics too, such as KID and IS.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
As a final step, let's visually inspect the `fake_images`.
|
||||
As a final step, let's visually inspect the `fake_images`.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/evaluation_diffusion_models/fake-images.png" alt="fake-images"><br>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,23 +22,23 @@ In a nutshell, Diffusers is built to be a natural extension of PyTorch. Therefor
|
||||
## Usability over Performance
|
||||
|
||||
- While Diffusers has many built-in performance-enhancing features (see [Memory and Speed](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/optimization/fp16)), models are always loaded with the highest precision and lowest optimization. Therefore, by default diffusion pipelines are always instantiated on CPU with float32 precision if not otherwise defined by the user. This ensures usability across different platforms and accelerators and means that no complex installations are required to run the library.
|
||||
- Diffusers aims to be a **light-weight** package and therefore has very few required dependencies, but many soft dependencies that can improve performance (such as `accelerate`, `safetensors`, `onnx`, etc...). We strive to keep the library as lightweight as possible so that it can be added without much concern as a dependency on other packages.
|
||||
- Diffusers aim at being a **light-weight** package and therefore has very few required dependencies, but many soft dependencies that can improve performance (such as `accelerate`, `safetensors`, `onnx`, etc...). We strive to keep the library as lightweight as possible so that it can be added without much concern as a dependency on other packages.
|
||||
- Diffusers prefers simple, self-explainable code over condensed, magic code. This means that short-hand code syntaxes such as lambda functions, and advanced PyTorch operators are often not desired.
|
||||
|
||||
## Simple over easy
|
||||
|
||||
As PyTorch states, **explicit is better than implicit** and **simple is better than complex**. This design philosophy is reflected in multiple parts of the library:
|
||||
As PyTorch states, **explicit is better than implicit** and **simple is better than complex**. This design philosophy is reflected in multiple parts of the library:
|
||||
- We follow PyTorch's API with methods like [`DiffusionPipeline.to`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/diffusion_pipeline#diffusers.DiffusionPipeline.to) to let the user handle device management.
|
||||
- Raising concise error messages is preferred to silently correct erroneous input. Diffusers aims at teaching the user, rather than making the library as easy to use as possible.
|
||||
- Complex model vs. scheduler logic is exposed instead of magically handled inside. Schedulers/Samplers are separated from diffusion models with minimal dependencies on each other. This forces the user to write the unrolled denoising loop. However, the separation allows for easier debugging and gives the user more control over adapting the denoising process or switching out diffusion models or schedulers.
|
||||
- Separately trained components of the diffusion pipeline, *e.g.* the text encoder, the unet, and the variational autoencoder, each have their own model class. This forces the user to handle the interaction between the different model components, and the serialization format separates the model components into different files. However, this allows for easier debugging and customization. DreamBooth or Textual Inversion training
|
||||
is very simple thanks to Diffusers' ability to separate single components of the diffusion pipeline.
|
||||
- Separately trained components of the diffusion pipeline, *e.g.* the text encoder, the unet, and the variational autoencoder, each have their own model class. This forces the user to handle the interaction between the different model components, and the serialization format separates the model components into different files. However, this allows for easier debugging and customization. Dreambooth or textual inversion training
|
||||
is very simple thanks to diffusers' ability to separate single components of the diffusion pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tweakable, contributor-friendly over abstraction
|
||||
|
||||
For large parts of the library, Diffusers adopts an important design principle of the [Transformers library](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers), which is to prefer copy-pasted code over hasty abstractions. This design principle is very opinionated and stands in stark contrast to popular design principles such as [Don't repeat yourself (DRY)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Don%27t_repeat_yourself).
|
||||
In short, just like Transformers does for modeling files, Diffusers prefers to keep an extremely low level of abstraction and very self-contained code for pipelines and schedulers.
|
||||
Functions, long code blocks, and even classes can be copied across multiple files which at first can look like a bad, sloppy design choice that makes the library unmaintainable.
|
||||
For large parts of the library, Diffusers adopts an important design principle of the [Transformers library](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers), which is to prefer copy-pasted code over hasty abstractions. This design principle is very opinionated and stands in stark contrast to popular design principles such as [Don't repeat yourself (DRY)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Don%27t_repeat_yourself).
|
||||
In short, just like Transformers does for modeling files, diffusers prefers to keep an extremely low level of abstraction and very self-contained code for pipelines and schedulers.
|
||||
Functions, long code blocks, and even classes can be copied across multiple files which at first can look like a bad, sloppy design choice that makes the library unmaintainable.
|
||||
**However**, this design has proven to be extremely successful for Transformers and makes a lot of sense for community-driven, open-source machine learning libraries because:
|
||||
- Machine Learning is an extremely fast-moving field in which paradigms, model architectures, and algorithms are changing rapidly, which therefore makes it very difficult to define long-lasting code abstractions.
|
||||
- Machine Learning practitioners like to be able to quickly tweak existing code for ideation and research and therefore prefer self-contained code over one that contains many abstractions.
|
||||
@@ -47,15 +47,15 @@ Functions, long code blocks, and even classes can be copied across multiple file
|
||||
At Hugging Face, we call this design the **single-file policy** which means that almost all of the code of a certain class should be written in a single, self-contained file. To read more about the philosophy, you can have a look
|
||||
at [this blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/transformers-design-philosophy).
|
||||
|
||||
In Diffusers, we follow this philosophy for both pipelines and schedulers, but only partly for diffusion models. The reason we don't follow this design fully for diffusion models is because almost all diffusion pipelines, such
|
||||
as [DDPM](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/ddpm), [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview#stable-diffusion-pipelines), [unCLIP (DALL·E 2)](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/pipelines/unclip) and [Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/) all rely on the same diffusion model, the [UNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models/unet2d-cond).
|
||||
In diffusers, we follow this philosophy for both pipelines and schedulers, but only partly for diffusion models. The reason we don't follow this design fully for diffusion models is because almost all diffusion pipelines, such
|
||||
as [DDPM](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.12.0/en/api/pipelines/ddpm), [Stable Diffusion](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.12.0/en/api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/overview#stable-diffusion-pipelines), [UnCLIP (Dalle-2)](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.12.0/en/api/pipelines/unclip#overview) and [Imagen](https://imagen.research.google/) all rely on the same diffusion model, the [UNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/models#diffusers.UNet2DConditionModel).
|
||||
|
||||
Great, now you should have generally understood why 🧨 Diffusers is designed the way it is 🤗.
|
||||
Great, now you should have generally understood why 🧨 Diffusers is designed the way it is 🤗.
|
||||
We try to apply these design principles consistently across the library. Nevertheless, there are some minor exceptions to the philosophy or some unlucky design choices. If you have feedback regarding the design, we would ❤️ to hear it [directly on GitHub](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=&template=feedback.md&title=).
|
||||
|
||||
## Design Philosophy in Details
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's look a bit into the nitty-gritty details of the design philosophy. Diffusers essentially consists of three major classes: [pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines), [models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models), and [schedulers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers).
|
||||
Now, let's look a bit into the nitty-gritty details of the design philosophy. Diffusers essentially consist of three major classes, [pipelines](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/pipelines), [models](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models), and [schedulers](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers).
|
||||
Let's walk through more in-detail design decisions for each class.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pipelines
|
||||
@@ -83,26 +83,26 @@ The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- Models correspond to **a type of model architecture**. *E.g.* the [`UNet2DConditionModel`] class is used for all UNet variations that expect 2D image inputs and are conditioned on some context.
|
||||
- All models can be found in [`src/diffusers/models`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/models) and every model architecture shall be defined in its file, e.g. [`unet_2d_condition.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unet_2d_condition.py), [`transformer_2d.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/transformer_2d.py), etc...
|
||||
- Models **do not** follow the single-file policy and should make use of smaller model building blocks, such as [`attention.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/attention.py), [`resnet.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/resnet.py), [`embeddings.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/embeddings.py), etc... **Note**: This is in stark contrast to Transformers' modeling files and shows that models do not really follow the single-file policy.
|
||||
- Models intend to expose complexity, just like PyTorch's `Module` class, and give clear error messages.
|
||||
- Models intend to expose complexity, just like PyTorch's module does, and give clear error messages.
|
||||
- Models all inherit from `ModelMixin` and `ConfigMixin`.
|
||||
- Models can be optimized for performance when it doesn’t demand major code changes, keeps backward compatibility, and gives significant memory or compute gain.
|
||||
- Models should by default have the highest precision and lowest performance setting.
|
||||
- To integrate new model checkpoints whose general architecture can be classified as an architecture that already exists in Diffusers, the existing model architecture shall be adapted to make it work with the new checkpoint. One should only create a new file if the model architecture is fundamentally different.
|
||||
- Models should be designed to be easily extendable to future changes. This can be achieved by limiting public function arguments, configuration arguments, and "foreseeing" future changes, *e.g.* it is usually better to add `string` "...type" arguments that can easily be extended to new future types instead of boolean `is_..._type` arguments. Only the minimum amount of changes shall be made to existing architectures to make a new model checkpoint work.
|
||||
- The model design is a difficult trade-off between keeping code readable and concise and supporting many model checkpoints. For most parts of the modeling code, classes shall be adapted for new model checkpoints, while there are some exceptions where it is preferred to add new classes to make sure the code is kept concise and
|
||||
readable long-term, such as [UNet blocks](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unet_2d_blocks.py) and [Attention processors](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/attention_processor.py).
|
||||
- The model design is a difficult trade-off between keeping code readable and concise and supporting many model checkpoints. For most parts of the modeling code, classes shall be adapted for new model checkpoints, while there are some exceptions where it is preferred to add new classes to make sure the code is kept concise and
|
||||
readable longterm, such as [UNet blocks](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unet_2d_blocks.py) and [Attention processors](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/attention_processor.py).
|
||||
|
||||
### Schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
Schedulers are responsible to guide the denoising process for inference as well as to define a noise schedule for training. They are designed as individual classes with loadable configuration files and strongly follow the **single-file policy**.
|
||||
|
||||
The following design principles are followed:
|
||||
- All schedulers are found in [`src/diffusers/schedulers`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers).
|
||||
- Schedulers are **not** allowed to import from large utils files and shall be kept very self-contained.
|
||||
- One scheduler Python file corresponds to one scheduler algorithm (as might be defined in a paper).
|
||||
- All schedulers are found in [`src/diffusers/schedulers`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/src/diffusers/schedulers).
|
||||
- Schedulers are **not** allowed to import from large utils files and shall be kept very self-contained.
|
||||
- One scheduler python file corresponds to one scheduler algorithm (as might be defined in a paper).
|
||||
- If schedulers share similar functionalities, we can make use of the `#Copied from` mechanism.
|
||||
- Schedulers all inherit from `SchedulerMixin` and `ConfigMixin`.
|
||||
- Schedulers can be easily swapped out with the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/configuration#diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config) method as explained in detail [here](../using-diffusers/schedulers.md).
|
||||
- Schedulers can be easily swapped out with the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/main/en/api/configuration#diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config) method as explained in detail [here](./using-diffusers/schedulers.md).
|
||||
- Every scheduler has to have a `set_num_inference_steps`, and a `step` function. `set_num_inference_steps(...)` has to be called before every denoising process, *i.e.* before `step(...)` is called.
|
||||
- Every scheduler exposes the timesteps to be "looped over" via a `timesteps` attribute, which is an array of timesteps the model will be called upon.
|
||||
- The `step(...)` function takes a predicted model output and the "current" sample (x_t) and returns the "previous", slightly more denoised sample (x_t-1).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
The library has three main components:
|
||||
|
||||
- State-of-the-art diffusion pipelines for inference with just a few lines of code. There are many pipelines in 🤗 Diffusers, check out the table in the pipeline [overview](api/pipelines/overview) for a complete list of available pipelines and the task they solve.
|
||||
- State-of-the-art [diffusion pipelines](api/pipelines/overview) for inference with just a few lines of code.
|
||||
- Interchangeable [noise schedulers](api/schedulers/overview) for balancing trade-offs between generation speed and quality.
|
||||
- Pretrained [models](api/models) that can be used as building blocks, and combined with schedulers, for creating your own end-to-end diffusion systems.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -46,3 +46,53 @@ The library has three main components:
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
| Pipeline | Paper/Repository | Tasks |
|
||||
|---|---|:---:|
|
||||
| [alt_diffusion](./api/pipelines/alt_diffusion) | [AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [audio_diffusion](./api/pipelines/audio_diffusion) | [Audio Diffusion](https://github.com/teticio/audio-diffusion.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [controlnet](./api/pipelines/controlnet) | [Adding Conditional Control to Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.05543) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [cycle_diffusion](./api/pipelines/cycle_diffusion) | [Unifying Diffusion Models' Latent Space, with Applications to CycleDiffusion and Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.05559) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [dance_diffusion](./api/pipelines/dance_diffusion) | [Dance Diffusion](https://github.com/williamberman/diffusers.git) | Unconditional Audio Generation |
|
||||
| [ddpm](./api/pipelines/ddpm) | [Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [ddim](./api/pipelines/ddim) | [Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [if](./if) | [**IF**](./api/pipelines/if) | Image Generation |
|
||||
| [if_img2img](./if) | [**IF**](./api/pipelines/if) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [if_inpainting](./if) | [**IF**](./api/pipelines/if) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752)| Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [latent_diffusion_uncond](./api/pipelines/latent_diffusion_uncond) | [High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10752) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [paint_by_example](./api/pipelines/paint_by_example) | [Paint by Example: Exemplar-based Image Editing with Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13227) | Image-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [pndm](./api/pipelines/pndm) | [Pseudo Numerical Methods for Diffusion Models on Manifolds](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09778) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_ve](./api/pipelines/score_sde_ve) | [Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [score_sde_vp](./api/pipelines/score_sde_vp) | [Score-Based Generative Modeling through Stochastic Differential Equations](https://openreview.net/forum?id=PxTIG12RRHS) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [semantic_stable_diffusion](./api/pipelines/semantic_stable_diffusion) | [Semantic Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12247) | Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_adapter](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/adapter) | [**T2I-Adapter**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.08453) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation | -
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_text2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/text2img) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_img2img](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/img2img) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_inpaint](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/inpaint) | [Stable Diffusion](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-public-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_panorama](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/panorama) | [MultiDiffusion](https://multidiffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Panorama Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix) | [InstructPix2Pix: Learning to Follow Image Editing Instructions](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09800) | Text-Guided Image Editing|
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_pix2pix_zero](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/pix2pix_zero) | [Zero-shot Image-to-Image Translation](https://pix2pixzero.github.io/) | Text-Guided Image Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_attend_and_excite](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/attend_and_excite) | [Attend-and-Excite: Attention-Based Semantic Guidance for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13826) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_self_attention_guidance](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/self_attention_guidance) | [Improving Sample Quality of Diffusion Models Using Self-Attention Guidance](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.00939) | Text-to-Image Generation Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_image_variation](./stable_diffusion/image_variation) | [Stable Diffusion Image Variations](https://github.com/LambdaLabsML/lambda-diffusers#stable-diffusion-image-variations) | Image-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_latent_upscale](./stable_diffusion/latent_upscale) | [Stable Diffusion Latent Upscaler](https://twitter.com/StabilityAI/status/1590531958815064065) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_model_editing](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/model_editing) | [Editing Implicit Assumptions in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models](https://time-diffusion.github.io/) | Text-to-Image Model Editing |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Image Inpainting |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Depth-Conditional Stable Diffusion](https://github.com/Stability-AI/stablediffusion#depth-conditional-stable-diffusion) | Depth-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_2](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_2) | [Stable Diffusion 2](https://stability.ai/blog/stable-diffusion-v2-release) | Text-Guided Super Resolution Image-to-Image |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_safe](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion_safe) | [Safe Stable Diffusion](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05105) | Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | Stable unCLIP | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_unclip](./stable_unclip) | Stable unCLIP | Image-to-Image Text-Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [stochastic_karras_ve](./api/pipelines/stochastic_karras_ve) | [Elucidating the Design Space of Diffusion-Based Generative Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00364) | Unconditional Image Generation |
|
||||
| [text_to_video_sd](./api/pipelines/text_to_video) | [Modelscope's Text-to-video-synthesis Model in Open Domain](https://modelscope.cn/models/damo/text-to-video-synthesis/summary) | Text-to-Video Generation |
|
||||
| [unclip](./api/pipelines/unclip) | [Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06125)(implementation by [kakaobrain](https://github.com/kakaobrain/karlo)) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Image Variations Generation |
|
||||
| [versatile_diffusion](./api/pipelines/versatile_diffusion) | [Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08332) | Dual Image and Text Guided Generation |
|
||||
| [vq_diffusion](./api/pipelines/vq_diffusion) | [Vector Quantized Diffusion Model for Text-to-Image Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.14822) | Text-to-Image Generation |
|
||||
| [stable_diffusion_ldm3d](./api/pipelines/stable_diffusion/ldm3d_diffusion) | [LDM3D: Latent Diffusion Model for 3D](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.10853) | Text to Image and Depth Generation |
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,10 +12,12 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is tested on Python 3.8+, PyTorch 1.7.0+, and Flax. Follow the installation instructions below for the deep learning library you are using:
|
||||
Install 🤗 Diffusers for whichever deep learning library you're working with.
|
||||
|
||||
- [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) installation instructions
|
||||
- [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) installation instructions
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is tested on Python 3.7+, PyTorch 1.7.0+ and Flax. Follow the installation instructions below for the deep learning library you are using:
|
||||
|
||||
- [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) installation instructions.
|
||||
- [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) installation instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install with pip
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +37,7 @@ Activate the virtual environment:
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You should also install 🤗 Transformers because 🤗 Diffusers relies on its models:
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers also relies on the 🤗 Transformers library, and you can install both with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
@@ -50,17 +52,11 @@ pip install diffusers["flax"] transformers
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Install with conda
|
||||
|
||||
After activating your virtual environment, with `conda` (maintained by the community):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
conda install -c conda-forge diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Install from source
|
||||
|
||||
Before installing 🤗 Diffusers from source, make sure you have PyTorch and 🤗 Accelerate installed.
|
||||
Before installing 🤗 Diffusers from source, make sure you have `torch` and 🤗 Accelerate installed.
|
||||
|
||||
For `torch` installation, refer to the `torch` [installation](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
To install 🤗 Accelerate:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -68,7 +64,7 @@ To install 🤗 Accelerate:
|
||||
pip install accelerate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then install 🤗 Diffusers from source:
|
||||
Install 🤗 Diffusers from source with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
|
||||
@@ -79,7 +75,7 @@ The `main` version is useful for staying up-to-date with the latest developments
|
||||
For instance, if a bug has been fixed since the last official release but a new release hasn't been rolled out yet.
|
||||
However, this means the `main` version may not always be stable.
|
||||
We strive to keep the `main` version operational, and most issues are usually resolved within a few hours or a day.
|
||||
If you run into a problem, please open an [Issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose) so we can fix it even sooner!
|
||||
If you run into a problem, please open an [Issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/new/choose), so we can fix it even sooner!
|
||||
|
||||
## Editable install
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -110,7 +106,7 @@ pip install -e ".[flax]"
|
||||
|
||||
These commands will link the folder you cloned the repository to and your Python library paths.
|
||||
Python will now look inside the folder you cloned to in addition to the normal library paths.
|
||||
For example, if your Python packages are typically installed in `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.8/site-packages/`, Python will also search the `~/diffusers/` folder you cloned to.
|
||||
For example, if your Python packages are typically installed in `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.7/site-packages/`, Python will also search the `~/diffusers/` folder you cloned to.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -127,29 +123,17 @@ git pull
|
||||
|
||||
Your Python environment will find the `main` version of 🤗 Diffusers on the next run.
|
||||
|
||||
## Cache
|
||||
## Notice on telemetry logging
|
||||
|
||||
Model weights and files are downloaded from the Hub to a cache which is usually your home directory. You can change the cache location by specifying the `HF_HOME` or `HUGGINFACE_HUB_CACHE` environment variables or configuring the `cache_dir` parameter in methods like [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`].
|
||||
|
||||
Cached files allow you to run 🤗 Diffusers offline. To prevent 🤗 Diffusers from connecting to the internet, set the `HF_HUB_OFFLINE` environment variable to `True` and 🤗 Diffusers will only load previously downloaded files in the cache.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
export HF_HUB_OFFLINE=True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about managing and cleaning the cache, take a look at the [caching](https://huggingface.co/docs/huggingface_hub/guides/manage-cache) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
## Telemetry logging
|
||||
|
||||
Our library gathers telemetry information during [`~DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained`] requests.
|
||||
The data gathered includes the version of 🤗 Diffusers and PyTorch/Flax, the requested model or pipeline class,
|
||||
and the path to a pretrained checkpoint if it is hosted on the Hugging Face Hub.
|
||||
Our library gathers telemetry information during `from_pretrained()` requests.
|
||||
This data includes the version of Diffusers and PyTorch/Flax, the requested model or pipeline class,
|
||||
and the path to a pre-trained checkpoint if it is hosted on the Hub.
|
||||
This usage data helps us debug issues and prioritize new features.
|
||||
Telemetry is only sent when loading models and pipelines from the Hub,
|
||||
and it is not collected if you're loading local files.
|
||||
Telemetry is only sent when loading models and pipelines from the HuggingFace Hub,
|
||||
and is not collected during local usage.
|
||||
|
||||
We understand that not everyone wants to share additional information,and we respect your privacy.
|
||||
You can disable telemetry collection by setting the `DISABLE_TELEMETRY` environment variable from your terminal:
|
||||
We understand that not everyone wants to share additional information, and we respect your privacy,
|
||||
so you can disable telemetry collection by setting the `DISABLE_TELEMETRY` environment variable from your terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
On Linux/MacOS:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ Thankfully, Apple engineers developed [a conversion tool](https://github.com/app
|
||||
Before you convert a model, though, take a moment to explore the Hugging Face Hub – chances are the model you're interested in is already available in Core ML format:
|
||||
|
||||
- the [Apple](https://huggingface.co/apple) organization includes Stable Diffusion versions 1.4, 1.5, 2.0 base, and 2.1 base
|
||||
- [coreml community](https://huggingface.co/coreml-community) includes custom finetuned models
|
||||
- [coreml](https://huggingface.co/coreml) organization includes custom DreamBoothed and finetuned models
|
||||
- use this [filter](https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=text-to-image&library=coreml&p=2&sort=likes) to return all available Core ML checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
If you can't find the model you're interested in, we recommend you follow the instructions for [Converting Models to Core ML](https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion#-converting-models-to-core-ml) by Apple.
|
||||
@@ -90,6 +90,7 @@ snapshot_download(repo_id, allow_patterns=f"{variant}/*", local_dir=model_path,
|
||||
print(f"Model downloaded at {model_path}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference[[python-inference]]
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have downloaded a snapshot of the model, you can test it using Apple's Python script.
|
||||
@@ -98,7 +99,7 @@ Once you have downloaded a snapshot of the model, you can test it using Apple's
|
||||
python -m python_coreml_stable_diffusion.pipeline --prompt "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars" -i models/coreml-stable-diffusion-v1-4_original_packages -o </path/to/output/image> --compute-unit CPU_AND_GPU --seed 93
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pass the path of the downloaded checkpoint with `-i` flag to the script. `--compute-unit` indicates the hardware you want to allow for inference. It must be one of the following options: `ALL`, `CPU_AND_GPU`, `CPU_ONLY`, `CPU_AND_NE`. You may also provide an optional output path, and a seed for reproducibility.
|
||||
`<output-mlpackages-directory>` should point to the checkpoint you downloaded in the step above, and `--compute-unit` indicates the hardware you want to allow for inference. It must be one of the following options: `ALL`, `CPU_AND_GPU`, `CPU_ONLY`, `CPU_AND_NE`. You may also provide an optional output path, and a seed for reproducibility.
|
||||
|
||||
The inference script assumes you're using the original version of the Stable Diffusion model, `CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4`. If you use another model, you *have* to specify its Hub id in the inference command line, using the `--model-version` option. This works for models already supported and custom models you trained or fine-tuned yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -108,6 +109,7 @@ For example, if you want to use [`runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5`](https://huggi
|
||||
python -m python_coreml_stable_diffusion.pipeline --prompt "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars" --compute-unit ALL -o output --seed 93 -i models/coreml-stable-diffusion-v1-5_original_packages --model-version runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Core ML inference in Swift
|
||||
|
||||
Running inference in Swift is slightly faster than in Python because the models are already compiled in the `mlmodelc` format. This is noticeable on app startup when the model is loaded but shouldn’t be noticeable if you run several generations afterward.
|
||||
@@ -147,6 +149,7 @@ You have to specify in `--resource-path` one of the checkpoints downloaded in th
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, please refer to the [instructions in Apple's repo](https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Diffusers Features
|
||||
|
||||
The Core ML models and inference code don't support many of the features, options, and flexibility of 🧨 Diffusers. These are some of the limitations to keep in mind:
|
||||
@@ -155,10 +158,10 @@ The Core ML models and inference code don't support many of the features, option
|
||||
- Only two schedulers have been ported to Swift, the default one used by Stable Diffusion and `DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`, which we ported to Swift from our `diffusers` implementation. We recommend you use `DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`, since it produces the same quality in about half the steps.
|
||||
- Negative prompts, classifier-free guidance scale, and image-to-image tasks are available in the inference code. Advanced features such as depth guidance, ControlNet, and latent upscalers are not available yet.
|
||||
|
||||
Apple's [conversion and inference repo](https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion) and our own [swift-coreml-diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/swift-coreml-diffusers) repos are intended as technology demonstrators to enable other developers to build upon.
|
||||
Apple's [conversion and inference repo](https://github.com/apple/ml-stable-diffusion) and our own [swift-coreml-diffusers](https://github.com/huggingface/swift-coreml-diffusers) repos are intended as technology demonstrators to enable other developers to build upon.
|
||||
|
||||
If you feel strongly about any missing features, please feel free to open a feature request or, better yet, a contribution PR 🙂.
|
||||
If you feel strongly about any missing features, please feel free to open a feature request or, better yet, a contribution PR :)
|
||||
|
||||
## Native Diffusers Swift app
|
||||
|
||||
One easy way to run Stable Diffusion on your own Apple hardware is to use [our open-source Swift repo](https://github.com/huggingface/swift-coreml-diffusers), based on `diffusers` and Apple's conversion and inference repo. You can study the code, compile it with [Xcode](https://developer.apple.com/xcode/) and adapt it for your own needs. For your convenience, there's also a [standalone Mac app in the App Store](https://apps.apple.com/app/diffusers/id1666309574), so you can play with it without having to deal with the code or IDE. If you are a developer and have determined that Core ML is the best solution to build your Stable Diffusion app, then you can use the rest of this guide to get started with your project. We can't wait to see what you'll build 🙂.
|
||||
One easy way to run Stable Diffusion on your own Apple hardware is to use [our open-source Swift repo](https://github.com/huggingface/swift-coreml-diffusers), based on `diffusers` and Apple's conversion and inference repo. You can study the code, compile it with [Xcode](https://developer.apple.com/xcode/) and adapt it for your own needs. For your convenience, there's also a [standalone Mac app in the App Store](https://apps.apple.com/app/diffusers/id1666309574), so you can play with it without having to deal with the code or IDE. If you are a developer and have determined that Core ML is the best solution to build your Stable Diffusion app, then you can use the rest of this guide to get started with your project. We can't wait to see what you'll build :)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,19 +10,13 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Speed up inference
|
||||
# Memory and speed
|
||||
|
||||
There are several ways to optimize 🤗 Diffusers for inference speed. As a general rule of thumb, we recommend using either [xFormers](xformers) or `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention` in PyTorch 2.0 for their memory-efficient attention.
|
||||
We present some techniques and ideas to optimize 🤗 Diffusers _inference_ for memory or speed. As a general rule, we recommend the use of [xFormers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers) for memory efficient attention, please see the recommended [installation instructions](xformers).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
We'll discuss how the following settings impact performance and memory.
|
||||
|
||||
In many cases, optimizing for speed or memory leads to improved performance in the other, so you should try to optimize for both whenever you can. This guide focuses on inference speed, but you can learn more about preserving memory in the [Reduce memory usage](memory) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The results below are obtained from generating a single 512x512 image from the prompt `a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars` with 50 DDIM steps on a Nvidia Titan RTX, demonstrating the speed-up you can expect.
|
||||
|
||||
| | latency | speed-up |
|
||||
| | Latency | Speedup |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------- |
|
||||
| original | 9.50s | x1 |
|
||||
| fp16 | 3.61s | x2.63 |
|
||||
@@ -30,9 +24,15 @@ The results below are obtained from generating a single 512x512 image from the p
|
||||
| traced UNet | 3.21s | x2.96 |
|
||||
| memory efficient attention | 2.63s | x3.61 |
|
||||
|
||||
## Use TensorFloat-32
|
||||
<em>
|
||||
obtained on NVIDIA TITAN RTX by generating a single image of size 512x512 from
|
||||
the prompt "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars" with 50 DDIM
|
||||
steps.
|
||||
</em>
|
||||
|
||||
On Ampere and later CUDA devices, matrix multiplications and convolutions can use the [TensorFloat-32 (TF32)](https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2020/05/14/tensorfloat-32-precision-format/) mode for faster, but slightly less accurate computations. By default, PyTorch enables TF32 mode for convolutions but not matrix multiplications. Unless your network requires full float32 precision, we recommend enabling TF32 for matrix multiplications. It can significantly speeds up computations with typically negligible loss in numerical accuracy.
|
||||
### Use tf32 instead of fp32 (on Ampere and later CUDA devices)
|
||||
|
||||
On Ampere and later CUDA devices matrix multiplications and convolutions can use the TensorFloat32 (TF32) mode for faster but slightly less accurate computations. By default PyTorch enables TF32 mode for convolutions but not matrix multiplications, and unless a network requires full float32 precision we recommend enabling this setting for matrix multiplications, too. It can significantly speed up computations with typically negligible loss of numerical accuracy. You can read more about it [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/v4.18.0/en/performance#tf32). All you need to do is to add this before your inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -40,11 +40,9 @@ import torch
|
||||
torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about TF32 in the [Mixed precision training](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/perf_train_gpu_one#tf32) guide.
|
||||
## Half precision weights
|
||||
|
||||
## Half-precision weights
|
||||
|
||||
To save GPU memory and get more speed, try loading and running the model weights directly in half-precision or float16:
|
||||
To save more GPU memory and get more speed, you can load and run the model weights directly in half precision. This involves loading the float16 version of the weights, which was saved to a branch named `fp16`, and telling PyTorch to use the `float16` type when loading them:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@@ -63,6 +61,351 @@ image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Don't use [`torch.autocast`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/amp.html#torch.autocast) in any of the pipelines as it can lead to black images and is always slower than pure float16 precision.
|
||||
It is strongly discouraged to make use of [`torch.autocast`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/amp.html#torch.autocast) in any of the pipelines as it can lead to black images and is always slower than using pure
|
||||
float16 precision.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Sliced VAE decode for larger batches
|
||||
|
||||
To decode large batches of images with limited VRAM, or to enable batches with 32 images or more, you can use sliced VAE decode that decodes the batch latents one image at a time.
|
||||
|
||||
You likely want to couple this with [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention`] to further minimize memory use.
|
||||
|
||||
To perform the VAE decode one image at a time, invoke [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_vae_slicing`] in your pipeline before inference. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
images = pipe([prompt] * 32).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You may see a small performance boost in VAE decode on multi-image batches. There should be no performance impact on single-image batches.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Tiled VAE decode and encode for large images
|
||||
|
||||
Tiled VAE processing makes it possible to work with large images on limited VRAM. For example, generating 4k images in 8GB of VRAM. Tiled VAE decoder splits the image into overlapping tiles, decodes the tiles, and blends the outputs to make the final image.
|
||||
|
||||
You want to couple this with [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention`] to further minimize memory use.
|
||||
|
||||
To use tiled VAE processing, invoke [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_vae_tiling`] in your pipeline before inference. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, UniPCMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = UniPCMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
prompt = "a beautiful landscape photograph"
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_tiling()
|
||||
pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe([prompt], width=3840, height=2224, num_inference_steps=20).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The output image will have some tile-to-tile tone variation from the tiles having separate decoders, but you shouldn't see sharp seams between the tiles. The tiling is turned off for images that are 512x512 or smaller.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="sequential_offloading"></a>
|
||||
## Offloading to CPU with accelerate for memory savings
|
||||
|
||||
For additional memory savings, you can offload the weights to CPU and only load them to GPU when performing the forward pass.
|
||||
|
||||
To perform CPU offloading, all you have to do is invoke [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_sequential_cpu_offload`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
pipe.enable_sequential_cpu_offload()
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And you can get the memory consumption to < 3GB.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this method works at the submodule level, not on whole models. This is the best way to minimize memory consumption, but inference is much slower due to the iterative nature of the process. The UNet component of the pipeline runs several times (as many as `num_inference_steps`); each time, the different submodules of the UNet are sequentially onloaded and then offloaded as they are needed, so the number of memory transfers is large.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
Consider using <a href="#model_offloading">model offloading</a> as another point in the optimization space: it will be much faster, but memory savings won't be as large.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
It is also possible to chain offloading with attention slicing for minimal memory consumption (< 2GB).
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
pipe.enable_sequential_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: When using `enable_sequential_cpu_offload()`, it is important to **not** move the pipeline to CUDA beforehand or else the gain in memory consumption will only be minimal. See [this issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/1934) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: `enable_sequential_cpu_offload()` is a stateful operation that installs hooks on the models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<a name="model_offloading"></a>
|
||||
## Model offloading for fast inference and memory savings
|
||||
|
||||
[Sequential CPU offloading](#sequential_offloading), as discussed in the previous section, preserves a lot of memory but makes inference slower, because submodules are moved to GPU as needed, and immediately returned to CPU when a new module runs.
|
||||
|
||||
Full-model offloading is an alternative that moves whole models to the GPU, instead of handling each model's constituent _modules_. This results in a negligible impact on inference time (compared with moving the pipeline to `cuda`), while still providing some memory savings.
|
||||
|
||||
In this scenario, only one of the main components of the pipeline (typically: text encoder, unet and vae)
|
||||
will be in the GPU while the others wait in the CPU. Components like the UNet that run for multiple iterations will stay on GPU until they are no longer needed.
|
||||
|
||||
This feature can be enabled by invoking `enable_model_cpu_offload()` on the pipeline, as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is also compatible with attention slicing for additional memory savings.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
This feature requires `accelerate` version 0.17.0 or larger.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: `enable_model_cpu_offload()` is a stateful operation that installs hooks on the models and state on the pipeline. In order to properly offload
|
||||
models after they are called, it is required that the entire pipeline is run and models are called in the order the pipeline expects them to be. Exercise caution
|
||||
if models are re-used outside the context of the pipeline after hooks have been installed. See [accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/v0.18.0/en/package_reference/big_modeling#accelerate.hooks.remove_hook_from_module)
|
||||
for further docs on removing hooks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Channels Last memory format
|
||||
|
||||
Channels last memory format is an alternative way of ordering NCHW tensors in memory preserving dimensions ordering. Channels last tensors ordered in such a way that channels become the densest dimension (aka storing images pixel-per-pixel). Since not all operators currently support channels last format it may result in a worst performance, so it's better to try it and see if it works for your model.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in order to set the UNet model in our pipeline to use channels last format, we can use the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(pipe.unet.conv_out.state_dict()["weight"].stride()) # (2880, 9, 3, 1)
|
||||
pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last) # in-place operation
|
||||
print(
|
||||
pipe.unet.conv_out.state_dict()["weight"].stride()
|
||||
) # (2880, 1, 960, 320) having a stride of 1 for the 2nd dimension proves that it works
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Tracing
|
||||
|
||||
Tracing runs an example input tensor through your model, and captures the operations that are invoked as that input makes its way through the model's layers so that an executable or `ScriptFunction` is returned that will be optimized using just-in-time compilation.
|
||||
|
||||
To trace our UNet model, we can use the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import functools
|
||||
|
||||
# torch disable grad
|
||||
torch.set_grad_enabled(False)
|
||||
|
||||
# set variables
|
||||
n_experiments = 2
|
||||
unet_runs_per_experiment = 50
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# load inputs
|
||||
def generate_inputs():
|
||||
sample = torch.randn(2, 4, 64, 64).half().cuda()
|
||||
timestep = torch.rand(1).half().cuda() * 999
|
||||
encoder_hidden_states = torch.randn(2, 77, 768).half().cuda()
|
||||
return sample, timestep, encoder_hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
unet = pipe.unet
|
||||
unet.eval()
|
||||
unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last) # use channels_last memory format
|
||||
unet.forward = functools.partial(unet.forward, return_dict=False) # set return_dict=False as default
|
||||
|
||||
# warmup
|
||||
for _ in range(3):
|
||||
with torch.inference_mode():
|
||||
inputs = generate_inputs()
|
||||
orig_output = unet(*inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
# trace
|
||||
print("tracing..")
|
||||
unet_traced = torch.jit.trace(unet, inputs)
|
||||
unet_traced.eval()
|
||||
print("done tracing")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# warmup and optimize graph
|
||||
for _ in range(5):
|
||||
with torch.inference_mode():
|
||||
inputs = generate_inputs()
|
||||
orig_output = unet_traced(*inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# benchmarking
|
||||
with torch.inference_mode():
|
||||
for _ in range(n_experiments):
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
for _ in range(unet_runs_per_experiment):
|
||||
orig_output = unet_traced(*inputs)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
print(f"unet traced inference took {time.time() - start_time:.2f} seconds")
|
||||
for _ in range(n_experiments):
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
for _ in range(unet_runs_per_experiment):
|
||||
orig_output = unet(*inputs)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
print(f"unet inference took {time.time() - start_time:.2f} seconds")
|
||||
|
||||
# save the model
|
||||
unet_traced.save("unet_traced.pt")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we can replace the `unet` attribute of the pipeline with the traced model like the following
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class UNet2DConditionOutput:
|
||||
sample: torch.FloatTensor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# use jitted unet
|
||||
unet_traced = torch.jit.load("unet_traced.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# del pipe.unet
|
||||
class TracedUNet(torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.in_channels = pipe.unet.in_channels
|
||||
self.device = pipe.unet.device
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, latent_model_input, t, encoder_hidden_states):
|
||||
sample = unet_traced(latent_model_input, t, encoder_hidden_states)[0]
|
||||
return UNet2DConditionOutput(sample=sample)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.unet = TracedUNet()
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.inference_mode():
|
||||
image = pipe([prompt] * 1, num_inference_steps=50).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Memory Efficient Attention
|
||||
|
||||
Recent work on optimizing the bandwitdh in the attention block has generated huge speed ups and gains in GPU memory usage. The most recent being Flash Attention from @tridao: [code](https://github.com/HazyResearch/flash-attention), [paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.14135.pdf).
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the speedups we obtain on a few Nvidia GPUs when running the inference at 512x512 with a batch size of 1 (one prompt):
|
||||
|
||||
| GPU | Base Attention FP16 | Memory Efficient Attention FP16 |
|
||||
|------------------ |--------------------- |--------------------------------- |
|
||||
| NVIDIA Tesla T4 | 3.5it/s | 5.5it/s |
|
||||
| NVIDIA 3060 RTX | 4.6it/s | 7.8it/s |
|
||||
| NVIDIA A10G | 8.88it/s | 15.6it/s |
|
||||
| NVIDIA RTX A6000 | 11.7it/s | 21.09it/s |
|
||||
| NVIDIA TITAN RTX | 12.51it/s | 18.22it/s |
|
||||
| A100-SXM4-40GB | 18.6it/s | 29.it/s |
|
||||
| A100-SXM-80GB | 18.7it/s | 29.5it/s |
|
||||
|
||||
To leverage it just make sure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
If you have PyTorch 2.0 installed, you shouldn't use xFormers!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
- PyTorch > 1.12
|
||||
- Cuda available
|
||||
- [Installed the xformers library](xformers).
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.inference_mode():
|
||||
sample = pipe("a small cat")
|
||||
|
||||
# optional: You can disable it via
|
||||
# pipe.disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,22 +10,25 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Habana Gaudi
|
||||
# How to use Stable Diffusion on Habana Gaudi
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is compatible with Habana Gaudi through 🤗 [Optimum](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/habana/usage_guides/stable_diffusion). Follow the [installation](https://docs.habana.ai/en/latest/Installation_Guide/index.html) guide to install the SynapseAI and Gaudi drivers, and then install Optimum Habana:
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is compatible with Habana Gaudi through 🤗 [Optimum Habana](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/habana/usage_guides/stable_diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade-strategy eager optimum[habana]
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
- Optimum Habana 1.6 or later, [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/habana/installation) is how to install it.
|
||||
- SynapseAI 1.10.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
To generate images with Stable Diffusion 1 and 2 on Gaudi, you need to instantiate two instances:
|
||||
- A pipeline with [`GaudiStableDiffusionPipeline`](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/habana/package_reference/stable_diffusion_pipeline). This pipeline supports *text-to-image generation*.
|
||||
- A scheduler with [`GaudiDDIMScheduler`](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/habana/package_reference/stable_diffusion_pipeline#optimum.habana.diffusers.GaudiDDIMScheduler). This scheduler has been optimized for Habana Gaudi.
|
||||
|
||||
- [`~optimum.habana.diffusers.GaudiStableDiffusionPipeline`], a pipeline for text-to-image generation.
|
||||
- [`~optimum.habana.diffusers.GaudiDDIMScheduler`], a Gaudi-optimized scheduler.
|
||||
|
||||
When you initialize the pipeline, you have to specify `use_habana=True` to deploy it on HPUs and to get the fastest possible generation, you should enable **HPU graphs** with `use_hpu_graphs=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, specify a [`~optimum.habana.GaudiConfig`] which can be downloaded from the [Habana](https://huggingface.co/Habana) organization on the Hub.
|
||||
When initializing the pipeline, you have to specify `use_habana=True` to deploy it on HPUs.
|
||||
Furthermore, in order to get the fastest possible generations you should enable **HPU graphs** with `use_hpu_graphs=True`.
|
||||
Finally, you will need to specify a [Gaudi configuration](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/habana/package_reference/gaudi_config) which can be downloaded from the [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/Habana).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from optimum.habana import GaudiConfig
|
||||
@@ -42,8 +45,7 @@ pipeline = GaudiStableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can call the pipeline to generate images by batches from one or several prompts:
|
||||
|
||||
You can then call the pipeline to generate images by batches from one or several prompts:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
outputs = pipeline(
|
||||
prompt=[
|
||||
@@ -55,20 +57,21 @@ outputs = pipeline(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, check out 🤗 Optimum Habana's [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/habana/usage_guides/stable_diffusion) and the [example](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-habana/tree/main/examples/stable-diffusion) provided in the official GitHub repository.
|
||||
For more information, check out Optimum Habana's [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/habana/usage_guides/stable_diffusion) and the [example](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-habana/tree/main/examples/stable-diffusion) provided in the official Github repository.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
We benchmarked Habana's first-generation Gaudi and Gaudi2 with the [Habana/stable-diffusion](https://huggingface.co/Habana/stable-diffusion) and [Habana/stable-diffusion-2](https://huggingface.co/Habana/stable-diffusion-2) Gaudi configurations (mixed precision bf16/fp32) to demonstrate their performance.
|
||||
Here are the latencies for Habana first-generation Gaudi and Gaudi2 with the [Habana/stable-diffusion](https://huggingface.co/Habana/stable-diffusion) and [Habana/stable-diffusion-2](https://huggingface.co/Habana/stable-diffusion-2) Gaudi configurations (mixed precision bf16/fp32):
|
||||
|
||||
For [Stable Diffusion v1.5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) on 512x512 images:
|
||||
- [Stable Diffusion v1.5](https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5) (512x512 resolution):
|
||||
|
||||
| | Latency (batch size = 1) | Throughput |
|
||||
| | Latency (batch size = 1) | Throughput (batch size = 8) |
|
||||
| ---------------------- |:------------------------:|:---------------------------:|
|
||||
| first-generation Gaudi | 3.80s | 0.308 images/s (batch size = 8) |
|
||||
| Gaudi2 | 1.33s | 1.081 images/s (batch size = 8) |
|
||||
| first-generation Gaudi | 3.80s | 0.308 images/s |
|
||||
| Gaudi2 | 1.33s | 1.081 images/s |
|
||||
|
||||
For [Stable Diffusion v2.1](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1) on 768x768 images:
|
||||
- [Stable Diffusion v2.1](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1) (768x768 resolution):
|
||||
|
||||
| | Latency (batch size = 1) | Throughput |
|
||||
| ---------------------- |:------------------------:|:-------------------------------:|
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,332 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Reduce memory usage
|
||||
|
||||
A barrier to using diffusion models is the large amount of memory required. To overcome this challenge, there are several memory-reducing techniques you can use to run even some of the largest models on free-tier or consumer GPUs. Some of these techniques can even be combined to further reduce memory usage.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In many cases, optimizing for memory or speed leads to improved performance in the other, so you should try to optimize for both whenever you can. This guide focuses on minimizing memory usage, but you can also learn more about how to [Speed up inference](fp16).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The results below are obtained from generating a single 512x512 image from the prompt a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars with 50 DDIM steps on a Nvidia Titan RTX, demonstrating the speed-up you can expect as a result of reduced memory consumption.
|
||||
|
||||
| | latency | speed-up |
|
||||
| ---------------- | ------- | ------- |
|
||||
| original | 9.50s | x1 |
|
||||
| fp16 | 3.61s | x2.63 |
|
||||
| channels last | 3.30s | x2.88 |
|
||||
| traced UNet | 3.21s | x2.96 |
|
||||
| memory-efficient attention | 2.63s | x3.61 |
|
||||
|
||||
## Sliced VAE
|
||||
|
||||
Sliced VAE enables decoding large batches of images with limited VRAM or batches with 32 images or more by decoding the batches of latents one image at a time. You'll likely want to couple this with [`~ModelMixin.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention`] to reduce memory use further if you have xFormers installed.
|
||||
|
||||
To use sliced VAE, call [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_vae_slicing`] on your pipeline before inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_slicing()
|
||||
#pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
images = pipe([prompt] * 32).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You may see a small performance boost in VAE decoding on multi-image batches, and there should be no performance impact on single-image batches.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tiled VAE
|
||||
|
||||
Tiled VAE processing also enables working with large images on limited VRAM (for example, generating 4k images on 8GB of VRAM) by splitting the image into overlapping tiles, decoding the tiles, and then blending the outputs together to compose the final image. You should also used tiled VAE with [`~ModelMixin.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention`] to reduce memory use further if you have xFormers installed.
|
||||
|
||||
To use tiled VAE processing, call [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_vae_tiling`] on your pipeline before inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, UniPCMultistepScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.scheduler = UniPCMultistepScheduler.from_config(pipe.scheduler.config)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
prompt = "a beautiful landscape photograph"
|
||||
pipe.enable_vae_tiling()
|
||||
#pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipe([prompt], width=3840, height=2224, num_inference_steps=20).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The output image has some tile-to-tile tone variation because the tiles are decoded separately, but you shouldn't see any sharp and obvious seams between the tiles. Tiling is turned off for images that are 512x512 or smaller.
|
||||
|
||||
## CPU offloading
|
||||
|
||||
Offloading the weights to the CPU and only loading them on the GPU when performing the forward pass can also save memory. Often, this technique can reduce memory consumption to less than 3GB.
|
||||
|
||||
To perform CPU offloading, call [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_sequential_cpu_offload`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
pipe.enable_sequential_cpu_offload()
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
CPU offloading works on submodules rather than whole models. This is the best way to minimize memory consumption, but inference is much slower due to the iterative nature of the diffusion process. The UNet component of the pipeline runs several times (as many as `num_inference_steps`); each time, the different UNet submodules are sequentially onloaded and offloaded as needed, resulting in a large number of memory transfers.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Consider using [model offloading](#model-offloading) if you want to optimize for speed because it is much faster. The tradeoff is your memory savings won't be as large.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
When using [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_sequential_cpu_offload`], don't move the pipeline to CUDA beforehand or else the gain in memory consumption will only be minimal (see this [issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/1934) for more information).
|
||||
|
||||
[`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_sequential_cpu_offload`] is a stateful operation that installs hooks on the models.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Model offloading
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Model offloading requires 🤗 Accelerate version 0.17.0 or higher.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
[Sequential CPU offloading](#cpu-offloading) preserves a lot of memory but it makes inference slower because submodules are moved to GPU as needed, and they're immediately returned to the CPU when a new module runs.
|
||||
|
||||
Full-model offloading is an alternative that moves whole models to the GPU, instead of handling each model's constituent *submodules*. There is a negligible impact on inference time (compared with moving the pipeline to `cuda`), and it still provides some memory savings.
|
||||
|
||||
During model offloading, only one of the main components of the pipeline (typically the text encoder, UNet and VAE)
|
||||
is placed on the GPU while the others wait on the CPU. Components like the UNet that run for multiple iterations stay on the GPU until they're no longer needed.
|
||||
|
||||
Enable model offloading by calling [`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload`] on the pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
pipe.enable_model_cpu_offload()
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
In order to properly offload models after they're called, it is required to run the entire pipeline and models are called in the pipeline's expected order. Exercise caution if models are reused outside the context of the pipeline after hooks have been installed. See [Removing Hooks](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/en/package_reference/big_modeling#accelerate.hooks.remove_hook_from_module) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
[`~StableDiffusionPipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload`] is a stateful operation that installs hooks on the models and state on the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Channels-last memory format
|
||||
|
||||
The channels-last memory format is an alternative way of ordering NCHW tensors in memory to preserve dimension ordering. Channels-last tensors are ordered in such a way that the channels become the densest dimension (storing images pixel-per-pixel). Since not all operators currently support the channels-last format, it may result in worst performance but you should still try and see if it works for your model.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to set the pipeline's UNet to use the channels-last format:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(pipe.unet.conv_out.state_dict()["weight"].stride()) # (2880, 9, 3, 1)
|
||||
pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last) # in-place operation
|
||||
print(
|
||||
pipe.unet.conv_out.state_dict()["weight"].stride()
|
||||
) # (2880, 1, 960, 320) having a stride of 1 for the 2nd dimension proves that it works
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Tracing
|
||||
|
||||
Tracing runs an example input tensor through the model and captures the operations that are performed on it as that input makes its way through the model's layers. The executable or `ScriptFunction` that is returned is optimized with just-in-time compilation.
|
||||
|
||||
To trace a UNet:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import functools
|
||||
|
||||
# torch disable grad
|
||||
torch.set_grad_enabled(False)
|
||||
|
||||
# set variables
|
||||
n_experiments = 2
|
||||
unet_runs_per_experiment = 50
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# load inputs
|
||||
def generate_inputs():
|
||||
sample = torch.randn(2, 4, 64, 64).half().cuda()
|
||||
timestep = torch.rand(1).half().cuda() * 999
|
||||
encoder_hidden_states = torch.randn(2, 77, 768).half().cuda()
|
||||
return sample, timestep, encoder_hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
unet = pipe.unet
|
||||
unet.eval()
|
||||
unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last) # use channels_last memory format
|
||||
unet.forward = functools.partial(unet.forward, return_dict=False) # set return_dict=False as default
|
||||
|
||||
# warmup
|
||||
for _ in range(3):
|
||||
with torch.inference_mode():
|
||||
inputs = generate_inputs()
|
||||
orig_output = unet(*inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
# trace
|
||||
print("tracing..")
|
||||
unet_traced = torch.jit.trace(unet, inputs)
|
||||
unet_traced.eval()
|
||||
print("done tracing")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# warmup and optimize graph
|
||||
for _ in range(5):
|
||||
with torch.inference_mode():
|
||||
inputs = generate_inputs()
|
||||
orig_output = unet_traced(*inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# benchmarking
|
||||
with torch.inference_mode():
|
||||
for _ in range(n_experiments):
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
for _ in range(unet_runs_per_experiment):
|
||||
orig_output = unet_traced(*inputs)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
print(f"unet traced inference took {time.time() - start_time:.2f} seconds")
|
||||
for _ in range(n_experiments):
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
for _ in range(unet_runs_per_experiment):
|
||||
orig_output = unet(*inputs)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
print(f"unet inference took {time.time() - start_time:.2f} seconds")
|
||||
|
||||
# save the model
|
||||
unet_traced.save("unet_traced.pt")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Replace the `unet` attribute of the pipeline with the traced model:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class UNet2DConditionOutput:
|
||||
sample: torch.FloatTensor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# use jitted unet
|
||||
unet_traced = torch.jit.load("unet_traced.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# del pipe.unet
|
||||
class TracedUNet(torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.in_channels = pipe.unet.config.in_channels
|
||||
self.device = pipe.unet.device
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, latent_model_input, t, encoder_hidden_states):
|
||||
sample = unet_traced(latent_model_input, t, encoder_hidden_states)[0]
|
||||
return UNet2DConditionOutput(sample=sample)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.unet = TracedUNet()
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.inference_mode():
|
||||
image = pipe([prompt] * 1, num_inference_steps=50).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Memory-efficient attention
|
||||
|
||||
Recent work on optimizing bandwidth in the attention block has generated huge speed-ups and reductions in GPU memory usage. The most recent type of memory-efficient attention is [Flash Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135) (you can check out the original code at [HazyResearch/flash-attention](https://github.com/HazyResearch/flash-attention)).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you have PyTorch >= 2.0 installed, you should not expect a speed-up for inference when enabling `xformers`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To use Flash Attention, install the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- PyTorch > 1.12
|
||||
- CUDA available
|
||||
- [xFormers](xformers)
|
||||
|
||||
Then call [`~ModelMixin.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention`] on the pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.inference_mode():
|
||||
sample = pipe("a small cat")
|
||||
|
||||
# optional: You can disable it via
|
||||
# pipe.disable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The iteration speed when using `xformers` should match the iteration speed of PyTorch 2.0 as described [here](torch2.0).
|
||||
@@ -10,16 +10,29 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Metal Performance Shaders (MPS)
|
||||
# How to use Stable Diffusion in Apple Silicon (M1/M2)
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is compatible with Apple silicon (M1/M2 chips) using the PyTorch [`mps`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/mps.html) device, which uses the Metal framework to leverage the GPU on MacOS devices. You'll need to have:
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers is compatible with Apple silicon for Stable Diffusion inference, using the PyTorch `mps` device. These are the steps you need to follow to use your M1 or M2 computer with Stable Diffusion.
|
||||
|
||||
- macOS computer with Apple silicon (M1/M2) hardware
|
||||
- macOS 12.6 or later (13.0 or later recommended)
|
||||
- arm64 version of Python
|
||||
- [PyTorch 2.0](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) (recommended) or 1.13 (minimum version supported for `mps`)
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
The `mps` backend uses PyTorch's `.to()` interface to move the Stable Diffusion pipeline on to your M1 or M2 device:
|
||||
- Mac computer with Apple silicon (M1/M2) hardware.
|
||||
- macOS 12.6 or later (13.0 or later recommended).
|
||||
- arm64 version of Python.
|
||||
- PyTorch 2.0 (recommended) or 1.13 (minimum version supported for `mps`). You can install it with `pip` or `conda` using the instructions in https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
The snippet below demonstrates how to use the `mps` backend using the familiar `to()` interface to move the Stable Diffusion pipeline to your M1 or M2 device.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
**If you are using PyTorch 1.13** you need to "prime" the pipeline using an additional one-time pass through it. This is a temporary workaround for a weird issue we detected: the first inference pass produces slightly different results than subsequent ones. You only need to do this pass once, and it's ok to use just one inference step and discard the result.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
We strongly recommend you use PyTorch 2 or better, as it solves a number of problems like the one described in the previous tip.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -31,44 +44,24 @@ pipe = pipe.to("mps")
|
||||
pipe.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
|
||||
# First-time "warmup" pass if PyTorch version is 1.13 (see explanation above)
|
||||
_ = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Results match those from the CPU device after the warmup pass.
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
## Performance Recommendations
|
||||
|
||||
Generating multiple prompts in a batch can [crash](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/363) or fail to work reliably. We believe this is related to the [`mps`](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/84039) backend in PyTorch. While this is being investigated, you should iterate instead of batching.
|
||||
M1/M2 performance is very sensitive to memory pressure. The system will automatically swap if it needs to, but performance will degrade significantly when it does.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
We recommend you use _attention slicing_ to reduce memory pressure during inference and prevent swapping, particularly if your computer has less than 64 GB of system RAM, or if you generate images at non-standard resolutions larger than 512 × 512 pixels. Attention slicing performs the costly attention operation in multiple steps instead of all at once. It usually has a performance impact of ~20% in computers without universal memory, but we have observed _better performance_ in most Apple Silicon computers, unless you have 64 GB or more.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using **PyTorch 1.13**, you need to "prime" the pipeline with an additional one-time pass through it. This is a temporary workaround for an issue where the first inference pass produces slightly different results than subsequent ones. You only need to do this pass once, and after just one inference step you can discard the result.
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5").to("mps")
|
||||
pipe.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
# First-time "warmup" pass if PyTorch version is 1.13
|
||||
+ _ = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Results match those from the CPU device after the warmup pass.
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshoot
|
||||
|
||||
M1/M2 performance is very sensitive to memory pressure. When this occurs, the system automatically swaps if it needs to which significantly degrades performance.
|
||||
|
||||
To prevent this from happening, we recommend *attention slicing* to reduce memory pressure during inference and prevent swapping. This is especially relevant if your computer has less than 64GB of system RAM, or if you generate images at non-standard resolutions larger than 512×512 pixels. Call the [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_attention_slicing`] function on your pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, variant="fp16", use_safetensors=True).to("mps")
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Attention slicing performs the costly attention operation in multiple steps instead of all at once. It usually improves performance by ~20% in computers without universal memory, but we've observed *better performance* in most Apple silicon computers unless you have 64GB of RAM or more.
|
||||
## Known Issues
|
||||
|
||||
- Generating multiple prompts in a batch [crashes or doesn't work reliably](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/363). We believe this is related to the [`mps` backend in PyTorch](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/84039). This is being resolved, but for now we recommend to iterate instead of batching.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,19 +10,24 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# ONNX Runtime
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 [Optimum](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum) provides a Stable Diffusion pipeline compatible with ONNX Runtime. You'll need to install 🤗 Optimum with the following command for ONNX Runtime support:
|
||||
# How to use ONNX Runtime for inference
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 [Optimum](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum) provides a Stable Diffusion pipeline compatible with ONNX Runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Install 🤗 Optimum with the following command for ONNX Runtime support:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -q optimum["onnxruntime"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to use the Stable Diffusion and Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL) pipelines with ONNX Runtime.
|
||||
pip install optimum["onnxruntime"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
To load and run inference, use the [`~optimum.onnxruntime.ORTStableDiffusionPipeline`]. If you want to load a PyTorch model and convert it to the ONNX format on-the-fly, set `export=True`:
|
||||
### Inference
|
||||
|
||||
To load an ONNX model and run inference with ONNX Runtime, you need to replace [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] with `ORTStableDiffusionPipeline`. In case you want to load a PyTorch model and convert it to the ONNX format on-the-fly, you can set `export=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from optimum.onnxruntime import ORTStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -34,22 +39,16 @@ image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
pipeline.save_pretrained("./onnx-stable-diffusion-v1-5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Generating multiple prompts in a batch seems to take too much memory. While we look into it, you may need to iterate instead of batching.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To export the pipeline in the ONNX format offline and use it later for inference,
|
||||
use the [`optimum-cli export`](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/main/en/exporters/onnx/usage_guides/export_a_model#exporting-a-model-to-onnx-using-the-cli) command:
|
||||
If you want to export the pipeline in the ONNX format offline and later use it for inference,
|
||||
you can use the [`optimum-cli export`](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/main/en/exporters/onnx/usage_guides/export_a_model#exporting-a-model-to-onnx-using-the-cli) command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
optimum-cli export onnx --model runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5 sd_v15_onnx/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then to perform inference (you don't have to specify `export=True` again):
|
||||
Then perform inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from optimum.onnxruntime import ORTStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "sd_v15_onnx"
|
||||
@@ -58,15 +57,36 @@ prompt = "sailing ship in storm by Leonardo da Vinci"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that we didn't have to specify `export=True` above.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/optimum/documentation-images/resolve/main/onnxruntime/stable_diffusion_v1_5_ort_sail_boat.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
You can find more examples in 🤗 Optimum [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/), and Stable Diffusion is supported for text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting.
|
||||
You can find more examples in [optimum documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported tasks
|
||||
|
||||
| Task | Loading Class |
|
||||
|--------------------------------------|--------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `text-to-image` | `ORTStableDiffusionPipeline` |
|
||||
| `image-to-image` | `ORTStableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline` |
|
||||
| `inpaint` | `ORTStableDiffusionInpaintPipeline` |
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
|
||||
To load and run inference with SDXL, use the [`~optimum.onnxruntime.ORTStableDiffusionXLPipeline`]:
|
||||
### Export
|
||||
|
||||
To export your model to ONNX, you can use the [Optimum CLI](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/main/en/exporters/onnx/usage_guides/export_a_model#exporting-a-model-to-onnx-using-the-cli) as follows :
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
optimum-cli export onnx --model stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0 --task stable-diffusion-xl sd_xl_onnx/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how you can load a SDXL ONNX model from [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0) and run inference with ONNX Runtime :
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from optimum.onnxruntime import ORTStableDiffusionXLPipeline
|
||||
@@ -77,10 +97,13 @@ prompt = "sailing ship in storm by Leonardo da Vinci"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To export the pipeline in the ONNX format and use it later for inference, use the [`optimum-cli export`](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/main/en/exporters/onnx/usage_guides/export_a_model#exporting-a-model-to-onnx-using-the-cli) command:
|
||||
### Supported tasks
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
optimum-cli export onnx --model stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0 --task stable-diffusion-xl sd_xl_onnx/
|
||||
```
|
||||
| Task | Loading Class |
|
||||
|--------------------------------------|--------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `text-to-image` | `ORTStableDiffusionXLPipeline` |
|
||||
| `image-to-image` | `ORTStableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline`|
|
||||
|
||||
SDXL in the ONNX format is supported for text-to-image and image-to-image.
|
||||
## Known Issues
|
||||
|
||||
- Generating multiple prompts in a batch seems to take too much memory. While we look into it, you may need to iterate instead of batching.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,21 +10,27 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# OpenVINO
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 [Optimum](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-intel) provides Stable Diffusion pipelines compatible with OpenVINO to perform inference on a variety of Intel processors (see the [full list](https://docs.openvino.ai/latest/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_Supported_Devices.html) of supported devices).
|
||||
# How to use OpenVINO for inference
|
||||
|
||||
You'll need to install 🤗 Optimum Intel with the `--upgrade-strategy eager` option to ensure [`optimum-intel`](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-intel) is using the latest version:
|
||||
🤗 [Optimum](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-intel) provides Stable Diffusion pipelines compatible with OpenVINO. You can now easily perform inference with OpenVINO Runtime on a variety of Intel processors ([see](https://docs.openvino.ai/latest/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_Supported_Devices.html) the full list of supported devices).
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Install 🤗 Optimum Intel with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install --upgrade-strategy eager optimum["openvino"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to use the Stable Diffusion and Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL) pipelines with OpenVINO.
|
||||
The `--upgrade-strategy eager` option is needed to ensure [`optimum-intel`](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-intel) is upgraded to its latest version.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
To load and run inference, use the [`~optimum.intel.OVStableDiffusionPipeline`]. If you want to load a PyTorch model and convert it to the OpenVINO format on-the-fly, set `export=True`:
|
||||
### Inference
|
||||
|
||||
To load an OpenVINO model and run inference with OpenVINO Runtime, you need to replace `StableDiffusionPipeline` with `OVStableDiffusionPipeline`. In case you want to load a PyTorch model and convert it to the OpenVINO format on-the-fly, you can set `export=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from optimum.intel import OVStableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +44,7 @@ image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
pipeline.save_pretrained("openvino-sd-v1-5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To further speed-up inference, statically reshape the model. If you change any parameters such as the outputs height or width, you’ll need to statically reshape your model again.
|
||||
To further speed up inference, the model can be statically reshaped :
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Define the shapes related to the inputs and desired outputs
|
||||
@@ -56,15 +62,30 @@ image = pipeline(
|
||||
num_images_per_prompt=num_images,
|
||||
).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In case you want to change any parameters such as the outputs height or width, you’ll need to statically reshape your model once again.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/optimum/documentation-images/resolve/main/intel/openvino/stable_diffusion_v1_5_sail_boat_rembrandt.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
You can find more examples in the 🤗 Optimum [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/intel/inference#stable-diffusion), and Stable Diffusion is supported for text-to-image, image-to-image, and inpainting.
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported tasks
|
||||
|
||||
| Task | Loading Class |
|
||||
|--------------------------------------|--------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `text-to-image` | `OVStableDiffusionPipeline` |
|
||||
| `image-to-image` | `OVStableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline` |
|
||||
| `inpaint` | `OVStableDiffusionInpaintPipeline` |
|
||||
|
||||
You can find more examples in the optimum [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/intel/inference#stable-diffusion).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Stable Diffusion XL
|
||||
|
||||
To load and run inference with SDXL, use the [`~optimum.intel.OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline`]:
|
||||
### Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how you can load a SDXL OpenVINO model from [stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0) and run inference with OpenVINO Runtime :
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from optimum.intel import OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline
|
||||
@@ -75,6 +96,15 @@ prompt = "sailing ship in storm by Rembrandt"
|
||||
image = pipeline(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To further speed-up inference, [statically reshape](#stable-diffusion) the model as shown in the Stable Diffusion section.
|
||||
To further speed up inference, the model can be statically reshaped as showed above.
|
||||
You can find more examples in the optimum [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/intel/inference#stable-diffusion-xl).
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported tasks
|
||||
|
||||
| Task | Loading Class |
|
||||
|--------------------------------------|--------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `text-to-image` | `OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline` |
|
||||
| `image-to-image` | `OVStableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline` |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can find more examples in the 🤗 Optimum [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/intel/inference#stable-diffusion-xl), and running SDXL in OpenVINO is supported for text-to-image and image-to-image.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,6 +12,6 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Generating high-quality outputs is computationally intensive, especially during each iterative step where you go from a noisy output to a less noisy output. One of 🤗 Diffuser's goals is to make this technology widely accessible to everyone, which includes enabling fast inference on consumer and specialized hardware.
|
||||
Generating high-quality outputs is computationally intensive, especially during each iterative step where you go from a noisy output to a less noisy output. One of 🧨 Diffuser's goal is to make this technology widely accessible to everyone, which includes enabling fast inference on consumer and specialized hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
This section will cover tips and tricks - like half-precision weights and sliced attention - for optimizing inference speed and reducing memory-consumption. You'll also learn how to speed up your PyTorch code with [`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html) or [ONNX Runtime](https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/), and enable memory-efficient attention with [xFormers](https://facebookresearch.github.io/xformers/). There are also guides for running inference on specific hardware like Apple Silicon, and Intel or Habana processors.
|
||||
This section will cover tips and tricks - like half-precision weights and sliced attention - for optimizing inference speed and reducing memory-consumption. You can also learn how to speed up your PyTorch code with [`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html) or [ONNX Runtime](https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/), and enable memory-efficient attention with [xFormers](https://facebookresearch.github.io/xformers/). There are also guides for running inference on specific hardware like Apple Silicon, and Intel or Habana processors.
|
||||
@@ -10,46 +10,35 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Token merging
|
||||
# Token Merging
|
||||
|
||||
[Token merging](https://huggingface.co/papers/2303.17604) (ToMe) merges redundant tokens/patches progressively in the forward pass of a Transformer-based network which can speed-up the inference latency of [`StableDiffusionPipeline`].
|
||||
Token Merging (introduced in [Token Merging: Your ViT But Faster](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.09461)) works by merging the redundant tokens / patches progressively in the forward pass of a Transformer-based network. It can speed up the inference latency of the underlying network.
|
||||
|
||||
Install ToMe from `pip`:
|
||||
After Token Merging (ToMe) was released, the authors released [Token Merging for Fast Stable Diffusion](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.17604), which introduced a version of ToMe which is more compatible with Stable Diffusion. We can use ToMe to gracefully speed up the inference latency of a [`DiffusionPipeline`]. This doc discusses how to apply ToMe to the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`], the expected speedups, and the qualitative aspects of using ToMe on the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install tomesd
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Using ToMe
|
||||
|
||||
You can use ToMe from the [`tomesd`](https://github.com/dbolya/tomesd) library with the [`apply_patch`](https://github.com/dbolya/tomesd?tab=readme-ov-file#usage) function:
|
||||
The authors of ToMe released a convenient Python library called [`tomesd`](https://github.com/dbolya/tomesd) that lets us apply ToMe to a [`DiffusionPipeline`] like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import tomesd
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import tomesd
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True,
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
+ tomesd.apply_patch(pipeline, ratio=0.5)
|
||||
|
||||
image = pipeline("a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars").images[0]
|
||||
image = pipeline("a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars").images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `apply_patch` function exposes a number of [arguments](https://github.com/dbolya/tomesd#usage) to help strike a balance between pipeline inference speed and the quality of the generated tokens. The most important argument is `ratio` which controls the number of tokens that are merged during the forward pass.
|
||||
And that’s it!
|
||||
|
||||
As reported in the [paper](https://huggingface.co/papers/2303.17604), ToMe can greatly preserve the quality of the generated images while boosting inference speed. By increasing the `ratio`, you can speed-up inference even further, but at the cost of some degraded image quality.
|
||||
`tomesd.apply_patch()` exposes [a number of arguments](https://github.com/dbolya/tomesd#usage) to let us strike a balance between the pipeline inference speed and the quality of the generated tokens. Amongst those arguments, the most important one is `ratio`. `ratio` controls the number of tokens that will be merged during the forward pass. For more details on `tomesd`, please refer to the original repository https://github.com/dbolya/tomesd and [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.17604).
|
||||
|
||||
To test the quality of the generated images, we sampled a few prompts from [Parti Prompts](https://parti.research.google/) and performed inference with the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] with the following settings:
|
||||
## Benchmarking `tomesd` with `StableDiffusionPipeline`
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/tome/tome_samples.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
We didn’t notice any significant decrease in the quality of the generated samples, and you can check out the generated samples in this [WandB report](https://wandb.ai/sayakpaul/tomesd-results/runs/23j4bj3i?workspace=). If you're interested in reproducing this experiment, use this [script](https://gist.github.com/sayakpaul/8cac98d7f22399085a060992f411ecbd).
|
||||
|
||||
## Benchmarks
|
||||
|
||||
We also benchmarked the impact of `tomesd` on the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] with [xFormers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/optimization/xformers) enabled across several image resolutions. The results are obtained from A100 and V100 GPUs in the following development environment:
|
||||
We benchmarked the impact of using `tomesd` on [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] along with [xformers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/optimization/xformers) across different image resolutions. We used A100 and V100 as our test GPU devices with the following development environment (with Python 3.8.5):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
- `diffusers` version: 0.15.1
|
||||
@@ -62,35 +51,66 @@ We also benchmarked the impact of `tomesd` on the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] wi
|
||||
- tomesd version: 0.1.2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To reproduce this benchmark, feel free to use this [script](https://gist.github.com/sayakpaul/27aec6bca7eb7b0e0aa4112205850335). The results are reported in seconds, and where applicable we report the speed-up percentage over the vanilla pipeline when using ToMe and ToMe + xFormers.
|
||||
We used this script for benchmarking: [https://gist.github.com/sayakpaul/27aec6bca7eb7b0e0aa4112205850335](https://gist.github.com/sayakpaul/27aec6bca7eb7b0e0aa4112205850335). Following are our findings:
|
||||
|
||||
| **GPU** | **Resolution** | **Batch size** | **Vanilla** | **ToMe** | **ToMe + xFormers** |
|
||||
|----------|----------------|----------------|-------------|----------------|---------------------|
|
||||
| **A100** | 512 | 10 | 6.88 | 5.26 (+23.55%) | 4.69 (+31.83%) |
|
||||
| | 768 | 10 | OOM | 14.71 | 11 |
|
||||
| | | 8 | OOM | 11.56 | 8.84 |
|
||||
| | | 4 | OOM | 5.98 | 4.66 |
|
||||
| | | 2 | 4.99 | 3.24 (+35.07%) | 2.1 (+37.88%) |
|
||||
| | | 1 | 3.29 | 2.24 (+31.91%) | 2.03 (+38.3%) |
|
||||
| | 1024 | 10 | OOM | OOM | OOM |
|
||||
| | | 8 | OOM | OOM | OOM |
|
||||
| | | 4 | OOM | 12.51 | 9.09 |
|
||||
| | | 2 | OOM | 6.52 | 4.96 |
|
||||
| | | 1 | 6.4 | 3.61 (+43.59%) | 2.81 (+56.09%) |
|
||||
| **V100** | 512 | 10 | OOM | 10.03 | 9.29 |
|
||||
| | | 8 | OOM | 8.05 | 7.47 |
|
||||
| | | 4 | 5.7 | 4.3 (+24.56%) | 3.98 (+30.18%) |
|
||||
| | | 2 | 3.14 | 2.43 (+22.61%) | 2.27 (+27.71%) |
|
||||
| | | 1 | 1.88 | 1.57 (+16.49%) | 1.57 (+16.49%) |
|
||||
| | 768 | 10 | OOM | OOM | 23.67 |
|
||||
| | | 8 | OOM | OOM | 18.81 |
|
||||
| | | 4 | OOM | 11.81 | 9.7 |
|
||||
| | | 2 | OOM | 6.27 | 5.2 |
|
||||
| | | 1 | 5.43 | 3.38 (+37.75%) | 2.82 (+48.07%) |
|
||||
| | 1024 | 10 | OOM | OOM | OOM |
|
||||
| | | 8 | OOM | OOM | OOM |
|
||||
| | | 4 | OOM | OOM | 19.35 |
|
||||
| | | 2 | OOM | 13 | 10.78 |
|
||||
| | | 1 | OOM | 6.66 | 5.54 |
|
||||
### A100
|
||||
|
||||
As seen in the tables above, the speed-up from `tomesd` becomes more pronounced for larger image resolutions. It is also interesting to note that with `tomesd`, it is possible to run the pipeline on a higher resolution like 1024x1024. You may be able to speed-up inference even more with [`torch.compile`](torch2.0).
|
||||
| Resolution | Batch size | Vanilla | ToMe | ToMe + xFormers | ToMe speedup (%) | ToMe + xFormers speedup (%) |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| 512 | 10 | 6.88 | 5.26 | 4.69 | 23.54651163 | 31.83139535 |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| 768 | 10 | OOM | 14.71 | 11 | | |
|
||||
| | 8 | OOM | 11.56 | 8.84 | | |
|
||||
| | 4 | OOM | 5.98 | 4.66 | | |
|
||||
| | 2 | 4.99 | 3.24 | 3.1 | 35.07014028 | 37.8757515 |
|
||||
| | 1 | 3.29 | 2.24 | 2.03 | 31.91489362 | 38.29787234 |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| 1024 | 10 | OOM | OOM | OOM | | |
|
||||
| | 8 | OOM | OOM | OOM | | |
|
||||
| | 4 | OOM | 12.51 | 9.09 | | |
|
||||
| | 2 | OOM | 6.52 | 4.96 | | |
|
||||
| | 1 | 6.4 | 3.61 | 2.81 | 43.59375 | 56.09375 |
|
||||
|
||||
***The timings reported here are in seconds. Speedups are calculated over the `Vanilla` timings.***
|
||||
|
||||
### V100
|
||||
|
||||
| Resolution | Batch size | Vanilla | ToMe | ToMe + xFormers | ToMe speedup (%) | ToMe + xFormers speedup (%) |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| 512 | 10 | OOM | 10.03 | 9.29 | | |
|
||||
| | 8 | OOM | 8.05 | 7.47 | | |
|
||||
| | 4 | 5.7 | 4.3 | 3.98 | 24.56140351 | 30.1754386 |
|
||||
| | 2 | 3.14 | 2.43 | 2.27 | 22.61146497 | 27.70700637 |
|
||||
| | 1 | 1.88 | 1.57 | 1.57 | 16.4893617 | 16.4893617 |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| 768 | 10 | OOM | OOM | 23.67 | | |
|
||||
| | 8 | OOM | OOM | 18.81 | | |
|
||||
| | 4 | OOM | 11.81 | 9.7 | | |
|
||||
| | 2 | OOM | 6.27 | 5.2 | | |
|
||||
| | 1 | 5.43 | 3.38 | 2.82 | 37.75322284 | 48.06629834 |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| 1024 | 10 | OOM | OOM | OOM | | |
|
||||
| | 8 | OOM | OOM | OOM | | |
|
||||
| | 4 | OOM | OOM | 19.35 | | |
|
||||
| | 2 | OOM | 13 | 10.78 | | |
|
||||
| | 1 | OOM | 6.66 | 5.54 | | |
|
||||
|
||||
As seen in the tables above, the speedup with `tomesd` becomes more pronounced for larger image resolutions. It is also interesting to note that with `tomesd`, it becomes possible to run the pipeline on a higher resolution, like 1024x1024.
|
||||
|
||||
It might be possible to speed up inference even further with [`torch.compile()`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/optimization/torch2.0).
|
||||
|
||||
## Quality
|
||||
|
||||
As reported in [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.17604), ToMe can preserve the quality of the generated images to a great extent while speeding up inference. By increasing the `ratio`, it is possible to further speed up inference, but that might come at the cost of a deterioration in the image quality.
|
||||
|
||||
To test the quality of the generated samples using our setup, we sampled a few prompts from the “Parti Prompts” (introduced in [Parti](https://parti.research.google/)) and performed inference with the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] in the following settings:
|
||||
|
||||
- Vanilla [`StableDiffusionPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] + ToMe
|
||||
- [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] + ToMe + xformers
|
||||
|
||||
We didn’t notice any significant decrease in the quality of the generated samples. Here are samples:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can check out the generated samples [here](https://wandb.ai/sayakpaul/tomesd-results/runs/23j4bj3i?workspace=). We used [this script](https://gist.github.com/sayakpaul/8cac98d7f22399085a060992f411ecbd) for conducting this experiment.
|
||||
@@ -10,82 +10,96 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PyTorch 2.0
|
||||
# Accelerated PyTorch 2.0 support in Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers supports the latest optimizations from [PyTorch 2.0](https://pytorch.org/get-started/pytorch-2.0/) which include:
|
||||
Starting from version `0.13.0`, Diffusers supports the latest optimization from [PyTorch 2.0](https://pytorch.org/get-started/pytorch-2.0/). These include:
|
||||
1. Support for accelerated transformers implementation with memory-efficient attention – no extra dependencies (such as `xformers`) required.
|
||||
2. [torch.compile](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html) support for extra performance boost when individual models are compiled.
|
||||
|
||||
1. A memory-efficient attention implementation, scaled dot product attention, without requiring any extra dependencies such as xFormers.
|
||||
2. [`torch.compile`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html), a just-in-time (JIT) compiler to provide an extra performance boost when individual models are compiled.
|
||||
|
||||
Both of these optimizations require PyTorch 2.0 or later and 🤗 Diffusers > 0.13.0.
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
To benefit from the accelerated attention implementation and `torch.compile()`, you just need to install the latest versions of PyTorch 2.0 from pip, and make sure you are on diffusers 0.13.0 or later. As explained below, diffusers automatically uses the optimized attention processor ([`AttnProcessor2_0`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/1a5797c6d4491a879ea5285c4efc377664e0332d/src/diffusers/models/attention_processor.py#L798)) (but not `torch.compile()`)
|
||||
when PyTorch 2.0 is available.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade torch diffusers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Scaled dot product attention
|
||||
## Using accelerated transformers and `torch.compile`.
|
||||
|
||||
[`torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention`](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention) (SDPA) is an optimized and memory-efficient attention (similar to xFormers) that automatically enables several other optimizations depending on the model inputs and GPU type. SDPA is enabled by default if you're using PyTorch 2.0 and the latest version of 🤗 Diffusers, so you don't need to add anything to your code.
|
||||
|
||||
However, if you want to explicitly enable it, you can set a [`DiffusionPipeline`] to use [`~models.attention_processor.AttnProcessor2_0`]:
|
||||
1. **Accelerated Transformers implementation**
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
+ from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnProcessor2_0
|
||||
PyTorch 2.0 includes an optimized and memory-efficient attention implementation through the [`torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention`](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention) function, which automatically enables several optimizations depending on the inputs and the GPU type. This is similar to the `memory_efficient_attention` from [xFormers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers), but built natively into PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
+ pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnProcessor2_0())
|
||||
These optimizations will be enabled by default in Diffusers if PyTorch 2.0 is installed and if `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention` is available. To use it, just install `torch 2.0` as suggested above and simply use the pipeline. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
SDPA should be as fast and memory efficient as `xFormers`; check the [benchmark](#benchmark) for more details.
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
pipe = pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases - such as making the pipeline more deterministic or converting it to other formats - it may be helpful to use the vanilla attention processor, [`~models.attention_processor.AttnProcessor`]. To revert to [`~models.attention_processor.AttnProcessor`], call the [`~UNet2DConditionModel.set_default_attn_processor`] function on the pipeline:
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
If you want to enable it explicitly (which is not required), you can do so as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
+ pipe.unet.set_default_attn_processor()
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
+ from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnProcessor2_0
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
+ pipe.unet.set_attn_processor(AttnProcessor2_0())
|
||||
|
||||
## torch.compile
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `torch.compile` function can often provide an additional speed-up to your PyTorch code. In 🤗 Diffusers, it is usually best to wrap the UNet with `torch.compile` because it does most of the heavy lifting in the pipeline.
|
||||
This should be as fast and memory efficient as `xFormers`. More details [in our benchmark](#benchmark).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
It is possible to revert to the vanilla attention processor ([`AttnProcessor`](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/1a5797c6d4491a879ea5285c4efc377664e0332d/src/diffusers/models/attention_processor.py#L402)), which can be helpful to make the pipeline more deterministic, or if you need to convert a fine-tuned model to other formats such as [Core ML](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.16.0/en/optimization/coreml#how-to-run-stable-diffusion-with-core-ml). To use the normal attention processor you can use the [`~diffusers.UNet2DConditionModel.set_default_attn_processor`] function:
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe.unet = torch.compile(pipe.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=steps, num_images_per_prompt=batch_size).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.models.attention_processor import AttnProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on GPU type, `torch.compile` can provide an *additional speed-up* of **5-300x** on top of SDPA! If you're using more recent GPU architectures such as Ampere (A100, 3090), Ada (4090), and Hopper (H100), `torch.compile` is able to squeeze even more performance out of these GPUs.
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe.unet.set_default_attn_processor()
|
||||
|
||||
Compilation requires some time to complete, so it is best suited for situations where you prepare your pipeline once and then perform the same type of inference operations multiple times. For example, calling the compiled pipeline on a different image size triggers compilation again which can be expensive.
|
||||
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. **torch.compile**
|
||||
|
||||
To get an additional speedup, we can use the new `torch.compile` feature. Since the UNet of the pipeline is usually the most computationally expensive, we wrap the `unet` with `torch.compile` leaving rest of the sub-models (text encoder and VAE) as is. For more information and different options, refer to the
|
||||
[torch compile docs](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe.unet = torch.compile(pipe.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=steps, num_images_per_prompt=batch_size).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on the type of GPU, `compile()` can yield between **5% - 300%** of _additional speed-up_ over the accelerated transformer optimizations. Note, however, that compilation is able to squeeze more performance improvements in more recent GPU architectures such as Ampere (A100, 3090), Ada (4090) and Hopper (H100).
|
||||
|
||||
Compilation takes some time to complete, so it is best suited for situations where you need to prepare your pipeline once and then perform the same type of inference operations multiple times. Calling the compiled pipeline on a different image size will re-trigger compilation which can be expensive.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information and different options about `torch.compile`, refer to the [`torch_compile`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/torch_compile_tutorial.html) tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
## Benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
We conducted a comprehensive benchmark with PyTorch 2.0's efficient attention implementation and `torch.compile` across different GPUs and batch sizes for five of our most used pipelines. The code is benchmarked on 🤗 Diffusers v0.17.0.dev0 to optimize `torch.compile` usage (see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/3313) for more details).
|
||||
We conducted a comprehensive benchmark with PyTorch 2.0's efficient attention implementation and `torch.compile` across different GPUs and batch sizes for five of our most used pipelines. We used `diffusers 0.17.0.dev0`, which [makes sure `torch.compile()` is leveraged optimally](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/3313).
|
||||
|
||||
Expand the dropdown below to find the code used to benchmark each pipeline:
|
||||
### Benchmarking code
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
#### Stable Diffusion text-to-image
|
||||
|
||||
### Stable Diffusion text-to-image
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -107,16 +121,19 @@ for _ in range(3):
|
||||
images = pipe(prompt=prompt).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Stable Diffusion image-to-image
|
||||
#### Stable Diffusion image-to-image
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image(url)
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
init_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
init_image = init_image.resize((512, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
path = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
@@ -137,18 +154,27 @@ for _ in range(3):
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Stable Diffusion inpainting
|
||||
#### Stable Diffusion - inpainting
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
def download_image(url):
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
return Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
img_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo.png"
|
||||
mask_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion/main/data/inpainting_examples/overture-creations-5sI6fQgYIuo_mask.png"
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image(img_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
mask_image = load_image(mask_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
init_image = download_image(img_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
mask_image = download_image(mask_url).resize((512, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
path = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -168,16 +194,19 @@ for _ in range(3):
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, mask_image=mask_image).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### ControlNet
|
||||
#### ControlNet
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionControlNetPipeline, ControlNetModel
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from io import BytesIO
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/main/assets/stable-samples/img2img/sketch-mountains-input.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
init_image = load_image(url)
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
init_image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content)).convert("RGB")
|
||||
init_image = init_image.resize((512, 512))
|
||||
|
||||
path = "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5"
|
||||
@@ -203,28 +232,28 @@ for _ in range(3):
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### DeepFloyd IF text-to-image + upscaling
|
||||
#### IF text-to-image + upscaling
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
run_compile = True # Set True / False
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_1 = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("DeepFloyd/IF-I-M-v1.0", variant="fp16", text_encoder=None, torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
pipe_1.to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("DeepFloyd/IF-I-M-v1.0", variant="fp16", text_encoder=None, torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe_2 = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("DeepFloyd/IF-II-M-v1.0", variant="fp16", text_encoder=None, torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
pipe_2.to("cuda")
|
||||
pipe_3 = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-x4-upscaler", torch_dtype=torch.float16, use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
pipe_3.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipe_1.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
pipe.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
pipe_2.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
pipe_3.unet.to(memory_format=torch.channels_last)
|
||||
|
||||
if run_compile:
|
||||
pipe_1.unet = torch.compile(pipe_1.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
pipe.unet = torch.compile(pipe.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
pipe_2.unet = torch.compile(pipe_2.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
pipe_3.unet = torch.compile(pipe_3.unet, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -234,22 +263,28 @@ prompt_embeds = torch.randn((1, 2, 4096), dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
neg_prompt_embeds = torch.randn((1, 2, 4096), dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
for _ in range(3):
|
||||
image_1 = pipe_1(prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds, negative_prompt_embeds=neg_prompt_embeds, output_type="pt").images
|
||||
image_2 = pipe_2(image=image_1, prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds, negative_prompt_embeds=neg_prompt_embeds, output_type="pt").images
|
||||
image_3 = pipe_3(prompt=prompt, image=image_1, noise_level=100).images
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds, negative_prompt_embeds=neg_prompt_embeds, output_type="pt").images
|
||||
image_2 = pipe_2(image=image, prompt_embeds=prompt_embeds, negative_prompt_embeds=neg_prompt_embeds, output_type="pt").images
|
||||
image_3 = pipe_3(prompt=prompt, image=image, noise_level=100).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
The graph below highlights the relative speed-ups for the [`StableDiffusionPipeline`] across five GPU families with PyTorch 2.0 and `torch.compile` enabled. The benchmarks for the following graphs are measured in *number of iterations/second*.
|
||||
To give you a pictorial overview of the possible speed-ups that can be obtained with PyTorch 2.0 and `torch.compile()`,
|
||||
here is a plot that shows relative speed-ups for the [Stable Diffusion text-to-image pipeline](StableDiffusionPipeline) across five
|
||||
different GPU families (with a batch size of 4):
|
||||
|
||||
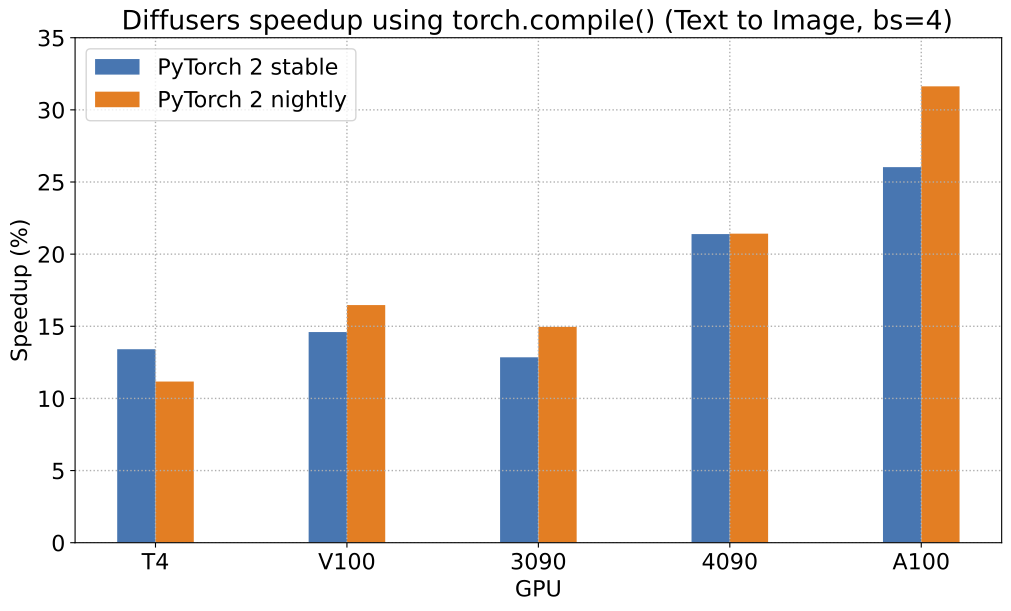
|
||||
|
||||
To give you an even better idea of how this speed-up holds for the other pipelines, consider the following
|
||||
graph for an A100 with PyTorch 2.0 and `torch.compile`:
|
||||
To give you an even better idea of how this speed-up holds for the other pipelines presented above, consider the following
|
||||
plot that shows the benchmarking numbers from an A100 across three different batch sizes
|
||||
(with PyTorch 2.0 nightly and `torch.compile()`):
|
||||
|
||||
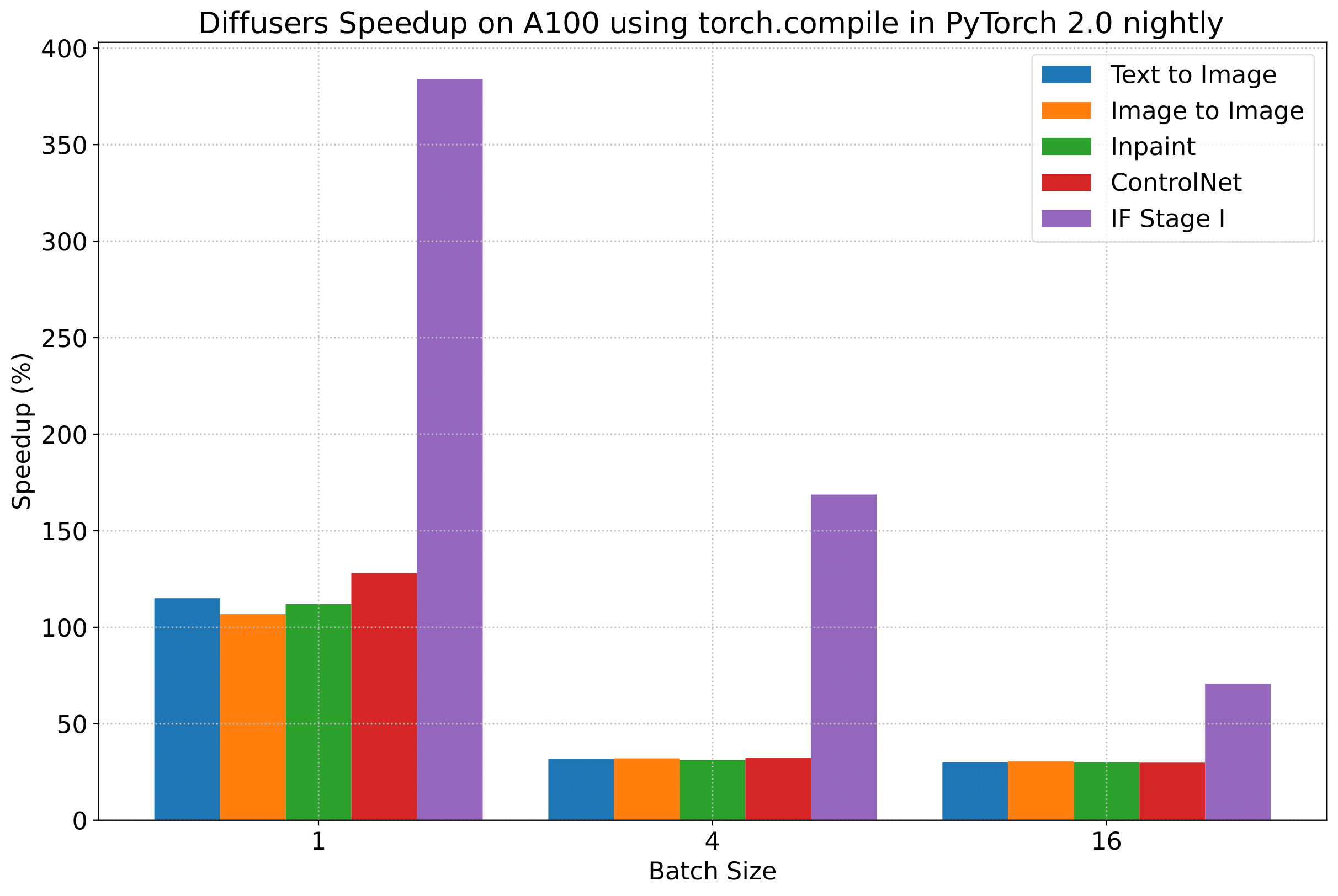
|
||||
|
||||
In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the *number of iterations/second*.
|
||||
_(Our benchmarking metric for the plots above is **number of iterations/second**)_
|
||||
|
||||
But we reveal all the benchmarking numbers in the interest of transparency!
|
||||
|
||||
In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the number of **_iterations processed per second_**.
|
||||
|
||||
### A100 (batch size: 1)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -260,7 +295,6 @@ In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the *number of itera
|
||||
| SD - inpaint | 22.24 | 23.23 | 43.76 | 49.25 |
|
||||
| SD - controlnet | 15.02 | 15.82 | 32.13 | 36.08 |
|
||||
| IF | 20.21 / <br>13.84 / <br>24.00 | 20.12 / <br>13.70 / <br>24.03 | ❌ | 97.34 / <br>27.23 / <br>111.66 |
|
||||
| SDXL - txt2img | 8.64 | 9.9 | - | - |
|
||||
|
||||
### A100 (batch size: 4)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -271,7 +305,6 @@ In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the *number of itera
|
||||
| SD - inpaint | 11.67 | 13.31 | 14.88 | 17.48 |
|
||||
| SD - controlnet | 8.28 | 9.38 | 10.51 | 12.41 |
|
||||
| IF | 25.02 | 18.04 | ❌ | 48.47 |
|
||||
| SDXL - txt2img | 2.44 | 2.74 | - | - |
|
||||
|
||||
### A100 (batch size: 16)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -282,7 +315,6 @@ In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the *number of itera
|
||||
| SD - inpaint | 3.04 | 3.66 | 3.9 | 4.76 |
|
||||
| SD - controlnet | 2.15 | 2.58 | 2.74 | 3.35 |
|
||||
| IF | 8.78 | 9.82 | ❌ | 16.77 |
|
||||
| SDXL - txt2img | 0.64 | 0.72 | - | - |
|
||||
|
||||
### V100 (batch size: 1)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -323,7 +355,6 @@ In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the *number of itera
|
||||
| SD - inpaint | 6.91 | 6.7 | 7.01 | 7.37 |
|
||||
| SD - controlnet | 4.89 | 4.86 | 5.35 | 5.48 |
|
||||
| IF | 17.42 / <br>2.47 / <br>18.52 | 16.96 / <br>2.45 / <br>18.69 | ❌ | 24.63 / <br>2.47 / <br>23.39 |
|
||||
| SDXL - txt2img | 1.15 | 1.16 | - | - |
|
||||
|
||||
### T4 (batch size: 4)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -334,7 +365,6 @@ In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the *number of itera
|
||||
| SD - inpaint | 1.81 | 1.82 | 2.09 | 2.09 |
|
||||
| SD - controlnet | 1.34 | 1.27 | 1.47 | 1.46 |
|
||||
| IF | 5.79 | 5.61 | ❌ | 7.39 |
|
||||
| SDXL - txt2img | 0.288 | 0.289 | - | - |
|
||||
|
||||
### T4 (batch size: 16)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -345,7 +375,6 @@ In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the *number of itera
|
||||
| SD - inpaint | 2.30s | 2.26s | OOM after 2nd iteration | 1.95s |
|
||||
| SD - controlnet | OOM after 2nd iteration | OOM after 2nd iteration | OOM after warmup | OOM after warmup |
|
||||
| IF * | 1.44 | 1.44 | ❌ | 1.94 |
|
||||
| SDXL - txt2img | OOM | OOM | - | - |
|
||||
|
||||
### RTX 3090 (batch size: 1)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -386,7 +415,6 @@ In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the *number of itera
|
||||
| SD - inpaint | 40.51 | 41.88 | 44.58 | 49.72 |
|
||||
| SD - controlnet | 29.27 | 30.29 | 32.26 | 36.03 |
|
||||
| IF | 69.71 / <br>18.78 / <br>85.49 | 69.13 / <br>18.80 / <br>85.56 | ❌ | 124.60 / <br>26.37 / <br>138.79 |
|
||||
| SDXL - txt2img | 6.8 | 8.18 | - | - |
|
||||
|
||||
### RTX 4090 (batch size: 4)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -397,7 +425,6 @@ In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the *number of itera
|
||||
| SD - inpaint | 12.65 | 12.81 | 15.3 | 15.58 |
|
||||
| SD - controlnet | 9.1 | 9.25 | 11.03 | 11.22 |
|
||||
| IF | 31.88 | 31.14 | ❌ | 43.92 |
|
||||
| SDXL - txt2img | 2.19 | 2.35 | - | - |
|
||||
|
||||
### RTX 4090 (batch size: 16)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -408,11 +435,10 @@ In the following tables, we report our findings in terms of the *number of itera
|
||||
| SD - inpaint | 3.17 | 3.2 | 3.85 | 3.85 |
|
||||
| SD - controlnet | 2.23 | 2.3 | 2.7 | 2.75 |
|
||||
| IF | 9.26 | 9.2 | ❌ | 13.31 |
|
||||
| SDXL - txt2img | 0.52 | 0.53 | - | - |
|
||||
|
||||
## Notes
|
||||
## Notes
|
||||
|
||||
* Follow this [PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/3313) for more details on the environment used for conducting the benchmarks.
|
||||
* For the DeepFloyd IF pipeline where batch sizes > 1, we only used a batch size of > 1 in the first IF pipeline for text-to-image generation and NOT for upscaling. That means the two upscaling pipelines received a batch size of 1.
|
||||
* Follow [this PR](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/3313) for more details on the environment used for conducting the benchmarks.
|
||||
* For the IF pipeline and batch sizes > 1, we only used a batch size of >1 in the first IF pipeline for text-to-image generation and NOT for upscaling. So, that means the two upscaling pipelines received a batch size of 1.
|
||||
|
||||
*Thanks to [Horace He](https://github.com/Chillee) from the PyTorch team for their support in improving our support of `torch.compile()` in Diffusers.*
|
||||
*Thanks to [Horace He](https://github.com/Chillee) from the PyTorch team for their support in improving our support of `torch.compile()` in Diffusers.*
|
||||
@@ -10,11 +10,11 @@ an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express o
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# xFormers
|
||||
# Installing xFormers
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend [xFormers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers) for both inference and training. In our tests, the optimizations performed in the attention blocks allow for both faster speed and reduced memory consumption.
|
||||
We recommend the use of [xFormers](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers) for both inference and training. In our tests, the optimizations performed in the attention blocks allow for both faster speed and reduced memory consumption.
|
||||
|
||||
Install xFormers from `pip`:
|
||||
Starting from version `0.0.16` of xFormers, released on January 2023, installation can be easily performed using pre-built pip wheels:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install xformers
|
||||
@@ -22,14 +22,14 @@ pip install xformers
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The xFormers `pip` package requires the latest version of PyTorch. If you need to use a previous version of PyTorch, then we recommend [installing xFormers from the source](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers#installing-xformers).
|
||||
The xFormers PIP package requires the latest version of PyTorch (1.13.1 as of xFormers 0.0.16). If you need to use a previous version of PyTorch, then we recommend you install xFormers from source using [the project instructions](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers#installing-xformers).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
After xFormers is installed, you can use `enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()` for faster inference and reduced memory consumption as shown in this [section](memory#memory-efficient-attention).
|
||||
After xFormers is installed, you can use `enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention()` for faster inference and reduced memory consumption, as discussed [here](fp16#memory-efficient-attention).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
According to this [issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/2234#issuecomment-1416931212), xFormers `v0.0.16` cannot be used for training (fine-tune or DreamBooth) in some GPUs. If you observe this problem, please install a development version as indicated in the issue comments.
|
||||
According to [this issue](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/issues/2234#issuecomment-1416931212), xFormers `v0.0.16` cannot be used for training (fine-tune or Dreambooth) in some GPUs. If you observe that problem, please install a development version as indicated in that comment.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ The quicktour will show you how to use the [`DiffusionPipeline`] for inference,
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The quicktour is a simplified version of the introductory 🧨 Diffusers [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/diffusers_intro.ipynb) to help you get started quickly. If you want to learn more about 🧨 Diffusers' goal, design philosophy, and additional details about its core API, check out the notebook!
|
||||
The quicktour is a simplified version of the introductory 🧨 Diffusers [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/diffusers/diffusers_intro.ipynb) to help you get started quickly. If you want to learn more about 🧨 Diffusers goal, design philosophy, and additional details about it's core API, check out the notebook!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ The [`DiffusionPipeline`] downloads and caches all modeling, tokenization, and s
|
||||
>>> pipeline
|
||||
StableDiffusionPipeline {
|
||||
"_class_name": "StableDiffusionPipeline",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.21.4",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.13.1",
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"scheduler": [
|
||||
"diffusers",
|
||||
@@ -133,7 +133,7 @@ Then load the saved weights into the pipeline:
|
||||
>>> pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("./stable-diffusion-v1-5", use_safetensors=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can run the pipeline as you would in the section above.
|
||||
Now you can run the pipeline as you would in the section above.
|
||||
|
||||
### Swapping schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -191,7 +191,7 @@ To use the model for inference, create the image shape with random Gaussian nois
|
||||
torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For inference, pass the noisy image and a `timestep` to the model. The `timestep` indicates how noisy the input image is, with more noise at the beginning and less at the end. This helps the model determine its position in the diffusion process, whether it is closer to the start or the end. Use the `sample` method to get the model output:
|
||||
For inference, pass the noisy image to the model and a `timestep`. The `timestep` indicates how noisy the input image is, with more noise at the beginning and less at the end. This helps the model determine its position in the diffusion process, whether it is closer to the start or the end. Use the `sample` method to get the model output:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
@@ -210,28 +210,23 @@ Schedulers manage going from a noisy sample to a less noisy sample given the mod
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For the quicktour, you'll instantiate the [`DDPMScheduler`] with its [`~diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config`] method:
|
||||
For the quicktour, you'll instantiate the [`DDPMScheduler`] with it's [`~diffusers.ConfigMixin.from_config`] method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from diffusers import DDPMScheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_pretrained(repo_id)
|
||||
>>> scheduler = DDPMScheduler.from_config(repo_id)
|
||||
>>> scheduler
|
||||
DDPMScheduler {
|
||||
"_class_name": "DDPMScheduler",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.21.4",
|
||||
"_diffusers_version": "0.13.1",
|
||||
"beta_end": 0.02,
|
||||
"beta_schedule": "linear",
|
||||
"beta_start": 0.0001,
|
||||
"clip_sample": true,
|
||||
"clip_sample_range": 1.0,
|
||||
"dynamic_thresholding_ratio": 0.995,
|
||||
"num_train_timesteps": 1000,
|
||||
"prediction_type": "epsilon",
|
||||
"sample_max_value": 1.0,
|
||||
"steps_offset": 0,
|
||||
"thresholding": false,
|
||||
"timestep_spacing": "leading",
|
||||
"trained_betas": null,
|
||||
"variance_type": "fixed_small"
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -239,13 +234,13 @@ DDPMScheduler {
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Unlike a model, a scheduler does not have trainable weights and is parameter-free!
|
||||
💡 Notice how the scheduler is instantiated from a configuration. Unlike a model, a scheduler does not have trainable weights and is parameter-free!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the most important parameters are:
|
||||
|
||||
* `num_train_timesteps`: the length of the denoising process or, in other words, the number of timesteps required to process random Gaussian noise into a data sample.
|
||||
* `num_train_timesteps`: the length of the denoising process or in other words, the number of timesteps required to process random Gaussian noise into a data sample.
|
||||
* `beta_schedule`: the type of noise schedule to use for inference and training.
|
||||
* `beta_start` and `beta_end`: the start and end noise values for the noise schedule.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -254,10 +249,9 @@ To predict a slightly less noisy image, pass the following to the scheduler's [`
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> less_noisy_sample = scheduler.step(model_output=noisy_residual, timestep=2, sample=noisy_sample).prev_sample
|
||||
>>> less_noisy_sample.shape
|
||||
torch.Size([1, 3, 256, 256])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `less_noisy_sample` can be passed to the next `timestep` where it'll get even less noisy! Let's bring it all together now and visualize the entire denoising process.
|
||||
The `less_noisy_sample` can be passed to the next `timestep` where it'll get even less noisier! Let's bring it all together now and visualize the entire denoising process.
|
||||
|
||||
First, create a function that postprocesses and displays the denoised image as a `PIL.Image`:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -311,10 +305,10 @@ Sit back and watch as a cat is generated from nothing but noise! 😻
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
Hopefully, you generated some cool images with 🧨 Diffusers in this quicktour! For your next steps, you can:
|
||||
Hopefully you generated some cool images with 🧨 Diffusers in this quicktour! For your next steps, you can:
|
||||
|
||||
* Train or finetune a model to generate your own images in the [training](./tutorials/basic_training) tutorial.
|
||||
* See example official and community [training or finetuning scripts](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples#-diffusers-examples) for a variety of use cases.
|
||||
* Learn more about loading, accessing, changing, and comparing schedulers in the [Using different Schedulers](./using-diffusers/schedulers) guide.
|
||||
* Explore prompt engineering, speed and memory optimizations, and tips and tricks for generating higher-quality images with the [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion) guide.
|
||||
* Learn more about loading, accessing, changing and comparing schedulers in the [Using different Schedulers](./using-diffusers/schedulers) guide.
|
||||
* Explore prompt engineering, speed and memory optimizations, and tips and tricks for generating higher quality images with the [Stable Diffusion](./stable_diffusion) guide.
|
||||
* Dive deeper into speeding up 🧨 Diffusers with guides on [optimized PyTorch on a GPU](./optimization/fp16), and inference guides for running [Stable Diffusion on Apple Silicon (M1/M2)](./optimization/mps) and [ONNX Runtime](./optimization/onnx).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,14 +9,14 @@ Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Effective and efficient diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Getting the [`DiffusionPipeline`] to generate images in a certain style or include what you want can be tricky. Often times, you have to run the [`DiffusionPipeline`] several times before you end up with an image you're happy with. But generating something out of nothing is a computationally intensive process, especially if you're running inference over and over again.
|
||||
Getting the [`DiffusionPipeline`] to generate images in a certain style or include what you want can be tricky. Often times, you have to run the [`DiffusionPipeline`] several times before you end up with an image you're happy with. But generating something out of nothing is a computationally intensive process, especially if you're running inference over and over again.
|
||||
|
||||
This is why it's important to get the most *computational* (speed) and *memory* (GPU vRAM) efficiency from the pipeline to reduce the time between inference cycles so you can iterate faster.
|
||||
This is why it's important to get the most *computational* (speed) and *memory* (GPU RAM) efficiency from the pipeline to reduce the time between inference cycles so you can iterate faster.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial walks you through how to generate faster and better with the [`DiffusionPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -68,7 +68,7 @@ image
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/diffusers/docs-images/resolve/main/stable_diffusion_101/sd_101_1.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
This process took ~30 seconds on a T4 GPU (it might be faster if your allocated GPU is better than a T4). By default, the [`DiffusionPipeline`] runs inference with full `float32` precision for 50 inference steps. You can speed this up by switching to a lower precision like `float16` or running fewer inference steps.
|
||||
This process took ~30 seconds on a T4 GPU (it might be faster if your allocated GPU is better than a T4). By default, the [`DiffusionPipeline`] runs inference with full `float32` precision for 50 inference steps. You can speed this up by switching to a lower precision like `float16` or running fewer inference steps.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's start by loading the model in `float16` and generate an image:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -108,7 +108,6 @@ pipeline.scheduler.compatibles
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_ddpm.DDPMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_dpmsolver_singlestep.DPMSolverSinglestepScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_k_dpm_2_ancestral_discrete.KDPM2AncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.utils.dummy_torch_and_torchsde_objects.DPMSolverSDEScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_heun_discrete.HeunDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_pndm.PNDMScheduler,
|
||||
diffusers.schedulers.scheduling_euler_ancestral_discrete.EulerAncestralDiscreteScheduler,
|
||||
@@ -116,7 +115,7 @@ pipeline.scheduler.compatibles
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The Stable Diffusion model uses the [`PNDMScheduler`] by default which usually requires ~50 inference steps, but more performant schedulers like [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`], require only ~20 or 25 inference steps. Use the [`~ConfigMixin.from_config`] method to load a new scheduler:
|
||||
The Stable Diffusion model uses the [`PNDMScheduler`] by default which usually requires ~50 inference steps, but more performant schedulers like [`DPMSolverMultistepScheduler`], require only ~20 or 25 inference steps. Use the [`ConfigMixin.from_config`] method to load a new scheduler:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DPMSolverMultistepScheduler
|
||||
@@ -156,13 +155,13 @@ def get_inputs(batch_size=1):
|
||||
Start with `batch_size=4` and see how much memory you've consumed:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import make_image_grid
|
||||
|
||||
images = pipeline(**get_inputs(batch_size=4)).images
|
||||
make_image_grid(images, 2, 2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Unless you have a GPU with more vRAM, the code above probably returned an `OOM` error! Most of the memory is taken up by the cross-attention layers. Instead of running this operation in a batch, you can run it sequentially to save a significant amount of memory. All you have to do is configure the pipeline to use the [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_attention_slicing`] function:
|
||||
Unless you have a GPU with more RAM, the code above probably returned an `OOM` error! Most of the memory is taken up by the cross-attention layers. Instead of running this operation in a batch, you can run it sequentially to save a significant amount of memory. All you have to do is configure the pipeline to use the [`~DiffusionPipeline.enable_attention_slicing`] function:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipeline.enable_attention_slicing()
|
||||
@@ -193,7 +192,7 @@ As the field grows, there are more and more high-quality checkpoints finetuned t
|
||||
|
||||
### Better pipeline components
|
||||
|
||||
You can also try replacing the current pipeline components with a newer version. Let's try loading the latest [autoencoder](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1/tree/main/vae) from Stability AI into the pipeline, and generate some images:
|
||||
You can also try replacing the current pipeline components with a newer version. Let's try loading the latest [autodecoder](https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1/tree/main/vae) from Stability AI into the pipeline, and generate some images:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import AutoencoderKL
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -87,4 +87,4 @@ accelerate launch --mixed_precision="fp16" train_text_to_image.py \
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you've created a dataset, you can plug it into the `train_data_dir` (if your dataset is local) or `dataset_name` (if your dataset is on the Hub) arguments of a training script.
|
||||
|
||||
For your next steps, feel free to try and use your dataset to train a model for [unconditional generation](unconditional_training) or [text-to-image generation](text2image)!
|
||||
For your next steps, feel free to try and use your dataset to train a model for [unconditional generation](uncondtional_training) or [text-to-image generation](text2image)!
|
||||
@@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ write_basic_config()
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's get our dataset. Download dataset from [here](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~custom-diffusion/assets/data.zip) and unzip it. To use your own dataset, take a look at the [Create a dataset for training](create_dataset) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
We also collect 200 real images using `clip-retrieval` which are combined with the target images in the training dataset as a regularization. This prevents overfitting to the given target image. The following flags enable the regularization `with_prior_preservation`, `real_prior` with `prior_loss_weight=1.`.
|
||||
We also collect 200 real images using `clip-retrieval` which are combined with the target images in the training dataset as a regularization. This prevents overfitting to the the given target image. The following flags enable the regularization `with_prior_preservation`, `real_prior` with `prior_loss_weight=1.`.
|
||||
The `class_prompt` should be the category name same as target image. The collected real images are with text captions similar to the `class_prompt`. The retrieved image are saved in `class_data_dir`. You can disable `real_prior` to use generated images as regularization. To collect the real images use this command first before training.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
@@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ accelerate launch train_custom_diffusion.py \
|
||||
|
||||
**Use `--enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention` for faster training with lower VRAM requirement (16GB per GPU). Follow [this guide](https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers) for installation instructions.**
|
||||
|
||||
To track your experiments using Weights and Biases (`wandb`) and to save intermediate results (which we HIGHLY recommend), follow these steps:
|
||||
To track your experiments using Weights and Biases (`wandb`) and to save intermediate results (whcih we HIGHLY recommend), follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
* Install `wandb`: `pip install wandb`.
|
||||
* Authorize: `wandb login`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Reinforcement learning training with DDPO
|
||||
|
||||
You can fine-tune Stable Diffusion on a reward function via reinforcement learning with the 🤗 TRL library and 🤗 Diffusers. This is done with the Denoising Diffusion Policy Optimization (DDPO) algorithm introduced by Black et al. in [Training Diffusion Models with Reinforcement Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.13301), which is implemented in 🤗 TRL with the [`~trl.DDPOTrainer`].
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, check out the [`~trl.DDPOTrainer`] API reference and the [Finetune Stable Diffusion Models with DDPO via TRL](https://huggingface.co/blog/trl-ddpo) blog post.
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +1,3 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Distributed inference with multiple GPUs
|
||||
|
||||
On distributed setups, you can run inference across multiple GPUs with 🤗 [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index) or [PyTorch Distributed](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/dist_overview.html), which is useful for generating with multiple prompts in parallel.
|
||||
@@ -25,7 +13,6 @@ To begin, create a Python file and initialize an [`accelerate.PartialState`] to
|
||||
Now use the [`~accelerate.PartialState.split_between_processes`] utility as a context manager to automatically distribute the prompts between the number of processes.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate import PartialState
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -105,4 +92,4 @@ Once you've completed the inference script, use the `--nproc_per_node` argument
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
torchrun run_distributed.py --nproc_per_node=2
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ the attention layers of a language model is sufficient to obtain good downstream
|
||||
|
||||
[cloneofsimo](https://github.com/cloneofsimo) was the first to try out LoRA training for Stable Diffusion in the popular [lora](https://github.com/cloneofsimo/lora) GitHub repository. 🧨 Diffusers now supports finetuning with LoRA for [text-to-image generation](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/text_to_image#training-with-lora) and [DreamBooth](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/tree/main/examples/dreambooth#training-with-low-rank-adaptation-of-large-language-models-lora). This guide will show you how to do both.
|
||||
|
||||
If you'd like to store or share your model with the community, login to your Hugging Face account (create [one](https://hf.co/join) if you don't have one already):
|
||||
If you'd like to store or share your model with the community, login to your Hugging Face account (create [one](hf.co/join) if you don't have one already):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
@@ -113,15 +113,14 @@ Load the LoRA weights from your finetuned model *on top of the base model weight
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pipe.unet.load_attn_procs(lora_model_path)
|
||||
>>> pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# use half the weights from the LoRA finetuned model and half the weights from the base model
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image = pipe(
|
||||
... "A pokemon with blue eyes.", num_inference_steps=25, guidance_scale=7.5, cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 0.5}
|
||||
... ).images[0]
|
||||
# use the weights from the fully finetuned LoRA model
|
||||
|
||||
# OR, use the weights from the fully finetuned LoRA model
|
||||
# >>> image = pipe("A pokemon with blue eyes.", num_inference_steps=25, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image = pipe("A pokemon with blue eyes.", num_inference_steps=25, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
>>> image.save("blue_pokemon.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -226,18 +225,17 @@ Load the LoRA weights from your finetuned DreamBooth model *on top of the base m
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pipe.unet.load_attn_procs(lora_model_path)
|
||||
>>> pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
# use half the weights from the LoRA finetuned model and half the weights from the base model
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image = pipe(
|
||||
... "A picture of a sks dog in a bucket.",
|
||||
... num_inference_steps=25,
|
||||
... guidance_scale=7.5,
|
||||
... cross_attention_kwargs={"scale": 0.5},
|
||||
... ).images[0]
|
||||
# use the weights from the fully finetuned LoRA model
|
||||
|
||||
# OR, use the weights from the fully finetuned LoRA model
|
||||
# >>> image = pipe("A picture of a sks dog in a bucket.", num_inference_steps=25, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image = pipe("A picture of a sks dog in a bucket.", num_inference_steps=25, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
>>> image.save("bucket-dog.png")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -323,7 +321,7 @@ pipe.fuse_lora()
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
images_fusion = pipe(
|
||||
"masterpiece, best quality, mountain", generator=generator, num_inference_steps=2
|
||||
"masterpiece, best quality, mountain", output_type="np", generator=generator, num_inference_steps=2
|
||||
).images
|
||||
|
||||
# To work with a different `lora_scale`, first reverse the effects of `fuse_lora()`.
|
||||
@@ -335,101 +333,10 @@ pipe.fuse_lora(lora_scale=0.5)
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
images_fusion = pipe(
|
||||
"masterpiece, best quality, mountain", generator=generator, num_inference_steps=2
|
||||
"masterpiece, best quality, mountain", output_type="np", generator=generator, num_inference_steps=2
|
||||
).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Serializing pipelines with fused LoRA parameters
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say you want to load the pipeline above that has its UNet fused with the LoRA parameters. You can easily do so by simply calling the `save_pretrained()` method on `pipe`.
|
||||
|
||||
After loading the LoRA parameters into a pipeline, if you want to serialize the pipeline such that the affected model components are already fused with the LoRA parameters, you should:
|
||||
|
||||
* call `fuse_lora()` on the pipeline with the desired `lora_scale`, given you've already loaded the LoRA parameters into it.
|
||||
* call `save_pretrained()` on the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a complete example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
lora_model_id = "hf-internal-testing/sdxl-1.0-lora"
|
||||
lora_filename = "sd_xl_offset_example-lora_1.0.safetensors"
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights(lora_model_id, weight_name=lora_filename)
|
||||
|
||||
# First, fuse the LoRA parameters.
|
||||
pipe.fuse_lora()
|
||||
|
||||
# Then save.
|
||||
pipe.save_pretrained("my-pipeline-with-fused-lora")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can load the pipeline and directly perform inference without having to load the LoRA parameters again:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("my-pipeline-with-fused-lora", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
images_fusion = pipe(
|
||||
"masterpiece, best quality, mountain", generator=generator, num_inference_steps=2
|
||||
).images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Working with multiple LoRA checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
With the `fuse_lora()` method as described above, it's possible to load multiple LoRA checkpoints. Let's work through a complete example. First we load the base pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLPipeline, AutoencoderKL
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
vae = AutoencoderKL.from_pretrained("madebyollin/sdxl-vae-fp16-fix", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
|
||||
vae=vae,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipe.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then let's two LoRA checkpoints and fuse them with specific `lora_scale` values:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# LoRA one.
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("goofyai/cyborg_style_xl")
|
||||
pipe.fuse_lora(lora_scale=0.7)
|
||||
|
||||
# LoRA two.
|
||||
pipe.load_lora_weights("TheLastBen/Pikachu_SDXL")
|
||||
pipe.fuse_lora(lora_scale=0.7)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Play with the `lora_scale` parameter when working with multiple LoRAs to control the amount of their influence on the final outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Let's see them in action:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "cyborg style pikachu"
|
||||
image = pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=30, guidance_scale=7.5).images[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, unfusing multiple LoRA checkpoints is not possible.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Supporting different LoRA checkpoints from Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Diffusers supports loading checkpoints from popular LoRA trainers such as [Kohya](https://github.com/kohya-ss/sd-scripts/) and [TheLastBen](https://github.com/TheLastBen/fast-stable-diffusion). In this section, we outline the current API's details and limitations.
|
||||
@@ -529,8 +436,8 @@ base_model_id = "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-0.9"
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(base_model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights(".", weight_name="Kamepan.safetensors")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "anime screencap, glint, drawing, best quality, light smile, shy, a full body of a girl wearing wedding dress in the middle of the forest beneath the trees, fireflies, big eyes, 2d, cute, anime girl, waifu, cel shading, magical girl, vivid colors, (outline:1.1), manga anime artstyle, masterpiece, official wallpaper, glint <lora:kame_sdxl_v2:1>"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "(deformed, bad quality, sketch, depth of field, blurry:1.1), grainy, bad anatomy, bad perspective, old, ugly, realistic, cartoon, disney, bad proportions"
|
||||
prompt = "anime screencap, glint, drawing, best quality, light smile, shy, a full body of a girl wearing wedding dress in the middle of the forest beneath the trees, fireflies, big eyes, 2d, cute, anime girl, waifu, cel shading, magical girl, vivid colors, (outline:1.1), manga anime artstyle, masterpiece, offical wallpaper, glint <lora:kame_sdxl_v2:1>"
|
||||
negative_prompt = "(deformed, bad quality, sketch, depth of field, blurry:1.1), grainy, bad anatomy, bad perspective, old, ugly, realistic, cartoon, disney, bad propotions"
|
||||
generator = torch.manual_seed(2947883060)
|
||||
num_inference_steps = 30
|
||||
guidance_scale = 7
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user